Submitted:
14 March 2023
Posted:
15 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
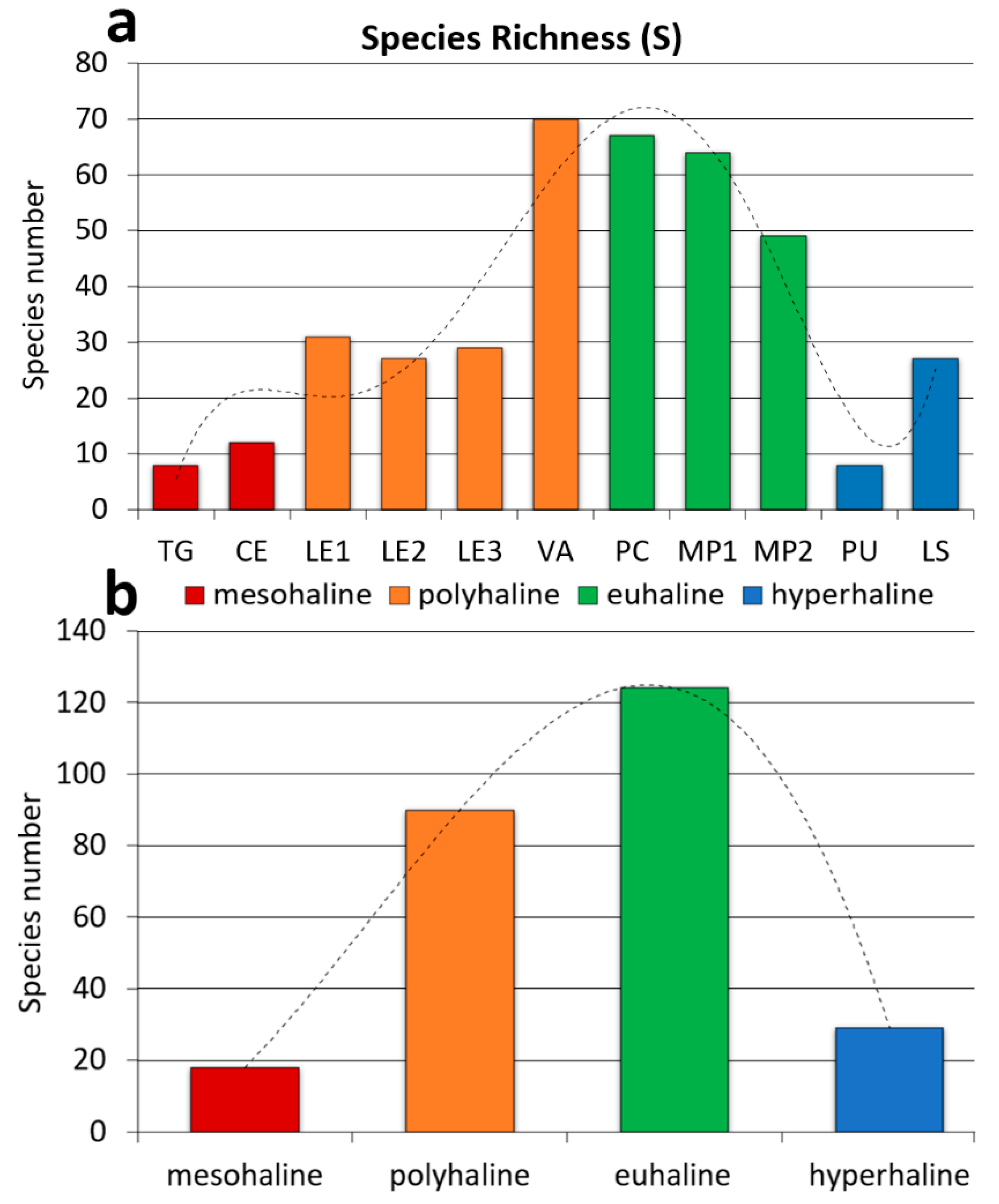
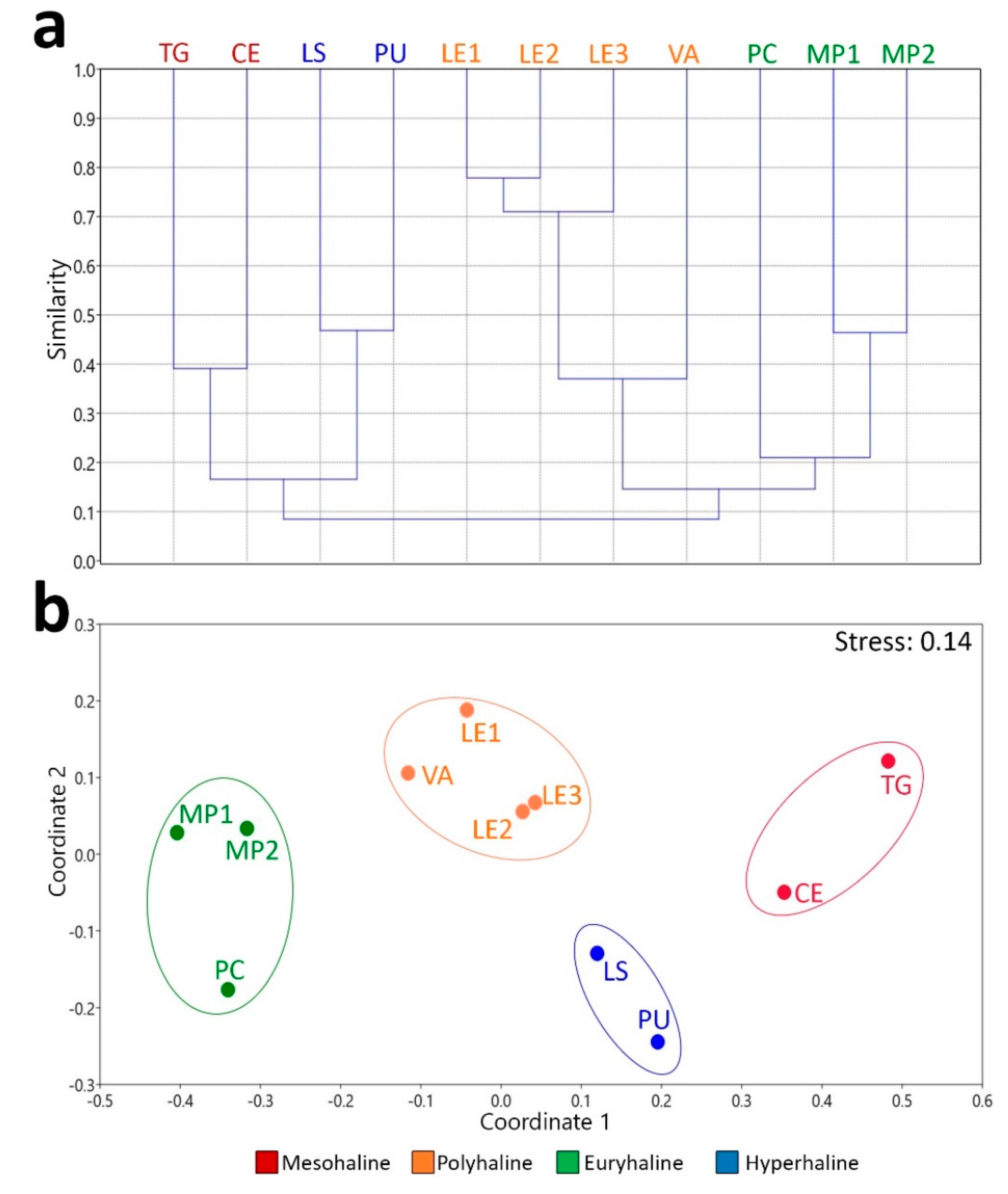
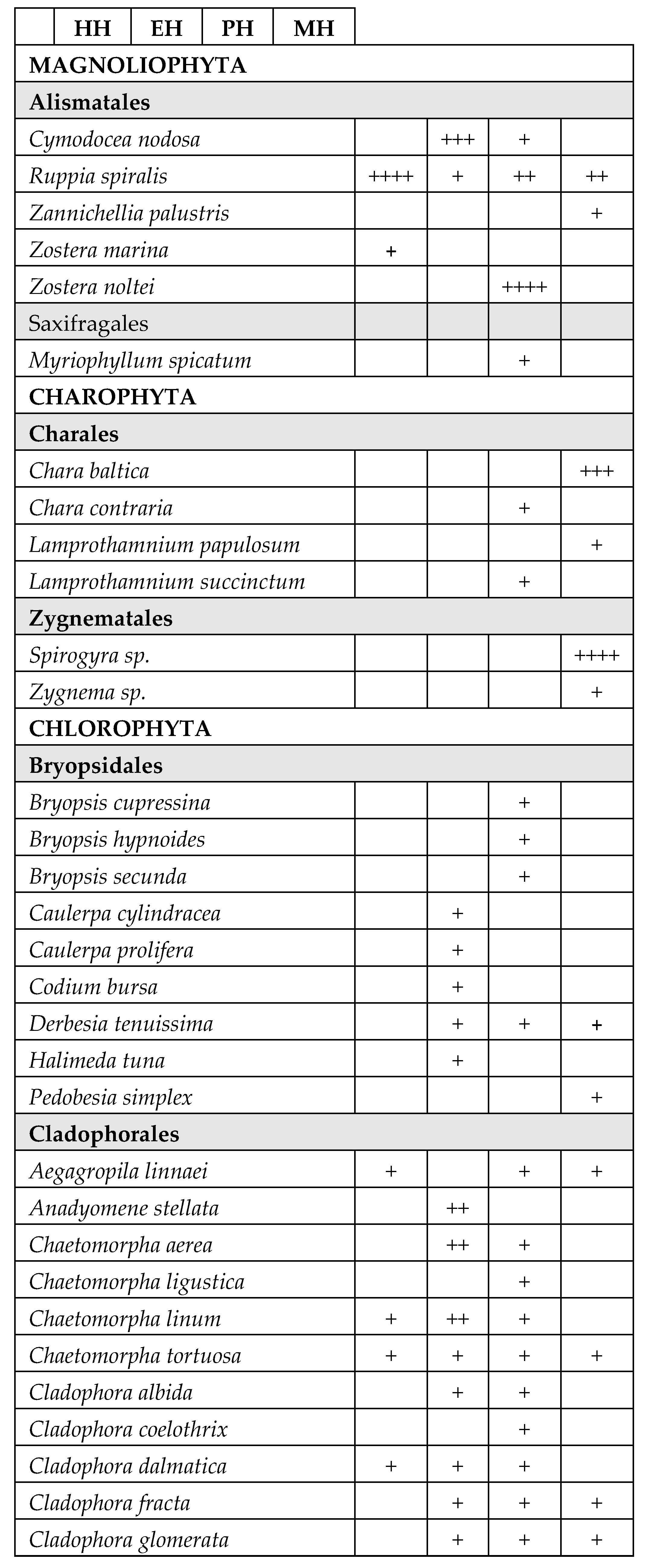
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Marcos, C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Pérez-Marcos, M. Coastal lagoons: “transitional ecosystems” between transitional and coastal waters. J. Coast. Conserv. 2011, 15, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Newton, A.; Marcos, C. Coastal lagoons: environmental variability, ecosystem complexity and goods and services uniformity. In Coasts and Estuaries, the Future; Wolanski, E., Day, J., Elliott, M., Ramesh, R., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, USA, 2019; pp. 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliapietra, D.; Sigovini, M.; Ghirardini, A.V. A review of terms and definitions to categorize estuaries, lagoons and associated environments. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2009, 60, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petihakis, G.; Triantafyllou, G.; Koutsoubas, D.; Allen, I.; Dounas, C. Modelling the annual cycles of nutrients and phytoplankton in a Mediterranean lagoon (Gialova, Greece). Mar. Environ. Res. 1999, 48, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plus, M.; Chapelle, A.; Lazure, P.; Auby, I.; Levavasseur, G.; Verlaque, M.; Belsher, T.; Deslous-Paoli, J.-M.; Zaldívar, J.-M.; Murray, C.N. Modelling of oxygen and nitrogen cycling as a function of macrophyte community in the Thau lagoon. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1877–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastres, R.; Solidoro, C.; Ciavatta, S.; Petrizzo, A.; Cossarini, G. Long-term changes of inorganic nutrients in the Lagoon of Venice (Italy). J. Marine Syst. 2004, 51, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, I. .; Wit, R.D.; Plus, M.; Oheix, J.; Simier, M.; Ouisse, V. Submerged benthic macrophytes in Mediterranean lagoons: distribution patterns in relation to water chemistry and depth. Hydrobiologia 2018, 808, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, P.; Bartoli, M.; Giordani, G.; Naldi, M.; Orfanidis, S.; Zaldivar, J.M. (2008). Community shifts, alternative stable states, biogeochemical controls and feedbacks in eutrophic coastal lagoons: a brief overview. Aquat. Conserv. 2008, 18, S105–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Ghetti, P.F. Rapid Quality Index (R-MaQI), based mainly on macrophyte associations, to assess the ecological status of Mediterranean transitional environments. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 23, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christia, C.; Tziortzis, I.; Fyttis, G.; Kashta, L.; Papastergiadou, E. A survey of the benthic aquatic flora in transitional water systems of Greece and Cyprus (Mediterranean Sea). Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Marcomini, A. Sedimentation rates and erosion processes in the lagoon of Venice. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcleod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A blueprint for blue carbon: toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, S.; Marchand, B.; Pergent, G. Temporal and spatial changes of seagrass meadows in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 25, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEC. Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. Comm. July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido, J.; Pérez-Bilbao, A.; Benetti, C.J. Biodiversity and Conservation of Coastal Lagoons. In Ecosystems Biodiversity; Grillo, O., Venora, G., Eds.