1. Introduction
The flood phenomenon is a dynamic problem. A good understanding of channel bed bathymetry and velocity field is required. Forecasting river and lake water flows are critical for flood warnings and water resource management. Few peer-reviewed articles specifically address flood forecasting in the Red River despite the Red River of the North’s propensity for flooding. Atashi et al. [
1] established effective methods that use a classical statistical method, a classical Machine learning algorithm, and a Deep Learning method. The results indicated that the LSTM approach outperformed the SARIMA and Random Forest methods in terms of prediction accuracy for three stations in the Red River: Pembina, Drayton, and Grand Forks. Lim and Voeller (2009) discussed methods for estimating flood levels in the Red River using two different techniques: L-Moment-Based Index-Flood and Bulletin 17B Procedures [
2]. Their findings showed that the L-moment-based index-flood (LMIF) approach has various benefits over standard moment methods, including higher resilience and identifiability of the best-fitted distribution, which is especially important for regional research. Todhunter [
3] investigated the maximum flow data for the Grand Forks, North Dakota station. Todhunter (2012) advised investigating the assumptions based on the LP3 distribution to apply the stationary frequency analysis suggested in Bulletin 17B, guidelines for Determining Flood Flow Frequency. The existence of climate cycles, the temporal independence of the records, changes in watersheds, and flood mechanisms were suggested in the Todhunter study [
3]. Deschamps et al. (2002) also concluded that the Red River floodplain is not clearly defined, although it does encompass the lakebed of ancient Lake Agassiz [
4].
Bathymetry and LiDAR data offer valuable insights into the topography of land and water bodies, enabling more effective flood prediction and prevention strategies. Bathymetry data provides information on the depth and shape of water bodies, aiding in flood forecasting and mitigation efforts. LiDAR data, on the other hand, can create highly detailed topographic maps of land and floodplains. Recently, the average current depth, velocity, and discharge field have been estimated using the ADCP [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. These devices can generate spatially extensive velocity and discharge patterns [
11,
12,
13,
14], which could be utilized to calibrate and validate numerical models.
In this study, we provide flow measurements using an ASV called HYCAT (
b) and an ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers) [
15], which measures flow discharge and velocities (Figure 3a). This ASV uses GPS to navigate autonomously along preprogrammed routes on the water surface. A bathymetric survey of the streambed around the bridge sites allows us to collect water depth data as point clouds for 3-D bathymetric mapping, which is created using the HEC-RAS model. The HEC-RAS model is a valuable tool for modeling floods and identifying flood maps for 10-, 25-, 50-, and 100-year return periods [
16]. Also, to gather input data on river geometry characteristics (cross sections, streamlines, river banks), several DEMs including Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (IFSAR) were integrated into HEC-RAS [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21].
The integration of bathymetry and LiDAR datasets can also lead to the creation of precise flood maps, which can be used to develop targeted flood prevention and mitigation strategies. By identifying at-risk communities and infrastructure and enabling precise flood forecasting, flood mapping plays a crucial role in mitigating and preventing the impact of floods.
The first part of the study used the Ras-Mapper tool in HEC-RAS to plot flood inundation mapping. Flood inundation mapping assists flood hazard management and flood extent area identification by visualizing prospective flooding scenarios, identifying locations and resources that may be in danger, and improving local response efforts during a flooding disaster [
22]. Inundation mapping accuracy can be improved by using high-resolution topographic data generated by LiDAR technologies associated with ADCP bathymetry data to reveal unprecedented-level topographic features. The maps typically show the extent of flooding, including the depth and velocity of the water, and may also include information on evacuation routes, critical infrastructure, and other relevant data.
The study of Namara et al. (2022) aimed to map flood inundation using the HEC-RAS model for the Awash Bello flood plain in Ethiopia. The HEC-HMS model was used to compute annual peak flood frequency analysis for different recurrence intervals. The results showed that the whole area is under the influence of flood inundation due to intensive rainfall events [
23]. Zheng et al. (2018) propose a new workflow called GeoFlood for flood inundation mapping using high-resolution terrain data. The approach involves automatic channel network extraction, computing a Height Above the Nearest Drainage (HAND) raster to quantify elevation differences, and generating inundation maps using synthetic stage-discharge rating curves. The approach is evaluated in the Onion Creek Watershed in Central Texas and shows promising results in capturing general inundation patterns, with potential for informing real-time flood disaster response [
24]. Pinos et al. (2019) evaluate the performance of three hydraulic 1D models (HEC-RAS, MIKE 11, and Flood Modeller) in estimating inundation water levels for a mountain river. The models were evaluated under steady-state conditions for 10 scenarios, using two types of cross-sectional data. The authors found that the models performed similarly when using detailed field survey data (type I), but the goodness of fit decreased when using cross-sections derived exclusively from DEM (type II). The authors recommend using type I geometric data for practitioners to obtain similar model performance [
25].
The second part of the research was focused on assessing the scour that occurs specifically around the pier of the bridge, known as local scour. Both bathymetry and LiDAR datasets can help prevent scouring near bridges by providing detailed information on the underwater topography, such as the depth of the water and the composition of the riverbed. Scouring at bridges is a highly intricate phenomenon that involves various processes such as local scour around the piers and abutments, contraction scour, channel bed degradation, channel widening, and lateral migration, which can occur simultaneously. The collective and interconnectedness of these river processes make the scouring process very complex and difficult to model mathematically. Furthermore, the presence of countermeasures such as riprap, grout bags, and gabions adds another layer of complexity to the analysis. To fully comprehend the scouring process around bridges, a thorough evaluation should account for all these factors. Engineers have been working to create and sustain bridge and hydraulic structure foundations that are secure from scouring for more than four decades. The HEC-RAS is a popular tool researchers used for analyzing bridge scour. While there are several equations available for computing scour around piers and abutments, the ones included in the HEC-RAS are widely preferred by researchers and engineers [
26,
27,
28].
By the introduction, the main goals of this project are as follows: 1) to map the 2022 flood in Red River of the North in Grafton using the bathymetric and LiDAR data, 2) to evaluate local scour around the bridge pier which employs the Colorado State University method as a default equation. Flow conditions were approximated for a 2022 flood event with a 16.5 return period in the Red River of the North using HEC-RAS flow modeling software. The outcomes will enable us to understand the hydraulics and scour potential, propose remedial design options, and revisit the site for measurements after implementing the countermeasure. It is important to note that one of the novelties of our study lies in the fact that we measured one of the rare flood events and due to a lack of tools and the risk involved in taking measurements during flood events, not many studies have been done on these measures in the past.
2. Study Area
The Red River originates near Wahpeton in North Dakota at the intersection of the Bois de Sioux and the Otter Tail rivers between the U.S. states of Minnesota and North Dakota. The river’s mouth is located northeast of Winnipeg in Manitoba, Canada, flowing into Lake Winnipeg. The slope of the Red River of the North varies along its length which is 545 miles. In the region of Fargo-Halstad, the gradient of the Red River averages 5 inches per mile of length. In the region of Drayton-Pembina, however, the gradient drops to 1.5 inches per mile. The Red River of the North is considered to have a relatively gentle slope with a catchment area of 178,645 mi2 (287,500 km2) (
Figure 1a) [
29]. Ice jams in the north cause major floods because of the backwater effect of the frozen water [
30]. The warmer, southern part of the Red River melts first during the spring thaw, and the meltwater flows north into colder temperatures while the northern portion of the Red River basin is still frozen, resulting in floods [
2]. Rainfall in the spring and early summer, when there is still snow on the ground, relates to quick melting, and when paired with the previously described features, the Red River Valley is extremely vulnerable to floods in March and April. These factors increase the need to study flooding in this region to better identify the precursors that influence the hydrological conditions generated during spring snowmelt floods.
