Submitted:
03 April 2023
Posted:
03 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
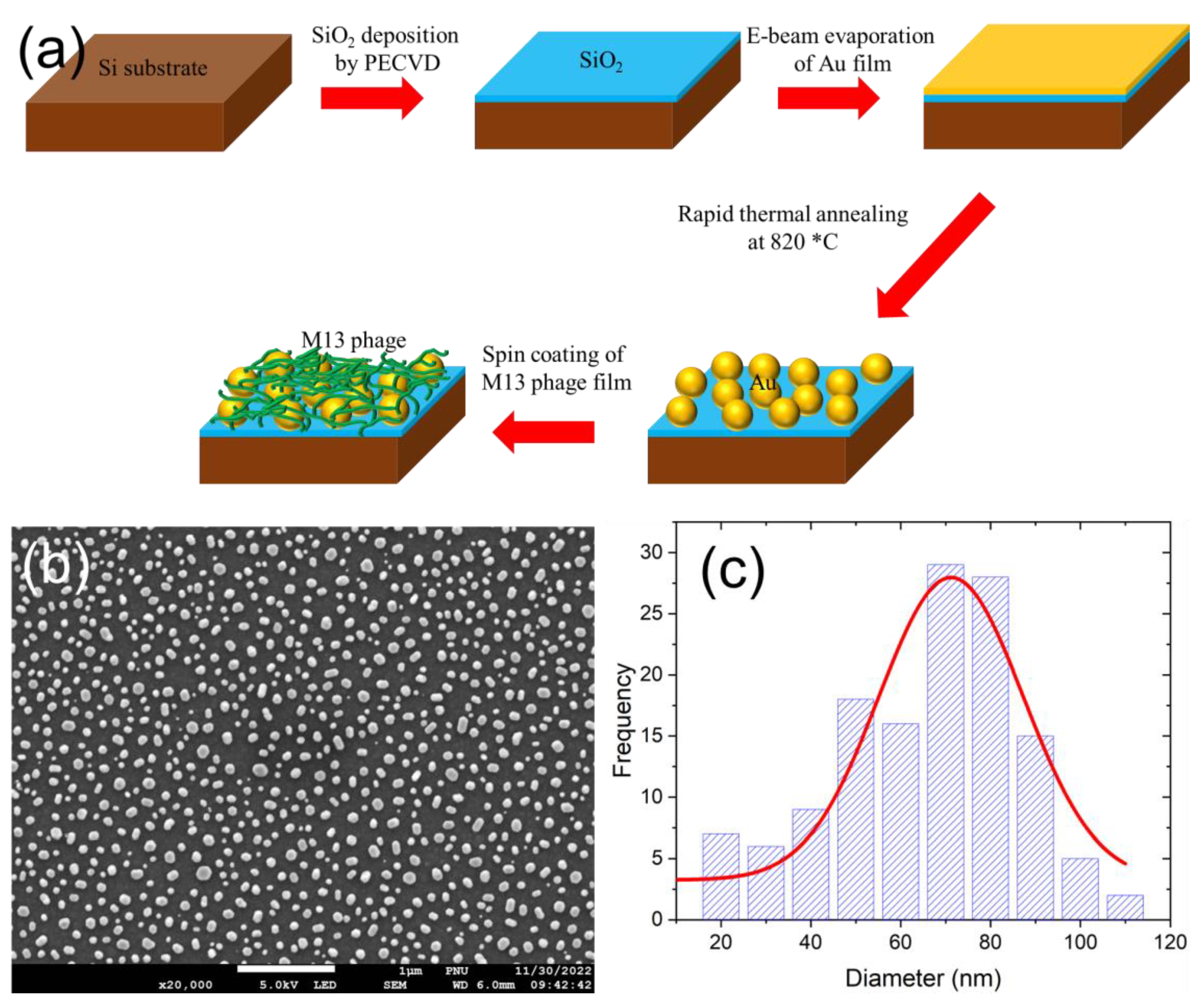
2.1. Fabrication of plasmonic nanoparticle – M13 bacteriophage biomaterial thin film nanostructure
2.2. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.3. Optical measurements
2.4. Three-dimensional electromagnetic simulations
3. Results and Discussion
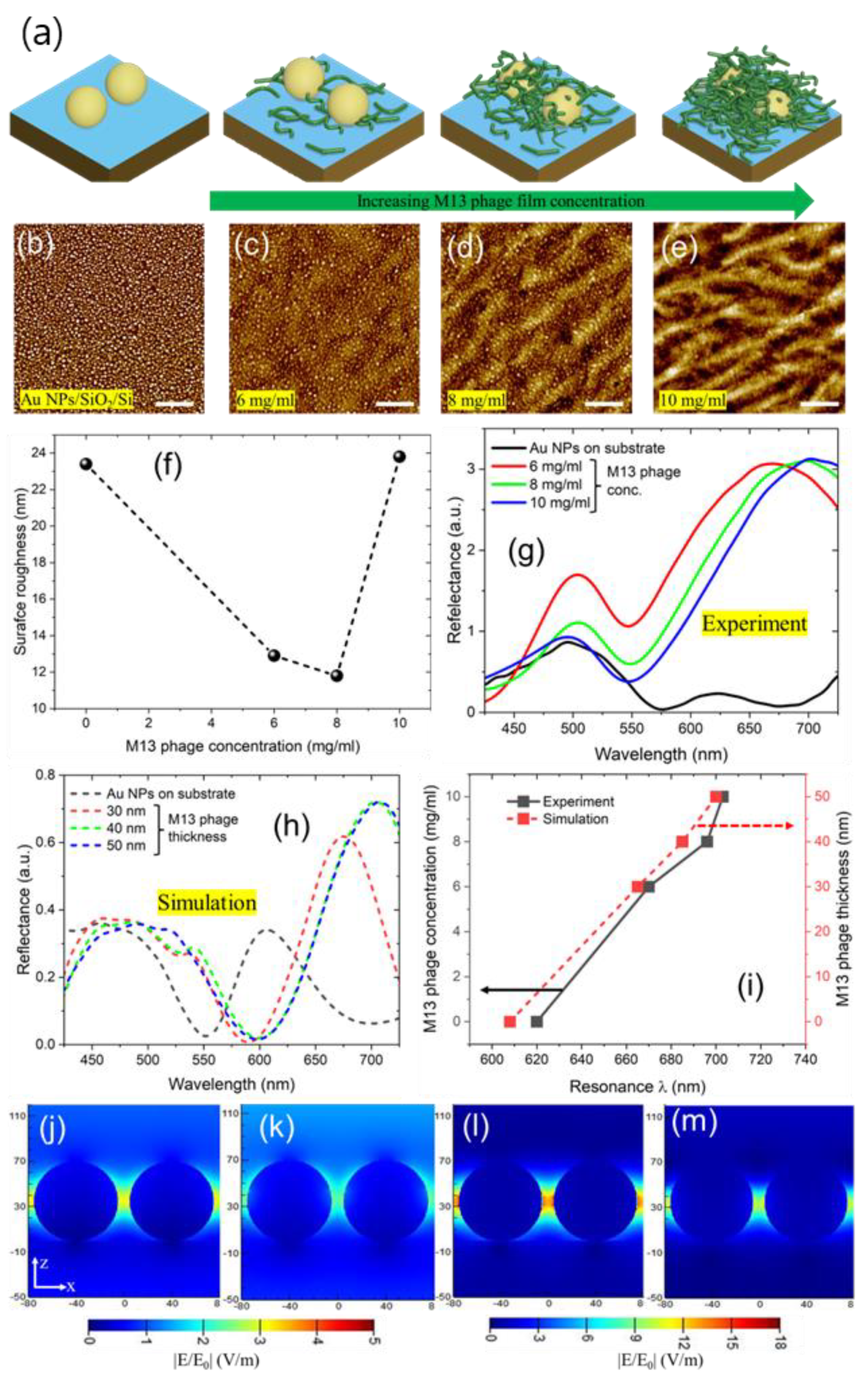
3.1. Fabrication analysis and optical properties
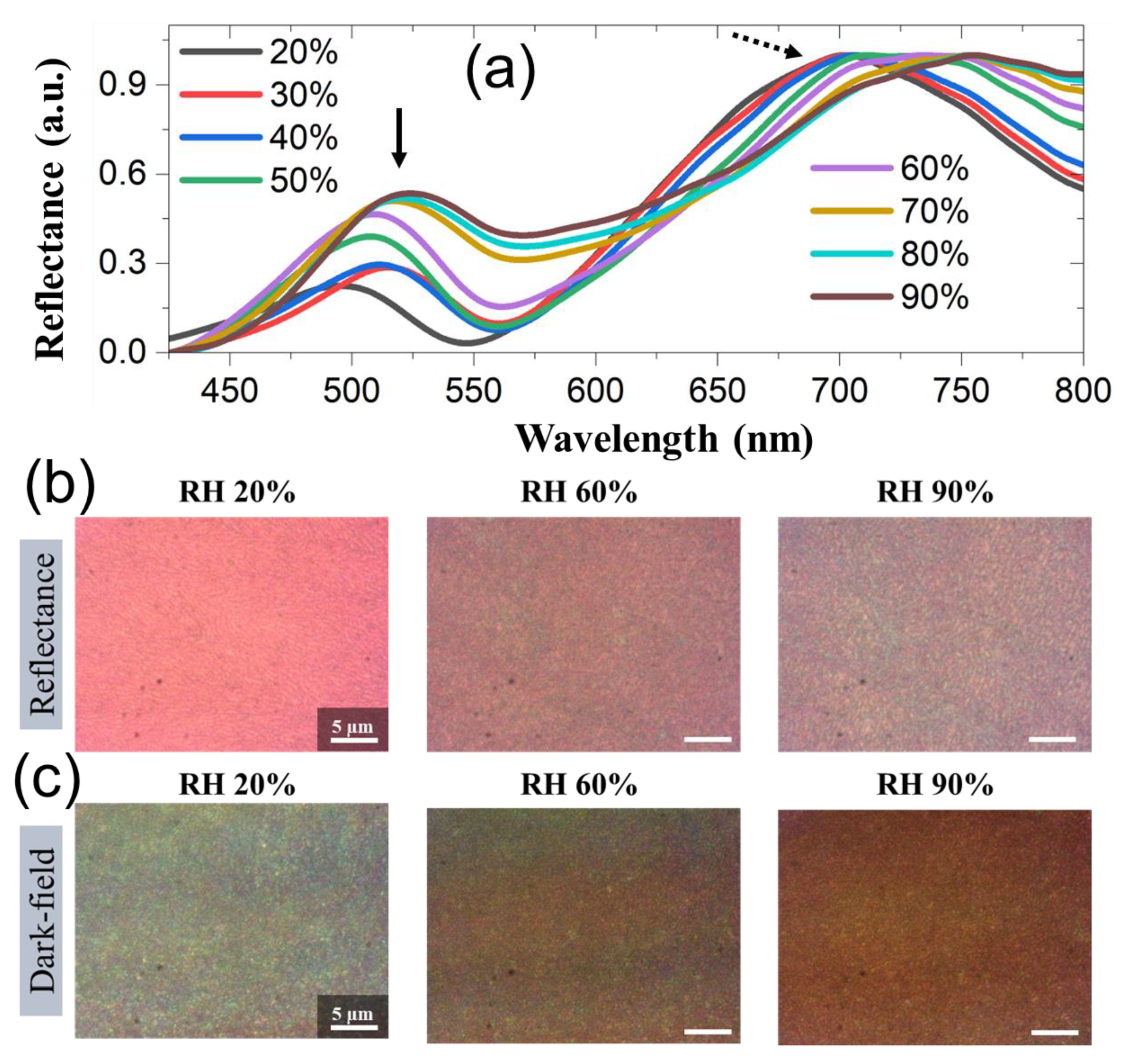
3.2. Dynamic response of M13 phage
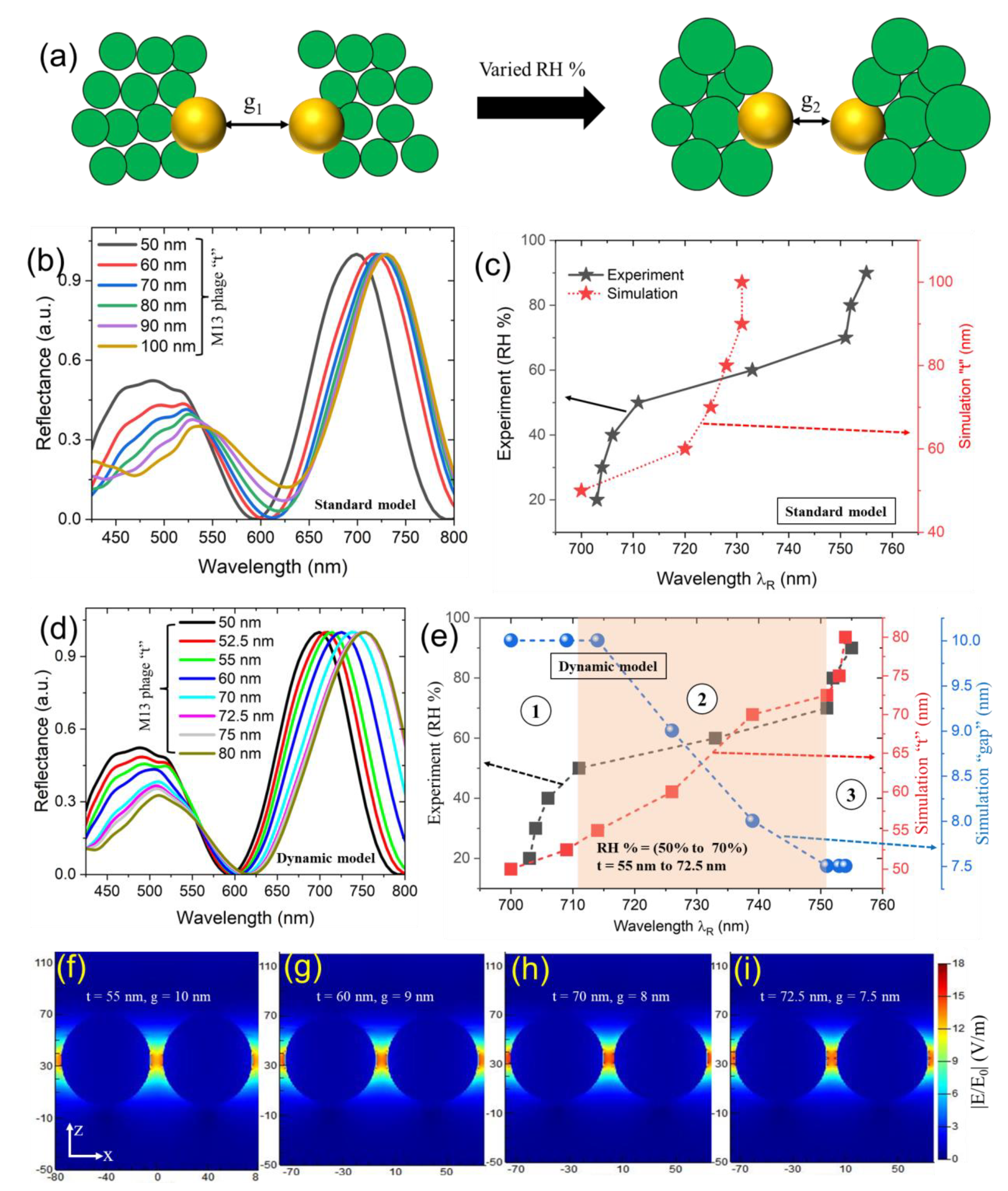
3.3. Understanding the optical and geometrical properties as a function of dynamic response
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Willner, I.; Rubin, S. Control of the Structure and Functions of Biomaterials by Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-Based Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Conductive Biomaterials for Muscle Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 229, 119584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. Memristors with Biomaterials for Biorealistic Neuromorphic Applications. Small Science 2022, 2, 2200028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorsi, M.T.; Curry, E.J.; Chorsi, H.T.; Das, R.; Baroody, J.; Purohit, P.K.; Ilies, H.; Nguyen, T.D. Piezoelectric Biomaterials for Sensors and Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.A.C.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Hussain, S.M.; Bilal, M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bioinspired Biomaterials and Enzyme-Based Biosensors for Point-of-Care Applications with Reference to Cancer and Bio-Imaging. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2019, 17, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-W.; Chung, W.-J.; Heo, K.; Jin, H.-E.; Lee, B.Y.; Wang, E.; Zueger, C.; Wong, W.; Meyer, J.; Kim, C.; et al. Biomimetic Virus-Based Colourimetric Sensors. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-S.; Kim, W.-G.; Kim, C.; Park, G.-T.; Heo, J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Oh, J.