1. Introduction
Nanotechnology is currently one of the most evolved scientific and technological fields in academic research and industry. Worldwide, the study of science and technology at the nanoscale has been one of the main areas in terms of research funding.
The use of peptides as a building block in nanotechnology has been increasingly exploited for its characteristics such as biocompatibility, flexibility and variability in molecular design [
1,
2,
3].
Aromatic dipeptide chiral diphenylalanine (FF or PhePhe) and N-tert-butoxycarbonyl diphenylalanine (Boc-L-phenylalanine-L-phenylalanine-OH, Boc-PhePhe), have in their crystal structures phenylalanine molecules linked by directional covalent bonds spontaneously self assembles into stable nanotubes (NT) and other nanostructures both in organic solvents and aqueous solutions [
4,
5,
6,
7].
Due to these directional intermolecular π-π interactions and hydrogen-bonding network, quantum confined (QC) structures with pronounced exciton effects are formed within these dipeptide assemblies: quantum dots (QD) occur due to formation of nanocrystalline regions possessing strong QC properties and originating a pronounced blue luminescence, as has been reported for dipeptides Boc-p-nitro-L-phenylalanyl-p-nitro-L-phenylalanine and Boc-L-phenylalanyl-L-tyrosine self-assembled either into microspheres or microtapes [
8].
Furthermore, hydrogen bonding networks in peptides and π-π interactions between aromatic moieties are responsible for the intrinsic semiconductor properties displayed by self-assembled dipeptides, polypeptide and proteins [
9,
10]. Consequently, dipeptide self-assemblies are direct-wide gap semiconductors, which form a new type of optoelectronic components and energy harvesting devices. For example, phenylalanine-tryptophan (FW) nanostructures display higher conductivity than diphenylalanine (L-Phe-L-Phe, FF) due to their smaller bandgap (3.04 eV), which is within the same range of energy as that of gallium nitride (3.39 eV) and silicon carbide (2.9 eV) for example [
11]. Cyclic dipeptides (CDPs) are a group of ring-shaped dipeptides which, as a result of multiple interactions, can self-assembled with different functional architectures, such as nanospheres, nanoribbons, nanotubes and nanowires [
12]. They exhibit semiconducting properties and improved stable photoluminescence (PL) in the visible, relatively to their linear-counterparts. These properties are due to extensive hydrogen bonding and increased aromatic interactions present in their supramolecular structures. They are promising materials for optical waveguiding, nonlinear optics and biomechanical energy harvesting applications due to their high piezoelectric coefficients [
11,
13]. For example, cyclization of diphenylalanine, by introduction of an aldehyde in self-assembling fibrous peptide networks, originated oriented crystallization into ordered superstructures uniaxially oriented along the longitudinal axis. This long-range oriented crystallization leaded to peptide platelets capable of functioning as optical waveguides exhibiting also blue photoluminescence emission under excitation at 330–380 nm [
14].
More recently, biocompatible organic materials based on CDPs, self-assembled in supramolecular structures with different morphologies, showed very interesting quantum confinement and photoluminescence [
12,
15]. Through selection of several amino acid side chains, or chemical modifications, that provide several non-covalent interactions (such as hydrophobic interactions, π−π interactions and electrostatic forces), CDPs can self-assembled for the construction of various nanostructures [
15]. The effect of external factors such as the pH, the substrate, the solvent and also the temperature used during the process, among others, allow the formation of various nanostructures such as nanospheres (NS), nanotubes (NT) and nanofibers (NF) [
16].
Nanostructures obtained from CDPs have a high potential for applications in several areas, such as energy storage devices, light emitting or display devices, use in hydrophobic surfaces for self-cleaning, piezoelectric devices, ultrasensitive sensors, in hydrogels for tissue engineering and drug delivery agents, among others [
12]. Therefore, they are able to form functional architectures with wide applications in the field of materials science [
17].
Dipeptide supramolecular structures that have in their constitution aromatic tryptophan amino acid, display enhanced properties such as high thermal stability and mechanical strength, conductivity and photoluminescence [
2,
3,
18]. Tao and co-workers [
2] showed that for
cyclo-phenylalanine–tryptophan (cyclo-FW) and cyclo-tryptophan–tryptophan (cyclo-WW), with extensive and directional hydrogen bonds between backbone diketopiperazine rings together with aromatic side-chains interactions dimerized into quantum dots (QD) as a result of quantum confinement. Both dipeptides
showed needle-like morphologies having high aspect-ratio. However, the two reported
cyclo-WW dipeptides crystallized in a centrosymmetric space group (), only cyclo(FW) crystallized in an acentric space group (
. Consequently, only this last one exhibited the piezoelectric effect and had the characteristics to be configured as a peptide-based generator.
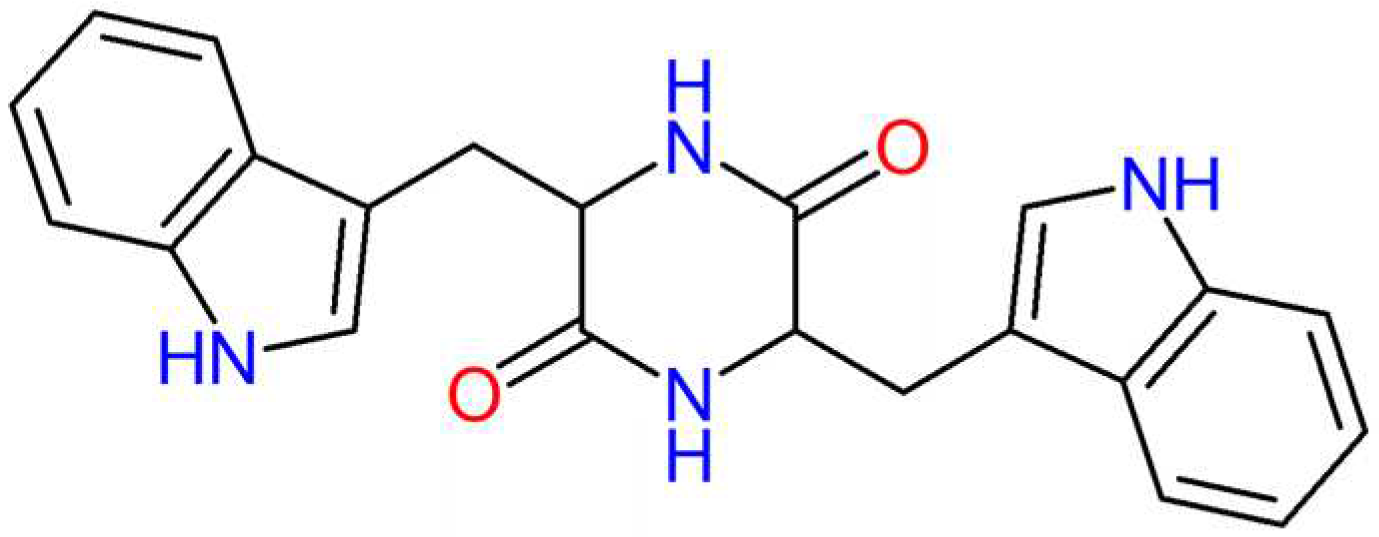
Unlike linear peptides, scaffolds of CDPs have higher molecular rigidity, resulting from the four hydrogen bonding sites in the ring (two donors and two acceptors) [
16], as can be seen in
Figure 1 for the molecular structure of chiral cyclic dipeptide cyclo-L-tryptophan-L-tryptophan formed by chiral tryptophan amino acids.
The simplest cyclic tryptophan-based dipeptide is cyclo-glycine-tryptophan (cyclo-DW), which forms crystals with a needlelike shape morphology from crystallization in a mixed methanol and water solution [
3]. The crystals belong to the polar point group 2 and are thermally stable until 370 °C. They are photoluminescent with a maximum of emission at 420 nm, in the blue light spectra region, when excited with wavelengths in the range of 300–400 nm. Due to its noncentrosymmetry, the crystal displays a high piezoelectric response,
d16 and
d36 approximately equal to 14 pC N
−1 [
3,
11]. The aromatic packing networks present in Cyclo-DW crystal supramolecular structure, promotes an output open-circuit voltage as high as 1.2 V under a force of 65 N applied periodically. Therefore, the crystals are suitable to be incorporated as active elements in energy harvester devices.
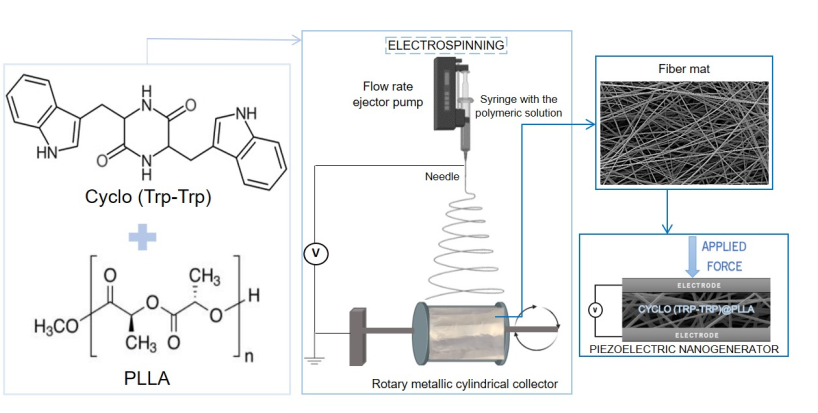
In this work, we focused on the fabrication and characterization of hybrid systems based on nanostructured chiral cyclo-dipeptide Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) incorporated into biopolymer fibers produced by the electrospinning technique. These nanofibers form anisotropic piezoelectric and pyroelectric self-assembled functional hybrid systems, suitable for thermal sensing and energy harvesting applications.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Cyclic dioxopiperazine-L-tryptophan-L-tryptophan, herein referred to as Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp), was purchased from Bachem AG (Bubendorf, Switzerland). 1,4-dioxane was purchased from Fischer Chemicals (Zurich, Switzerland). N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), dichloromethane (DCM), N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), methanol and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFP) were purchased from Merck/Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany) and used as received.
Polycaprolactone (PCL, Mw 80,000) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA, Mw 217–225,000) was purchased from Corbion (Gorinchem, The Netherlands) and BDH Chemicals (Poole, UK), respectively.
2.2. Self-assembling of dipeptide micro and nanostructures in solution
Fresh solution of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) was prepared by dissolving the dipeptide in HFP to a concentration of 100 mg/mL. This solution was afterwards diluted in methanol (MeOH) to the desired final concentrations according to the studies to be undertaken. After dilution in methanol, the solutions were left at room temperature during 24 h for self-assembling to take place. A few drops of a 5.37 mM solution of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) are placed on a silica slide and removed the solvent by slow evaporation at room temperature and sent to SEM analysis and to Confocal Microscopy.