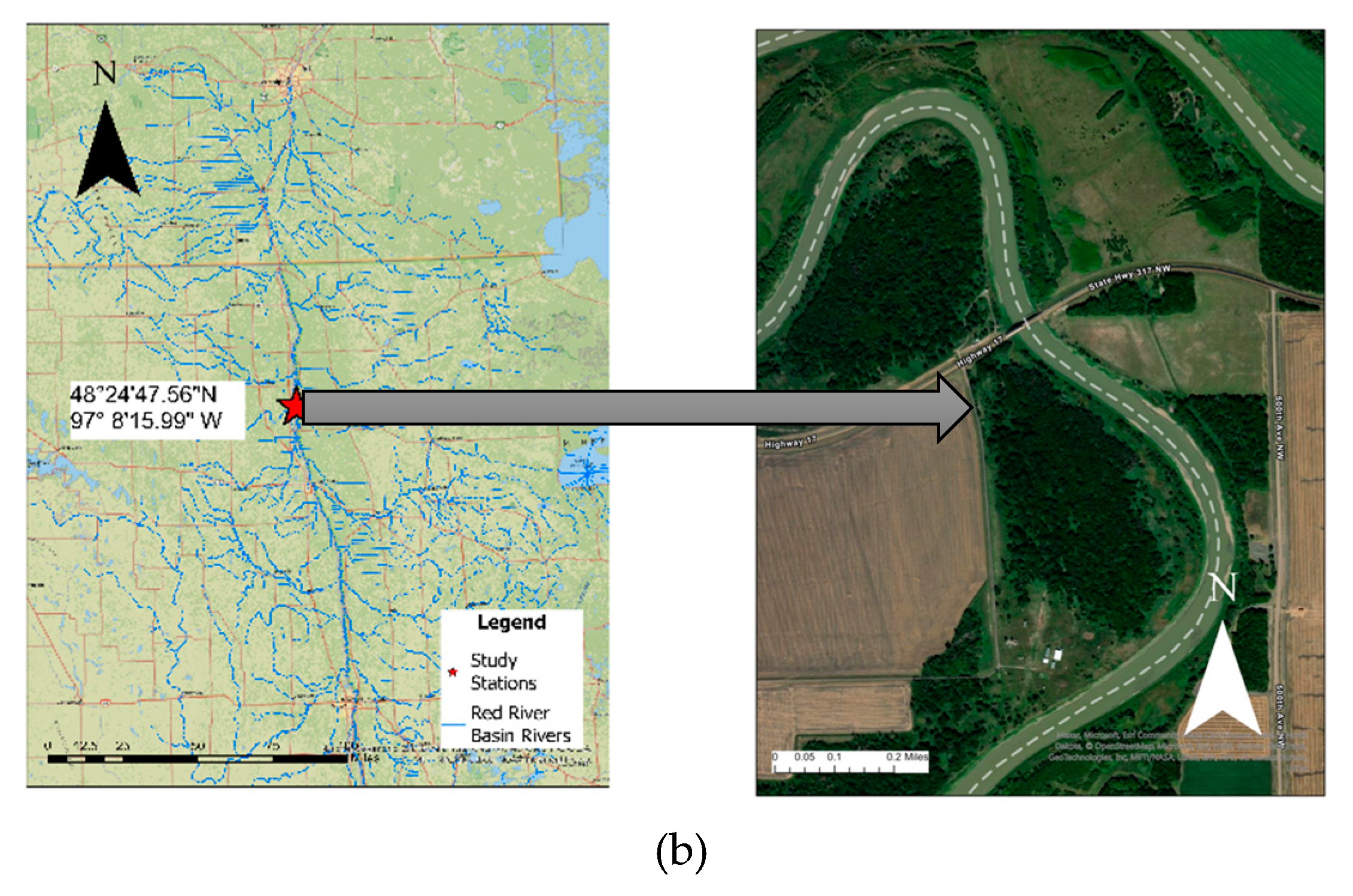
A section of the Red River east of Grafton, Walsh County, North Dakota (48°24’47.56”N 97° 8’15.99” W) and Marshall County, Minnesota has been chosen for this study (
Figure 1b). The study reach is approximately 11 miles upstream of the Drayton USGS station, No. 05092000, which is in Pembina County, North Dakota. This study location is between two USGS stations that provide discharge data: the Red River at Drayton, ND (05092000) and the Red River at Grand Forks, ND (05082500), therefore, there are no stations with discharge information for around 50 miles. Additionally, there were concerns about potential scour holes near the Red River of the North the Grafton Bridge (Bridge 5872 in Minnesota and Bridge 0017-140.372 in North Dakota) is a two-span Parker through truss that carries State Highway 17 in Walsh County, North Dakota, and Minnesota Trunk Highway 317 in Marshall County, Minnesota since the bridge scour is the primary cause of bridge failure in the United States, making the risks associated with it substantial [
31].
3. Material and Methods
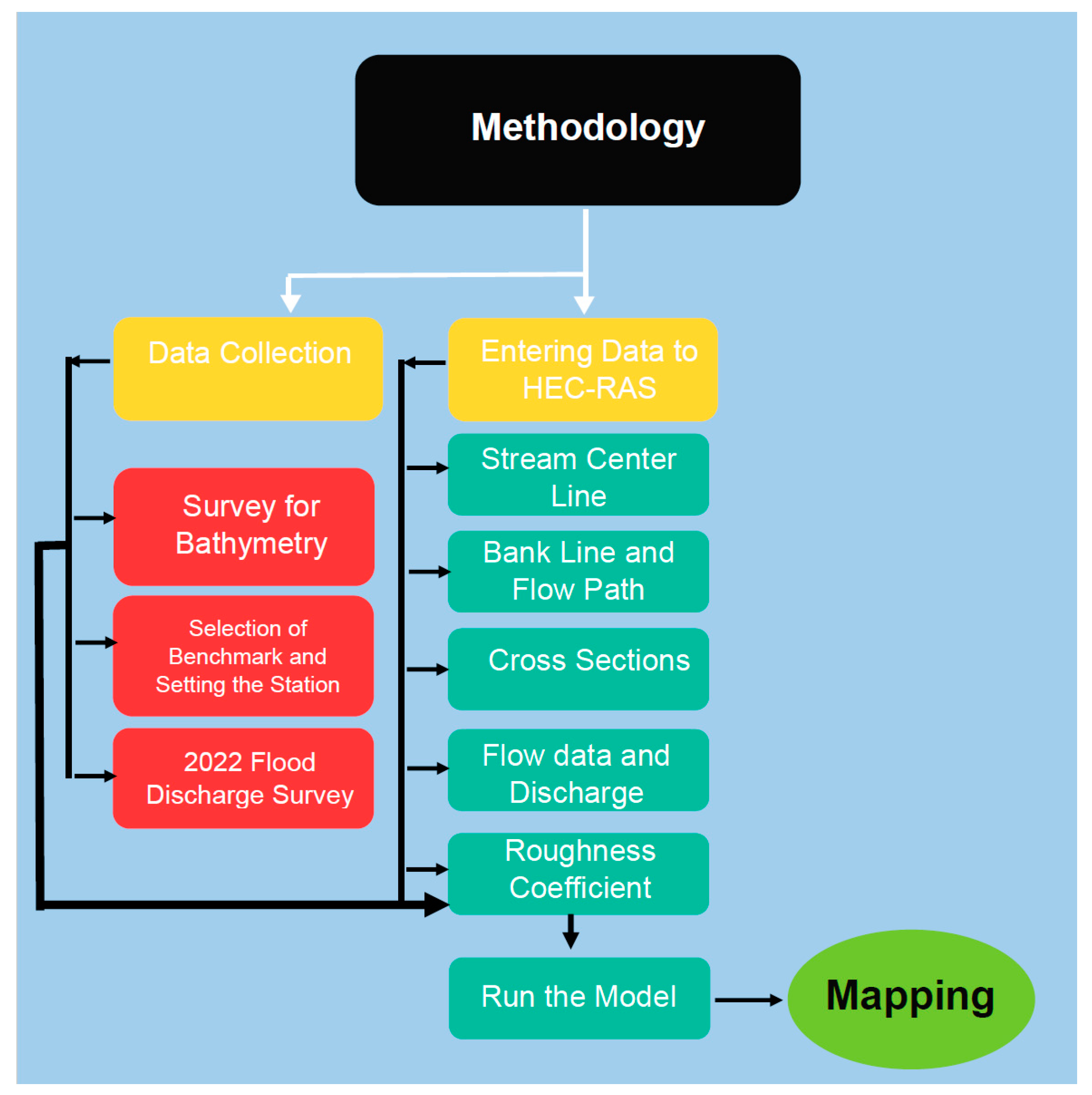
To produce the flood inundation map and investigate scour depth around the bridge in HEC-RAS, we first constructed a hydraulic model of the river or channel using the most reliable bathymetry and Lidar data available. Subsequently, we introduced the roughness coefficient for the channel and overbanks based on previous research, as well as any other necessary parameters into the model. We executed the model to compare predicted water surface elevations and velocities with observed data. The primary data employed in this study included pier dimensions, pier shapes, flow depth, sediment samples, and river cross-section, while secondary data consisted of discharge data, topographic maps, maps of the study area, and river length, all of which were entered as input data. Finally, we utilized HEC-RAS software 6.0.0 to analyze the data and determine the local scour depth around the bridge piers, and to generate the flood map of the study area.
