1. Introduction
Agriculture is the primary activity for mankind, and it provides a living for around 60% of the world's population. Many scientific techniques are required to increase the sustainability of agricultural products so that population demand can be reduced. It is vital to create analytical methods that can detect environmental toxins quickly, accurately, and economically. In fact, EU Regulation 2013/39/EU promotes the development of such methods with the need that they be sensitive enough to assure that any infraction of surface water EQS limits is accurately identified and quantified [
1].The development of novel sensing techniques for the detection of pesticides in water, soil, and food is currently the focus of many researchers. Liquid/gas chromatography (GC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), electrophoresis, and mass spectroscopy are the most frequently used sensing techniques. But these techniques show some of the disadvantages that includes; site specific and sensitivity towards target pollutants. There have since been various attempts to develop new technologies for the quick, sensitive, focused, accurate, and user-friendly identification of pesticides[
2]. This review article's goal is to propose an alternate method for effective pesticide sensing that makes use of nanotechnology.
Due to their super surface effect and small size effect, nanoparticles such carbon nanomaterials, semiconductor nanomaterials, polymeric nanomaterials, and metal nanomaterials have drawn considerable attention and were connected in multiple sectors. The use of biosensors to detect toxins in food and the environment is thought to be a promising technology. Biosensors are rapid, economical, practical, and highly sensitive devices that can identify and measure targets by converting the target's physical recognition into optical, electrical, and magnetic signals[
3].Pesticide sensing values can be determined directly through the biosensors by translating the acquisition signal. Nanomaterial is used in a biosensor component to reduce electro active chemical power density. Also, it serves as labels and multiplies the observed signals at various time intervals [
4].
The main objective of this review article is to provide readers a brief overview of the very recent developments of GO-rGO biosensors for pesticide detection in aqueous medium. The time span for the literature survey has been restricted to the previous four years (2020-2023) only. After a brief overview of electrochemical biosensors, FRET biosensors and their capabilities and performance in environmental pesticide detection are critically assessed. We believe that the scientific fraternity involved in the study of pesticides and those with an interest in the development of GO-rGO nanomaterial-based biosensors will find this review to be useful. Future research opportunities and current obstacles are also critically discussed.
2. Pesticides detection and toxicity
As per the United States Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) classification, a pesticide is any substance or combination of ingredients designed to be employed as a plant promoter, selective herbicide, or desiccant (United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2004) [