2.3. Electrospinning of nanofibers
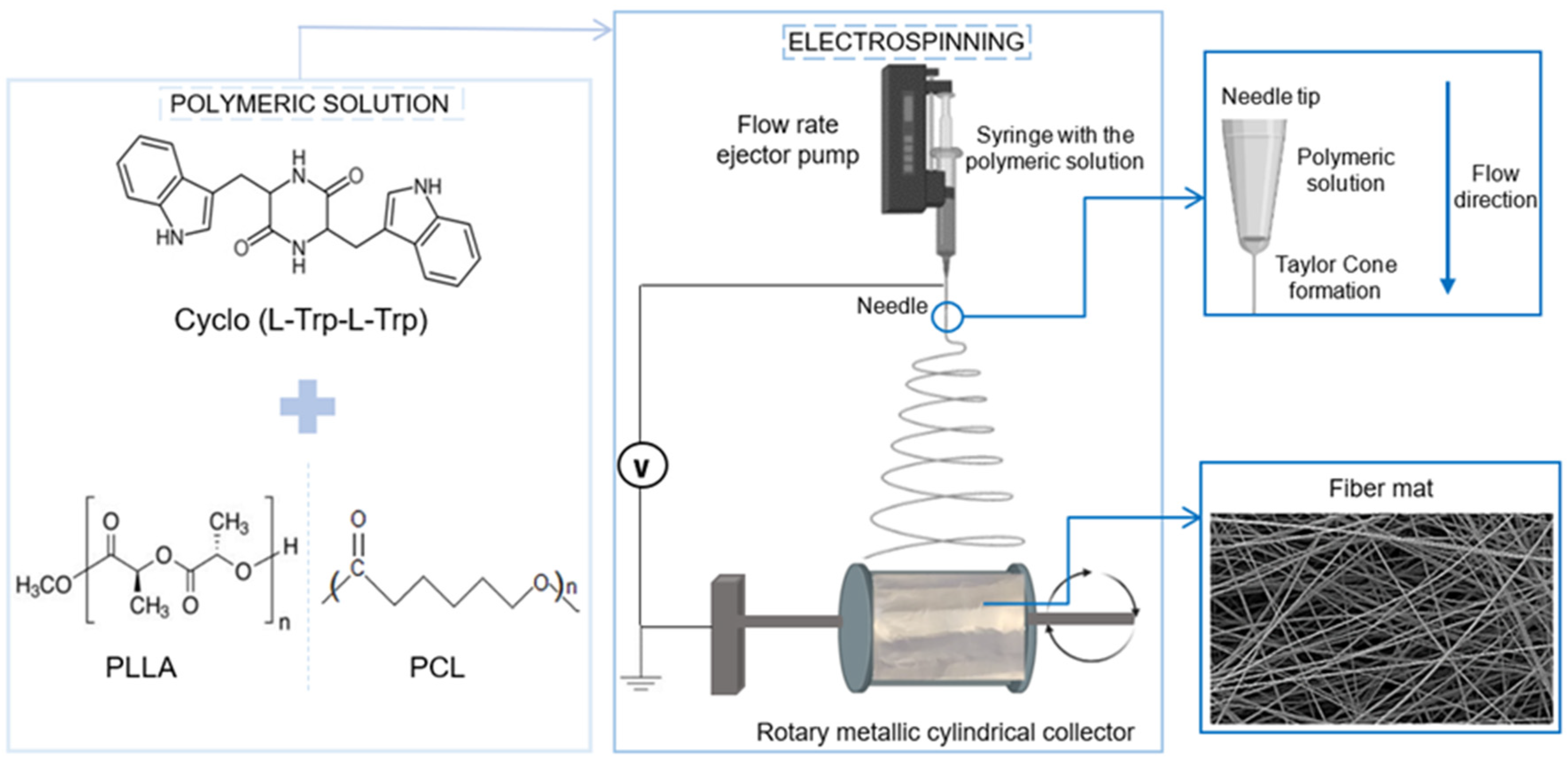
The 10% (w/v) polymer solution of PLLA was prepared by dissolving the polymer in a DCM/DMF solvent blend system (8:1, v/v), with vigorous stirring at room temperature. The 10 % polymer solution of PCL was prepared by dissolving the polymer in a DMAc/DMF solvent blend system (7:1, v/v). After complete dissolution, Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide was incorporated, previously dissolved in DMF or DMAc in a 1:5 weight ratio. The incorporation of DMAc in some of the samples arises from the need to avoid precipitate formation in the solution during the addition of the dipeptide (some solutions became milky color or much higher viscosity than desirable). The resulting precursor solutions were stirred for several hours under ambient conditions before the electrospinning process.
The obtained solutions were loaded into a 5 mL syringe with its needle (0.5 mm outer diameter and 0.232 mm inner diameter) connected to the anode of a high-voltage power supply (Spellmann CZE2000, Bochum, Germany). The electrospinning apparatus has a vertical geometry and electrospinning process was performed at room temperature. Several parameters were changed to obtain bead free fibers and stable spinning conditions, namely, the solution feeding flow rate, the electric potential difference and the needle-collector distance. An electric potential difference between 18-20 kV, depending of the polymer and solvent ratio, was used. The needle-collector distance was 11 cm and flow rate 0.15-0.40 mL/h. An aluminum foil is attached to the collector in order to collect the prepared fibers. The fibers have been collected as a random mesh on high purity aluminium foil which served as electrodes,
Figure 2.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The morphology, size, and shape of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) structures were studied using a Nova Nano SEM 200 scanning electron microscope operated at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV. Prior SEM analysis the silica slide with Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) structures and fiber mats were covered with a thin film (10 nm thickness) of Au-Pd (80-20 weight %) using a high-resolution sputter cover, 208HR Cressington Company, coupled to a Cressigton MTM-20 high-resolution thickness controller. The diameter range of the Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) structures and fibers was measured by SEM images using ImageJ 1.51n image analysis software (NIH,
https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/, October 2022). The average diameter and diameter distribution were determined by measuring 665 random nanospheres or 72 – 75 random fibers from the SEM images, and the results fit to a log-normal function.
2.5. Mechanical Tests
A Zwick/Roell Z005 (ZwickRoell, Germany) universal testing machine was used to access the mechanical properties of electrospun fiber mat, following the ASTM D882-02 standard. Rectangular specimens (40 x 10 mm) were cut from the fiber mat and tested under a crosshead velocity of 25 mm/min, with a gauge length of 26 mm. The results represent an average value of, at least, 5 specimens.
2.6. Optical absorption and Photoluminescence
Optical absorption (OA) measurements on Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) solutions and fiber mats were carried out using a Shimadzu UV-3101PC UV–Vis-NIR (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) spectrophotometer. Photoluminescence spectra were recorded on a Fluorolog 3 spectrofluorimeter (HORIBA Jobin Yvon IBH Ltd., Glasgow, UK).
For optical absorption measurements, Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) solutions were prepared in methanol. The samples were measured in a quartz cuvette with 1 cm path length. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra acquired in the wavelength range of 290 – 600 nm using an excitation wavelength of 280 nm, with input and output slits fixed to provide a spectral resolution of 2 nm. Photoluminescence Excitation (PLE) spectra were acquired in the wavelength range of 220 – 300 nm.
A UV-2501PC (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) spectrophotometer equipped with an integration sphere, Shimadzu ISR-205 240A, and barium sulfate taken as reference, was used to measure the diffuse reflectance spectrum for the nanofiber mats in the wavelength range of 200 – 800 nm with 1 nm step size. The energy of the bandgap, (E
g), was determined using the Kubelka-Munk function given by [[hvF(R)]
1⁄2]=α(hv–E
g), where hv represents the energy of the incident photon, E
g corresponds to the energy of the bad gap, and F(R) is called the Kubelka-Munk function which is directly determined from the total reflectance coefficient of the material (R) through the equation F(R)=(1–R)
2⁄2R [
19,
20].
2.7. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
The autofluorescence of the fibers were observed with an Olympus™ FluoView FV1000 (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) confocal scanning laser microscope, using a 40x objective, with emission/detection settings: (i) excitation wavelength 405 nm, detection filters BA 430 – 470. Images were acquired with 800 x 800-pixel resolution. A 1 cm2 fiber mat with 600 μm thickness was observed on a glass slide. A scan over the sample was performed at room temperature.
2.8. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) measurements
The size, polydispersity and zeta potential of the 0.5 µM water solutions of the dipeptides (500 µl of a previously prepared solution of the dipeptides at concentration of 3 µM, HFP/MeOH (0.2/9.8 v/v) were diluted in water to prepare the DLS samples) were measured on a Litesizer 500, a detection angle of 175°, DLS equipment from Anton Paar (Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), using a semiconductor laser diode of λ = 658 nm and 40 mW. Each sample was measured three times, at room temperature, and experimental data were processed using software Kalliope™.
2.9. Pyroelectric Coefficient
Pyroelectricity is the property of some low-symmetry crystalline materials to convert a variation of temperature (T) within a certain time interval (dT/dt) into electric energy. The phenomena result from the temperature dependence of material spontaneous polarization (Ps). By changing the temperature, an electric field originated from changes in intrinsic dipoles is compensated by the surface layer of free charges. The rate of change of the spontaneous polarization with temperature during heating or cooling, p=dPs/dT, is the pyroelectric coefficient. The change in polarization was detected by measuring the pyroelectric current I = A (dPs/dT)(dT/dt), with a Keithley 617 electrometer (Keithley Instruments GmbH, Landsberg, Germany), where A is the electrode area and dT/dt is the rate of temperature change. The measurements were performed in a capacitor geometry under short-circuit conditions. The fiber mat sample, with area (10 × 10) mm2 (20 - 330 µm thickness) formed a plane parallel capacitor covered with high purity metal plates.