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Orfanidis, S.; Panayotidis, P.; Stamatis, N. An insight to the ecological evaluation index (EEI). Ecol. Indic. 2003, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Marcos, C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Suitability of benthic macrophyte indices (EEI, E-MaQI and BENTHOS) for detecting anthropogenic pressures in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Ecol. Indic. 2012, 19, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.; Dencheva, K.; Nakou, K.; Tsioli, S.; Papathanasiou, V.; Rosati, I. Benthic macrophyte metrics as bioindicators of water quality: towards overcoming typological boundaries and methodological tradition in Mediterranean and Black Seas. Hydrobiologia 2014, 740, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziortzis, I.; Kadis, K.; Papastegiadou, E. Use of Macrophyte assemblages for the ecological evaluation of two coastal lagoons of Greece according to WFD 2000/60/EC. J. Wetl. Biodivers. 2014, 4, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- EEC. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 on establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, L327, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Ghetti, P.F. Validation of the Macrophyte Quality Index (MaQI) set up to assess the ecological status of Italian marine transitional environments. Hydrobiologia 2009, 617, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Bonometto, A.; Boscolo, R. Compliance of the macrophyte quality index (MaQI) with the WFD (2000/60/EC) and ecological status assessment in transitional areas: The Venice lagoon as study case. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISPRA, 2010. Implementazione della Direttiva 2000/60/CE - Linea guida per l’applicazione dell’indice MaQI.