3.1. Bathymetry and LiDAR Data
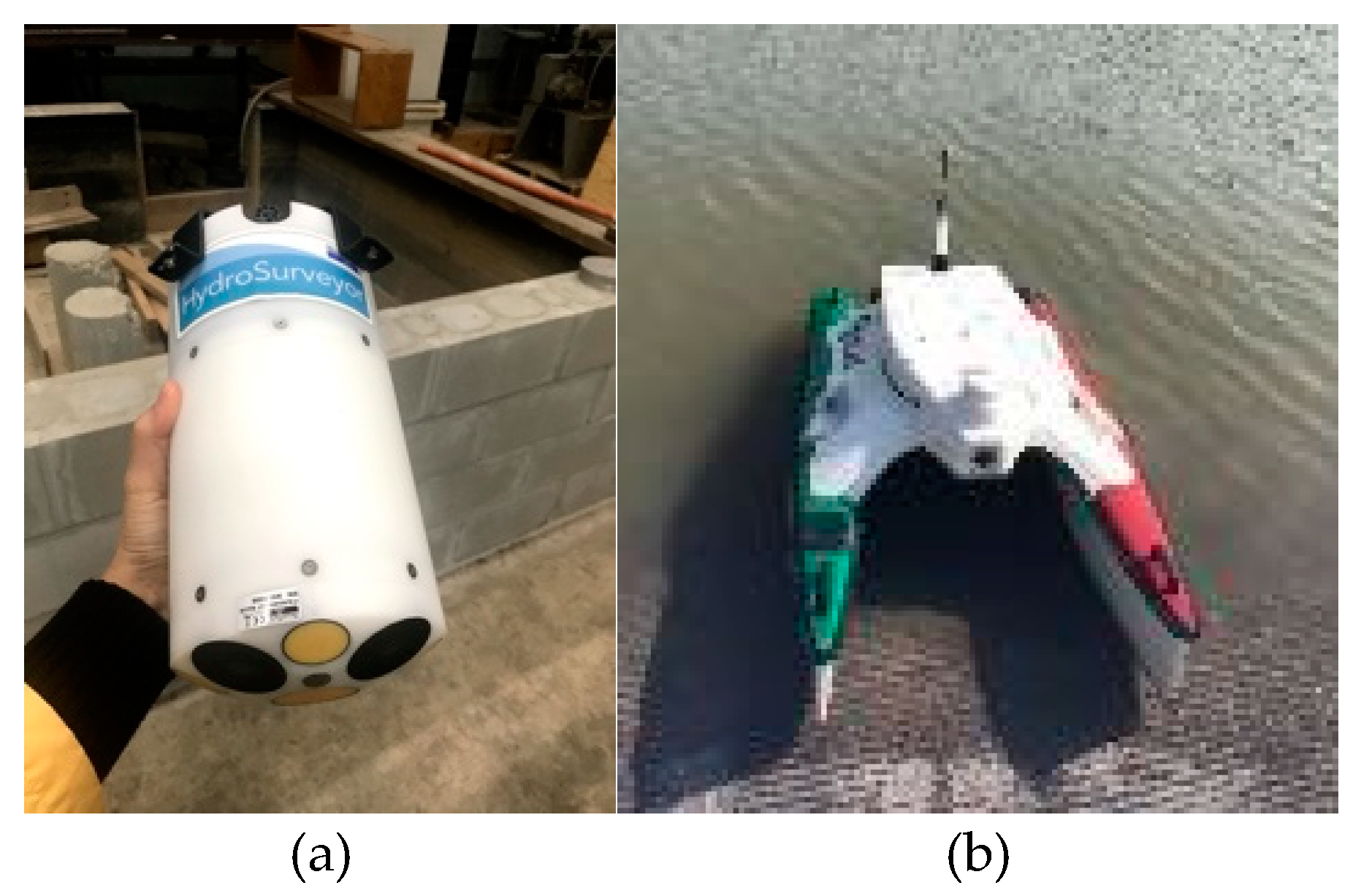
RiverSurveyor and HYPACK software was used to collect discharge and raw velocity and bathymetry data from the Red River, respectively. The stationary measurement instrument M9 ADCP (
Figure 3a) was deployed on an Autonomous Surface Vehicle (ASV), and kept in position using a remote controller on the channel riverbed (
Figure 3b). The M9 can monitor water depth (ranging from 0.2 to 131.23 feet at velocities ranging from 0 to 65.6 ft/s), velocity, and discharge profiles [
32].
3.2. Model Description
HEC-RAS simulates 1D hydraulic processes for a complete network of natural and man-made channels. Four 1D hydraulic components in HEC-RAS simulate water quality, moveable boundary sediment transport, steady water flow, and unsteady water flow surface profiles. The HECRAS 6.0.0 software was used in this paper to generate a 1D hydrodynamic model and determine and map the flooding of the present Red River reach. The conventional step method is used to calculate water surface profiles from one cross-section to the next by solving the energy equation iteratively. The coefficients of contraction or expansion were multiplied with the change in velocity head to determine energy losses when the channel geometry changed. The following is the energy equation [
36]:
Y1, Y2 = flow depth at cross sections (ft)
Z1, Z2 = elevation of the main channel inverts (ft)
V1, V2 = average velocities (ft/s)
α1, α2 = velocity weighting coefficients
g = gravitational acceleration (ft2/s)
he = energy head loss (ft)
The empirical Energy equation, in the form of equation (1), was used in the model to provide the relationship between river discharge, hydraulic resistance, river geometry, and friction energy loss. The determination of total conveyance and the velocity coefficient for a cross-section requires that flow be subdivided into units for which the velocity is uniformly distributed.