2.10. Piezoelectric output voltage and current
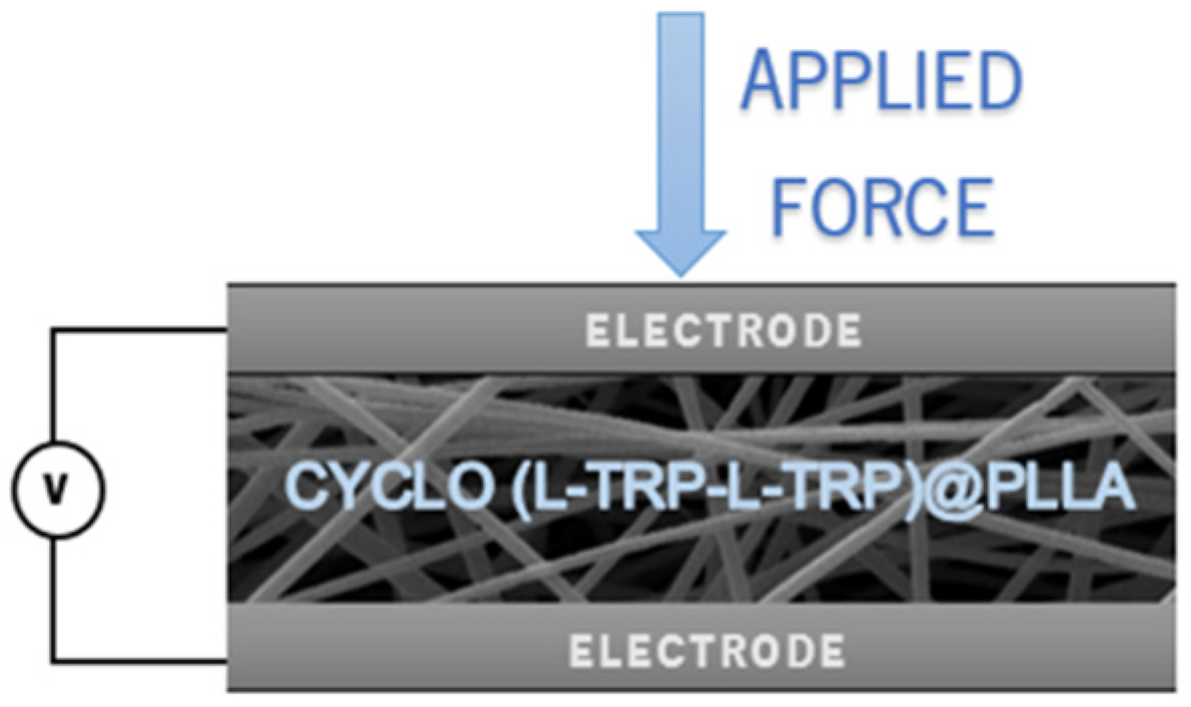
Piezoelectric output voltage and current were measured across a 100 MW load resistance connected to a low-pass filter followed by a low-noise preamplifier (Research systems SR560, Stanford Research Systems, Stanford, CA, USA) before being registered with a digital storage oscilloscope (Agilent Technologies DS0-X-3012A, Waldbronn, Germany). The fiber array sample with a 30 x 40 mm
2 area (20 - 160 µm thickness) was subjected to applied periodic mechanical forces imposed by a vibration generator (Frederiksen SF2185) with a frequency of 3 Hz determined by a signal generator (Hewlett Packard 33120A). The forces applied were previously calibrated using a force-sensing resistor (FSR402, Interlink Electronics Sensor Technology, Graefelfing, Germany). The fibers were directly deposited, during the electrospinning process, on high-purity aluminum foil, which served as electrodes. The samples were fixed on a stage, and the forces were applied uniformly and perpendicularly over the surface area of each sample. A piezoelectric nanogenerator, fabricated using an Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA electrospun fiber mat as the active piezoelectric component, is described in
Figure 3. The top (area 23 x 30 mm
2) and bottom electrodes (area 30 x 33 mm
2) are high-purity copper thin plates. Thin copper wires were attached to the electrodes.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of self-assembled dipeptide in solution
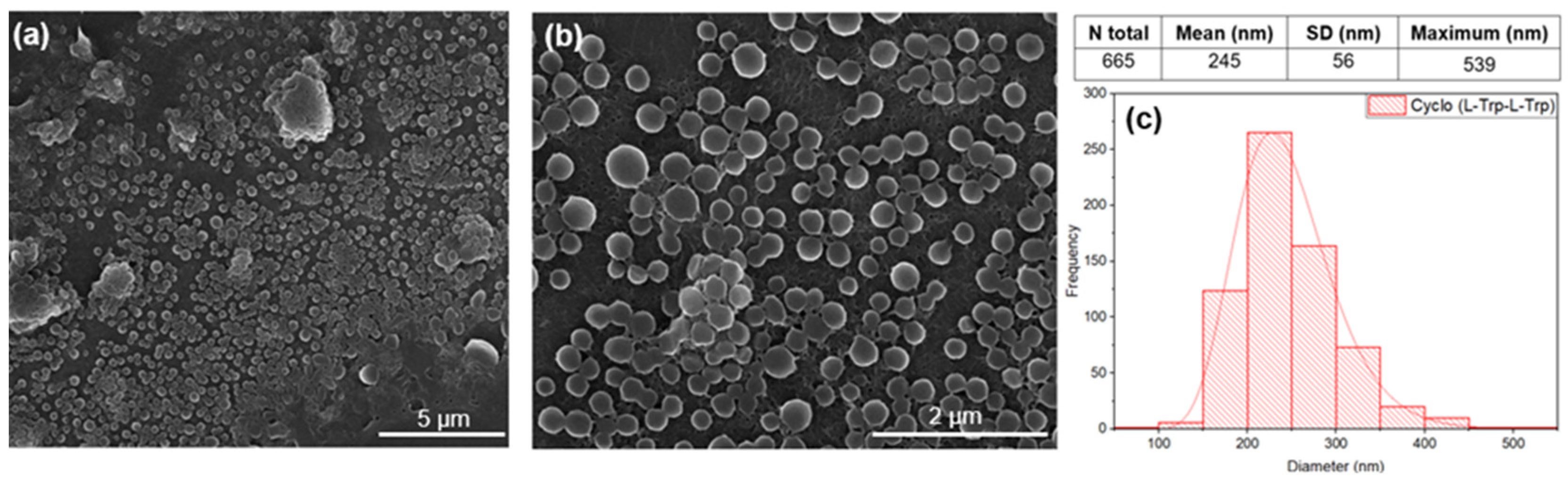
The dipeptide cyclo-(L)-tryptophan-(L)-tryptophan, hereafter cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) self-assembles as nanospheres (NS) with a 245 nm average diameter from a 5.4 mM methanol solution. Note that the nanospheres observed in the SEM image tend to self-organize and self-assembled into structures of larger dimensions, as can be seen in
Figure 4 a) to c).
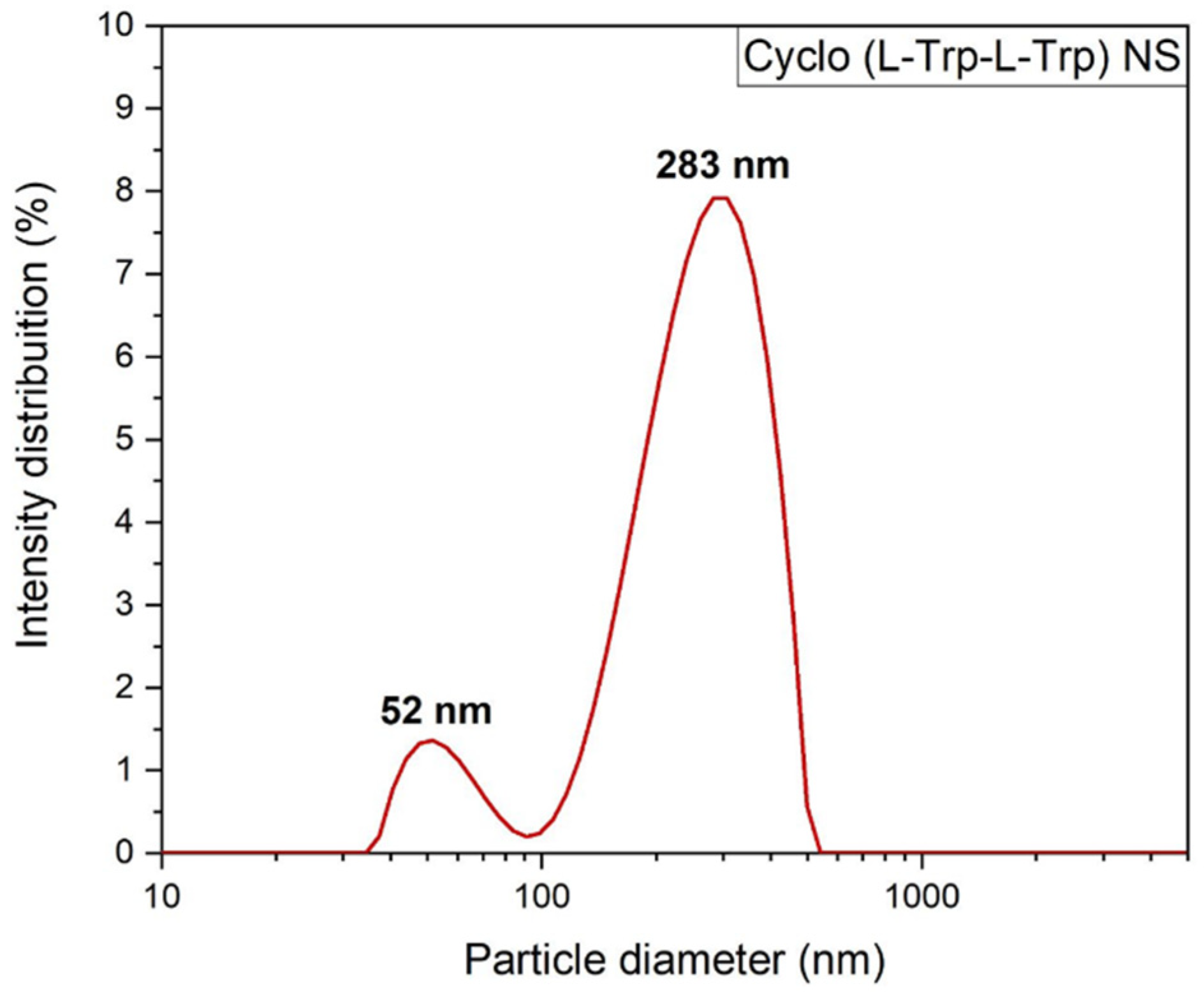
To better understand the self-assembling process of the Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp), the average size distribution of the dipeptide nanospheres was measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS). It is possible to make a comparison between the sizes of the nanospheres, obtained by SEM and by DLS, however the latter only allows to obtain the hydrodynamic size, i.e., it is the size of the particles in movement. This technique permits to obtain the overall size of particles dispersed in a liquid. Thus, the dipeptides were dissolved in HFP at room temperature followed by addition of methanol to have a concentration of 3 µM, HFP/MeOH (0.2/9.8 v/v). From this solution, 500 µl was diluted to a concentration of 0.5 µM in water, followed by ultrasonic treatment and DLS analysis [
18]. The intensity-weighted distribution measurements indicated that the Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) self-assembles as large molecular superstructures with several hundreds of nanometer size, have a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 283 nm, consistent with that obtained by SEM (245 nm) for dipeptide self-assembling as nanospheres (NS),
Figure 5. Other parameters obtained were transmittance of 75 % and zeta potential of 19.6 ± 0.3 mV. A positive zeta potential demonstrates that Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) NS possibly aggregate into a mass at the neutral condition. The obtained value was the desirable minimum zeta potential to achieve electrostatic and steric stabilization [
21,
22,
23].
3.2. Morphology of electrospun fibers
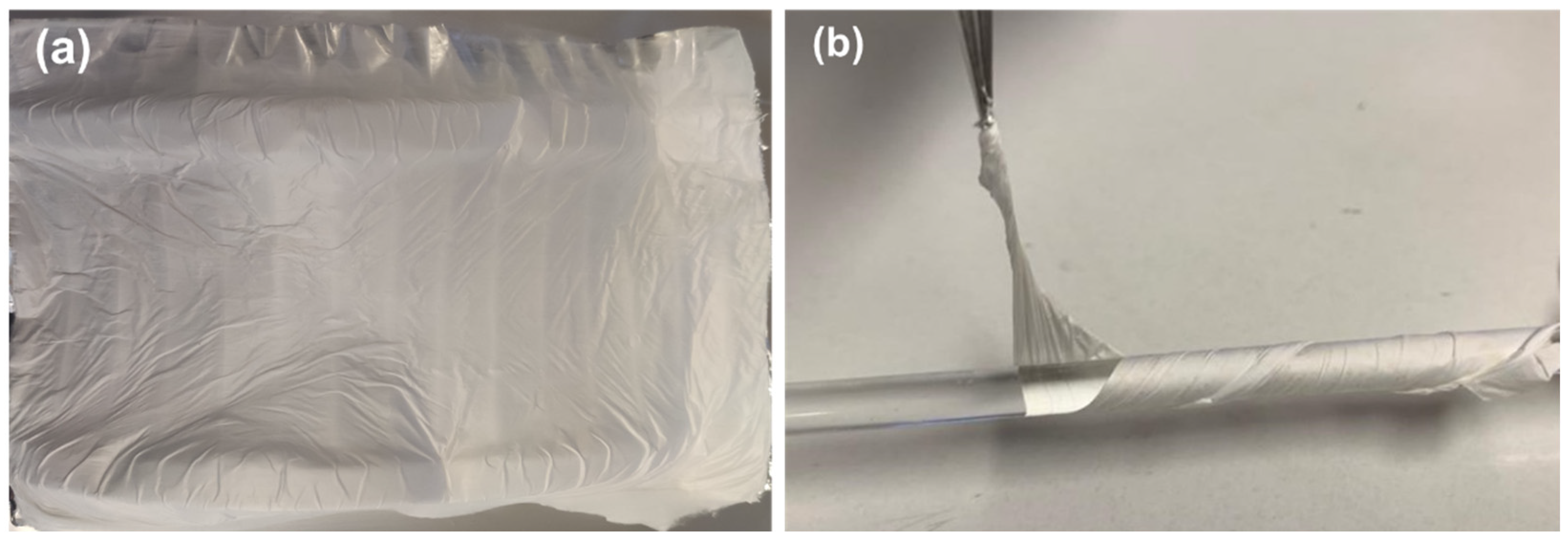
The electrospinning process is stable with no current fluctuations and a steady flow of the polymer solution at the tip of the needle. The fabricated fibers show no beads or crystallites grown on their surface, have a white appearance, and are very flexible,
Figure 6).