5].The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO, USA) defines pesticides as any compound or combination of molecules used for eradicating pests, disease-carrying animals, undesirable plant or animal species, and pests that affect food production, management, sale, storage, and transportation. As per a recent estimate, more than 4.19 million metric tonnes of pesticides were consumed globally in 2019. China was the highest consumer (1.76 million metric tonnes), followed by the US (408 thousand tonnes), Brazil (377 thousand tonnes), and Argentina (204 thousand tonnes). In another alarming statistic, WHO cautioned about an increase in pesticide use each year in Southeast Asian countries, which includes Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam [
1].
The fatal effect of exposure to pesticides persisting over a longer time period is referred to as chronic toxicity. As per the commonly used "WHO Recommended Categorization of Pesticides by Hazard," pesticide residues are now grouped into "WHO Hazard classifications."
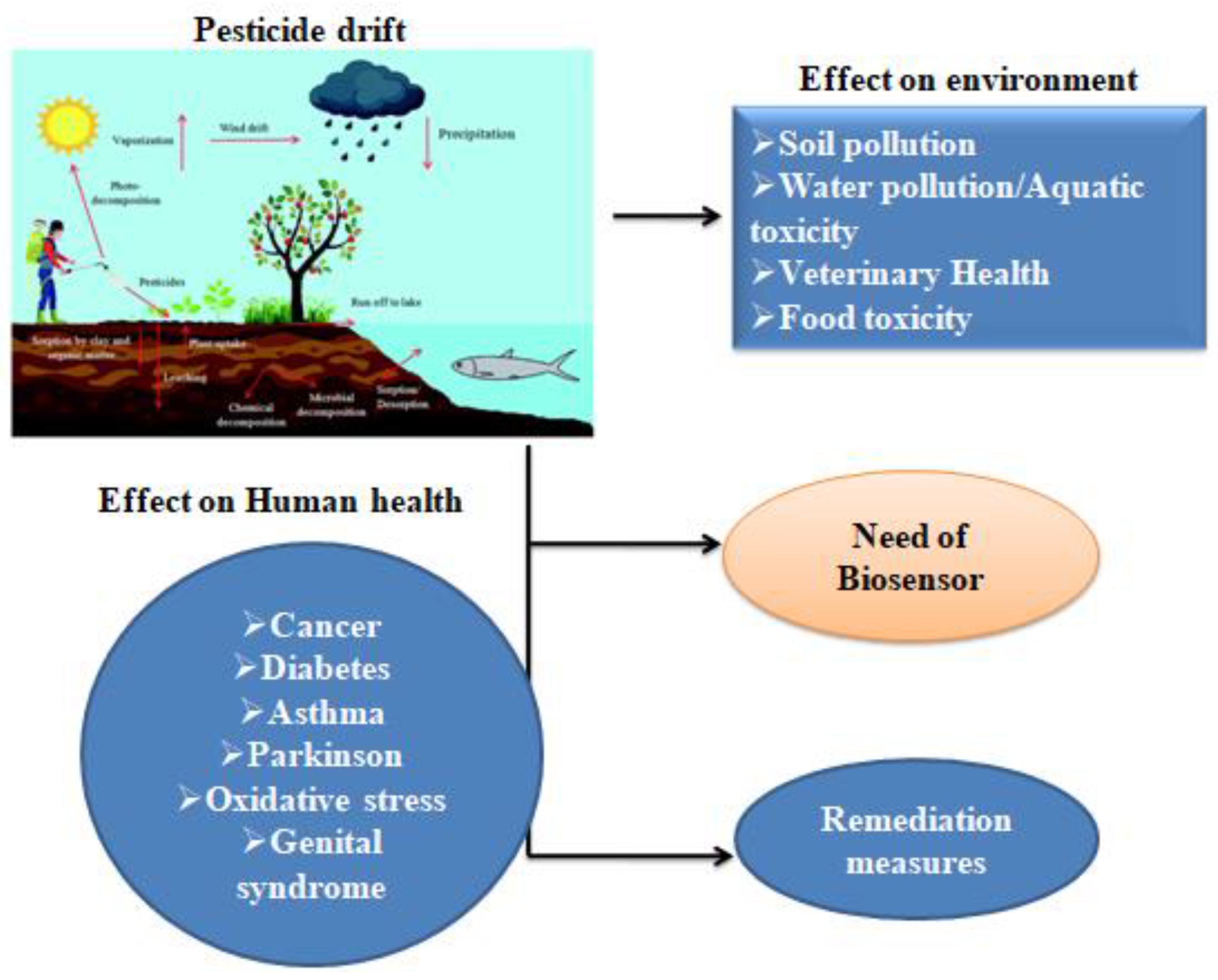
Figure 1.
Drifting of pesticides into the environment and its toxic effect.
Figure 1.
Drifting of pesticides into the environment and its toxic effect.
Amongst the various pesticide residues, organochlorine substances (OCPs) have already been widely utilised all across world to manage agricultural pests and disease vector ailments (dengue and other disease outbreaks). The application of these compounds in an unrestrained manner seems to have the risk of harming the environment, portable water, and health impacts. Over time, continuous exposure to numerous OCPs may cause immune system disorders, cancer, birth defects, neurological damage, and reproductive issues[
6]. Different pesticides are also to held responsible for causing cancer; prostate cancer is the most prevalent of all different cancer and is linked to organophosphorus (malathion and parathion), which have an impact on cellular growth and proliferation. There have been reports that a number of pesticides residues, including DDT, chlorpyrifos methyl, and organochlorine, can alter the epigenetic methylation sequence in humans [
7].
According to research, pesticides can affect acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, which can affect the neurological system and lead to a variety of neurotoxic effects (neurotoxicity) in fish. Pesticide application offers a barrier of defence against other pests that feed on pods, but defected pods might not even produce seeds or they might be of poor quality and unusable. The risk of abnormalities in germ cells is increased by the synergistic interaction between the pesticides pyrethroids (PYR) and organophosphates (OP).Previously, Salazar-Arredondo et al.(2008) disclosed chromatin and nucleic acid damage in human spermatozoa by in-vitro exposure to a combination of different organophosphorus pesticide residues such as chlorpyrifosoxon, chlorpyrifos, diazoxon and MePO (methyl-paraoxon) [
8].