Using the input cross-section n-value break points as the foundation for subdivision, the HEC-RAS method divides flow into main channel and the overbank regions. Manning’s equation, expressed in equation (2), is used to determine conveyance within each subdivision [
37]:
In the equations above:
Q = flow rate (cfs)
= energy slope (ft/ft)
n = Manning’s roughness coefficient
A = flow area (ft2)
R = hydraulic radius (ft)
3.3. Geometric and Hydrologic Data and Data processing in the RAS-mapper tool
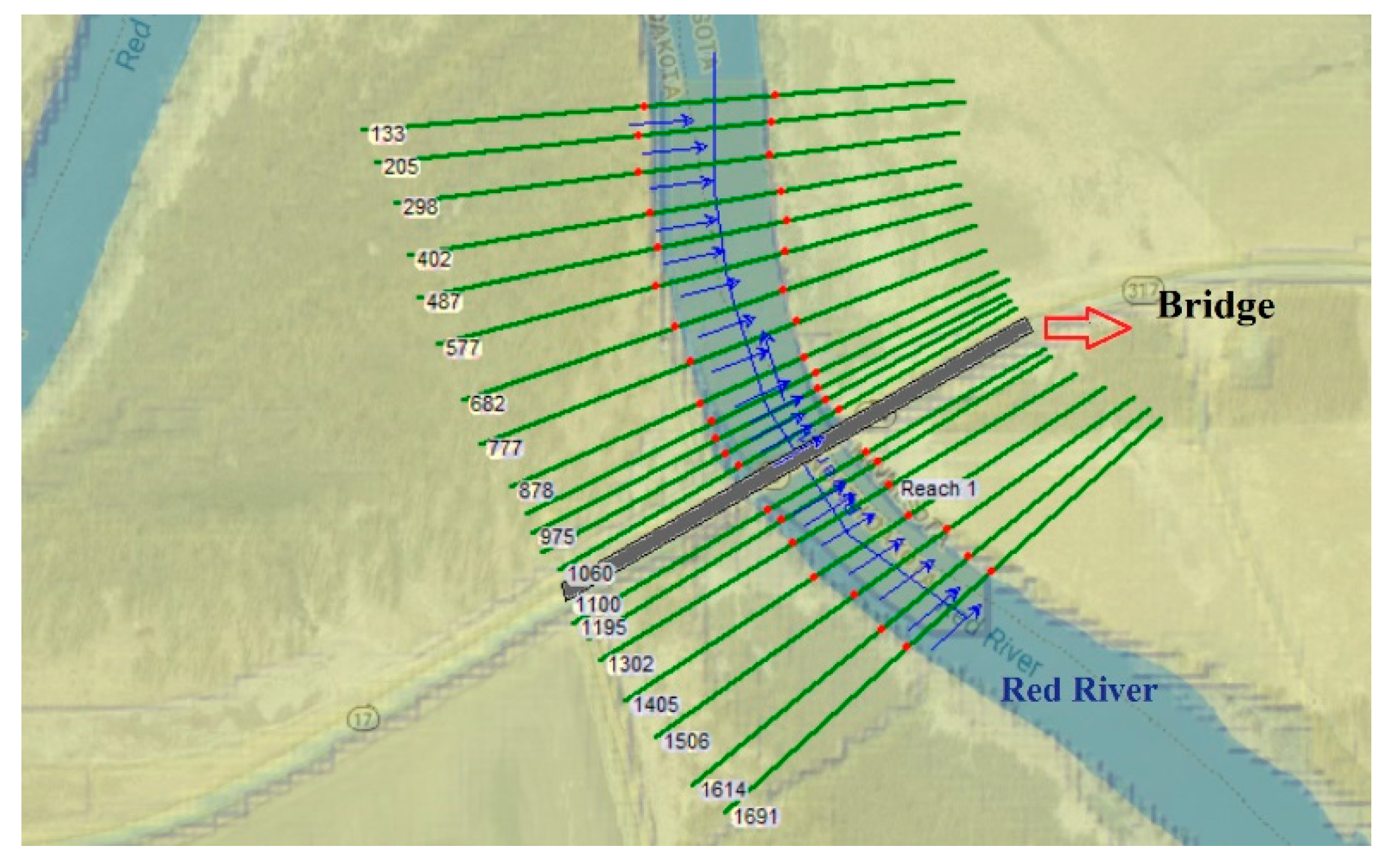
The bathymetry data obtained from both ADCP and LiDAR was used to prepare cross-sectional data and hydraulic structure data for river networks. Discharge and boundary conditions are provided in a steady flow file. Discharge data were established for the calculation procedure and completing the model building after geometric data entry. Six different discharges collected in the 2022 flood have been used as steady flow data to run HEC-RAS. In this study, the normal depth was used as the boundary condition for both the upstream and downstream areas. The normal depth was determined based on the slope of the study area. The defined plan is executed in a steady flow analysis when the proper data is entered into the geometry and steady flow files. Twenty 100-foot interval cross-sections were surveyed along the 2000-foot study reach, with two 40-foot interval cross-sections upstream and downstream of the bridge for greater bathymetry precision. RAS-Mapper was used to generate terrain models and display HEC-RAS data on maps by using river digitization to extract GIS data from overbank lines, centerlines, flow, and cross-section lines (
Figure 4) [
38]. In
Figure 4, red points show channel overbanks which describe a cross-section’s primary channel overbanks, the blue lines indicate the flow path lines and the green lines are representative of cross-sections cut lines are used to obtain the terrain’s elevation data to build a ground profile spanning channel flow.
3.4. Bridge Scour Modeling
The scour depth of bridge piers located on rivers can be determined by the software using hydraulic flow data, along with the shape and geometric characteristics of the bridge pier, and the composition and form of the riverbed substrate. The default model for estimating the local scour depth around bridge piers in the software is known as the CSU model, which is described as follows [
27].
where:
= the maximum scour depth; α= width or diameter of the pier;
= the flow depth in the pier upstream;
= the pier shape coefficient;
=the coefficient of the impact angle;
=the bed condition coefficient;
=the bed’s coefficient of reinforcement by the sediment particles;
= Froude number.
To calculate bridge scour, one can open the Hydraulic Design Functions window and choose the scour at bridges function. This selection will prompt the program to retrieve output for the approach section, upstream section, and sections within the bridge from the output file. Input data, a graphic, and a summary results window are also available. Input data tabs can be accessed for contraction scour, pier scour, and abutment scour. When entering contraction scour data, variables other than and can be automatically obtained from the HEC-RAS output file. When calculating contraction scour, the user needs to input only the (average size of bed material) and water temperature to determine the factor. To enter pier scour data, the user only needs to provide the pier nose shape (), the angle of attack for incoming flow, the bed condition (), and the size fraction of bed material, with all other values, obtained automatically from the HEC-RAS output file.
Morphological changes were measured with an acoustic Doppler current profiler on peak discharge days in April, May, and June 2022. Moving boat measurements for the repeat transects perpendicular to the flow were obtained at each transect location to begin collecting bathymetry data [
33,
34]. Most of the transects captured several acoustic reciprocal pairs, whereas the remaining transects contained one to three traversing passes. There was a total of 64 transects, and each transect took an average contact time of 4.5 minutes. The discharge was measured between April 2022 and June 2022, which was a flood event with a 16.5-year return period. The occurrence frequency of a specific flood event, also known as its return period, was computed using PeakFQ software obtained from the US Geological Survey [
35]. The dataset used for the analysis spans from the year 1882 up to 2021 and is based on peak discharge measurements collected at the Grand Forks station. The maximum discharge based on which the return period was estimated is 63,900 cfs, which is the highest recorded discharge for Grand Forks USGS station on April 24th, 2022. The return period of a flood refers to the average number of years between occurrences of a flood of a certain size or greater. It is calculated based on the probability of the flood occurring and the frequency of occurrence. The discharge in this investigation ranged from 13,000 to 47,150 cfs. LiDAR data is commonly used to create high-resolution topographic maps and digital elevation models. In this study, the overbank’s elevation was obtained from LiDAR data using the National Map of the U.S. Geological Survey with a resolution of 7.5 x 7.5 minutes to complete the cross-sections as input for the source of elevation information for flood mapping in HEC-RAS.
4. Results
4.1. Model Manning Coefficient
An observed flow of 13,250 cfs, 47,150 cfs, 36,250 cfs, 27,700 cfs, 19,500 cfs, and 13,000 cfs at the river upstream was used from the flood event in 2022 with a 16.5-year return period. These flow rates are considered low, medium, and high flow in the Red River. In this study, we selected the value for Manning’s roughness coefficient based on previous studies. The previous studies introduced ranges of Manning’s
n-coefficient values and we evaluated these ranges using statistical parameters to determine the best
n-coefficient value for our case study. The selected
n-coefficient value was then used in our hydrological analysis to improve the accuracy of flood prediction. Based on the literature review [
37,
39], the initial value of the
n-coefficient was set to be between 0.04 and 0.05 for the channel bed river and between 0.06 and 0.16 for the river banks.
Table 1 presents information on water level data that was both observed and simulated for a range of discharge data collected on the 2022 flood. R-squared is a statistical measure that indicates how well a regression model fits the observed data, with higher values indicating a better fit. For statistical analysis, the R-squared for Red River bathymetry data and simulated data were calculated, and the formula is:
is the ith water level value generated by the model,
is the ith water level value generated by measured data,
is the mean water level value of measured data series,
n is the total number of data series.
The value of the coefficient of determination (R2), 93%, indicates that 0.046 for the river channel, and 0.06 for the overbanks, is the best Manning’s n-coefficient value to use because it offers an excellent match between the observed and simulated water surface profile. shows the value of Manning’s n-coefficient for the main channel, and indicates the value of Manning’s n-coefficient for the overbanks. Since the left overbank (LOB) and right overbank (ROB) areas have similar vegetation, so only one value used is used for both overbanks.
4.2. Model Flood Mapping
Figure 5 depicts the topographical surface, which comprises multiple cross-sections in the HEC-RAS model for the research area at the Red River near the Grafton Bridge (Bridge 5872 in Minnesota and Bridge 0017-140.372 in North Dakota). The 3D Viewer’s multiple cross-sections visualize HEC-RAS simulation results and terrain data in three dimensions, which assists engineers when communicating hydraulic modeling results to decision-makers. The simulated inflow discharge water surface profile of 47,150 cfs and 13,000 cfs are depicted in
Figure 5a, and
Figure 5b, which are the high and low flow values of the measured data, respectively. The river flow entered the overbanks on the left overbank first due to the lower altitudes of the left overbank incorporated into the backwater phenomena when the flow gets close to the bridge or any obstacles. The term “backwater” refers to the rise in water level [
40]. The bridge’s pier will obstruct the flow and raise water levels upstream for subcritical flows. The entire overbank was underwater during the April 2022 Red River flood near Grafton (
Figure 5b).