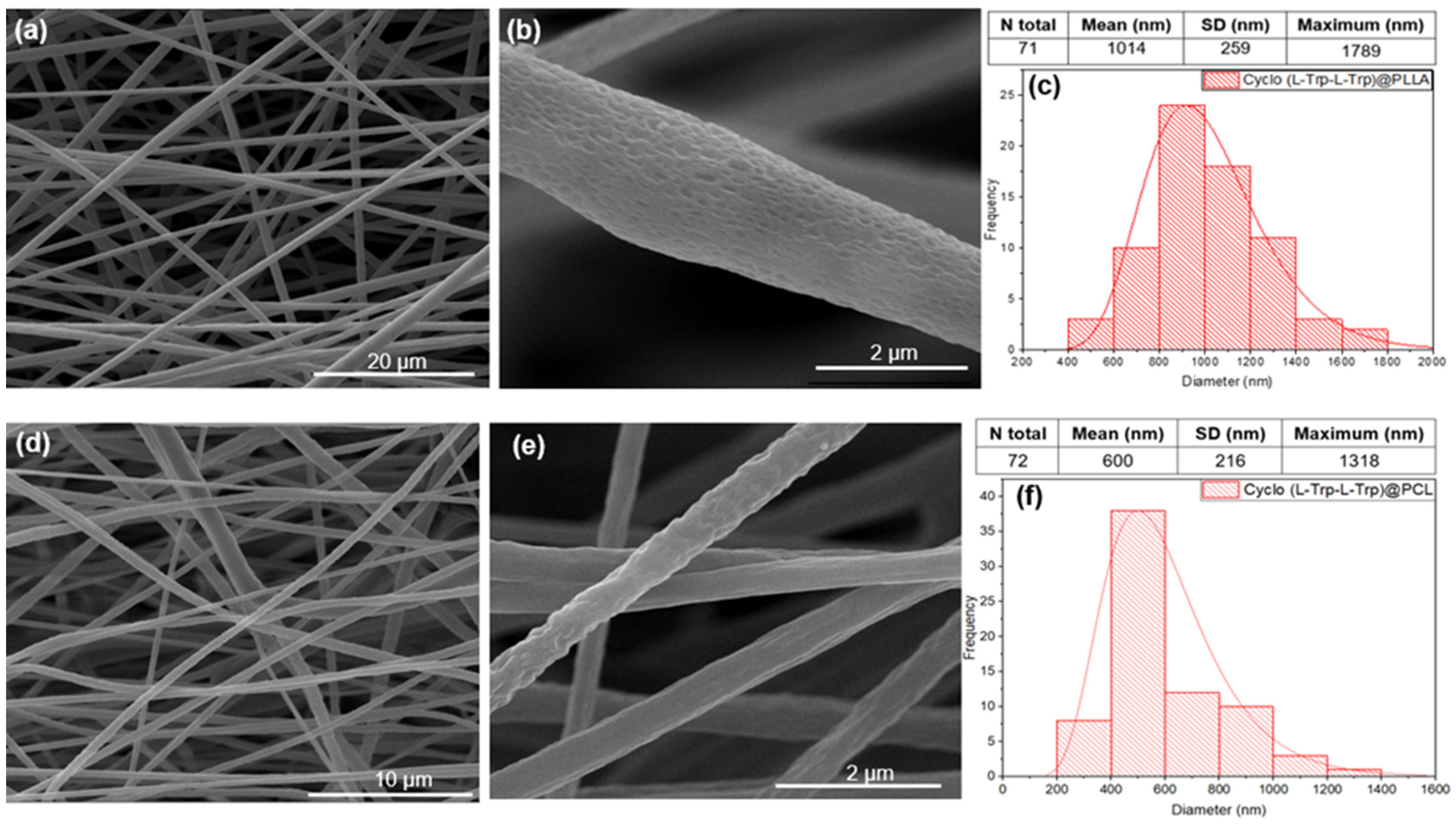
Figure 7 shows scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the fibers prepared with different polymers with embedded Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide, along with the corresponding histograms of the diameter sizes. The diameter distributions follow a log-normal dependence, with average values from 600 to 1014 nm. The fibers electrospun from the two polymers show,
Figure 7d-f), average diameters from approximately 600 nm for cyclo-tryptophan-tryptophan embedded into PCL (Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL), to thousands of nanometers (average 1014 nm) for cyclo-L-tryptophan-L-tryptophan embedded into PLLA (Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA),
Figure 7a-c).
3.3. Mechanical properties of electrospun fibers
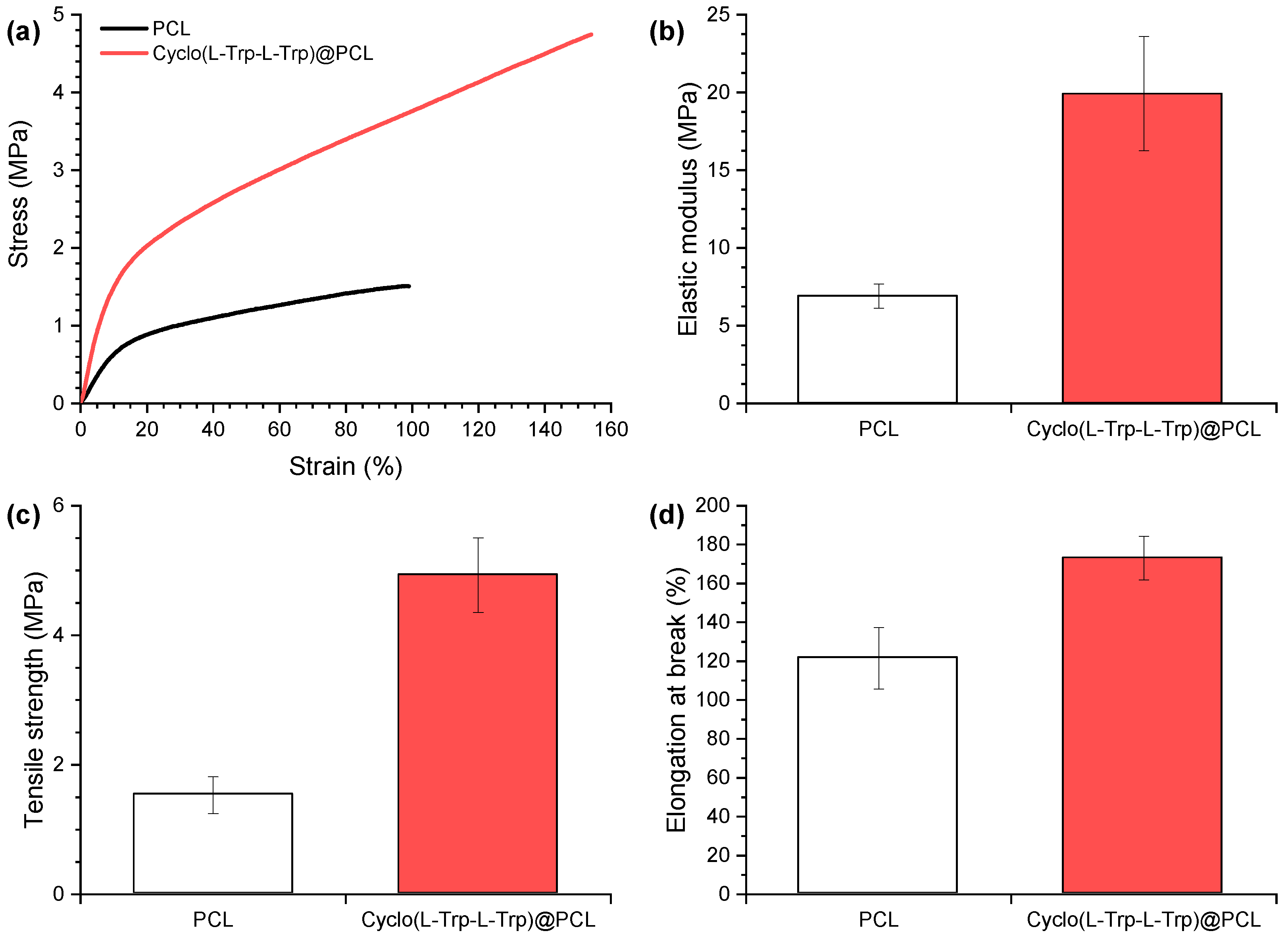
The mechanical properties of the electrospun PCL nanofibers are shown in
Figure 8, as an example. The stress-strain curves reveal a substantial improvement in mechanical performance (elasticity and ductility) of the nanofibers with the introduction of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide inside the polymer matrix. The elastic modulus increased 188%, the tensile strength 221% and the elongation at break 42%. As previously shown in SEM analysis, the nanotube-shape and good dispersion of cyclo-dipeptides explain the obtained mechanical results. The well-distributed Cyclo-dipeptides NS with great interface are beneficial for the transfer of the applied forces between polymer and NS, having a reinforcing effect on the polymeric matrix. The present behaviour is similar to those from electrospun polymer fibers with embedded carbon nanotubes [
24]. This variation is beneficial for the material piezoelectric response, allowing the fiber mat to withstand higher forces and deformations. It was found that the Young's modulus depends significantly on the angle between the stretch direction and the fiber direction. In our case, the direction of stretching is the same as the fiber longitudinal axis orientation. [
25]. In our previous work, we have demonstrated that the incorporation of lead-free organic ferroelectric perovskite N-methyl-N′-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octonium)-ammonium triiodide (MDABCO-NH
4I
3) nanocrystals embedded in polyvinyl chloride microfibers [
26] and
N,N-dimethyl-4-nitroaniline embedded in PLLA microfibers [
27] improve the Young's modulus compared to polymer microfibers alone. In this work we demonstrate that not only the Young modulus increases, as well all the mechanical properties measured for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL are improved.
3.4. Optical Absorption and photoluminescence of dipeptide self-assemblies
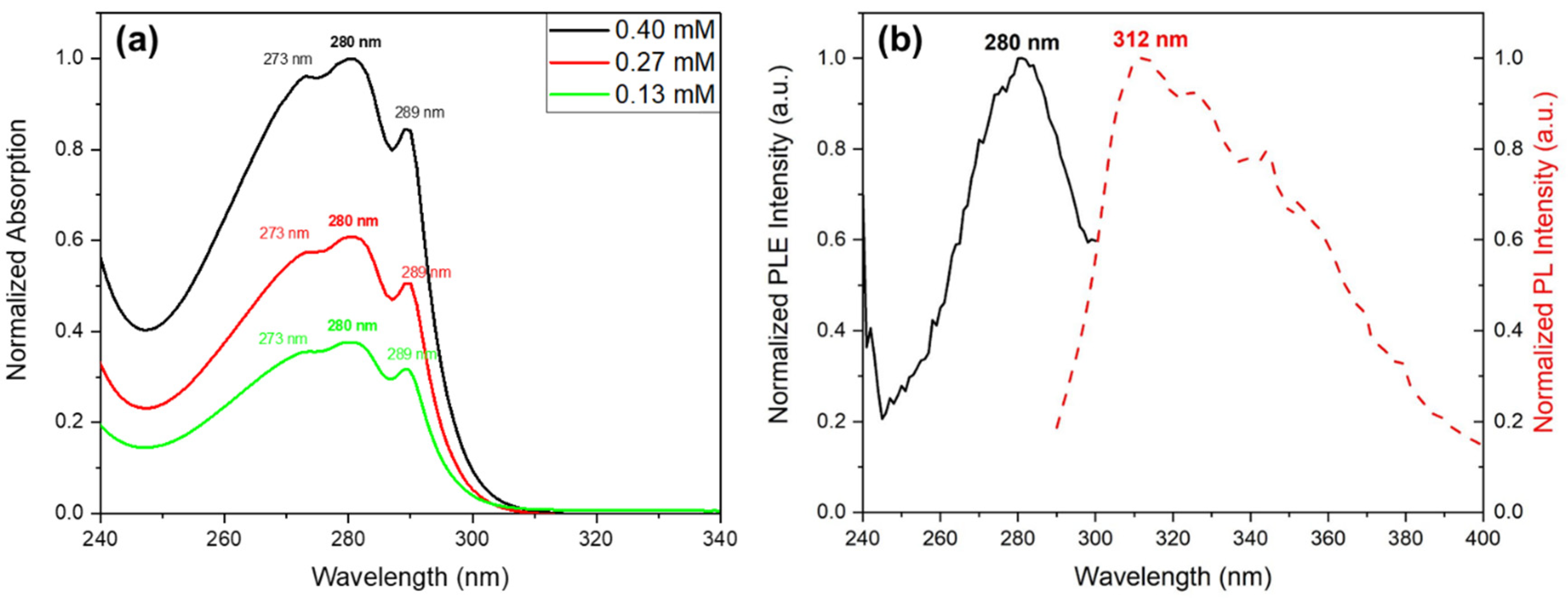
UV-Vis absorption spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanospheres in solution at three different concentrations shows, over a broad maximum at 276 nm, three spike-like absorption peaks at 273 nm, 280 nm and 289 nm (indicating the formation of quantum dot (QD) structures,
Figure 9 a). As expected, the spike-like intensity increases with the increase of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) concentration of in the methanol solution, indicating that the number of QD formed also increases, resulting in a higher contribution to the absorption spectra.