3. Nanomaterials used in biosensing application
There have been significant advancements in the synthesis, processing, characterization, and potential applications of a wide range of nanoscale materials, including zero-dimensional (0D) nanoparticles (such as metallic and semiconducting nanoparticles), one-dimensional (1D) nanostructures (nanowires, nanorods, and nanotubes), and two-dimensional (2D) nanostructures, including graphene nanosheets (GNs), transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). These nanoscale materials have been utilized in numerous products over the past 20 years, including light-emitting diodes, memory and communication systems, magnetic discs, solar and fuel cells, batteries, supercapacitors, and catalysts. Biosensors frequently incorporate the above nanomaterials because they considerably enhance performance and enable faster, more effective, and more cheap detection. The unique optical and electrical properties of materials like silver (Ag), gold (Au) and its different forms nanowires, nanorods, nanostars and carbon nanotubes (CNT), and MWCNTs result in high interaction surface-to-volume ratio, good conductivity, catalytic performance, and biocompatible. Several hybrid nanostructures have also been studied in addition to pure nanomaterials. Because of their distinct optical and electrical properties, Au nanomaterials are frequently used to develop biosensors. The material's ability to absorb strong and distinct surface plasmon resonance signals in the visible-spectrum is one of its key features. SPR is a process that occurs when metal electrons are excited by electromagnetic radiation, changing the dielectric constant (Au is sensitive to this dielectric constant)[
3] . Some of widely used nanomaterials in designing biosensors for pesticide detection and their sensitivity has been given below.
As pointed out by Zhao et al. in the sensing of methomyl, AuNM-based biosensors displayed low LOD value of 81 ng L
-1with AChE immobilization employing the substrate mercapto methamidophos and Au nanomaterials in conjunction with a working carbon electrode[
9]. Through using Au-S bonds in an electrochemical biosensor, Lin et al. were able to identify chlorpyrifos in fruit samples with a LOD of 36 ng L
-1[
10]. Studies using AuNMs have shown strong specificity and sensitivity for chlorpyrifos, isocarbophos carbamate, and methomyl, with LOD ranging from 70 * 10
-3[
11] to 2.48 * 10
3 ng L
-1[
12].
AgNMs has a wide surface ratio, increased electron transport efficacy, and easy availability which makes it more suitable for designing biosensor. By using malathion-specific aptamers which interact with AgNPs to produce a colorimetric value, Bala et al. created an nano biosensor with AgNPs to sense malathion in apples with a LOD of 5 *10
