Submitted:
31 March 2023
Posted:
03 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Cell lines and cell culture reagents
Flow cytometry [FCM] analysis and antibodies
Cell imaging
Sample preparation, mass spectrometer setup and proteins identification
Electron microscopy
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
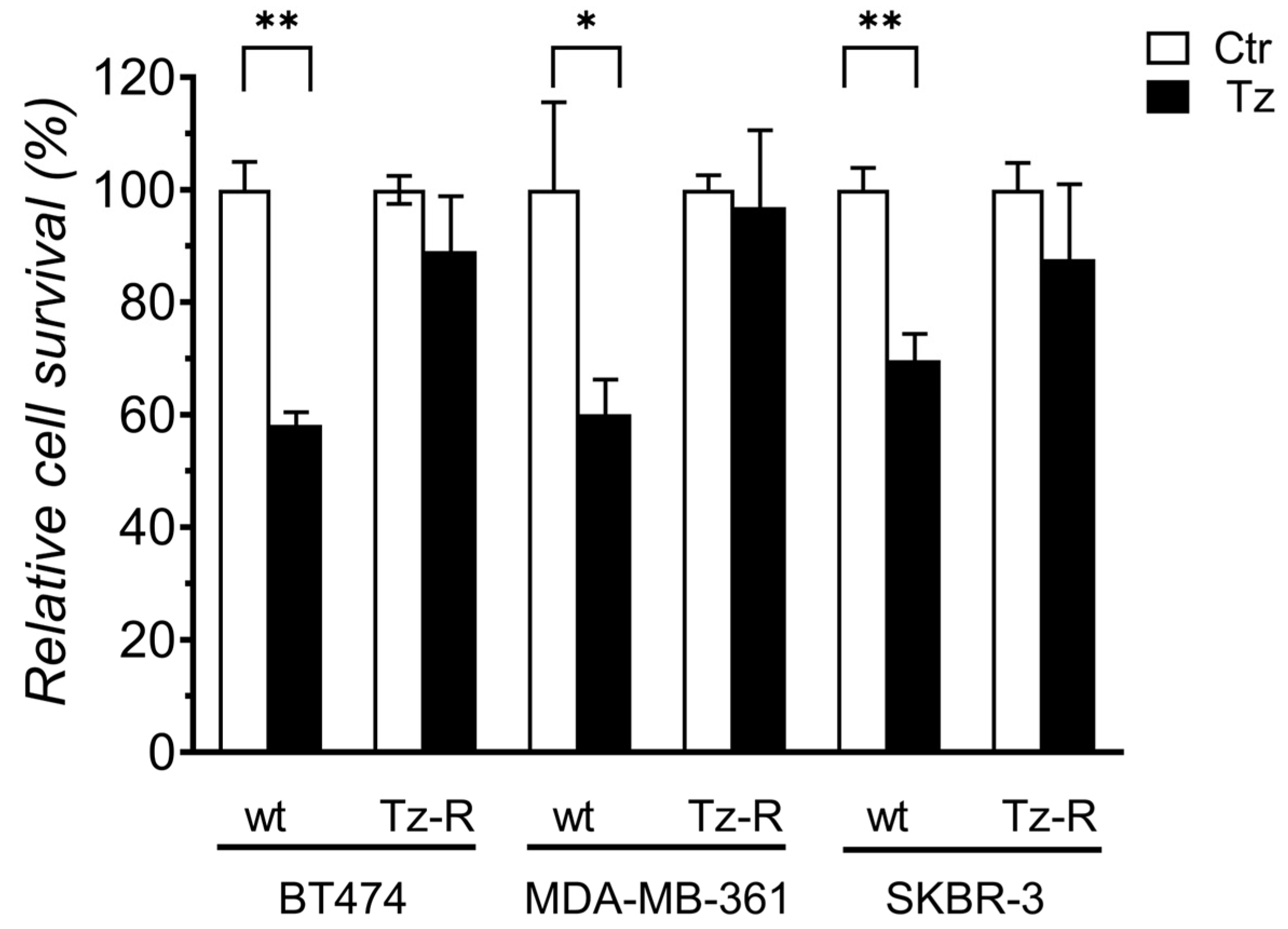
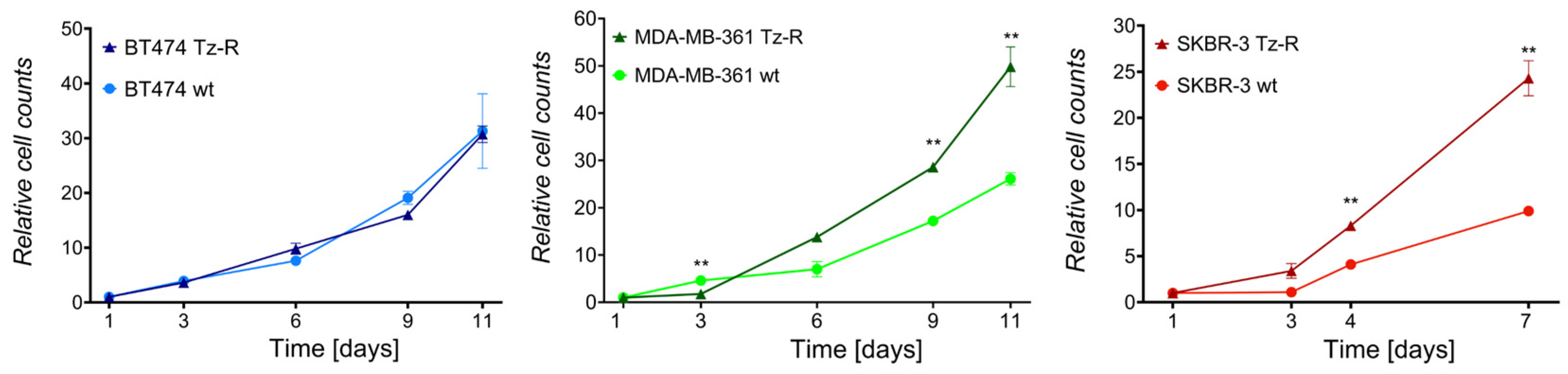
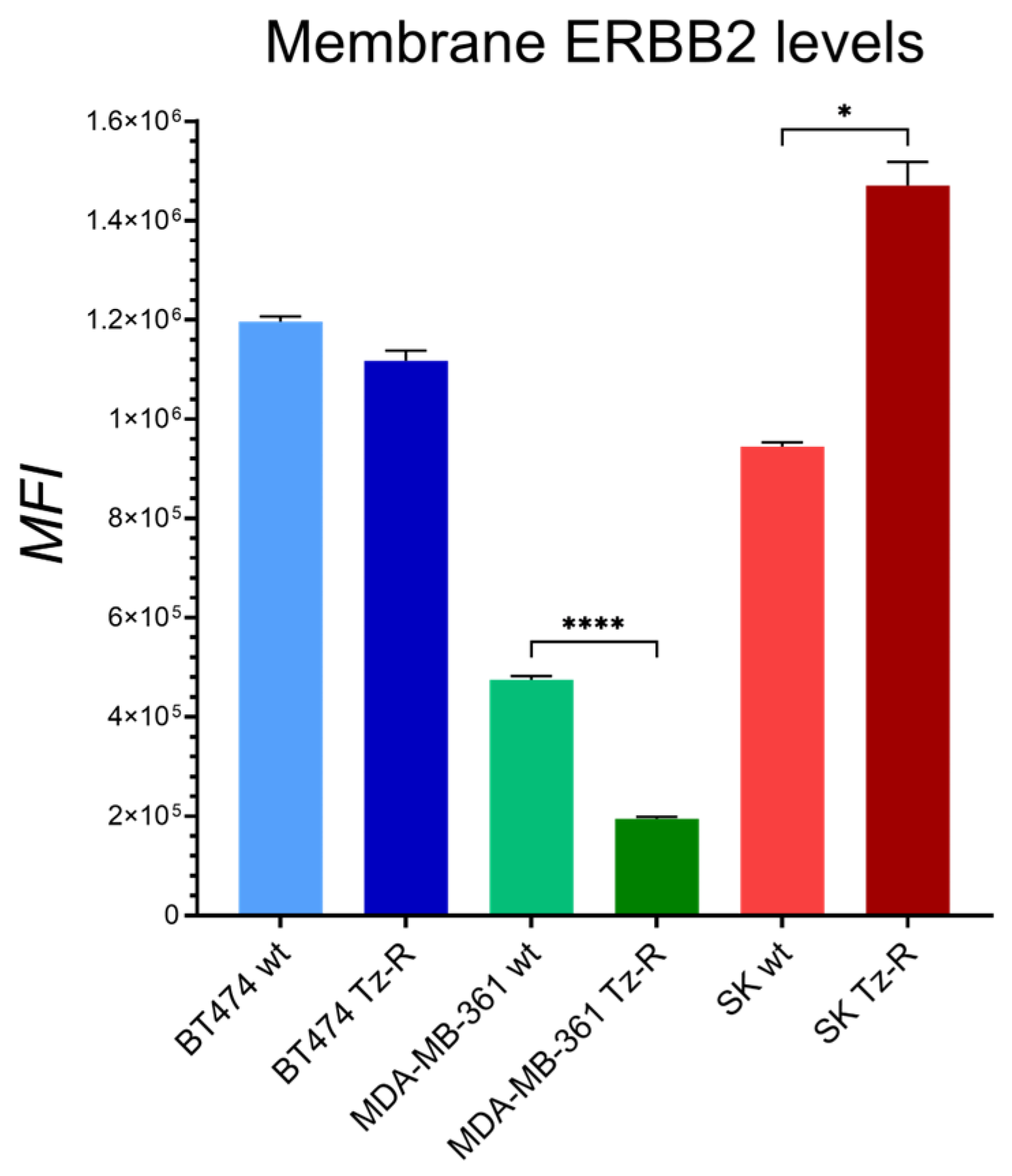