Figure 9 b) shows the excitation spectra from a Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) solution obtained for the maximum of emission at 312 nm reproducing the absorption spectra shown in
Figure 9 a). The observed spike-like peaks are consistent with those reported for cyclo-WW quantum confined structures reported in [
18].
The dimensions of the quantum confined structures may be calculated for the present Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) chiral dipeptide, from the correspondent OA and PLE spectra in
Figure 9, following a theoretical model of quantum dots [
28]. For cyclo dipeptide QD the calculated radius is R≈1.41 nm, see SI. This is in agreement with those reported for QD formed in diphenylalanine (R≈1.65 nm) [
29] and for
cyclo-WW (R≈1.12 nm).
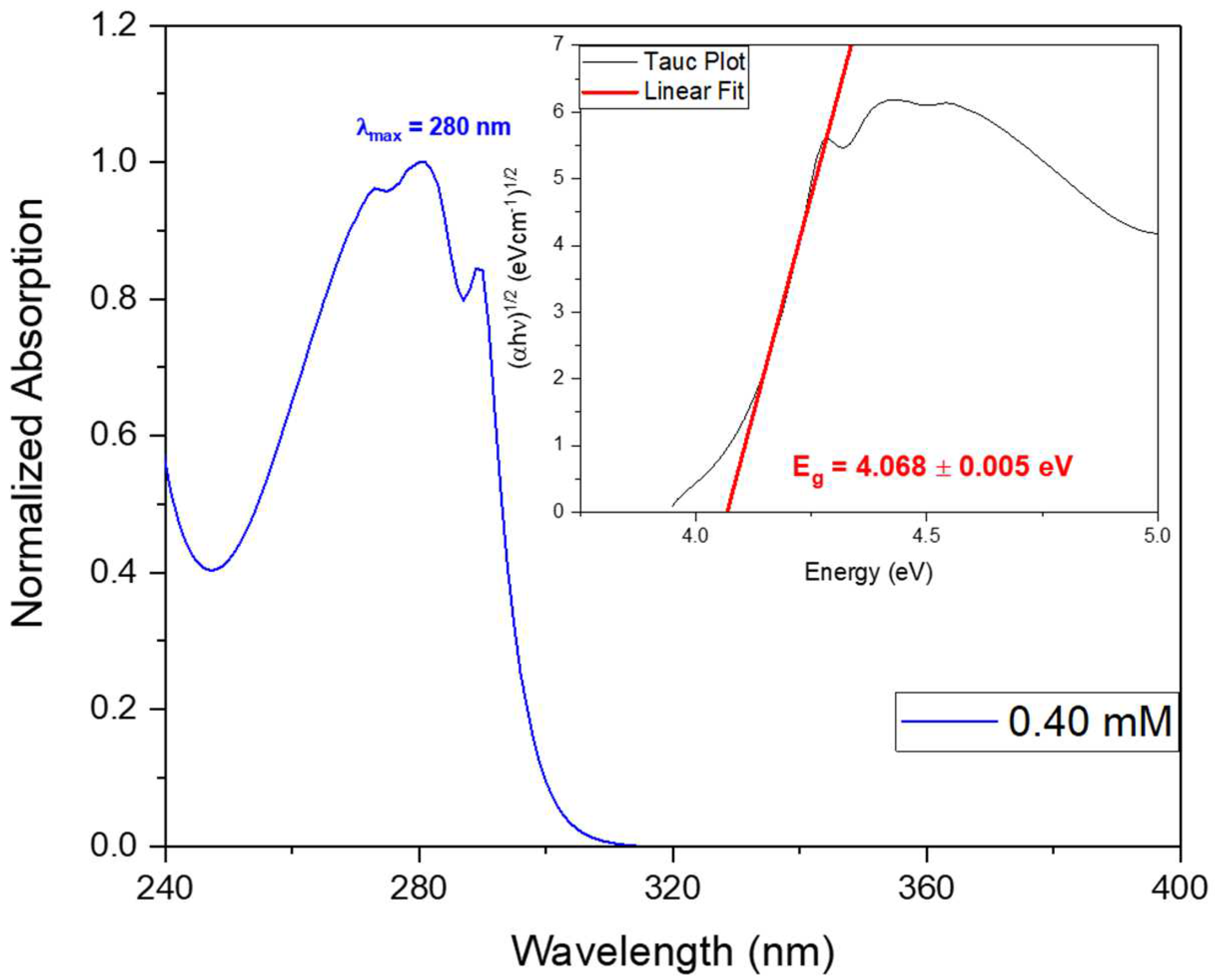
The bandgap energy (Eg) may be calculated from the absorption spectra, through the Tauc plot, as shown in
Figure 10 inset. Calculations indicate an energy of Eg = 4.068 ± 0.005 eV, slighlty higher than that calculated for Cyclo(FW) reported to be 3.1 eV, using Density Functional Theory and reported to be 3.1 eV [
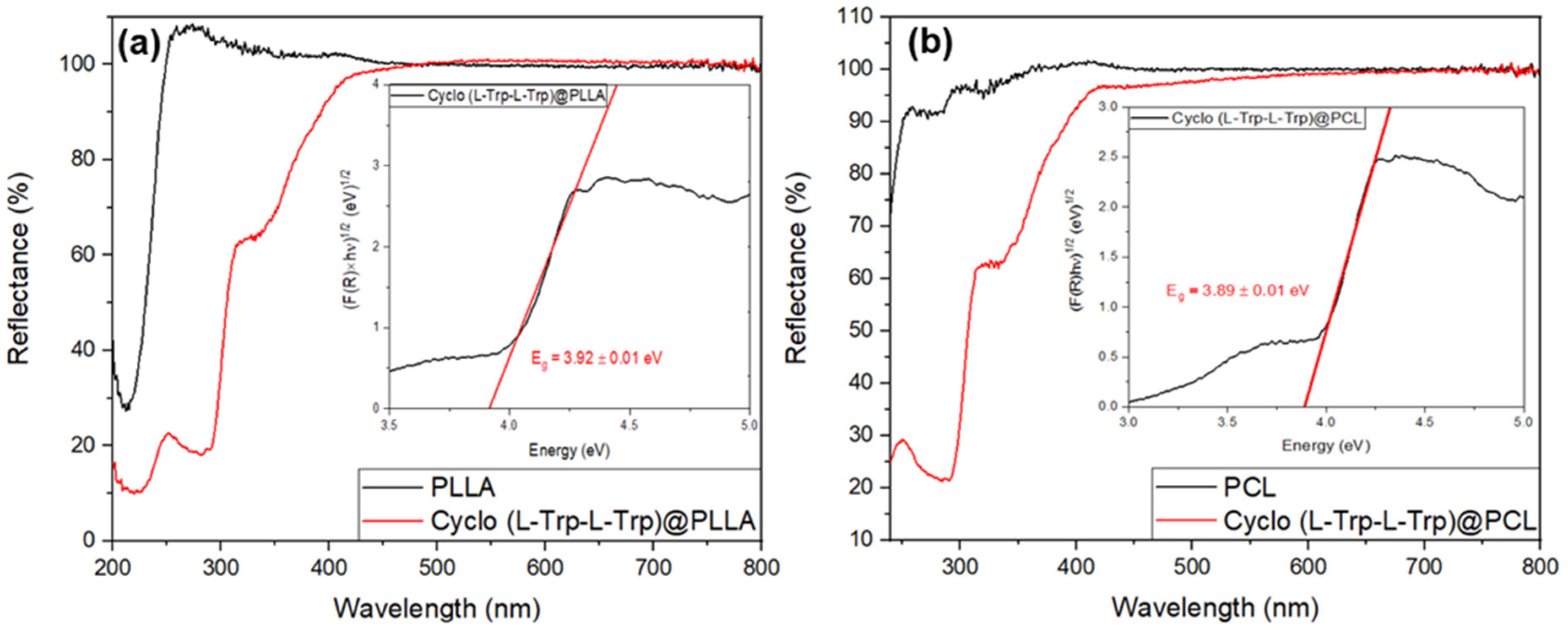
2]. When Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) is embedded into polymer fibers the optical bandgap decreases to aproximately 3.9 eV for both Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers, as shown in
Figure 11 a) and b) insets. Therefore we may say that self-assembled nanostructures of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) are bioorganic wide-bandgap semiconductors [
30,
31].
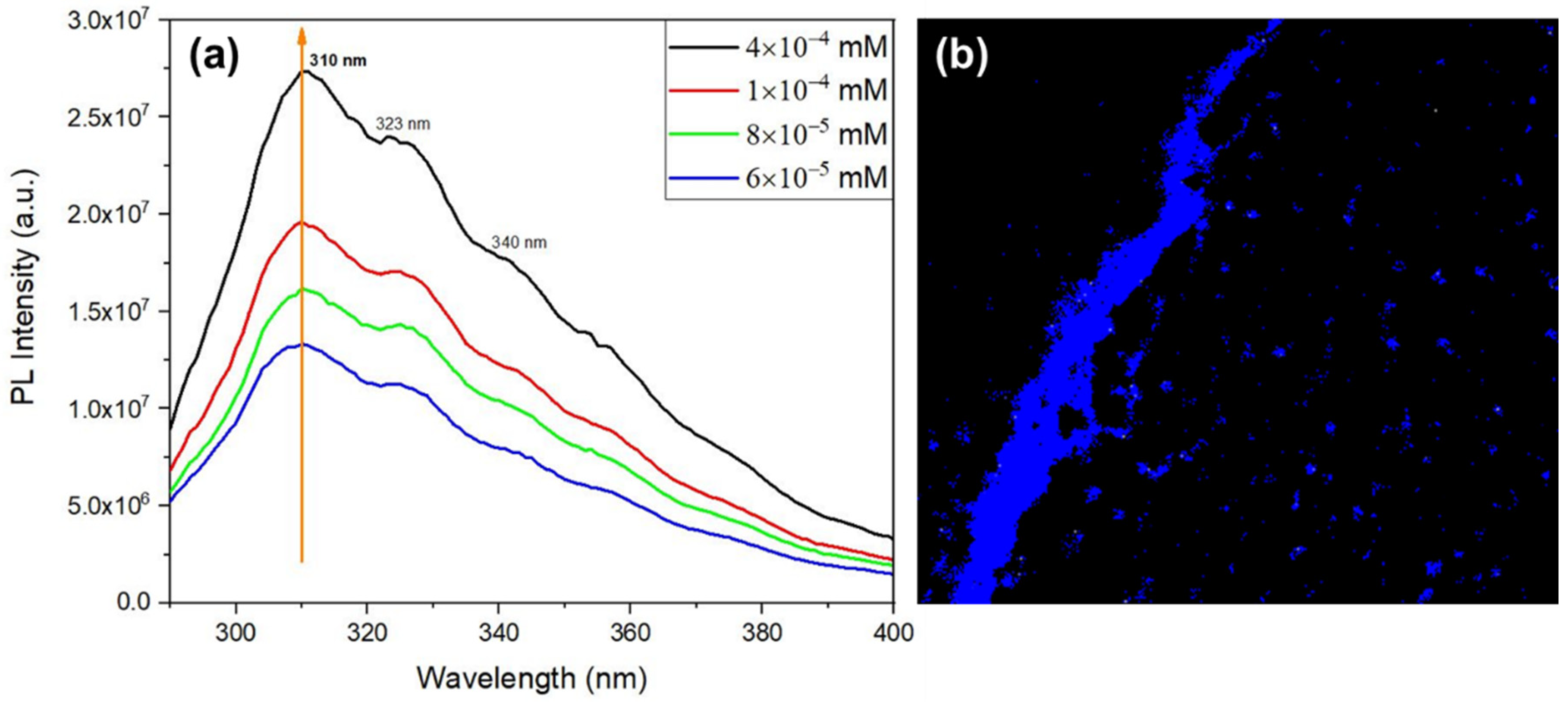
The QD intrinsic photoluminescence is shown in
Figure 12, where the emission spectra was measured for four different dipeptide concentrations, for excitation at 280 nm. Besides a maximum at 310 nm , there are also two less intense broad peaks at around 323 nm, and 340 nm resulting from the QD emitting structures. The intensities also increase with the increasing concentration as a result of an increase of the number of QC structures in the solution. These photoluminescent properties results from the organized QD inside the self-assembled structures. The confocal microscopy image,
Figure 12 b) shows that Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) NS formed from self-assembling of QD resulting from the dipeptide dimerization.