4 nM[
13].
Since TiO
2 NMs maintain catalytic activity and operate as an excellent electron donor in a reaction among biomolecules and sample that takes place in biosensors, it has frequently been considered as an interface for the enzyme immobilisation of biomolecules. In order to create a TiO
2-based sensor sol-gel carrier, Hu et al biosensor's combines carbon electrodes with TiO
2NP and chitosan. The AChE was inhibited in order to identify dichlorvos in samples of cabbage juice as the mechanism of action. The LOD for this biosensor was 0.23 nM[
14].
4. GO-rGO based sensor applications
Graphene is a hexagonal channel of sp2 hybridised carbon atoms covalently linked. Strong oxidants are used to treat graphite, adding epoxy, hydroxyl, and carboxyl groups to its sheet like structure. This results in the production of reduced graphene oxide (rGO). Better conductivity compared to graphene oxide, improved solvent dispersion because to the presence of functional groups, flexibility of control over rGO's electrochemical efficiency and solubility, simplicity in manufacturing and relatively low cost are some of the features of rGO for better utilization in biosensor designing. Overall, the properties of GO and rGO are extremely good, including incredibly high rigidity and tensile strength, desirability for the creation of malleable devices, excellent conductivity of electricity, good optical transparency, and low cytotoxicity; as a result, they may find use in devices that are portable.
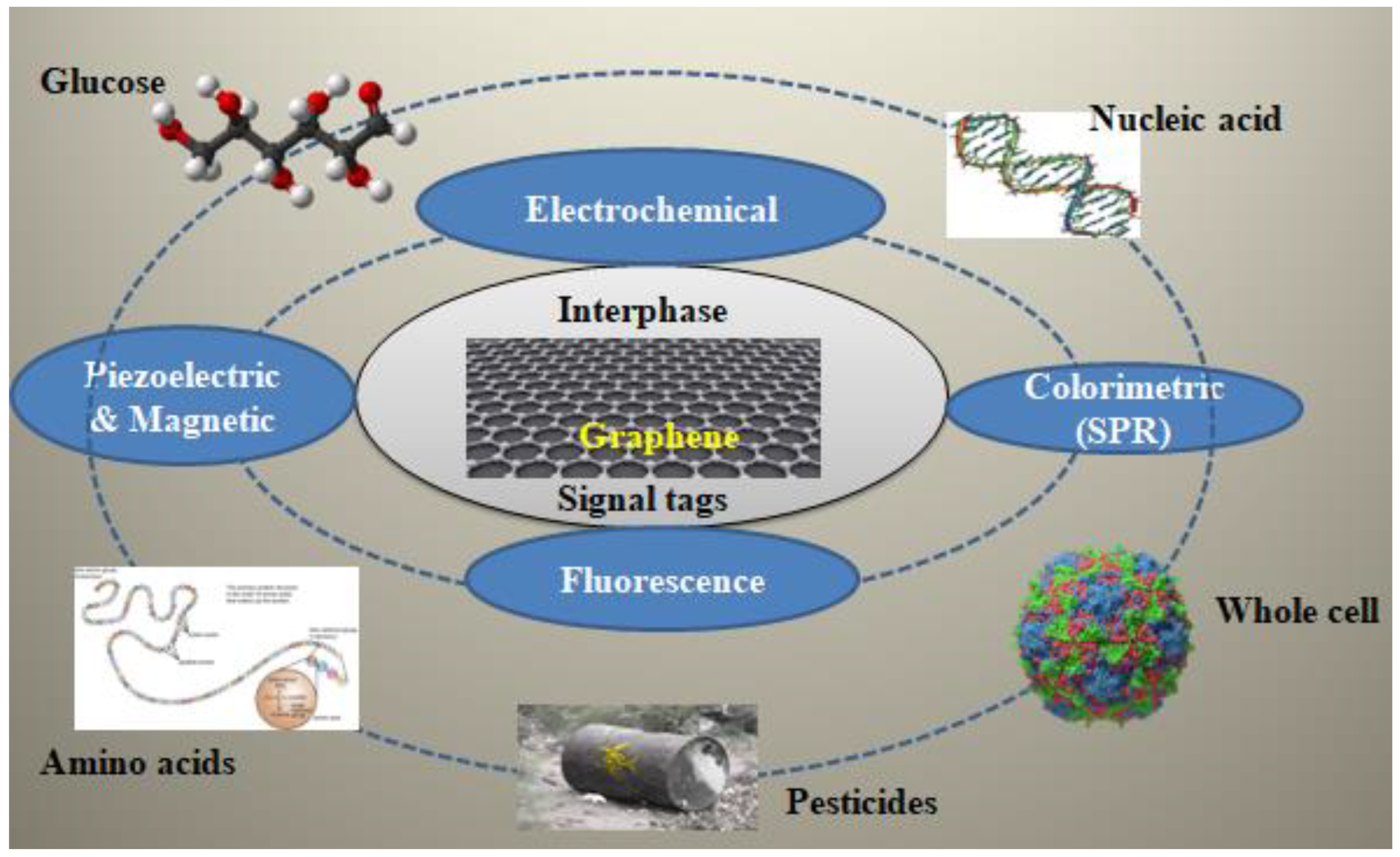
In broad sense, GO properties have been applied to numerous types of biosensors, that can be roughly categorised into different types of biosensors based on (1) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), (2) Laser desorption and ionization- mass spectrometry (LDI-MS), (3) Surface-Enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), and (4) Electrochemistry[
15].
The significance of graphene and its derivatives as a signalling device for the identification and quantification of biomolecules, antigens, antibodies, chemicals, drugs, pesticides, DNA, whole cell viruses/bacteria, etc. is due to its suitable and excellent attributes. Chlorpyrifos and other pesticides, as well as antibiotics like chloramphenicol, tetracycline, streptomycin, and kanamycin, are detected using it in the environmental field. Through incorporating nanoparticles and graphene sheets, the biosensor's sensitivity, limit of detection (LOD), and reproducibility can all be enhanced[
16].
Figure 2.
Graphene based sensing techniques for different analytes.
Figure 2.
Graphene based sensing techniques for different analytes.