-W. M13 Bacteriophage-Based Self-Assembly Structures and Their Functional Capabilities. Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry 2015, 12, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.-J.; Lee, D.-Y.; Yoo, S.Y. Chemical Modulation of M13 Bacteriophage And Its Functional Opportunities for Nanomedicine. IJN 2014, 9, 5825–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.; Jin, H.-E.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Wang, E.; Lee, S.-W. Transient Self-Templating Assembly of M13 Bacteriophage for Enhanced Biopiezoelectric Devices. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Moon, J.-S.; Oh, J.-W. Recent Advances in M13 Bacteriophage-Based Optical Sensing Applications. Nano Convergence 2016, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, G.T.; Guimaraes, C.P.; Spooner, E.; Ploegh, H.L.; Belcher, A.M. Orthogonal Labeling of M13 Minor Capsid Proteins with DNA to Self-Assemble End-to-End Multiphage Structures. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsedev, U.; Lin, C.-W.; Hess, G.T.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Lam, F.C.; Belcher, A.M. Phage Particles of Controlled Length and Genome for In Vivo Targeted Glioblastoma Imaging and Therapeutic Delivery. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11676–11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Duc, T.-T.; Plank, J.M.; Chen, G.; Harrison, R.E.S.; Morikis, D.; Liu, H.; Haberer, E.D. M13 Bacteriophage Spheroids as Scaffolds for Directed Synthesis of Spiky Gold Nanostructures. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13055–13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, V.; Han, J.; Kim, C.; Kang, Y.-C.; Oh, J.-W. Self-Assembled Nanoporous Biofilms from Functionalized Nanofibrous M13 Bacteriophage. Viruses 2018, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Qu, S.; Weng, J.; Feng, B. Fabrication of Nanostructured M13 Bacteriophage Films on Titanium Surfaces. Materials Letters 2016, 182, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Chung, W.-J.; Wang, D.; Lee, S.