- Wilkinson, M. Benthic estuarine algae and their environment: a review. In The Shore Environment: Methods and Ecosytems; Price, J.H., Irvine, D.E.G., Farnham, W.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1980; Volume 2, pp. 425–486. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, G. Salinity and seaweed vegetation. In The physiological vegetation of amphibious and intertidal plants; Crawford, R.M., Ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Christia, C.; Giordani, G.; Papastergiadou, E. Environmental Variability and Macrophyte Assemblages in Coastal Lagoon Types of Western Greece (Mediterranean Sea). Water 2018, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, F.; Rapaglia, J.; Zaggia, L.; Umgiesser, G.; Zuppi, G.M. Coincident application of a mass balance of radium and a hydrodynamic model for the seasonal quantification of groundwater flux into the Venice Lagoon, Italy. Mar. Chem. 2008, 10, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumgalz, B.S.; Hornung, H.; Oren, O.H. The study of a natural hypersaline lagoon in a desert area (the Bardawil Lagoon in Northern Sinai). Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1980, 10, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutron, O.; Paugam, C.; Luna-Laurent, E.; Chauvelon, P.; Sous, D.; Rey, V.; Meulé, S.; Chérain, Y.; Cheiron, A.; Migne, E. Hydro-Saline Dynamics of a Shallow Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon: Complementary Information from Short and Long Term Monitoring. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.I.L.; Katupotha, J.; Amarasinghe, O.; Manthrithilake, H.; Ariyaratna, R. Lagoons of Sri Lanka: From the Origins to the Present; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, R.N.; Batten, S.D.; Sheader, M.; Bridgwater, M.D. On the ecology of brackish water lagoons in Great Britain. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1992, 2, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, A.; Pedersen, P.M.; Moseholm, L. Salinity-temperature effects on growth and reproduction of Scytosiphon lomentaria (Fucophyceae) along the salinity gradient in Danish waters. Phycologia 1994, 33, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düwel, L. Experimental studies on macroalgae along the salinity gradient in the Baltic Sea area. Ph.D. Dissertation, Botanical Institute, Faculty of Science, University of Copenhagen, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ISPRA, 2007. Guida alla tipizzazione dei corpi idrici di transizione ed alla definizione delle condizioni di riferimento ai sensi della direttiva 2000/60/CE.
- Battaglia, B. Final resolution of the symposium on the classification of brackish waters. Archo Oceanography Limnology 1959, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Basset, A.; Sabetta, L.; Fonnesu, A.; Mouillot, D.; Do Chi, T.; Viaroli, P.; Giordani, G.; Reizopoulou, S.; Abbiati, M.; Carrada, G.C. Typology in Mediterranean transitional waters: new challenges and perspectives. Aquat. Conserv. 2006, 16, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, E.; Petrocelli, A.; Izzo, G.; Sfriso, A. Flora and vegetation of the Italian transitional water systems (pp. 278). In Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Yasmine-Hammamet, Tunisia, 2–4 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Varvaglione, B.; Sabetta, L.; Basset, A. Tra Terra e Mare. Ecoguida alla Scoperta Delle Lagune e dei Laghi Costieri in Puglia; Università degli Studi di Lecce: Lecce, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Apulian Region. Regional Water Protection Plan, Water Protection Service, General Report Area (In Italian), 2009.
- ISPRA, 2011. Protocols for sampling and determination of the biological and the physicochemical quality in the framework of the transitional water monitoring programs ex 2000/60/EC.
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway, 2022. https://www.algaebase.org; searched on 06 March 2023. 06 March.
- Lucena-Moya, P.; Pardo, I.; Álvarez, M. Development of a typology for transitional waters in the Mediterranean ecoregion: The case of the islands. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, M.; Claussen, U.; Bergemann, M.; Gaumert, T. Transitional waters in Germany: The Elbe estuary as an example. Aquat. Conserv. 2004, 14(1), 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, D.; Gascón, S.; Sala, J.; Martinoy, M.; Gifre, J.; Quintana, X.D. A new index of water quality assessment in Mediterranean wetlands based on crustacean and insect assemblages: the case of Catalunya (NE Iberian peninsula). Aquat. Conserv. 2005, 15, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.G.; Nobre, A.M.; Simas, T.C.; Silva, M.C.; Newton, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Wolff, W.J.; Stacey, P.E.; Sequeira, A. A methodology for defining homogeneous water bodies in estuaries e application to the transitional systems of the EU water Framework Directive. Estuar. 2006, 66, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalou, I.; Leonardos, I. Typology, classification and management issues of Greek lakes: implication of the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Environ. 2009, 150, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Por, F.D. A classification of hypersaline waters, based on trophic criteria. Mar. Ecol. 1980, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Knoop, W.T.; Bate, G.C. The distribution of estuarine macrophytes in relation to freshwater. Bot. Mar. 1992, 35, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, M.; Hernandez, O.; Comin, F.A. Spatial distribution and ecophysiological characteristics of macrophytes in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, T.M.; Binzer, T. Which factors regulate seagrass growth and distribution? In: Borum, J., C.M. Duarte, D. Krause-Jensen & T. M. Greve (eds), European Seagrasses an Introduction to Monitoring and Management. The M&Ms Project, Hillerød: 19–23, 2004.