5. Sensing strategies
5.1. Electrochemical sensing
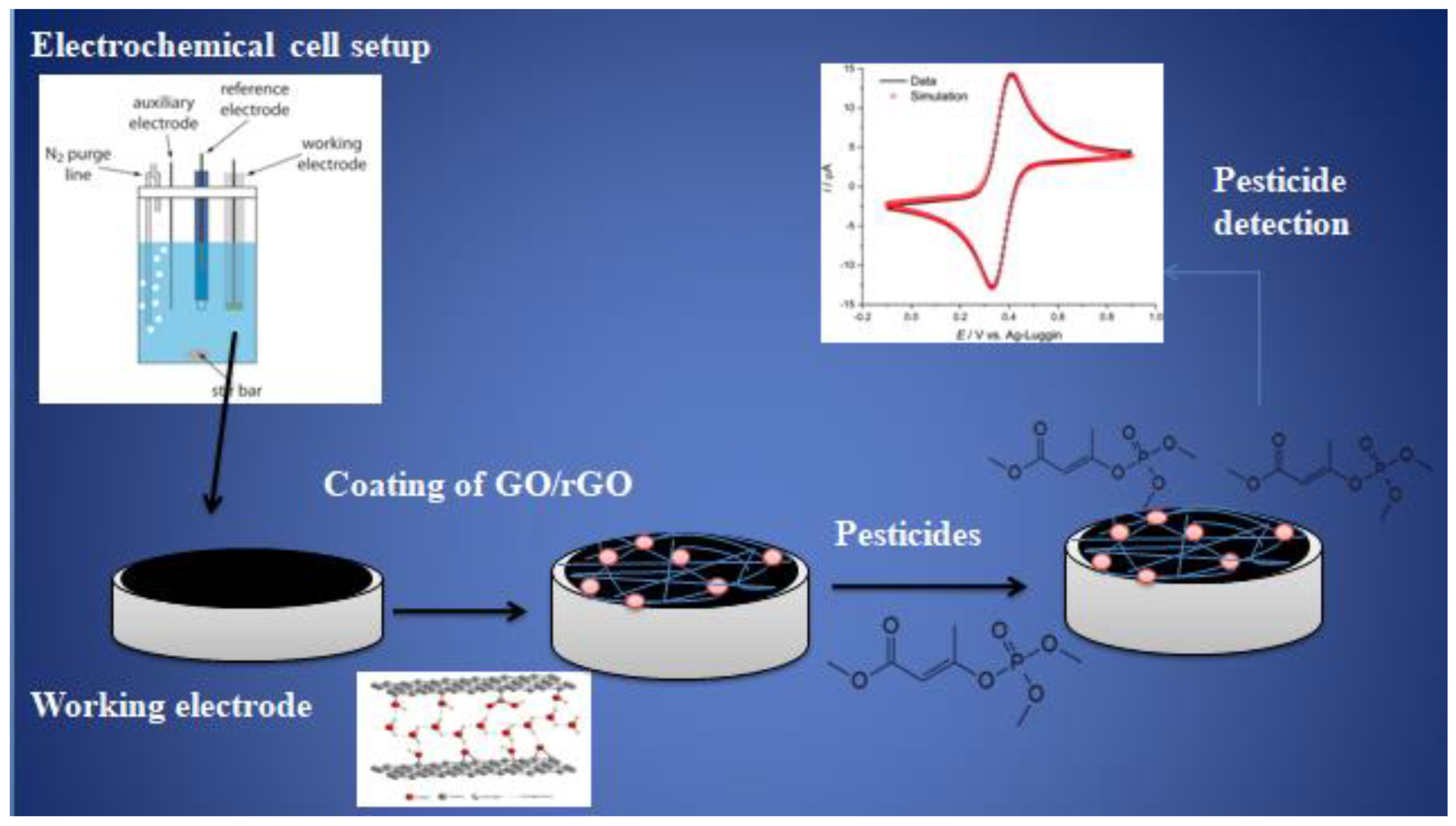
Due to their numerous distinctive qualities, graphene-based nanomaterials are currently frequently employed to develop highly efficient and relatively affordable electrochemical sensors. The two main factors that contribute to graphene's increased electrochemical activity are (1) the large surface area of its 2D sheets, which gives it a large number of electroactive sites for recognising target molecules, increasing sensitivity, and (2) its stability over a wide temperature range, which makes it a highly reliable conductive material for the advancement of electrochemical sensors. Furthermore, the faster electron transfer kinetics of sp
2 hybridised p
z orbital electrons lead to shorter response times with lower detection limits. The redox behaviour of the target pesticide with the working electrode material over the applied potential range is a key factor in the electrochemical detection of pesticides. Due to the presence of "π- π" stacking and electrostatic interaction, which facilitate rapid absorbance of a variety of compounds due to synergetic effects in composites, graphene-based nanocomposites are promising materials for electrochemical sensor applications. Enzymes, antibodies, and DNA can be immobilised to produce a biosensing platform due to the large surface area. Particularly, a lot of study has been conducted on electrochemical biosensors based on the catalytic enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which is found in the central nervous system. A comprehensive summary of the research on graphene-based bio-functionalized nanocomposites used as electrode materials for electrochemical pesticide detection is given in
Table 1.
Figure 3.
GO/rGO for electrochemical sensing of pesticides.
Figure 3.
GO/rGO for electrochemical sensing of pesticides.