Figure 6 depicts the water levels at the first and the last cross-section (
Figure 4) extracted from DEMs using geometry data. The ADCP bathymetry and LiDAR data could be combined into a single point cloud because the ADCP incorporated with ASV used in this study is a sensor platform capable of using data from multiple sources. A broad framework of standard specifications, practices, and guidelines is also necessary to enable multiple groups to consistently contribute well-described LiDAR and integrated digital elevation models (DEMs) to the development of an elevation in the river area. The National Geophysical Data Center (NOAA) and the USGS Earth Resources Observation & Science Center collaborated to create this framework to provide a single national representation of bathymetry and topography in the United States. Combining these two sets of information in the Ras Mapper’s terrain-making capability enables the creation of a single, continuous surface from several tiles that are all registered, have the same cell resolution, and are edge matched. This option can use many LiDAR tiles that line up.
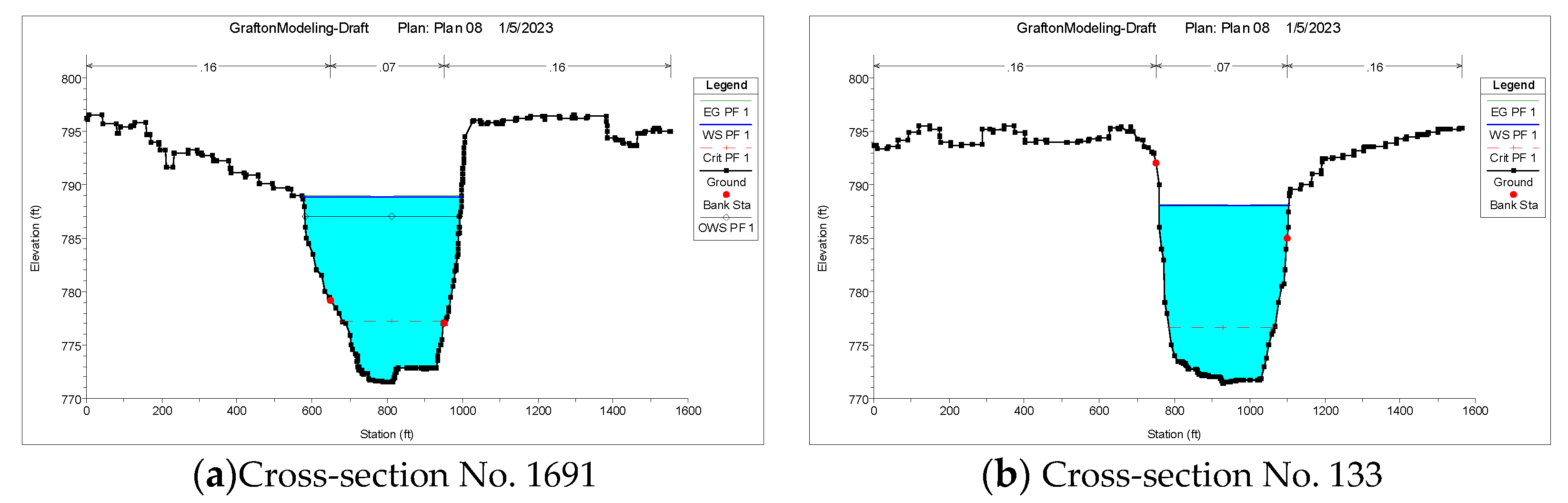
The simulation results indicate that cross-section No. 133, the last designed cross-section, is less impacted by the flood, whereas cross-section No. 1691, located upstream of the bridge, is more susceptible to flooding at low flow discharge conditions, which is 13,000 cfs (
Figure 6a,b). The water level for cross-sections No. 133 and No. 1691 is 788.14 ft and 789.00 ft, respectively. The existence of bridge piers or abutments in the streams will affect the stream flow and riverbed locally, causing the water to flow faster, the bridge to scour, and potentially jeopardizing the structure. A faster cross-section would have less depth when the discharge is the same, according to the continuity equation.
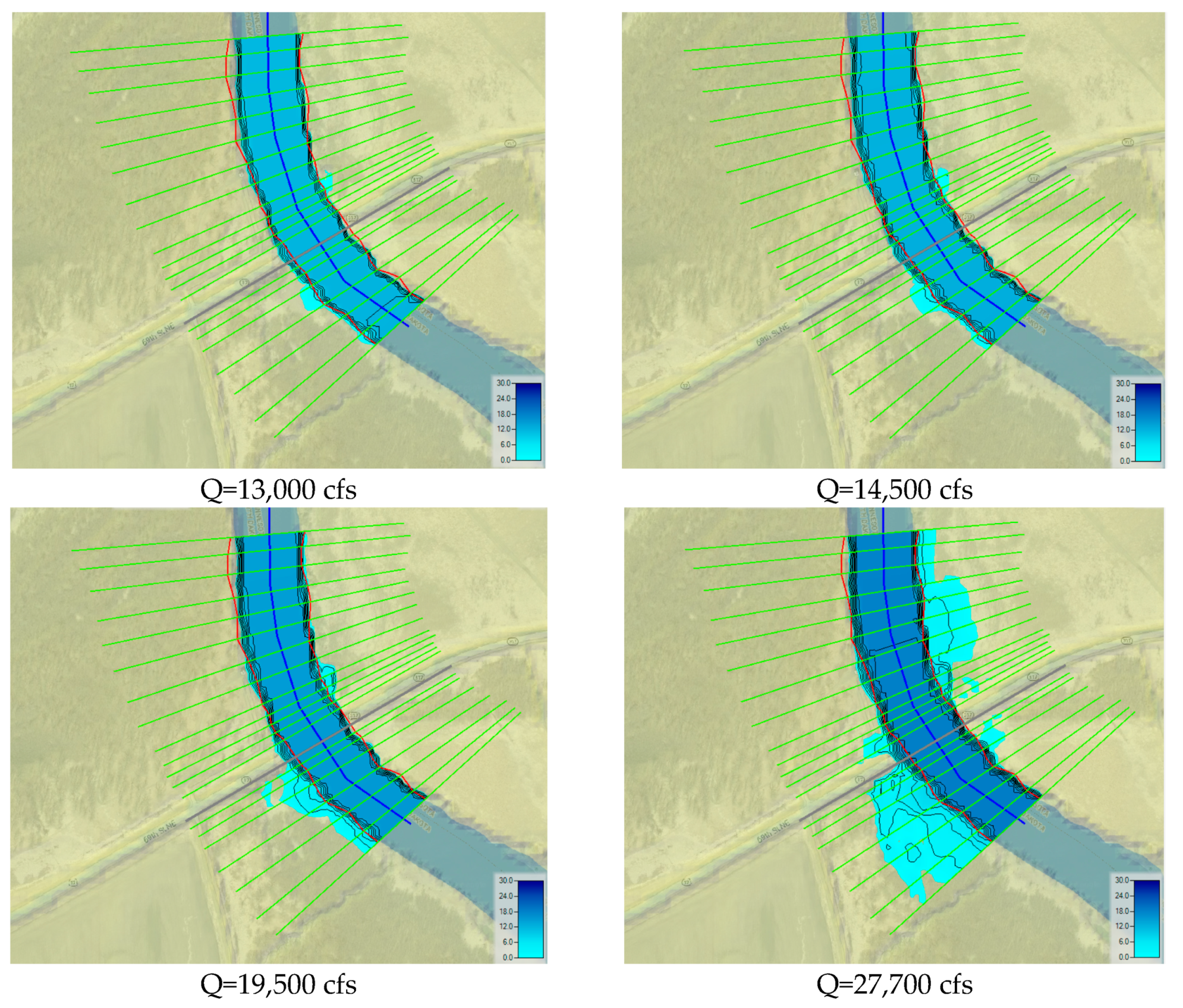
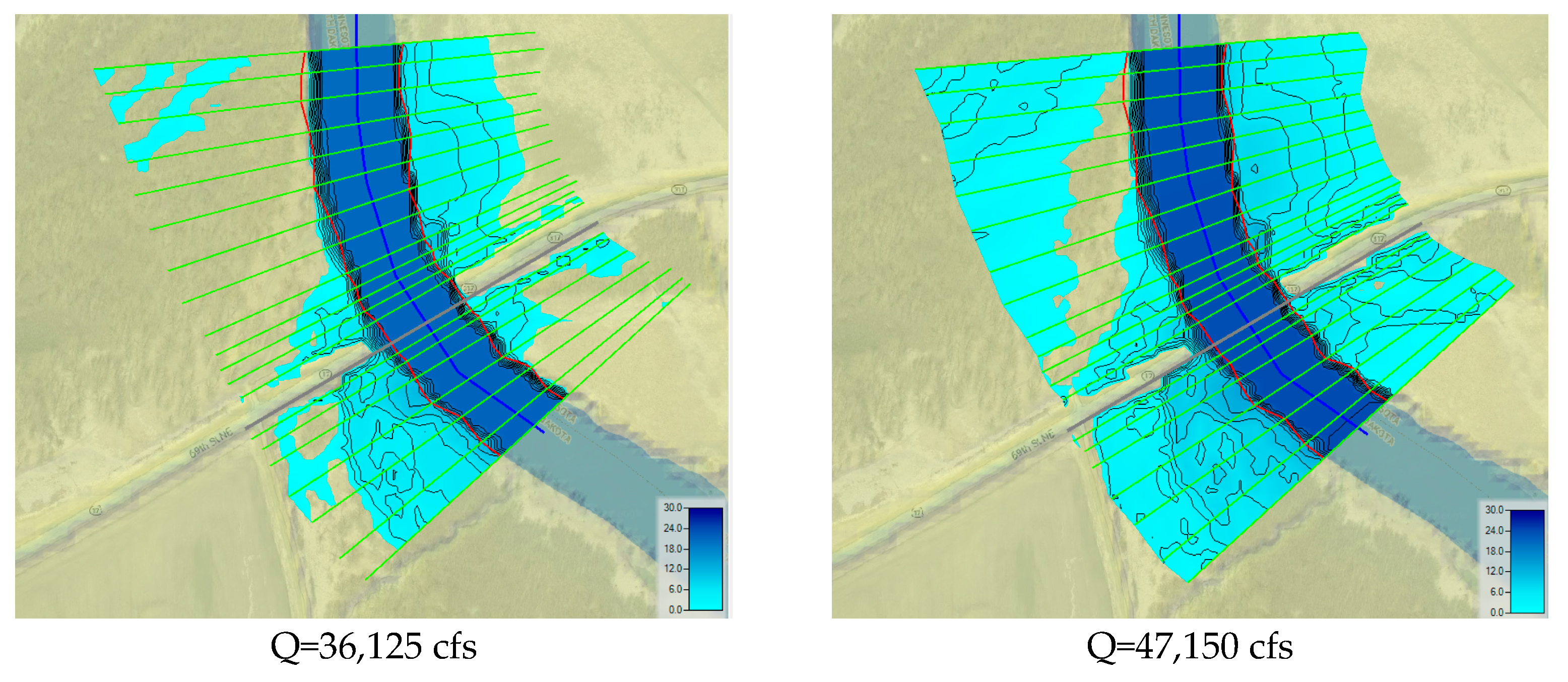
The flood map presented in