- Casagranda, C.; Boudouresque, C.F. Biomass of Ruppia cirrhosa and Potamogeton pectinatus in a Mediterranean brackish lagoon, Lake Ichkeul, Tunisia. Fundam. 2007, 168, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christia, C. , Papastergiadou, E.S. Spatial and temporal variations of aquatic macrophytes and water quality in six coastal lagoons of western Greece. Belg. J. Bot. 2007, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Obrador, B.; Moreno-Ostos, E.; Pretus, J.L. A Dynamic Model to Simulate Water Level and Salinity in a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon. Estuaries and Coasts 2008, 31, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, C.; Correia, O.; da Silva, J.M.; Cruces, A.; da Conceição Freitas, M.; Branquinho, C. Factors involved in spatiotemporal dynamics of submerged macrophytes in a Portuguese coastal lagoon under Mediterranean climate. Estuar., Coast. and Shelf Sci. 2012, 110, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H.; Feuerpfeil, P.; Marquardt, R.; Telesh, I.; Skarlato, S. Macroalgal diversity along the Baltic Sea salinity gradient challenges Remane’s species-minimum concept. Mar. Pollut. 2011, 62, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Fernández, A.I.; Marcos, C.; Gilabert, J.; Quispe, J.I.; García-Charton, J.A. Spatial and temporal variations of hydrological conditions, nutrients and chlorophyll in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Franzoi, P.; Torricelli, P. Structure