The network-like structure of the 3DG-CuO NFs nanocomposites improves the effective specific surface area and creates a suitable microenvironment for AChE loading, which could enhance the performance of the biosensor for malathion detection. The AChE-CS/3DG-CuO NFs/GCE biosensor exhibits advantages such as a broad linear relationship to malathion extending from 1 ppt to 15.555 ppb under ideal detection conditions (3 pM-46.665 nM)[
17].According to Jianhua et al., adding chitosan to graphene will increase its mechanical flexibility while also enhancing the biosensor's stability and detection accuracy. The surface of a glassy carbon electrode was progressively drip coated with graphene nanofragments modified with CS and AChE using a layer-by-layer construction technique. The limit of detection for the sensor used to detect dichlorvos was 54 pM, with a concentration range of 0.1-100,000 nM[
18]. Hossein et al. prepared novel biosensor based on vanadium disulfide quantum dots doped graphene nanoplatelets/carboxylated MWCNTs on carbon electrode. With a LOD of 1.1*10
-14 and 2.0 *10
-15 mol L
-1 for the DPV and EIS approaches, the devised electrochemical aptasensing strategy produced a highly sensitive quantitative detection of DZN. The analytical method was also used to determine the presence of DZN in human serum, Zayandehrood river water, soil, apple, and lettuce samples. The recovery rate for this method, utilizing the GCE/VS2QDs-GNP/CMWCNTs/DZBA/BSA aptasensing technique, ranged from 97.0% to 107.0%[
19]. MoTe
2 NPs/RGO heterostrctures with a suitable Schottky barrier were produced using a one-step hydrothermal synthesis by Lijun et al. to improve the photoelectric performance of MoTe
2.A label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor for the detection of profenofos was successfully built using MoTe
2 nanoparticles/RGO, demonstrating the material's high visible light responsiveness and potential as a light-responsive photoactive material for biosensors. Wide linear range (10
-9 g L
-1 and 10
-2 g L
-1) and a comparatively low detection limit (3.3*10
-10 g L
-1) were both characteristics of this aptasensor[
20].Teerapat et al., reported designing of CuInS
2 microspheres on rGO able to detect chlorpyrifos in vegetable with a detection limit of 0.023 ng mL
-1[
21].
Table 1.
Electrochemical sensing of pesticides using GO-rGO based nanocomposite.
Table 1.
Electrochemical sensing of pesticides using GO-rGO based nanocomposite.
| Nanomaterial |
Pesticide |
Linear range |
Limit of detection |
Ref |
| AChE-CS/3DG-CuO NFs/GCE |
Malathion |
3 pm-46.665 nm |
0.93 pM |
[17] |
| Gra-CS AChE |
Dichlorvos |
0.1-100,000 nM |
54 pM |
[22] |
| GCE/VS2QDs-GNP/CMWCNTs/DZBA |
Diazinon |
5*10-14 mol L-1 to 1.0*10-8 nmol L-1
|
1.1*10-14 mol L-1
|
[19] |
| MoTe2 NPs/RGO |
Profenofos |
10-9 g L-1 and 10-2 g L-1
|
3.3*10-10 g L-1
|
[20] |
| CIS/rGO |
Chlorpyrifos |
0.5-470 ng mL-1
|
0.023 ng mL-1
|
[21] |
| AuNPs/FcDr/rGO/GCE |
Dichlorvos |
0.45-281.4 μM |
0.21 μM |
[23] |
5.2. Fluorescence sensing
Both graphene and GO have the ability to quench fluorescence, that has raised interest in their potential use in clinical and environmental research. Because graphene's remarkable ability for Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer, it is used in fluorescence detection (FRET). This was found that GO has the maximum quenching ability, rapid binding with DNA molecules, repeatability, and selectivity to various DNA sequences when compared to nanomaterials like gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. The amphiphilicity of graphene oxide enables biomolecules to adsorb on its flat surface. If the adsorbed molecule is paired with a fluorescent dye, it has the potential to conduct appropriate energy transfer, leading to fluorescence quenching with a minimal background signal.
At a detection limit of 5.73 nM, acetamiprid can be detected with high selectivity and minimal interference. Only one strand of dsDNA, two strands of ssDNA, and non-modified GO, which is enzyme-and label-free, are present in the test system. More significantly, the new technique shows strong potential for use in the sectors of environmental monitoring and food regulation[
24]. The development of biosensor based on rGQDs, diazinon specific aptamer and MWCNTs able to detect diazinon with the detection limit of 0.4 nM (0.1μg/L) and linear range of 4-31 nM [
25].A new aptasensor for the detection of diazinon was invented by Majid et al., based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between a quantum dot (QD) as a donor and graphene oxide (GO) as an acceptor. When target diazinon was added to the bioconjugates containing GO, photoluminescence recovery appeared to be the result of GO being detached from the aptamer due to the aptamer's different affinity for GO. The biosensor's detection limit was 0.13 nM, and linearity was from 1.05 to 206 nM[
26]. Yawen et al. developed a fast and accurate fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) approach for the detection of diazinon in food at low concentrations. Graphene oxide (GO) was coupled with the synthesized aptamer-modified up conversion nanoparticles (Apt-UCNPs) via a π-π interaction. The fluorescence was diminished of the FRET between UCNPs and GO. The aptamer formed a strong preference for binding with diazinon, which separated GO and improved the fluorescence signal. Under ideal circumstances, a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.023 ng/mL was attained with a broad linear detection range of 0.05 to 500 ng/mL[
27].The performance of nano biosensors for the rapid and precise detection of pesticides can be considerably enhanced by the introduction of nanomaterials, particularly carbon quantum dots (CD).In order to create a fluorescent biosensor, Mariaet al. designed a naturally fluorescence and nontoxic CD coupled with acetylcholinesterase (AChE) as a bioreceptor. The biosensor was tested for the ability to detect profenofos, pure chlorpyrifos, and a commercial formulation known as Lorsban. For chlorpyrifos and lorsban, respectively, a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.14 and 2.05 ppb was attained[
28].