-W.; Yoreo, J.J.D. Growth of Au and ZnS Nanostructures via Engineered Peptide and M13 Bacteriophage Templates. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 2996–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S.; Lee, D.; Kang, D.-K.; Kim, K. M13 Virus-Templated Open Mouth-like Platinum Nanostructures Prepared by Electrodeposition: Influence of M13-Virus on Structure and Electrocatalytic Activity. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2020, 879, 114755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Fang, H.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, S.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Leng, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. M13 Bacteriophage as Biometric Component for Orderly Assembly of Dynamic Light Scattering Immunosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2022, 217, 114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, B.Y.; Lee, B.D.; Okada, K.; Ji, S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.-W. M13 Virus Triboelectricity and Energy Harvesting. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 6851–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Fan, B.; Samdin, T.D.; Monteiro, D.A.; Desai, M.S.; Scheideler, O.; Jin, H.-E.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-W. Phage-Based Structural Color Sensors and Their Pattern Recognition Sensing System. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3632–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-W.; Mao, C.; Flynn, C.E.; Belcher, A.M. Ordering of Quantum Dots Using Genetically Engineered Viruses. Science 2002, 296, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.W.; Kim, K.W.; Hong, Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Gwak, D.; Heo, K. Recent Developments and Prospects of M13- Bacteriophage Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Devices. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, M.H.; Park, C.W.; Lee, S.M.; Soh, J.O.; Lee, J.H. M13 Bacteriophage-Based Bio-Nano Systems for Bioapplication. BioChip J 2022, 16, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courchesne, N.