and functioning of Mediterranean lagoon fish assemblages: a key for the identification of water body types. Estuar., Coast. and Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.; Graham, J.; Wilcox, L. Algae; Pearson Education, Inc.: San Francisco, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boegle, M.G.; Schneider, S.; Mannschreck, B.; Melzer, A. Differentiation of Chara intermedia and C. baltica compared to C. hispida based on morphology and amplified fragment length polymorphism. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, C. The Seagrasses of the World; North Holland: Amsterdam, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Barra, D.; Coppa, M.G.; Valente, A.; Zeni, F. Recent infralittoral foraminiferida and ostracoda from the porto Cesareo Lagoon (Ionian Sea, Mediterranean). Boll. Soc. Paleontol. 2006, 45, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cardellicchio, N.; Annicchiarico, C.; Di Leo, A.; Giandomenico, S.; Spada, L. The Mar Piccolo of Taranto: an interesting marine ecosystem for the environmental problems studies. Environ. 2016, 23, 12495–12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecere, E.; Petrocelli, A.; Saracino, O.D. Biodiversity of phytobenthic communities in the marine reserve of Porto Cesareo. Biol. Mar. Medit. 2005, 2005 12, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog, C.; Triest, L. A profound view and discourse on the typification and status of three confused taxa: Ruppia maritima, R. spiralis and R. cirrhosa. Bot. Mar. 2020, 63, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, A.; Ponis, E.; Cacciatore, F.; Riccardi, E.; Pigozzi, S.; Parati, P.; Novello, M.; Ungaro, N.; Acquavita, A.; Manconi, P.; et al. A New Multi-Index Method for the Eutrophication Assessment in Transitional Waters: Large-Scale Implementation in Italian Lagoons. Environments 2022, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Bon, D.; Buosi, A. Macrophytes and ecological status assessment in the Po delta transitional systems, Adriatic Sea (Italy). Application of Macrophyte Quality Index (MaQI). Acta Adriat. 2016, 57, 209–225. [Google Scholar]
- Wallentinus, I. The Baltic Sea. Ecosys. World 1991, 24, 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, Y.I.; Ogawa, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; Ohki, K.; Kamiya, M. Genetic and ecophysiological diversity of Cladophora (Cladophorales, Ulvophyceae) in various salinity regimes. Phycological Res. 2012, 60, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, A.S. Species of Ulva (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta) as indicators of salinity. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
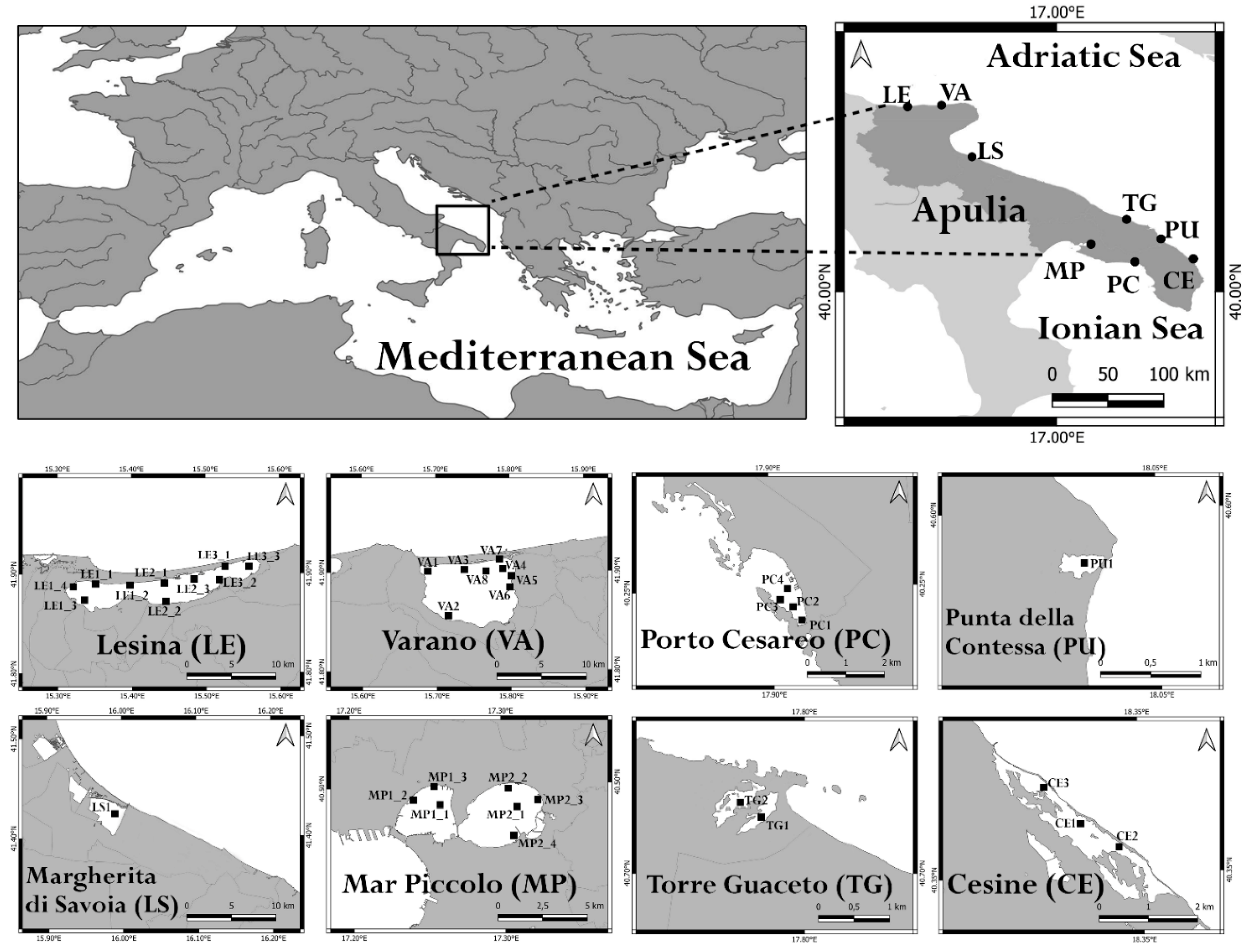
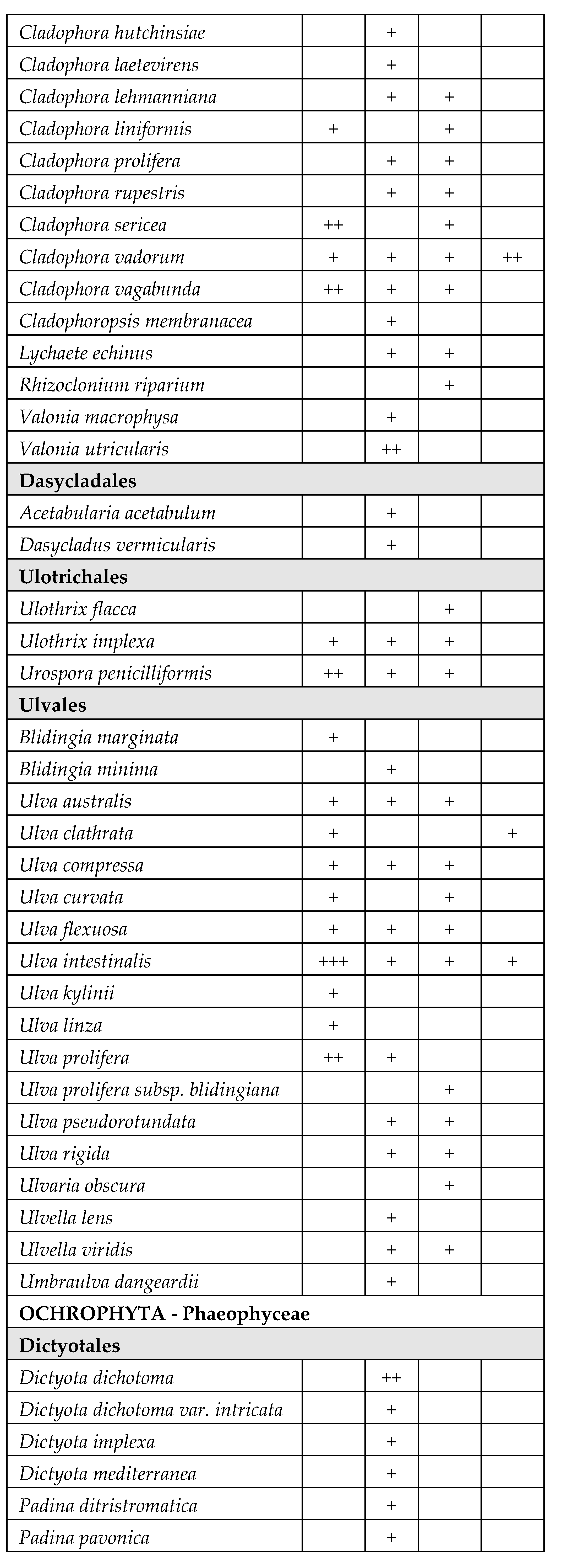
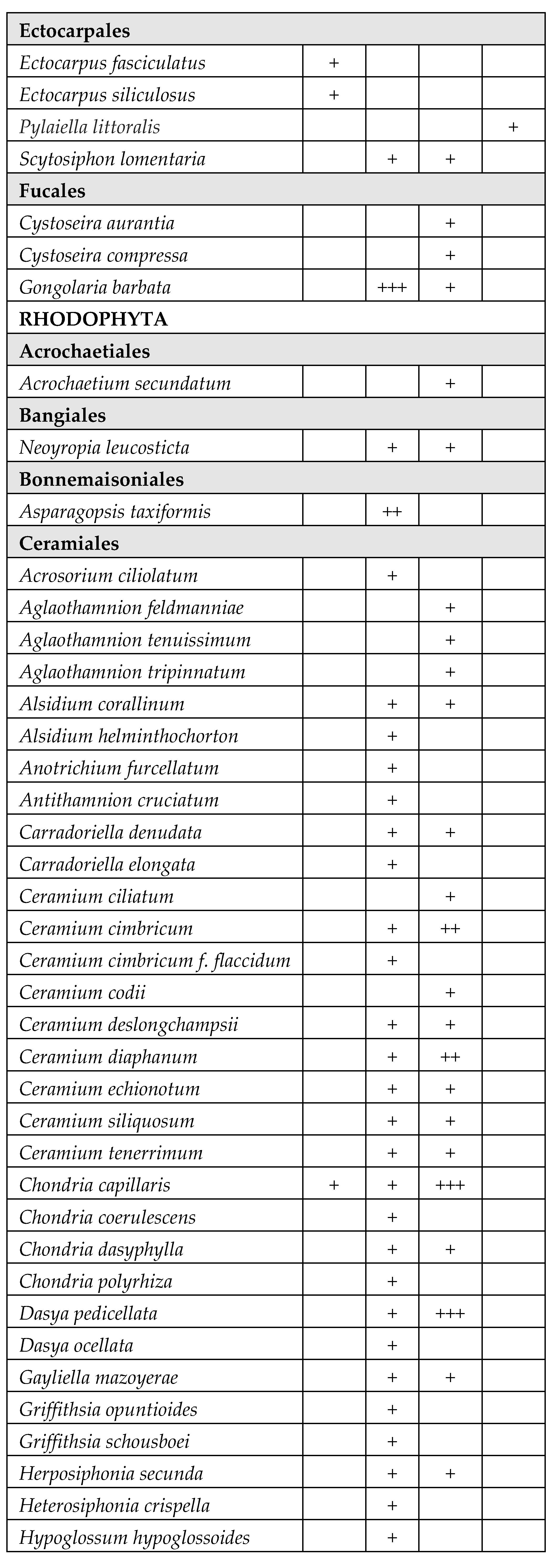
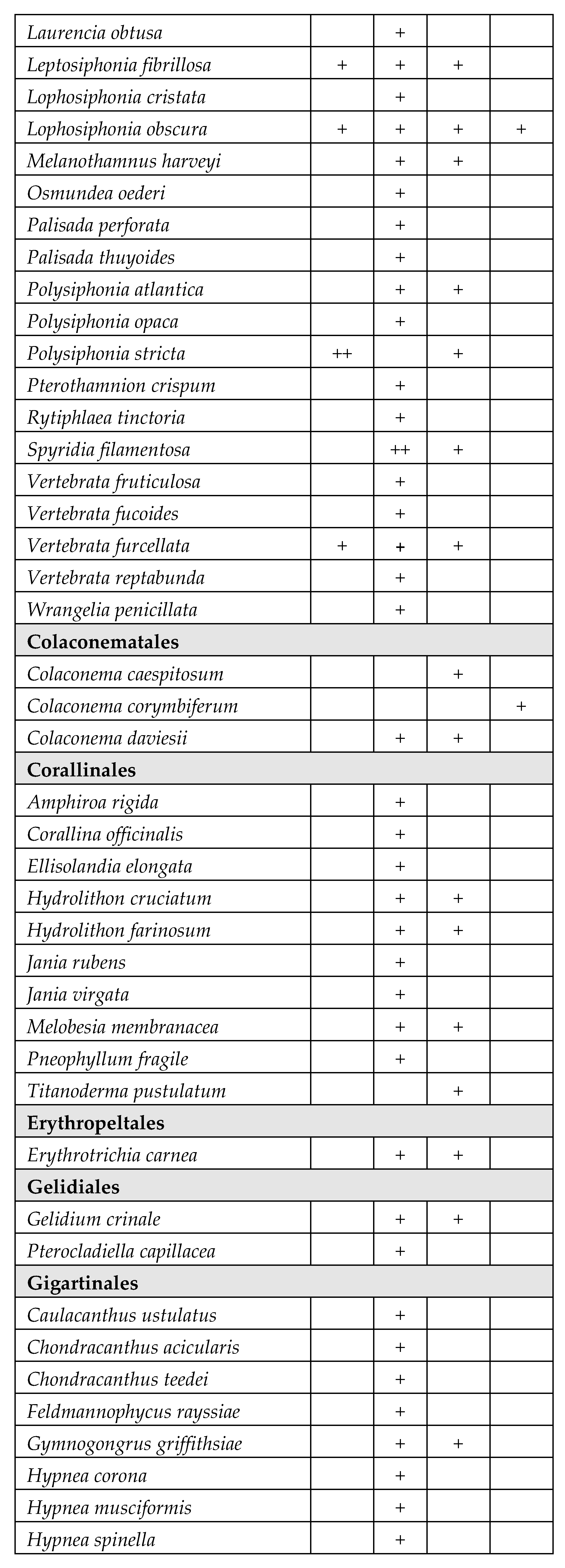
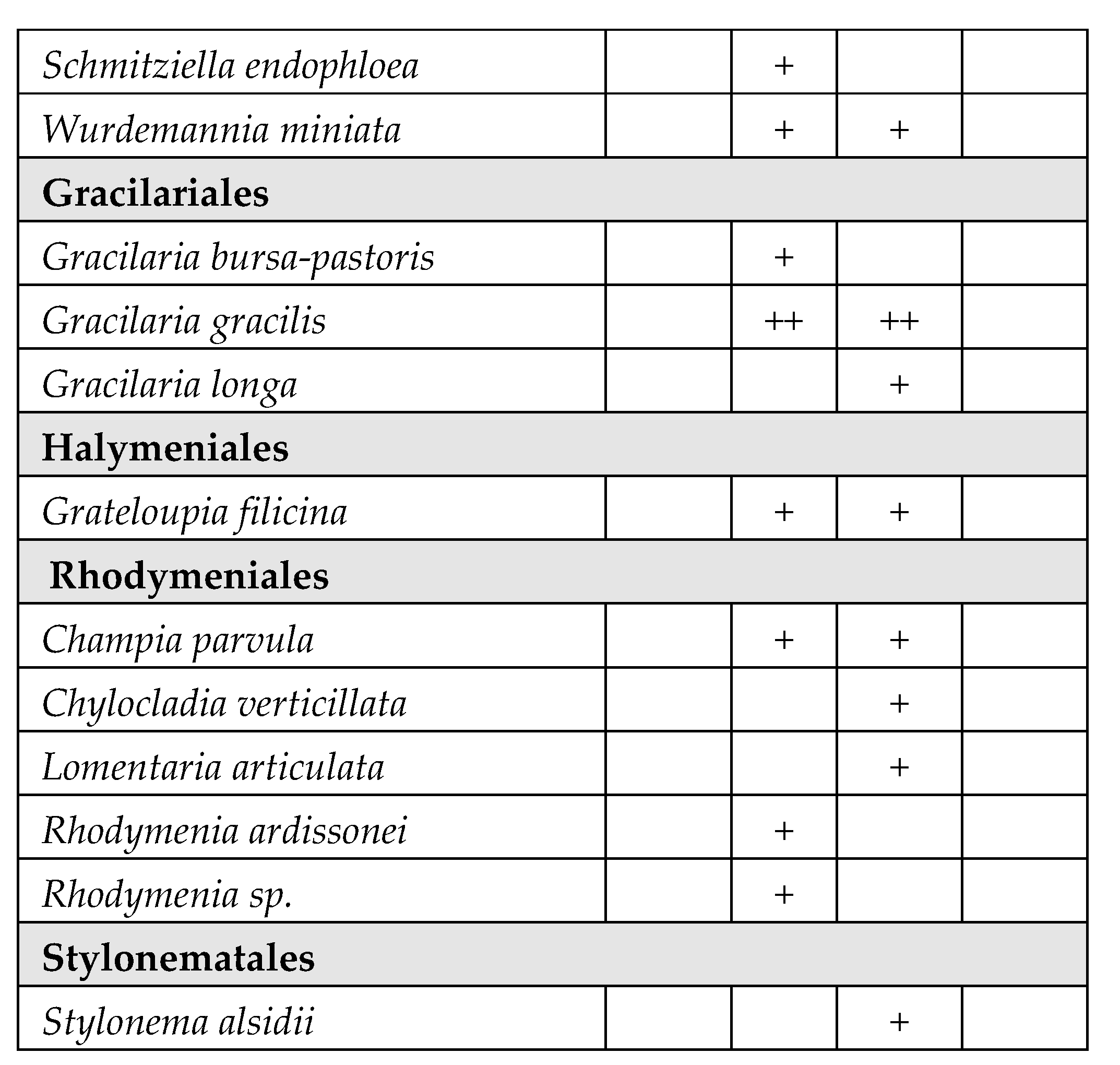