Table 2.
Fluorescence sensing of pesticides using GO/rGO nanocomposite
Table 2.
Fluorescence sensing of pesticides using GO/rGO nanocomposite
| Nanomaterial |
Pesticide |
Linear range |
Limit of detection |
Ref |
| Aptamer-GO-PEG |
Profenofos |
0.5-100 ng/mL |
0.21 ng/mL |
[29] |
| DNA TWJ-assembled G-quadruplex |
Acetamiprid |
0-500 nM |
5.73 nM |
[24] |
| rGQDs-MWCNT-aptamer |
Diazinon |
4-31 nM |
0.4 nM (0.1μg/L) |
[25] |
| GO-L-cysteine capped CdS QDs/DF20 aptamer |
Diazinon |
1.05 to 206 nM |
0.13 nM |
[26] |
| Apt-UCNPs-GO |
Diazinon |
0.05 to 500 ng/mL |
0.023 ng/mL |
[27] |
| AChE-Carbon dots-GO |
Chlorpyrifos |
1 and 25 ppb (2.8-71 nM) |
2.05 ppb (5.84 nM) |
[28] |
6. Limitation and Future perspectives
Though there has been a number of recent developments in design of graphene-based hybrid nanocomposites for multiple biosensor applications, it has remained difficult to comprehend the functionalities of graphene, GO, and rGO. It is also imperative to understand how they will interact with surface-modified polymers or inorganic nanoparticles. Though GO has a lot of oxygen functional groups on its surface, using these functional groups effectively has been challenging because of their amorphous structure. It is quite challenging to achieve controlled uniform deposition, assembly onto graphene surfaces, and thus surface stability remains a major bottleneck in the synthetic methods. To obtain precisely controlled synthesis and a thorough understanding of the structure-property connections of graphene nanomaterials, more research efforts concentrating on novel yet inexpensive synthetic techniques are required.
Due to numerous advantages over the conventional electrochemical method for sensing the pollutants, GO/rGO-based microfluidic devices are gaining increasing attention nowadays. The development of electrochemical biosensors and immunosensors for the detection of biologically significant markers is greatly facilitated by the excellent electrochemical characteristics of GO-based nanomaterials and nanocomposites. With improved sensitivity and detection limits that can reach sub picomolar levels, devices are being designed employing a microporous 3D architecture. This approach appears to be effective for the detection of several biomolecules in a single-chip device at a time. However further studies are needed to work on affordable, on-site devices for detecting and measuring various harmful pesticide residues in water samples.
7. Conclusions
In this review, we have highlighted various GO/rGO nanocomposites and their features for designing various sensor systems. We have presented the recent developments in GO/rGO based sensors. The numerous types of sensors work on diverse principals, such as electrochemical, fluorescence, etc. It is evident that unique functional properties of graphene and its various derivatives, such as excellent electrical conductivity, increased mobility of electrons, tuneable optical properties, ambient temperature quantum Hall effect, a significant surface-to-volume ratio, strong mechanical properties, and easiness of functionalization, make them quiteexcellent candidates for the development of biosensors. The development of intelligent sensors for on-site point-of-care diagnostic testing using graphene-based materials seems possible and is expected to be cost-effective.