Figure 7 illustrates the depth changes at each cross-section with a steady flow simulation, where dark blue denotes deeper depths, and light blue denotes lower depths. The simulated flood maps illustrate the variance in water depths along the channel in terms of color. All discharges were measured for six time periods, from April 2022 to June 2022, and the highest flow was on April 27th at the Red River study location. The current study’s results indicate that the corresponding discharge was between 13,000 cfs and 47,150 cfs from April 2022 to June 2022. Downstream cross-sections, which were located downstream from the bridge, had a shallower depth during peak discharge conditions, and the upstream cross-sections were more affected by the flood (
Figure 7a,b). The water level tends to be higher on the upstream side of a bridge because the bridge deck acts as an obstacle to the water flow, causing it to flow through a narrower space. This creates a barrier, which in turn causes the water to accumulate and rise around the bridge as it flows around it. The results indicate that a substantial change in the water flow of 34,150 cfs resulted in a significant difference in flooding extent. The flood inundation extent determined using the HEC-RAS model varied substantially with slight changes in water depth because the Red River has a flat landscape.
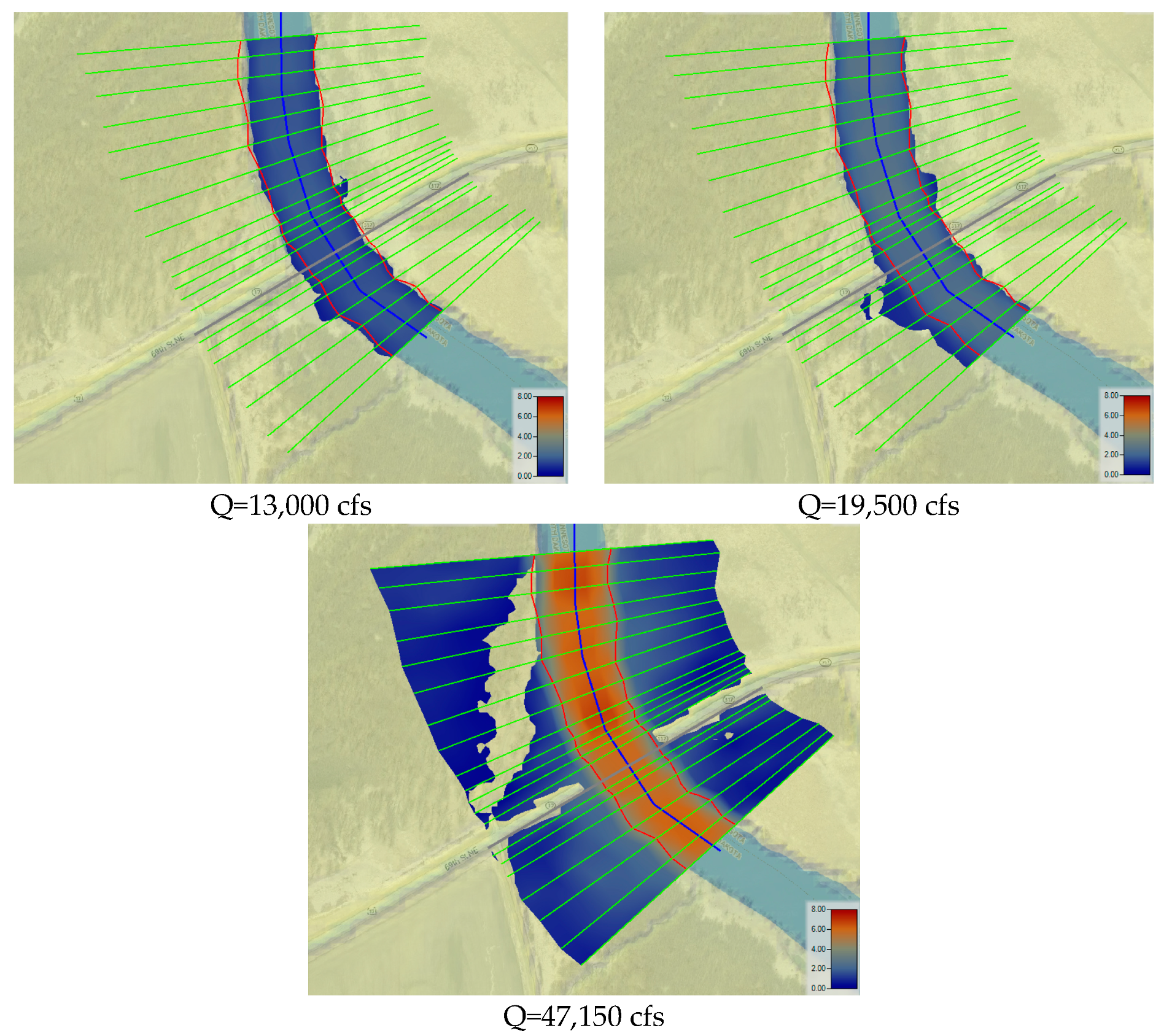
Figure 8 illustrates the simulation results of the velocity distribution for Q= 13,000 cfs, 19,500 cfs, and 47,150 cfs. These velocity mapping effects will help prevent erosion in the river overbanks and around bridge piers. The results from all three scenarios, which are low, medium, and high flow in the 2022 flood event, indicate that the flow velocity near the right side of the river overbank after the bridge location had higher values; therefore, protection may be required on this side of the river overbank. Furthermore, a high-velocity counter line, which is eddy flow, can be observed at all three discharges after bridge pier cross-section No. 933 (
Figure 4) in the river’s center. The existence of piers can cause the formation of eddies, which are circular currents that can change the flow patterns and speed of the water downstream of the pier. This fast-moving eddy flow becomes larger at higher velocities after the bridge pier, which could increase scour after the bridge pier. The maximum recorded velocity in the study area was 1.85 ft/s, 2.79 ft/s, and 6.75 ft/s for discharge values of 13,000 cfs, 19,500 cfs, and 47,700 cfs, respectively, occurring after cross-section No. 933 (
Figure 4).