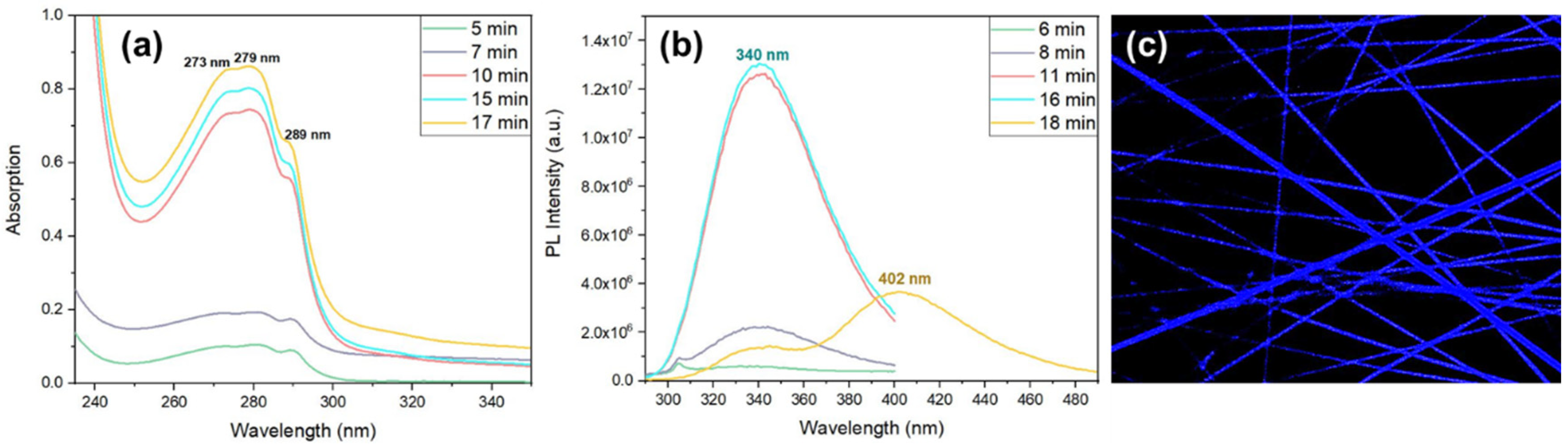
Aiming at understanding the dipeptide self-assembly when embedded into the polymer fiber matrix, OA and PL spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) embedded into PCL fibers was measured after polymer dissolution in DCM/MeOH (4:1 v/v), as a function of time. Similarly to
Figure 9 a), a broad band with maximum at 276 nm is contains three spike-like absorption peaks at 273 nm, 279 nm and 289 nm indicating the formation of QD structures,
Figure 13 a). The number of QD formed also increseas with time resulting in an increasing of intensity over time. PL spectrum (under excitation at 280 nm) displayed by the self-assembled nanostructures formed inside the Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanofibers is presented in
Figure 13 b). Here an emission band with maximum at 340 nm increases in intensity with time, accompained by a 30 nm shift relatively to the PL maximum from the cyclo dipeptide self-assembly in solution ( which is 310 nm). Besides and very interestling, there is also an evolution of PL emission after times over 18 minutes with a broader small PL band grows at expenses of the previous one and shifts to higher wavelenghts, with a maximum at 402 nm with time. This broader band results from crystallization of the dipeptide nanostructures inside the fibers. Fluorescence confocal microscopy,
Figure 13 c), indeed shows blue luminescence from the dipeptide nanostructures crystallized inside the fibers.
3.5. Pyroelectricity in fibers
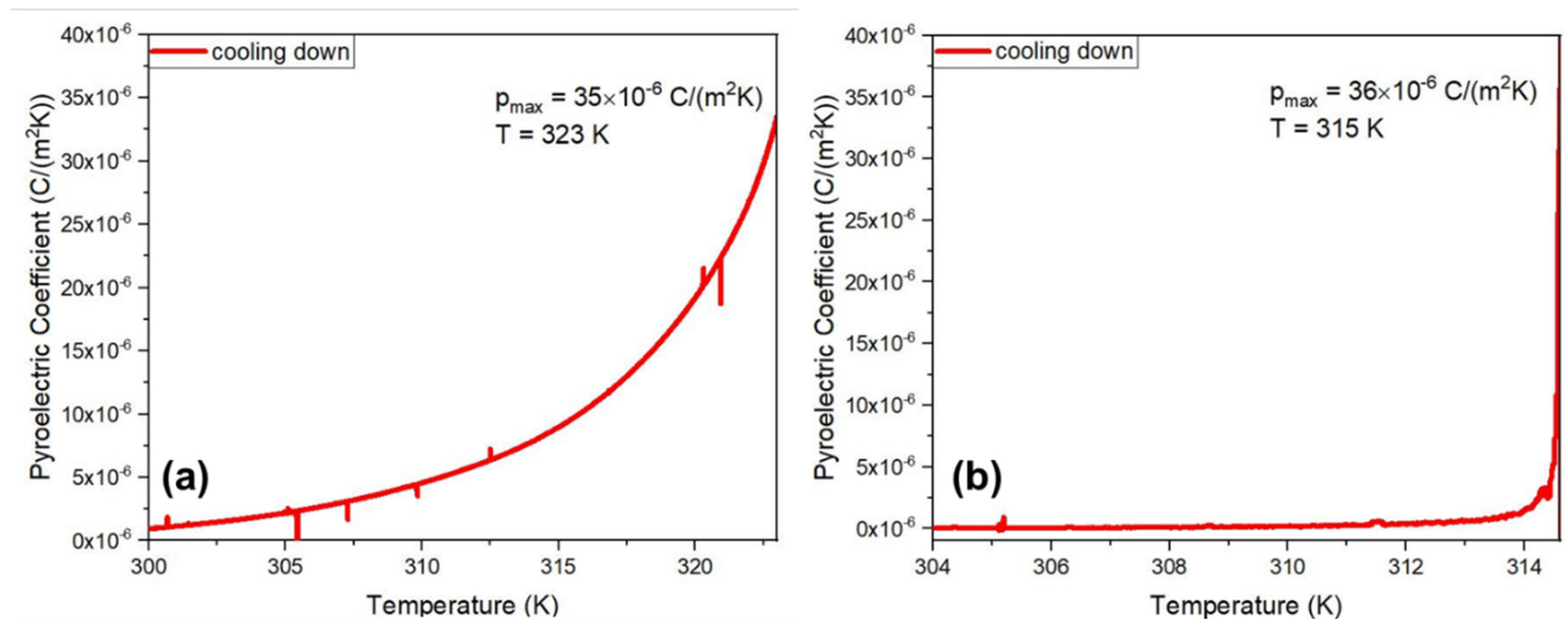
In this work, we report for the first time the measurement of the pyroelectric effect of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide embedded in PLLA and PCL fibers. The measured coefficients, as a function of temperature, are shown in
Figure 14 a) and b) respectively for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA. Although the crystal structure of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) is not known, the existence of a piroelectric effect indicates that the crystal point group is one of the eleven polar crystallographic point groups and therefore the dipeptide might also display ferroelectricity.
The pyroelectric coefficient of the Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA reaches respectively 35×10
-6 Cm
-2k
-1 at 323K and 36×10
-6 Cm
-2k
-1 at 315 K, which is far bellow the melting temperature of the cyclic dipeptide. The pyroelectric coefficient value obtained is four times higher than that reported for electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofibers doped with the hydrogen bonded molecular ferroelectric 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]-octane perrhenate (dabcoHReO
4),which is 8.5×10
-6 Cm
-2k
-1 at 300 K [
32]. Remarkable, the pyroelectric coefficient of polycrystalline dipeptide Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) embedded into polymer fibers is only one order of magnitude smaller than that reported for the state-of-the-art semiorganic ferroelectric triglycine sulfate (TGS) oriented single crystal, reported to be 306×10
-6 Cm
-2k
-1 at the ferroelectric-paraelectric phase transition (322 K) [
33].
Importantly, the pyroelectric coefficient measured on a bundle of diphenylalanine microtubes was reported to be around 2×10
-6 Cm
-2k
-1 [
34], one order of magnitude smaller than that presented in this work for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) embedded into biocompatible electropsun fibers. Our results are significant and indicate that Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA electrospun fiber mats are potential candidates to integrate into pyroelectric sensing [
35]. Moreover, this is the first work reporting the pyroelectric properties of a cyclo-dipeptide.