Author Contributions
Geetha Gopal; investigation, writing—original draft preparation, Amitava Mukherjee; conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) INSPIRE fellowship for Selected Research Scholars of India (Grant No: IF190196).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alex, A.V.; Mukherjee, A. Review of recent developments (2018–2020) on acetylcholinesterase inhibition based biosensors for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Microchem. J. 2020, 161, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, F.C.; Kumar, P.S.; Christopher, F.J.; Joshiba, G.J.; Madhesh, P. Recent advancements in rapid analysis of pesticides using nano biosensors: A present and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, J.; Melo, J.S.; Sandaka, B.P. Progressive development in biosensors for detection of dichlorvos pesticide: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, J.; Von Brömssen, C.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Ohlsson, Å.; Le Godec, T.; Jonsson, O.; Kreuger, J.; Oskarsson, A. Assessment of pesticides in surface water samples from Swedish agricultural areas by integrated bioanalysis and chemical analysis. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, H.; Arbabzadeh, O.; Falaki, M.; Majidi, M.R.; Han, N.; Yoon, Y.; Khataee, A. Electrochemical layered double hydroxide (LDH)-based biosensors for pesticides detection in food and environment samples: A review of status and prospects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonsioroski, A.; Mourikes, V.E.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine disruptors in water and their effects on the reproductive system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, V.A.; Deosarkar, T.; N, C.; Mukherjee, A. An ultra-sensitive and selective AChE based colorimetric detection of malathion using silver nanoparticle-graphene oxide (Ag-GO) nanocomposite. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1142, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, B. Detection of organophosphorus pesticides by nanogold/mercaptomethamidophos multi-residue electrochemical biosensor. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H. Electrochemical aptasensor based on Mo2C/Mo2N and gold nanoparticles for determination of chlorpyrifos. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Kong, M.; Jiang, G.; Sun, Y.; Mo, W.; Lin, T.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S. A competitive immunoassay for electrochemical impedimetric determination of chlorpyrifos using a nanogold-modified glassy carbon electrode based on enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. Design an aptamer-based sensitive lateral flow biosensor for rapid determination of isocarbophos pesticide in foods. Food Control. 2021, 129, 108208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Mittal, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Wangoo, N. A supersensitive silver nanoprobe based aptasensor for low cost detection of malathion residues in water and food samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 196, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L. Acetylcholinesterase Sensor with Patterned Structure for Detecting Organophosphorus Pesticides Based on Titanium Dioxide Sol-gel Carrier. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Cheng, N.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Du, D. Recent advances in nanomaterials-based electrochemical (bio)sensors for pesticides detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, P.; Meyyappan, M.; Singh Nalwa, H. A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8778–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Geng, X.; Xu, G.; Samalo, M.; Sakinati, M.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. 3D graphene/copper oxide nano-flowers based acetylcholinesterase biosensor for sensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 279, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wu, M.; Yang, L. A stable biosensor for organophosphorus pesticide detection based on chitosan modified graphene. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 69, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosropour, H.; Rezaei, B.; Rezaei, P.; Ensafi, A.A. Ultrasensitive voltammetric and impedimetric aptasensor for diazinon pesticide detection by VS2 quantum dots-graphene nanoplatelets/carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a new group nanocomposite for signal enrichment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1111, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wei, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Qian, J.; Hao, N.; Ding, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, K. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of telluride molybdenum/reduced graphene oxide with Schottky barrier for fabricating label-free photoelectrochemical profenofos aptasensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 407, 127213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsoponpan, T.; Thanachayanont, C.; Hasin, P. Sponge-like CuInS2 microspheres on reduced graphene oxide as an electrocatalyst to construct an immobilized acetylcholinesterase electrochemical biosensor for chlorpyrifos detection in vegetables. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, B. A multi-residue electrochemical biosensor based on graphene/chitosan/parathion for sensitive organophosphorus pesticides detection. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yan, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Fu, S.; Zhang, G.; Qian, C.; Yang, H.; Han, J.; et al. Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets and gold nanoparticles covalently linked to ferrocene-terminated dendrimer to construct electrochemical sensor with dual signal amplification strategy for ultra-sensitive detection of pesticide in vegetable. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Lu, L. A low-background fluorescent aptasensor for acetamiprid detection based on DNA three-way junction-formed G-quadruplexes and graphene oxide. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talari, F.F.; Bozorg, A.; Faridbod, F.; Vossoughi, M. A novel sensitive aptamer-based nanosensor using rGQDs and MWCNTs for rapid detection of diazinon pesticide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Mirroshandel, A.A. An efficient fluorescence resonance energy transfer system from quantum dots to graphene oxide nano sheets: Application in a photoluminescence aptasensing probe for the sensitive detection of diazinon. Food Chem. 2018, 280, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Ali, S.; Chen, Q. Rapid and sensitive detection of diazinon in food based on the FRET between rare-earth doped upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 239, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaviria, M.I.; Barrientos, K.; Arango, J.P.; Cano, J.B.; Peñuela, G.A. Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Biosensor Based on Acetylcholinesterase and Carbon Dots–Graphene Oxide Quenching Test for Analytical and Commercial Organophosphate Pesticide Detection. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gan, J.; Ju, J.; Xian, Y.; Xiong, X. Fluorescent Aptamer-Polyethylene Glycol Functionalized Graphene Oxide Biosensor for Profenofos Detection in Food. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 36, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).