-M.D.; Klug, M.T.; Chen, P.-Y.; Kooi, S.E.; Yun, D.S.; Hong, N.; Fang, N.X.; Belcher, A.M.; Hammond, P.T. Assembly of a Bacteriophage-Based Template for the Organization of Materials into Nanoporous Networks. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-M.; Devaraj, V.; Jeong, N.-N.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, T.; Yi, S.H.; Kim, W.-G.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, H.-M.; et al. Neural Mechanism Mimetic Selective Electronic Nose Based on Programmed M13 Bacteriophage. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2022, 196, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; Lee, Y.; Devaraj, V.; Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, C.; Choi, E.J.; Han, D.-W.; Oh, J.-W. Investigation of Colorimetric Biosensor Array Based on Programable Surface Chemistry of M13 Bacteriophage towards Artificial Nose for Volatile Organic Compound Detection: From Basic Properties of the Biosensor to Practical Application. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2021, 188, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Ladewski, R.; Miller, R.; Dang, X.; Qi, J.; Liau, F.; Belcher, A.M.; Hammond, P.T. Layer-by-Layer Assembled Porous Photoanodes for Efficient Electron Collection in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Dang, X.; Klug, M.T.; Qi, J.; Dorval Courchesne, N.-M.; Burpo, F.J.; Fang, N.; Hammond, P.T.; Belcher, A.M. Versatile Three-Dimensional Virus-Based Template for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells with Improved Electron Transport and Light Harvesting. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6563–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Solis, D.J.; Reiss, B.D.; Kottmann, S.T.; Sweeney, R.Y.; Hayhurst, A.; Georgiou, G.; Iverson, B.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-Based Toolkit for the Directed Synthesis of Magnetic and Semiconducting Nanowires. Science 2004, 303, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Records, W.C.; Yoon, Y.; Ohmura, J.F.; Chanut, N.