3.6. Piezoelectric voltage and effective piezoelectric coefficients in fibers
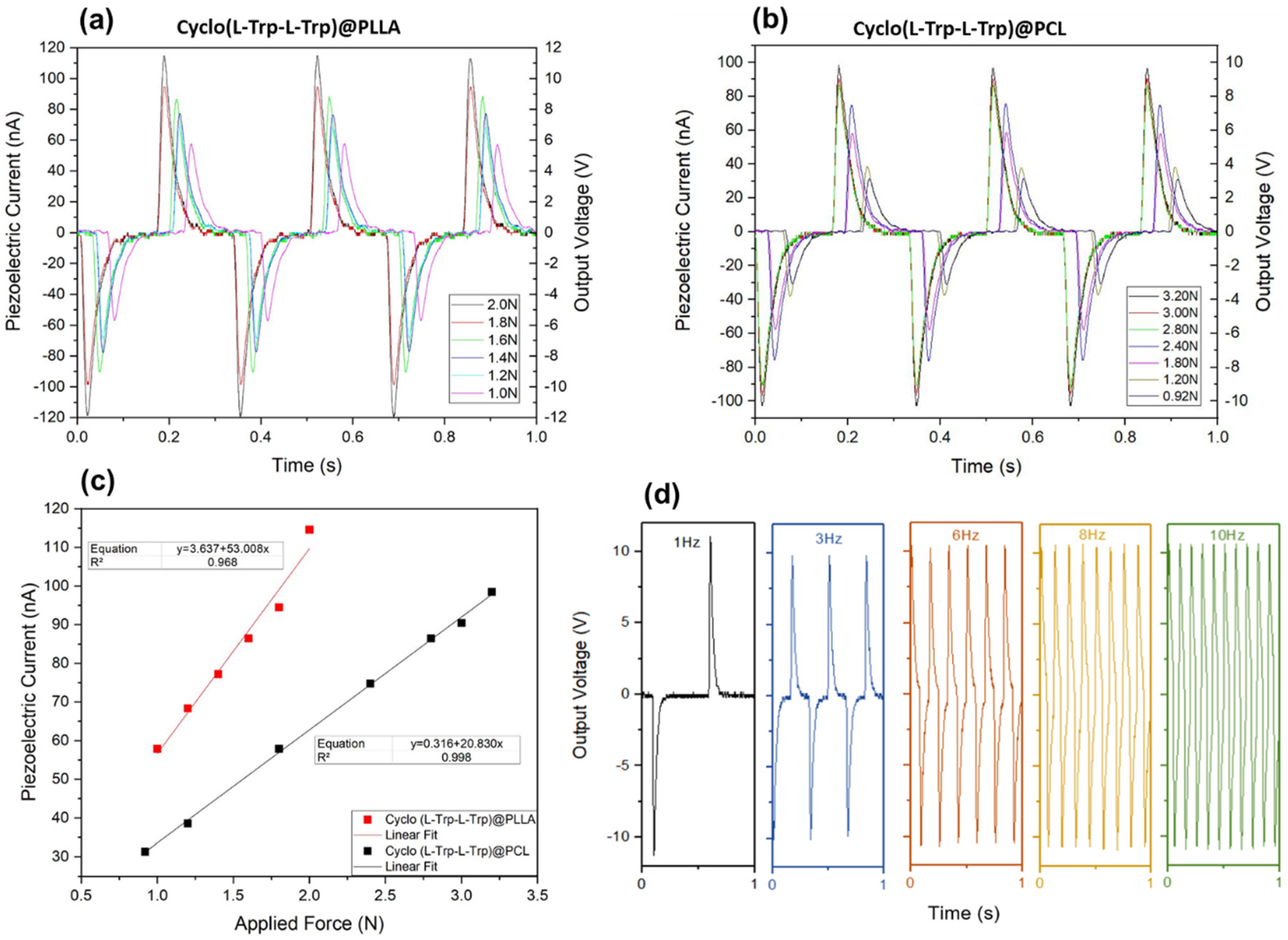
The electrospun Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL nanofiber mats fabricated with the active piezoelectric dipeptide are now demonstarted to behave as piezoelectric energy generators transforming mechanical energy, due to a periodically applied force per unit area, into electric energy. When the fiber mats are compressed or released, there is a reorientation of the molecular dipoles within the crystalline Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide material followed by charges separation of which originates an output voltage and consequently an external electric current outside is generated trough an external circuit. In the present work, we demonstrate that incorporating Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanostructures into electrospun polymer fibers, processed at room temperature without poling, is an easy and straightforward way to fabricate piezoelectric generators using organic biomolecules as active materials.
Figure 15 show that for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL nanofiber mats, the maximum open-circuit voltage and current, measured through a load resistence of 100 MΩ reaches respectively 11.5V and 115 nA and 9.6 V and 96 nA under periodically compressive forces of 2 N (5 kPa )and 3.2 N (8 kPa). PCL is not a piezoelectric polymer and therefore all the piezoelectric voltage generated by Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers is due to the dipeptide. PLLA is itself a piezoelectric polymer having a small contribution to the piezoelectric response in the case of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA fibers.
Figure 15 c) shows that the output voltage is proprotional to the applied forces confirming thus the linear piezoelectric properties of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp). We can calculate the piezoelectric charge, equation Q=∫Idt (C), generated by the piezoelectric mats upon compression and using the maximum intensity achieved from
Figure 15 a) and b) during a 10
-3 s material response time. For Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers, the charges generated are 115 pC and 96 pC when the applied force are respectively 3.2 N and 2.0 N. Therefore, the correspondent effective or average piezoelectric coefficients, defined as d
eff = Q/F (pCN
-1), are 57 pCN
-1 and 30 pCN
-1, as indicated in
Table 1. These coefficients are higher than those predicted for dipeptides Cyclo(GW) oriented single crystals (on average 5.6 pCN
-1) and measured in biological materials such as viruses (8 pCN
-1) and rat tail collagen (12 pCN
-1 [
3]). Futhermore, they are also comparable to those reported for lead-free organic ferroelectric perovskite N-methyl-N′-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octonium)-ammonium triiodide (MDABCO-NH
4I
3) nanocrystals embedded respectively in polyvinyl chloride (MDABCO-NH
4I
3@PVC), which is 64 pCN
-1. Another quantity that is interesting to calculate is the peak power density given by
(μWcm
-2), where R=100 MΩ is the load resistance and A is the electrodes are, delivered by the nanofiber mats. These values are 0.18 μWcm
-2 and 0.13 μWcm
-2 respectively for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers.
Finally, and very importantly to know, is the piezoelectric voltage coefficient g
eff = d
eff/(ε´ε
0) VmN
-1, a figure of merit which quantifies the materials adequacy as a piezoelectric sensor. Assuming a dielectric constant of ε´~ 10 at 10 Hz (common to dipeptides in
Table 1) we obtain g
eff = 4.7 VmN
-1 and g
eff = 2.6 VmN
-1 for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mats, respectively. These values are within the same order of magnitude of those obtained for crystal powder Boc-Dip-Dip nanogenerator and higher than that for polycrystalline Cyclo(GW) nanogenerator,
Table 1. One should notice, that remarkably, our results were measured using compressive forces per unit area two orders of magnitude smaller than those which is for pratical applications an important parameter to consider when using organic crystals therefore avoinding their damage with time. In fact,
Figure S3 shows for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA fiber mat, as an example, its unchangable continous piezoelectric output voltage over a long period of time. We may conclude that cyclic dipeptide Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanocrystals embedded into biopolymers and fabricated by the electrospinning technique, form easily handled nanomaterials systems capable of performing as piezoelectric energy nanogenerators with relevant piezoelectric voltage coefficients
. 4. Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrate that chiral cyclo(L-Tryptophan- L-Tryptophan) dipeptide when embedded into PLLA and PCL biopolymer electrospun fibers, namely Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL, form very flexible mats with improved mechanical stability. The dipeptide self-assemblies both in solution and when embedded into the polymer matrix as nanospheres displaying quantum confinement, having a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 283 nm. The nanospheres show blue luminescence in the solid state. The dimensions of the quantum-confined structures may be calculated from the corresponding optical spectra, which indicate that the cyclo-dipeptide quantum dots have a radius approximately equal to 1.41 nm, in agreement with the values reported for dipeptide diphenylalanine nanotubes (1.65 nm) and centrosymmetric cyclo-tryptophan-tryptophan needle-shaped crystals (1.12 nm).
The bandgap energy of cyclo(L-Tryptophan- L-Tryptophan) nanospheres both, free and when embedded into the fibers, are around 4 eV, close to that calculated for cyclo(L-phenylalanine-tryptophan) which is 3.1 eV. Therefore, self-assembled nanostructures of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) are bioorganic wide-bandgap semiconductors.
The nano/microfiber Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL mats were tested as potential energy harvesting systems both as piezoelectric and pyroelectric active hybrid functional materials. Under periodical applied force of only several Newtons, the average piezoelectric coefficients obtained are respectively 57 pCN-1 and 30 pCN-1. These coefficients are comparable to those reported for lead-free organic ferroelectric perovskite N-methyl-N′-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octonium)-ammonium triiodide (MDABCO-NH4I3) nanocrystals embedded respectively in polyvinyl chloride (MDABCO-NH4I3@PVC), which is 64 pCN-1. Moreover, the piezoelectric voltage coefficient, a figure of merit which quantifies the materials adequacy as a piezoelectric sensor is geff = 4.7 VmN-1 and geff = 2.6 VmN-1 for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mats, respectively. These values are higher than that obtained for polycrystalline Cyclo(GW) nanogenerator of 1.6 VmN-1.
Finally, the pyroelectric coefficient of the fiber mats reaches respectively 35×10-6 Cm-2k-1 at and 36×10-6 Cm-2k-1, for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA far below the melting temperature of the cyclo-dipeptide. Remarkably, these values are one order of magnitude larger than that reported for a bundle of diphenylalanine microtubes which was 2×10-6 Cm-2k-1. The present work reports for the first time the pyroelectric properties of a cy-clo-dipeptide.
Chiral cyclo(L-Tryptophan- L-Tryptophan) dipeptide nanocrystals, when embedded into biopolymers using the electrospinning technique, form easily handled nanomaterials systems capable of incorporation into piezoelectric energy harvesting and pyroelectric temperature sensing devices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Figure S1: Optical microscopy; Figure S2: UV–vis reflectance; Figure S3: Output voltage as a function of time from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA electrospun nanofibers; Figure S4: Piezoelectric current versus applied force for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and PLLA neat fibers, with the respective linear fits; Figure S5: Output voltage for low frequencies up to 10 Hz and output voltage as a function of time, from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL electrospun nanofibers. Reference [37] is cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.F.B. and E.d.M.G.; investigation, D.S., R.M.F.B., A.H., B.A., P.V.R., A.R.T., A.M. and M.B.; writing-original draft preparation, R.M.F.B. and E.d.M.G.; writing-review and editing, R.M.F.B., E.d.M.G., B.A., M.B.; supervision, R.M.F.B. and E.d.M.G.; project administration, R.M.F.B. and E.d.M.G.; funding acquisition, R.M.F.B. and E.d.M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia through FEDER (European Fund for Regional Development)-COMPETE-QREN-EU (ref. UID/FIS/04650/2013 and UID/FIS/04650/2019) and E-Field - "Electric-Field Engineered Lattice Distortions (E-FiELD) for optoelectronic devices", ref. PTDC/NAN-MAT/0098/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
This study did not involve humans or animals.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge national funds (OE), through FCT − Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., in the scope of the framework contract foreseen in the numbers 4, 5, and 6 of the article 23, of the Decree-Law 57/2016, of August 29, changed by Law 57/2017, of July 19.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tao, K.; Tang, Y.; Rencus-Lazar, S.; Yao, Y.; Xue, B.; Gilead, S.; Wei, G.; Gazit, E. Bioinspired Supramolecular Packing Enables High Thermo-Sustainability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19037–19041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Xue, B.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Makam, P.; Si, M.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; et al. Stable and optoelectronic dipeptide assemblies for power harvesting. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Hu, W.; Xue, B.; Chovan, D.; Brown, N.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Maraba, O.; Cao, Y.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Thompson, D.; et al. Bioinspired Stable and Photoluminescent Assemblies for Power Generation. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, R.M.F.; de Matos Gomes, E.; Raposo, M.M.M.; Costa, S.P.G.; Lopes, P.E.; Almeida, B.; Belsley, M.S. Self-assembly of dipeptide Boc-diphenylalanine nanotubes inside electrospun polymeric fibers with strong piezoelectric response. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4339–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xiong, S.; Wu, X.; Chu, P.K. Effects of Water Molecules on Photoluminescence from Hierarchical Peptide Nanotubes and Water Probing Capability. Small 2011, 7, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler-Abramovich, L.; Gazit, E. Controlled patterning of peptide nanotubes and nanospheres using inkjet printing technology. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Y.; Dai, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Controlled Rod Nanostructured Assembly of Diphenylalanine and Their Optical Waveguide Properties. Acs Nano 2015, 9, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, R.M.F.; Lopes, P.E.; Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Cerca, N.; Belsley, M.S.; de Matos Gomes, E. Self-assembly of Boc-p-nitro-l-phenylalanyl-p-nitro-l-phenylalanine and Boc-l-phenylalanyl-l-tyrosine in solution and into piezoelectric electrospun fibers. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotsi, D.; Grisanti, L.; Mahou, P.; Gebauer, R.; Kaminski, C.F.; Hassanali, A.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S. Proton Transfer and Structure-Specific Fluorescence in Hydrogen Bond-Rich Protein Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3046–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, M.; Zakrassov, A.; Lerner-Yardeni, J.; Ashkenasy, N. Charge transport in vertically aligned, self-assembled peptide nanotube junctions. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdim, B.; Pachter, R.; Naik, R.R. Self-assembled peptide nanotubes as electronic materials: An evaluation from first-principles calculations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 183707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorna, A.; Stopczyk, K.; Skorupska, E.; Luberda-Durnas, K.; Oszajca, M.; Lasocha, W.; Górecki, M.; Frelek, J.; Potrzebowski, M.J. Cyclic Dipeptides as Building Units of Nano- and Microdevices: Synthesis, Properties, and Structural Studies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 5138–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilead, S.; Gazit, E. Self-organization of short peptide fragments: From amyloid fibrils to nanoscale supramolecular assemblies. Supramol. Chem. 2005, 17, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Früh, J.; Möhwald, H. Uniaxially Oriented Peptide Crystals for Active Optical Waveguiding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11186–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Xing, R.; Yan, X. Cyclic dipeptides: Biological activities and self-assembled materials. Pept. Sci. 2021, 113, e24202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, K.; Ji, W.; Makam, P.; Rencus-Lazar, S.; Gazit, E. Self-Assembly of Cyclic Dipeptides: Platforms for Functional Materials. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchineella, S.; Govindaraju, T. Molecular Self-Assembly of Cyclic Dipeptide Derivatives and Their Applications. Chempluschem 2017, 82, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Fan, Z.; Sun, L.; Makam, P.; Tian, Z.; Ruegsegger, M.; Shaham-Niv, S.; Hansford, D.; Aizen, R.; Pan, Z.; et al. Quantum confined peptide assemblies with tunable visible to near-infrared spectral range. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubelka, P. New Contributions to the Optics of Intensely Light-Scattering Materials. Part I. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuła, P.; Pacia, M.; Macyk, W. How To Correctly Determine the Band Gap Energy of Modified Semiconductor Photocatalysts Based on UV–Vis Spectra. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6814–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, S.P.; Lim, J.; Ngang, H.P.; Ooi, B.S.; Ahmad, A.L. Role of particle-particle interaction towards effective interpretation of Z-average and particle size distributions from dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno 2018, 18, 6957–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Jacobs, C. Buparvaquone mucoadhesive nanosuspension: preparation, optimisation and long-term stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 237, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems-a review (Part 2). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.-Y.; Zhou, X.-P.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Mai, Y.-W. Electrospun aligned PLLA/PCL/functionalised multiwalled carbon nanotube composite fibrous membranes and their bio/mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, M.; Ribeiro, S.; Ribeiro, C.; Francesko, A.; Maceiras, A.; Vilas, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Relation between fiber orientation and mechanical properties of nano-engineered poly (vinylidene fluoride) electrospun composite fiber mats. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2018, 139, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, R.M.F.; Moreira, G.; Silva, B.; Oliveira, J.; Almeida, B.; Castro, C.; Rodrigues, P.V.; Machado, A.; Belsley, M.; de Matos Gomes, E. Lead-Free MDABCO-NH4I3 Perovskite Crystals Embedded in Electrospun Nanofibers. Materials 2022, 15, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, R.M.F.; Silva, B.; Oliveira, J.; Isfahani, V.B.; Almeida, B.; Pereira, M.R.; Cerca, N.; Castro, C.; Rodrigues, P.V.; Machado, A.; et al. High Piezoelectric Output Voltage from Blue Fluorescent N,N-Dimethyl-4-nitroaniline Nano Crystals in Poly-L-Lactic Acid Electrospun Fibers. Materials 2022, 15, 7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amdursky, N.; Molotskii, M.; Gazit, E.; Rosenman, G. Self-assembled bioinspired quantum dots: Optical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 261907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdursky, N.; Molotskii, M.; Gazit, E.; Rosenman, G. Elementary Building Blocks of Self-Assembled Peptide Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15632–15636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, R.; Sahoo, S.R.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, S. Anisotropic charge transport and optoelectronic properties of wide band gap organic semiconductors based on biphenyl derivatives: A computational study. Synth. Met. 2020, 267, 116474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Popescu, F.; Rao, M.R.; Meng, H.; Perepichka, D.F. A Wide Band Gap Naphthalene Semiconductor for Thin-Film Transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1600556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, D.; Gomes, E.D.; Almeida, B.; Kholkin, A.L.; Zelenovskiy, P.; Neradovskiy, M.; Shur, V.Y. Energy harvesting from nanofibers of hybrid organic ferroelectric dabcoHReO(4). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane-Motlagh, R.; Kroener, M.; Goldschmidtboeing, F.; Danilewsky, A.N.; Woias, P. A dynamic method for the measurement of pyroelectric properties of materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 084004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esin, A. Pyroelectric effect and polarization instability in self-assembled diphenylalanine microtubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, A.; Pandini, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Zaccheroni, N.; Pierini, F.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C. Thermoactive Smart Electrospun Nanofibers. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2022, 43, 2100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavalingappa, V.; Bera, S.; Xue, B.; O’Donnell, J.; Guerin, S.; Cazade, P.-A.; Yuan, H.; Haq, E.u.; Silien, C.; Tao, K.; et al. Diphenylalanine-Derivative Peptide Assemblies with Increased Aromaticity Exhibit Metal-like Rigidity and High Piezoelectricity. Acs Nano 2020, 14, 7025–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of the chiral dipeptide Cyclo(L-Tryptophan-L- Tryptophan).
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of the chiral dipeptide Cyclo(L-Tryptophan-L- Tryptophan).
Figure 2.
Schematic flow chart for the preparation of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL electrospun nanofibers.
Figure 2.
Schematic flow chart for the preparation of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL electrospun nanofibers.
Figure 3.
Schematic of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA piezoelectric nanogenerator. Electrospun nanofiber mat sandwiched between two copper electrodes. .
Figure 3.
Schematic of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA piezoelectric nanogenerator. Electrospun nanofiber mat sandwiched between two copper electrodes. .
Figure 4.
SEM images at magnification levels of 15,000x (a) and 50,000x (b) and the diameter distribution (c) of the nanospheres (NS) of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp), self-assembled in methanol solution. The logarithmic normal distribution is indicated by the red curve.
Figure 4.
SEM images at magnification levels of 15,000x (a) and 50,000x (b) and the diameter distribution (c) of the nanospheres (NS) of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp), self-assembled in methanol solution. The logarithmic normal distribution is indicated by the red curve.
Figure 5.
Intensity weighted particle size distributions for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanostructures measured by Dynamic Light Scattering.
Figure 5.
Intensity weighted particle size distributions for Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) nanostructures measured by Dynamic Light Scattering.
Figure 6.
Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA electrospun fiber mat (a) and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mat folded around a cylindrical rod, demonstrating the flexibility of the fibers (b).
Figure 6.
Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA electrospun fiber mat (a) and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mat folded around a cylindrical rod, demonstrating the flexibility of the fibers (b).
Figure 7.
SEM images at magnification levels of 5,000x and 100,000x and the respective fiber diameter distribution histograms for PLLA (a,b,c) and PCL (d,e,f) with embedded Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) peptide. The red curves indicate logarithmic normal distributions using the mean, maximum and standard deviations of each set of fibers.
Figure 7.
SEM images at magnification levels of 5,000x and 100,000x and the respective fiber diameter distribution histograms for PLLA (a,b,c) and PCL (d,e,f) with embedded Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) peptide. The red curves indicate logarithmic normal distributions using the mean, maximum and standard deviations of each set of fibers.
Figure 8.
Mechanical properties of electrospun fibers of PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL: (a) representative tensile curves, (b) Elastic modulus, (c) Tensile strength and (d) Elongation at break.
Figure 8.
Mechanical properties of electrospun fibers of PCL and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL: (a) representative tensile curves, (b) Elastic modulus, (c) Tensile strength and (d) Elongation at break.
Figure 9.
(a) Normalized UV-vis absorption spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide in MeOH, at different solution concentrations; (b) Normalized excitation and emission spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) in MeOH. The emission wavelength is 312 nm.
Figure 9.
(a) Normalized UV-vis absorption spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide in MeOH, at different solution concentrations; (b) Normalized excitation and emission spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) in MeOH. The emission wavelength is 312 nm.
Figure 10.
Normalized UV-vis absorption spectrum of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide at the concentration of 0.40 mM. The inset shows the bandgap energy calculated from Tauc plot.
Figure 10.
Normalized UV-vis absorption spectrum of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) dipeptide at the concentration of 0.40 mM. The inset shows the bandgap energy calculated from Tauc plot.
Figure 11.
Reflectance spectra of (a) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and (b) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers. The inset shows the bandgap energy calculated from Kubelka-Munk function with the linear fit in red.
Figure 11.
Reflectance spectra of (a) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and (b) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fibers. The inset shows the bandgap energy calculated from Kubelka-Munk function with the linear fit in red.
Figure 12.
(a) Photoluminescent emission spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) in MeOH at several concentrations. The excitation wavelength is 280 nm. (b) Confocal microscopy image of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) crystallized nanospheres, under laser excitation at 405 nm.
Figure 12.
(a) Photoluminescent emission spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) in MeOH at several concentrations. The excitation wavelength is 280 nm. (b) Confocal microscopy image of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) crystallized nanospheres, under laser excitation at 405 nm.
Figure 13.
(a) Optical Absorption and (b) Photoluminescence spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) embedded into PCL fibers after polymer fiber dissolution in DCM/MeOH (4:1 v/v), as a function of time; The excitation wavelength is 280 nm. (c) Confocal microscopy image of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mats, under laser excitation at 405 nm.
Figure 13.
(a) Optical Absorption and (b) Photoluminescence spectra of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) embedded into PCL fibers after polymer fiber dissolution in DCM/MeOH (4:1 v/v), as a function of time; The excitation wavelength is 280 nm. (c) Confocal microscopy image of Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL fiber mats, under laser excitation at 405 nm.
Figure 14.
Pyroelectric coefficient as function of temperature (measured on cooling) of (a) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and (b) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA.
Figure 14.
Pyroelectric coefficient as function of temperature (measured on cooling) of (a) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL and (b) Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA.
Figure 15.
(a), (b) Piezoelectric current and output voltage as a function of time; (c) Piezoelectric current as a function of different applied periodical forces from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL; (d) Output voltage for low frequencies up to 10 Hz from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) incorporated into electrospun PLLA polymer fibers.
Figure 15.
(a), (b) Piezoelectric current and output voltage as a function of time; (c) Piezoelectric current as a function of different applied periodical forces from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA and Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL; (d) Output voltage for low frequencies up to 10 Hz from Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp) incorporated into electrospun PLLA polymer fibers.
Table 1.
Piezoelectric nanogenerator parameters for some dipeptides.
Table 1.
Piezoelectric nanogenerator parameters for some dipeptides.
| Nanogenerator |
Force/area
(N/m2) |
Vout
(V) |
deff
(pC/N) |
geff
(Vm/N) |
Power density
(μWcm-2) |
Ref. |
Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PLLA
(fiber mat) |
3 x103
|
11.5 |
57 |
4.7 |
0.18 |
This work |
Cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp)@PCL
(fiber mat) |
5 x103
|
9.6 |
30 |
2.6 |
0.13 |
This work |
Cyclo(GW)
(crystal powder) |
7 x105
|
1.2 |
5.6§
|
1.6#
|
0.002 |
[3] |
Cyclo(FW)
(crystal powder) |
6 x105
|
1.4 |
16* |
1.3** |
0.003 |
[2] |
Boc-PhePhe@PLLA
(fiber mat) |
4 x103
|
30 |
8.4 |
0.3 |
2.3 |
[8] |
Boc-PheTyr@PLLA
(fiber mat) |
4 x103
|
24 |
7 |
0.3 |
1.0 |
[8] |
| Boc-pNPhepNPhe@PLLA(fiber mat) |
4 x103
|
58 |
16 |
0.6 |
9.0 |
[8] |
Boc-DipDip
(crystal powder) |
4 x104
|
1 |
73 |
2.8 |
__ |
[36] |
MDABCO-NH4I3@PVC
(fiber mat) |
11 x103
|
16.5 |
175 |
3.6 |
0.20 |
[26] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).