4.3. Model Scour Bridge
In this project, hydraulic analysis was conducted using the HEC-RAS 6.0.0 software, which uses a steady flow simulation. The study aimed to predict local scour depth around an existing bridge, specifically caused by contraction scour and piers with square nose shapes. Most of the data required for calculating contraction scour was generated automatically by the HEC-RAS program, based on the steady flow analysis. The remaining data, including sediment diameter (
) on each left and right overbank and channel, were entered manually. The HEC-RAS program automatically calculated the coefficient
using the available
field measurements. Finally, the program analyzed the contraction scour depth around the piers using the CSU equation. Then the modeling of local contraction scour depth with HEC-RAS 6.0.0 can be seen in
Figure 9.
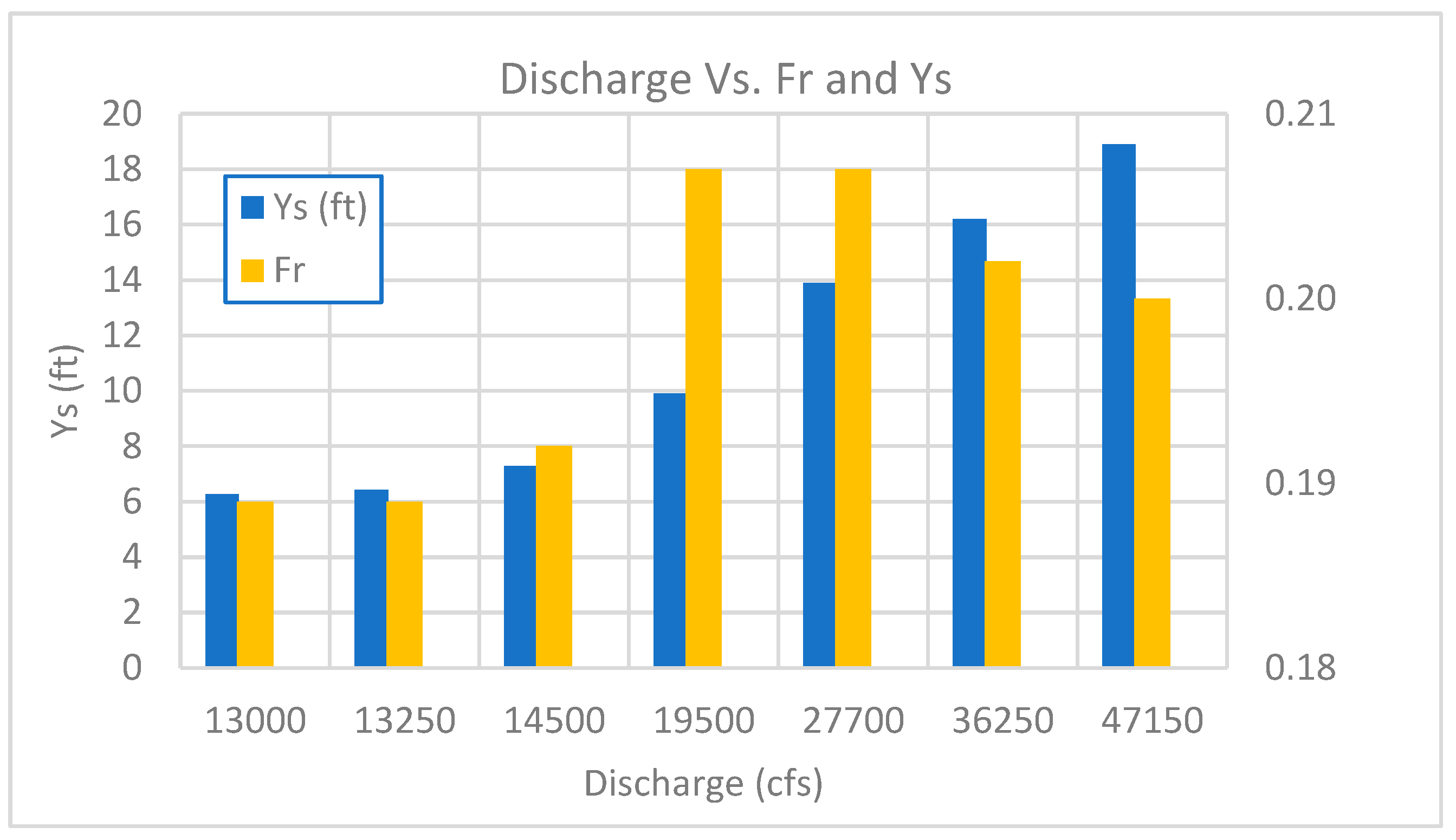
Figure 9 shows the relationship between contraction scour depth (
and the Froude number (
on the existing bridge concerning discharge increasing. There is a rise in Froude number between Q=19,500 cfs and Q=36,250 cfs. The contraction scours depth and the Froude’s number increase further for the Q=13,000 cfs to Q=14,500 cfs of as the water level overtopped to the deck of the bridge. For the discharge of 47,150 cfs the water level reaches the deck of the bridge and due to this contraction scour depth increases whereas Froude’s number decreases.
When the discharge increases in a river, the velocity of the water also increases, which leads to a higher Froude number. This is because the inertial forces become relatively more significant as the velocity increases. However, as the water reaches the deck, the depth of the water decreases, and the gravitational forces become more important. This causes a decrease in the Froude number, even though the velocity may still be high.
As water flows towards a bridge, the channel or riverbed in which it is flowing becomes constricted due to the presence of the bridge piers or abutments. This narrowing of the channel causes an increase in the velocity of the water as it passes through the bridge opening and the cross-sectional area of the channel must decrease to maintain the same mass flow rate. Therefore, as the water passes through the bridge opening, the depth of the water decreases. This can lead to a concentrated flow of water around the piers or abutments, which can increase the potential for erosion and scour around the bridge foundations. On the other hand, the contraction scours depth continues to increase even after the Froude number has decreased. This is because the velocity of the water is still high, and it can still cause erosion of the riverbed, leading to deeper contraction scour depths.
5. Conclusions
Authors should discuss the results and how they can be interpreted from the perspective of previous studies and the working hypotheses. The findings and their implications should be discussed in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted.
Our measurement of one of the most extreme flood occurrences in this paper’s invention allowed us to validate the accuracy of the HEC-RAS model’s flood predictions and evaluate the model’s performance under extreme flood events. By using geospatial techniques, we were able to enhance the accuracy of the model’s flood mapping by incorporating topographic data and other relevant information. This study’s findings can contribute to better flood management and emergency response planning in the study area and other regions facing similar flood events.
The study aims to determine the best value for the Manning coefficient to improve the accuracy of flood prediction in the Red River. The selected value for Manning’s roughness coefficient was based on previous studies, and statistical analysis was performed to determine the best value for the case study. The value of the coefficient of determination (R2), which was 93%, indicates that 0.046 for the river channel and 0.06 for the overbanks is the best Manning’s n-coefficient value to use.
The bathymetry data were collected using ADCP and ASV combined with LiDAR data to determine the flow for a flood event in 2022, and the flood mapping was generated using HEC-RAS modeling. Flood inundation mapping indicates that an eddy flow occurs immediately after the bridge and becomes relatively larger with an increase in flow discharge and velocity. The results showed good agreement between the methodologies, indicating the potential of using ADCPs incorporated with ASV and LiDAR data together for flood inundation mapping studies due to the advantages of integrating bathymetry, flow velocity, and discharge flood data.