3.1. Generation and characterization of ERBB2+ Tz-R cell lines.
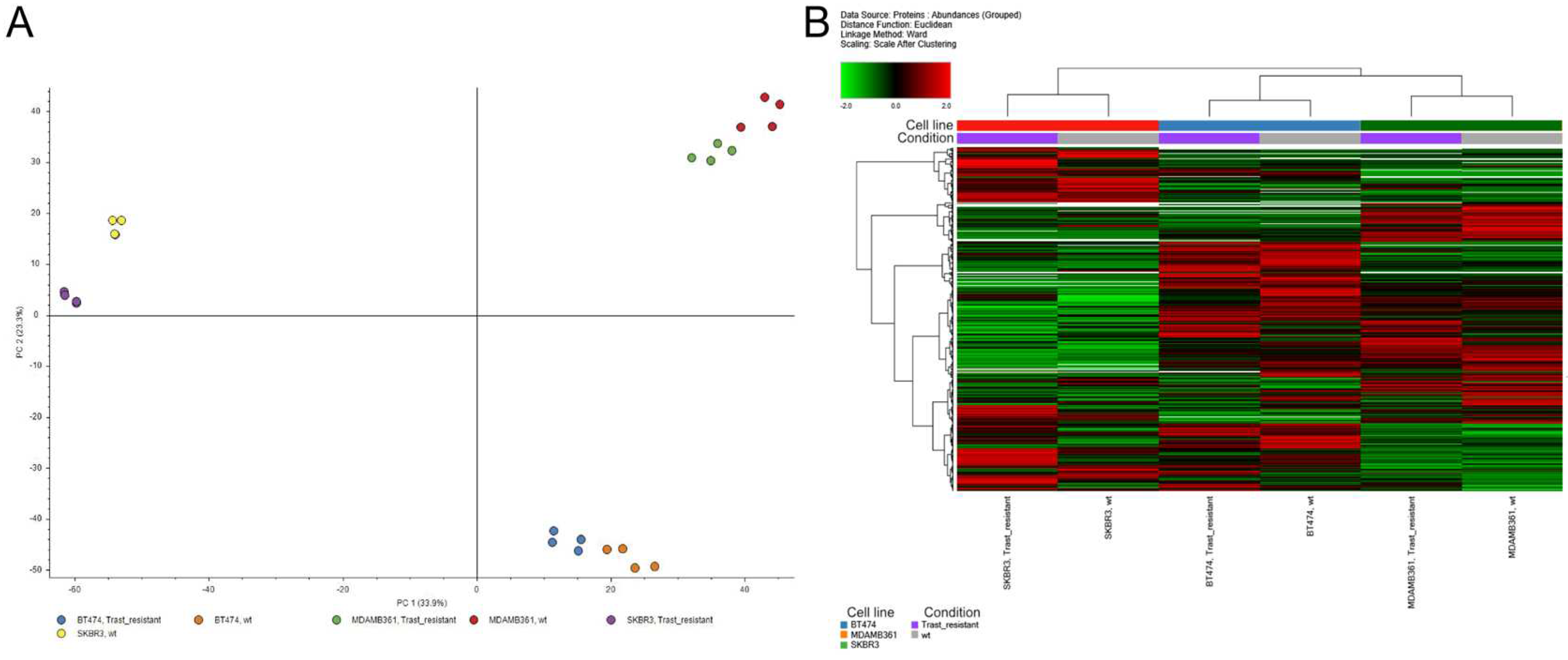
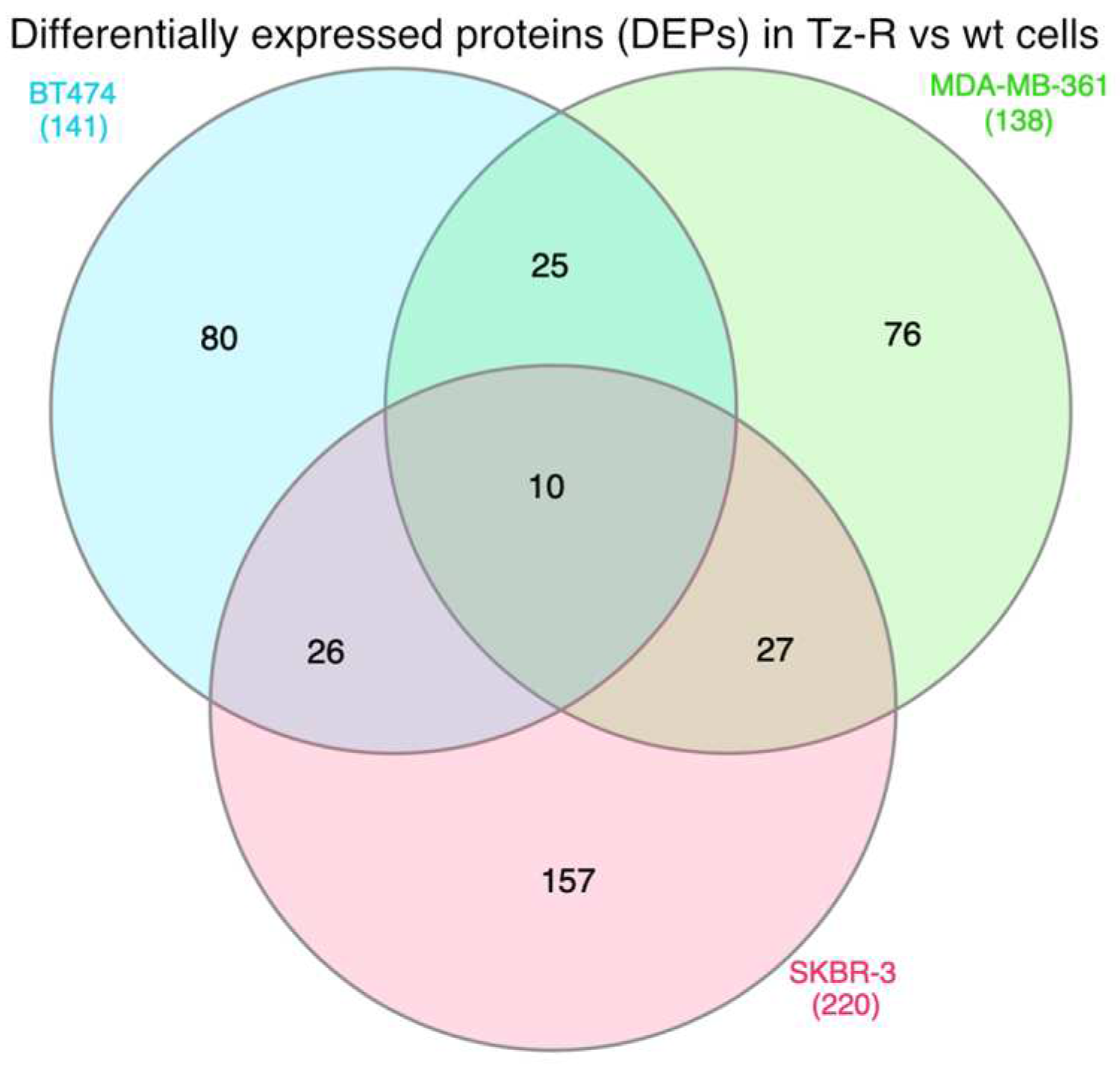
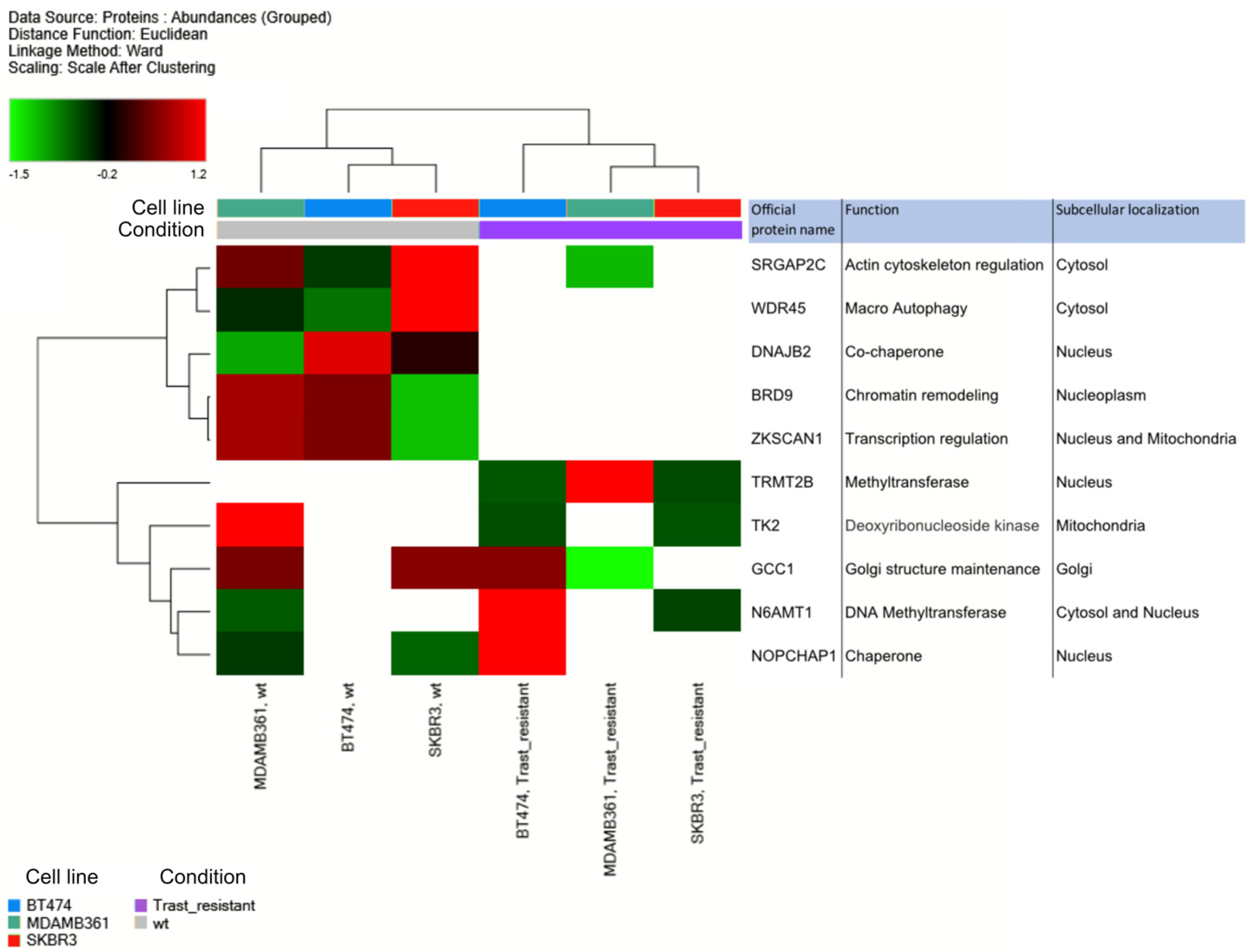
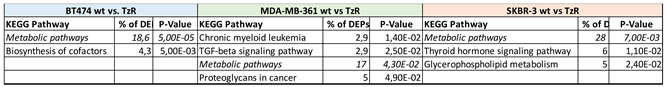
3.2. Proteomic analysis of ERBB2+ and Tz-R cell lines reveals deregulation of lipid metabolism, organophosphate biosynthetic process, and macromolecule methylation
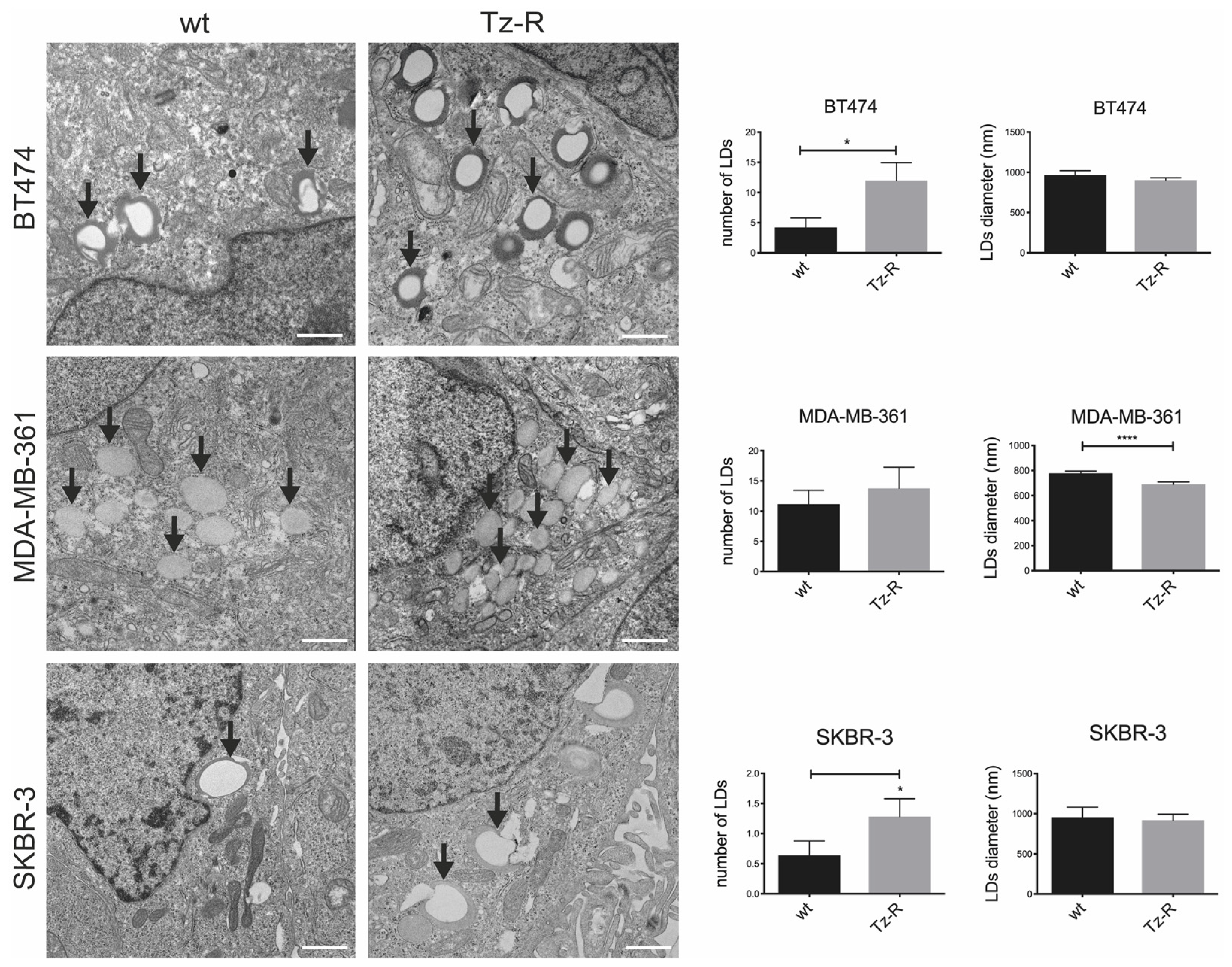
3.3. Electron microscopy revealed changes in lipid droplets content in Tz-R cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–82. [CrossRef]