| WB | Coordinates | Surface area (km2) | Depth (m) | Salinity Class (PSU)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torre Guaceto (TG) | 40°42′51.34” N – 17°47′42.91” E | 1.2 | 0.4 – 0.6 | Mesohaline (5–20) |
| Cesine (CE) | 40°21′33.46” N – 18°20′09.30” E | 0.7 | 0.2 – 0.8 | Mesohaline (5 – 20) |
| Lesina (LE1) | 41°53′12.64” N – 15°21′15.65” E | 18 | 0.7 – 2 | Polyhaline (20 – 30) |
| Lesina (LE2) | 41°53′01.23” N – 15°27′20.15” E | 17 | 0.7 – 2 | Polyhaline (20 – 30) |
| Lesina (LE3) | 41°53′57.20” N – 15°31′00.45” E | 16 | 0.7 – 2 | Polyhaline (20 – 30) |
| Varano (VA) | 41°52′43.65” N – 15°44′35.42” E | 60.5 | 0.5 – 5 | Polyhaline (20 – 30) |
| Porto Cesareo (PC) | 40°14′31.80” N – 17°54′32.82” E | 2 | 0.3 – 5 | Euhaline (30 – 40) |
| Mar Piccolo (MP1) | 40°29′19.68” N – 17°15′29.51” E | 9.7 | 0.5 – 12 | Euhaline (30 – 40) |
| Mar Piccolo (MP2) | 40°29′22.92” N – 17°18′29.18” E | 11 | 0.5 – 12 | Euhaline (30 – 40) |
| Margherita di Savoia (LS) | 41°25′27.34” N – 15°59′53.29” E | 45 | 0.4 – 0.6 | Hyperhaline (> 40) |
| Punta della Contessa (PU) | 40°35′42.31” N – 18°02′30.05” E | 2 | 0.4 – 1 | Hyperhaline (> 40) |
| pairwise ANOSIM | R-values | p-values |
|---|---|---|
| hyperhaline vs euhaline | 1 | 0.1019 |
| hyperhaline vs polyhaline | 1 | 0.0649 |
| hyperhaline vs mesohaline | 1 | 0.3290 |
| euhaline vs polyhaline | 0.9630 | 0.0278* |
| euhaline vs mesohaline | 1 | 0.0986 |
| polyhaline vs mesohaline | 1 | 0.0659 |
| Global ANOSIM | R-values | p-values |
| 0.9545 | 0.0002*** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