The study also showed that as discharge increases, the Froude number and contraction scour depth increase, but as the water level reached the deck of the bridge, the Froude number decreases while contraction scour depth continues to increase due to high velocity. Narrowing the channel by bridge piers can lead to concentrated flow and increase scour potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A.; methodology, V.A., software, V.A.; validation, V.A., and Y.H.L; formal analysis, V.A.; investigation, V.A., resources, V.A.; data curation, V.A., writing—original draft preparation, V.A.; writing—review and editing, V.A., and Y.H.L.; visualization, V.A.; supervision, Y.H.L.; project administration, Y.H.L.; funding acquisition, Y.H.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the North Dakota Department of Transportation, grant number UND0026475.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank The North Dakota Department of Transportation (NDDOT) for their financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lim, Y.H. and D.L. Voeller, Regional flood estimations in Red River using L-moment-based index-flood and Bulletin 17B procedures. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2009. 14(9): p. 1002-1016. [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H. and D.L. Voeller, Regional flood estimations in Red River using L-moment-based index-flood and Bulletin 17B procedures. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2009. 14(9): p. 1002-1016. [CrossRef]
- Todhunter, P.E., Uncertainty of the assumptions required for estimating the regulatory flood: Red River of the North. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2012. 17(9): p. 1011-1020.
- Deschamps, A., et al. Geospatial data integration for applications in flood prediction and management in the Red River Basin.
- Abad, J.D., et al. Exploratory study of the influence of the wake produced by acoustic Doppler velocimeter probes on the water velocities within measurement volume. in World Water and Environmental Resources Congress. 2004. Salt Lake City.
- Garcia, C.M., K. Oberg, and M.H. García, ADCP measurements of gravity currents in the Chicago River, Illinois. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007. 133(12): p. 1356-1366. [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, B., A.J.F. Hoitink, and R.J. Labeur, Flow structure caused by a local cross-sectional area increase and curvature in a sharp river bend. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2015. 120(9): p. 1771-1783. [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, B., A.J.F. Hoitink, and M.G. Sassi, Coupled ADCPs can yield complete Reynolds stress tensor profiles in geophysical surface flows. Geophysical Research Letters 2011. 38(6). [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, B., M.G. Sassi, and A.J.F. and Hoitink, Improved flow velocity estimates from moving-boat ADCP measurements. Water Resources Research, 2014. 50(5): p. 4186-4196. [CrossRef]
- Parsapour-Moghaddam, P. and C.D. Rennie. 3D versus 2D calibration of a 3D hydrodynamic model. in 37th IAHR World Congress. 2017a. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
- Muste, M., K. Yu, and M. Spasojevic, Practical aspects of ADCP data use for quantification of mean river flow characteristics; part I: moving-vessel measurements. Flow measurement and instrumentation, 2004. 15(1): p. 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M., et al., The acoustic properties of suspended sediment in large rivers: consequences on ADCP methods applicability. Water, 2016. 8(1): p. 13. [CrossRef]
- Rennie, C.D. and F. Rainville, Case study of precision of GPS differential correction strategies: Influence on aDcp velocity and discharge estimates. Journal of hydraulic engineering, 2006. 132(3): p. 225-234. [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, B., M. Sassi, and A. Hoitink, Improved flow velocity estimates from moving-boat ADCP measurements. Water resources research, 2014. 50(5): p. 4186-4196. [CrossRef]
- Atashi, V., et al. Characteristics of Seasonality on 3D Velocity and Bathymetry Profiles in Red River of the North. in World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2022.
- Prabnakorn, S., et al., Development of an integrated flood hazard assessment model for a complex river system: a case study of the Mun River Basin, Thailand. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2019. 5(4): p. 1265-1281. [CrossRef]
- Bhuyian, M.N., A.J. Kalyanapu, and F. Nardi, Approach to digital elevation model correction by improving channel conveyance. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2015. 20(5): p. 04014062. [CrossRef]
- Cook, A. and V. Merwade, Effect of topographic data, geometric configuration and modeling approach on flood inundation mapping. Journal of hydrology, 2009. 377(1-2): p. 131-142. [CrossRef]
- Getahun, Y.S. and S.L. Gebre, Flood hazard assessment and mapping of flood inundation area of the Awash River Basin in Ethiopia using GIS and HEC-GeoRAS/HEC-RAS model. Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering, 2015. 5(4): p. 1.
- Saksena, S. and V. Merwade, Incorporating the effect of DEM resolution and accuracy for improved flood inundation mapping. Journal of Hydrology, 2015. 530: p. 180-194. [CrossRef]
- Huţanu, E., et al., Using 1D HEC-RAS modeling and LiDAR data to improve flood hazard maps accuracy: A case study from Jijia Floodplain (NE Romania). Water, 2020. 12(6): p. 1624. [CrossRef]
- Merz, B., A. Thieken, and M. Gocht, Flood risk mapping at the local scale: concepts and challenges, in Flood risk management in Europe. 2007, Springer. p. 231-251.
- Namara, W.G., T.A. Damisse, and F.G. Tufa, Application of HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS model for Flood Inundation Mapping, the case of Awash Bello Flood Plain, Upper Awash River Basin, Oromiya Regional State, Ethiopia. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2022. 8(2): p. 1449-1460.
- Zheng, X., et al., GeoFlood: Large-scale flood inundation mapping based on high-resolution terrain analysis. Water Resources Research, 2018. 54(12): p. 10,013-10,033. [CrossRef]
- Pinos, J., L. Timbe, and E. Timbe, Evaluation of 1D hydraulic models for the simulation of mountain fluvial floods: a case study of the Santa Bárbara River in Ecuador. Water Practice and Technology, 2019. 14(2): p. 341-354. [CrossRef]
- Noor, M., et al., Experimental and HEC-RAS modelling of bridge pier scouring. Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences, 2020. 74(1): p. 119-132.
- Ghaderi, A., R. Daneshfaraz, and M. Dasineh, Evaluation and prediction of the scour depth of bridge foundations with HEC-RAS numerical model and empirical equations (Case Study: Bridge of Simineh Rood Miandoab, Iran). Engineering Journal, 2019. 23(6): p. 279-295. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.J. and S. Yadav, Analysis of scour depth in the case of parallel bridges using HEC-RAS. Water Supply, 2020. 20(8): p. 3419-3432. [CrossRef]
- Babiracki, D., Lateral Migration of the Red River, in the Vicinity of Grand Forks, North Dakota. 2015.
- Lindenschmidt, K.-E., et al., Ice jam modelling of the Lower Red River. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2012. 4(1): p. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.V. and S.R. Davis, Evaluating scour at bridges. 2001, United States. Federal Highway Administration. Office of Bridge Technology.
- Carlson, D.F., et al., An affordable and portable autonomous surface vehicle with obstacle avoidance for coastal ocean monitoring. HardwareX, 2019. 5: p. e00059. [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.S., et al., Measuring discharge with acoustic Doppler current profilers from a moving boat. 2009: US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey Reston, Virginia (EUA).
- SonTek, RiverSurveyor S5/M9 system manual firmware version 3.00. 2012, SonTek/YSI San Diego, California.
- Veilleux, A.G., et al., Estimating magnitude and frequency of floods using the PeakFQ 7.0 program: US Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2013–3108. US Geological Survey Fact Sheet, 2014. 2.
- Brunner, G., CEIWR-HEC HEC-RAS River Analysis System: User’s Manual Version 6.0. US Army Corps of Engineers Institute for Water Resources, HEC, January: Davis, CA, USA, 2021.
- Chow, V.T., Open-channel Hydraulics. New York: McGram-Hill Book Company. 1959, Inc.
- Banks, J.C., J.V. Camp, and M.D. Abkowitz, Adaptation planning for floods: a review of available tools. Natural hazards, 2014. 70(2): p. 1327-1337. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, S.P.D., 180 Fifth Street East, Suite 700, St. Paul, Minnesota 55101-1678, Lower Red Basin Retention (LRBR) Study. 2019.
- Charbeneau, R.J. and E.R. Holley, Backwater effects of bridge piers in subcritical flow. 2001: Center for Transportation Research, Bureau of Engineering Research ….
- Pro, G.E., Grafton Bridge, Marshal County. 08/10/2015. p. 48.4133, -97.1377.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).