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–12. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z. ErbB Receptors and Cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1652:3–35. [CrossRef]
- Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, Drula R, Gulei D, Raduly L, et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers [Basel]. 2019;11:E1618. [CrossRef]
- Revathidevi S, Munirajan AK. Akt in cancer: Mediator and more. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:80–91. [CrossRef]
- Greenberg PA, Hortobagyi GN, Smith TL, Ziegler LD, Frye DK, Buzdar AU. Long-term follow-up of patients with complete remission following combination chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:2197–205. [CrossRef]
- Vogel CL, Cobleigh MA, Tripathy D, Gutheil JC, Harris LN, Fehrenbacher L, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:719–26. [CrossRef]
- Cortés J, Kim S-B, Chung W-P, Im S-A, Park YH, Hegg R, et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan versus Trastuzumab Emtansine for Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1143–54. [CrossRef]
- Lane HA, Motoyama AB, Beuvink I, Hynes NE. Modulation of p27/Cdk2 complex formation through 4D5-mediated inhibition of HER2 receptor signaling. Ann Oncol. 2001;12 Suppl 1:S21-22. [CrossRef]
- Denny EC, Kane SE. t-Darpp Promotes Enhanced EGFR Activation and New Drug Synergies in Her2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0132267. [CrossRef]
- Maadi H, Soheilifar MH, Choi W-S, Moshtaghian A, Wang Z. Trastuzumab Mechanism of Action; 20 Years of Research to Unravel a Dilemma. Cancers [Basel]. 2021;13:3540. [CrossRef]
- Moasser MM. Inactivating Amplified HER2: Challenges, Dilemmas, and Future Directions. Cancer Res. 2022;82:2811–20. [CrossRef]
- D’Alesio C, Bellese G, Gagliani MC, Lechiara A, Dameri M, Grasselli E, et al. The chromodomain helicase CHD4 regulates ERBB2 signaling pathway and autophagy in ERBB2+ breast cancer cells. Biology Open. 2019;bio.038323. [CrossRef]
- Nagata Y, Lan K-H, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, et al. PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:117–27. [CrossRef]
- Kreutzfeldt J, Rozeboom B, Dey N, De P. The trastuzumab era: current and upcoming targeted HER2+ breast cancer therapies. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10:1045–67.