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-Templated Pt–Ni(OH)2 Nanonetworks for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Reduction of Water. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Kohli, A.G.; Moser, F.; Endy, D.; Belcher, A.M. Refactored M13 Bacteriophage as a Platform for Tumor Cell Imaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Synth. Biol. 2012, 1, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neltner, B.; Peddie, B.; Xu, A.; Doenlen, W.; Durand, K.; Yun, D.S.; Speakman, S.; Peterson, A.; Belcher, A. Production of Hydrogen Using Nanocrystalline Protein-Templated Catalysts on M13 Phage. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3227–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, S.-J.; Devaraj, V.; Song, H.; Lee, J.-M.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jang, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, H.; et al. Biomaterial Actuator of M13 Bacteriophage in Dynamically Tunable Plasmonic Coupling Structure. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 369, 132326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokullu, E.; Pinsard, M.; Zhang, J.; Plathier, J.; Kolhatkar, G.; Blum, A.S.; Légaré, F.; Ruediger, A.; Ozaki, T.; Gauthier, M.A. Plasmonic Enhancement of Two-Photon Excitation Fluorescence by Colloidal Assemblies of Very Small AuNPs Templated on M13 Phage. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhong, X.; Yang, C.-T.; Zhou, X. Gold Nanoparticles-Decorated M13 Phage SPR Probe for Dual Detection of Antigen Biomarkers in Serum. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2023, 374, 132811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Charlermroj, R.; Morton, M.J.; Oplatowska-Stachowiak, M.; Grant, I.R.; Elliott, C.T. Development of a M13 Bacteriophage-Based SPR Detection Using Salmonella as a Case Study. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2014, 190, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourakbari, R.; Yousefi, M.; Khalilzadeh, B.; Irani-nezhad, M.H.; Khataee, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Soleimanian, A.; Kamrani, A.; Chakari-Khiavi, F.; Abolhasan, R.; et al. Early Stage Evaluation of Colon Cancer Using Tungsten Disulfide Quantum Dots and Bacteriophage Nano-Biocomposite as an Efficient Electrochemical Platform. Cancer Nanotechnology 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, D.; Xu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Song, X. Simultaneous Detection of Three Zoonotic Pathogens Based on Phage Display Peptide and Multicolor Quantum Dots. Analytical Biochemistry 2020, 608, 113854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi Lai, J.; Inoue, N.; Wei Oo, C.; Kawasaki, H.; Soon Lim, T. One-Step Synthesis of M13 Phage-Based Nanoparticles and Their Fluorescence Properties. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.M.; Podgornik, R.; Strangi, G.; Steinmetz, N.F. Photonics and Plasmonics Go Viral: Self-Assembly of Hierarchical Metamaterials. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2015, 26, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrescu, D.S.; Blum, A.S. Viral-based Nanomaterials for Plasmonic and Photonic Materials and Devices. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, V.; Lee, I.H.; Kim, M.; Nguyen, T.M.; Son, J.P.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, J.-W. Unveiling Facet Effects in Metallic Nanoparticles to Design an Efficient Plasmonic Nanostructure. Current Applied Physics 2022, 44, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-G.; Devaraj, V.; Yang, Y.; Lee, J.-M.; Kim, J.T.; Oh, J.-W.; Rho, J. Three-Dimensional Plasmonic Nanoclusters Driven by Co-Assembly of Thermo-Plasmonic Nanoparticles and Colloidal Quantum Dots. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 16450–16457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical Constants of the Noble Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List of Contributors for Volume I. In Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Palik, E.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Academic Press, 1997; pp. xv–xvi. ISBN 9780125444156. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