- Vivekanandhan S, Knutson KL. Resistance to Trastuzumab. Cancers [Basel]. 2022;14:5115. [CrossRef]
- Dai X, Cheng H, Bai Z, Li J. Breast Cancer Cell Line Classification and Its Relevance with Breast Tumor Subtyping. J Cancer. 2017;8:3131–41. [CrossRef]
- Narayan M, Wilken JA, Harris LN, Baron AT, Kimbler KD, Maihle NJ. Trastuzumab-induced HER reprogramming in “resistant” breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2191–4. [CrossRef]
- Cardinali B, Lunardi G, Millo E, Armirotti A, Damonte G, Profumo A, et al. Trastuzumab quantification in serum: a new, rapid, robust ELISA assay based on a mimetic peptide that specifically recognizes trastuzumab. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406:4557–61. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol Y, Bai J, Bandla C, García-Seisdedos D, Hewapathirana S, Kamatchinathan S, et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: a hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D543–52. [CrossRef]
- D’Alesio C, Bellese G, Gagliani MC, Aiello C, Grasselli E, Marcocci G, et al. Cooperative antitumor activities of carnosic acid and Trastuzumab in ERBB2+ breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:154. [CrossRef]
- Zuo Q, Liu J, Zhang J, Wu M, Guo L, Liao W. Development of trastuzumab-resistant human gastric carcinoma cell lines and mechanisms of drug resistance. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11634. [CrossRef]
- Swain SM, Shastry M, Hamilton E. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer: advances and future directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22:101–26. [CrossRef]
- Menyhárt O, Santarpia L, Győrffy B. A Comprehensive Outline of Trastuzumab Resistance Biomarkers in HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15:665–83. [CrossRef]
- Ignatov T, Gorbunow F, Eggemann H, Ortmann O, Ignatov A. Loss of HER2 after HER2-targeted treatment. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;175:401–8. [CrossRef]
- Marko TA, Shamsan GA, Edwards EN, Hazelton PE, Rathe SK, Cornax I, et al. Slit-Robo GTPase-Activating Protein 2 as a metastasis suppressor in osteosarcoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39059. [CrossRef]
- Fei H, Chen X. A Novel Autophagy-Related Prognostic Risk Model and a Nomogram for Survival Prediction of Oral Cancer Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:2067540. [CrossRef]
- Feng WW, Kurokawa M. Lipid metabolic reprogramming as an emerging mechanism of resistance to kinase inhibitors in breast cancer. CDR [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Jan 13]; Available from: https://cdrjournal.com/article/view/3303. [CrossRef]
- Menendez JA, Vellon L, Mehmi I, Oza BP, Ropero S, Colomer R, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase [FAS] suppresses HER2/neu [ erb B-2] oncogene overexpression in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10715–20. [CrossRef]
- Feng WW, Wilkins O, Bang S, Ung M, Li J, An J, et al. CD36-Mediated Metabolic Rewiring of Breast Cancer Cells Promotes Resistance to HER2-Targeted Therapies. Cell Rep. 2019;29:3405-3420.e5. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita S, Hattori N, Fujii S, Yamaguchi T, Takahashi M, Hozumi Y, et al. Multi-omics analyses identify HSD17B4 methylation-silencing as a predictive and response marker of HER2-positive breast cancer to HER2-directed therapy. Sci Rep. 2020;10:15530. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi T, Mukai H, Yamashita S, Fujii S, Ushijima T. Comprehensive DNA Methylation and Extensive Mutation Analyses of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Oncology. 2015;88:377–84. [CrossRef]
- Palomeras S, Diaz-Lagares Á, Viñas G, Setien F, Ferreira HJ, Oliveras G, et al. Epigenetic silencing of TGFBI confers resistance to trastuzumab in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21:79. [CrossRef]

 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





