Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
01 February 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
- Should Africa’s science and development not be better served by the creation of regional research and innovation systems, that as an example, is aiming to create an African Research Union?
- How do the high dependencies on non-African collaboration affect the continent’s research evolution and priorities?
- Is African research individualism and inspiration stifled by excessive collaboration?
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
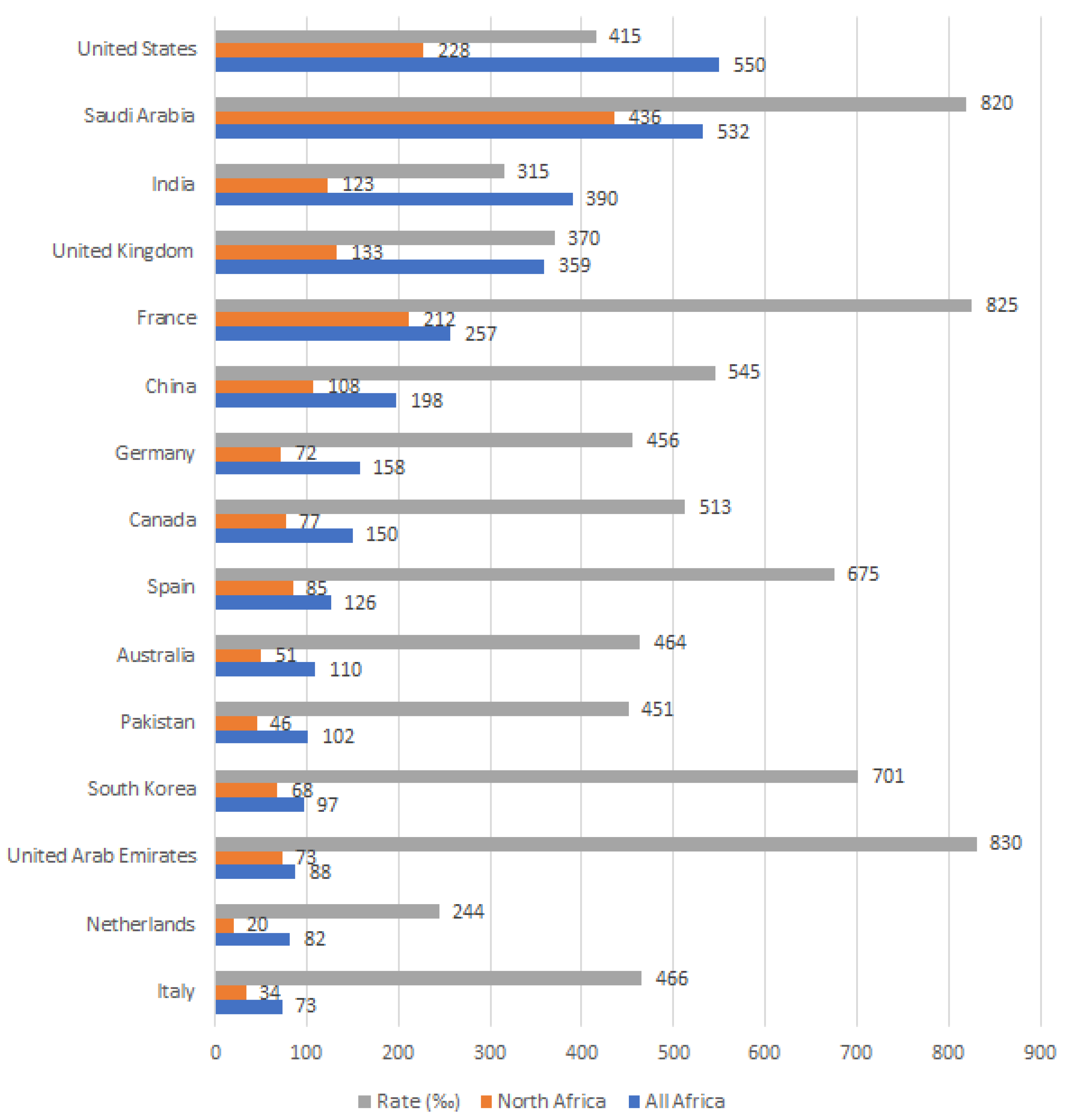
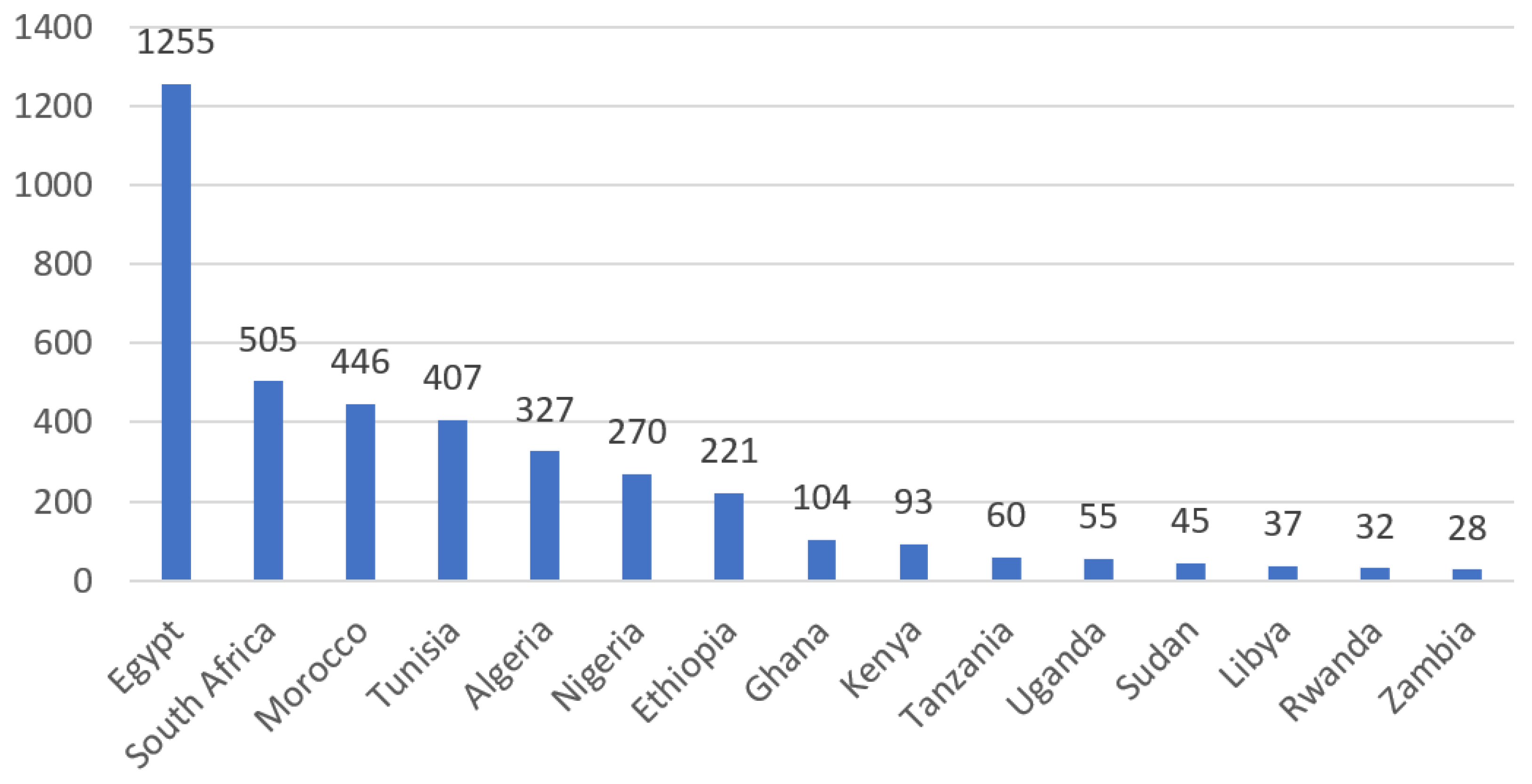
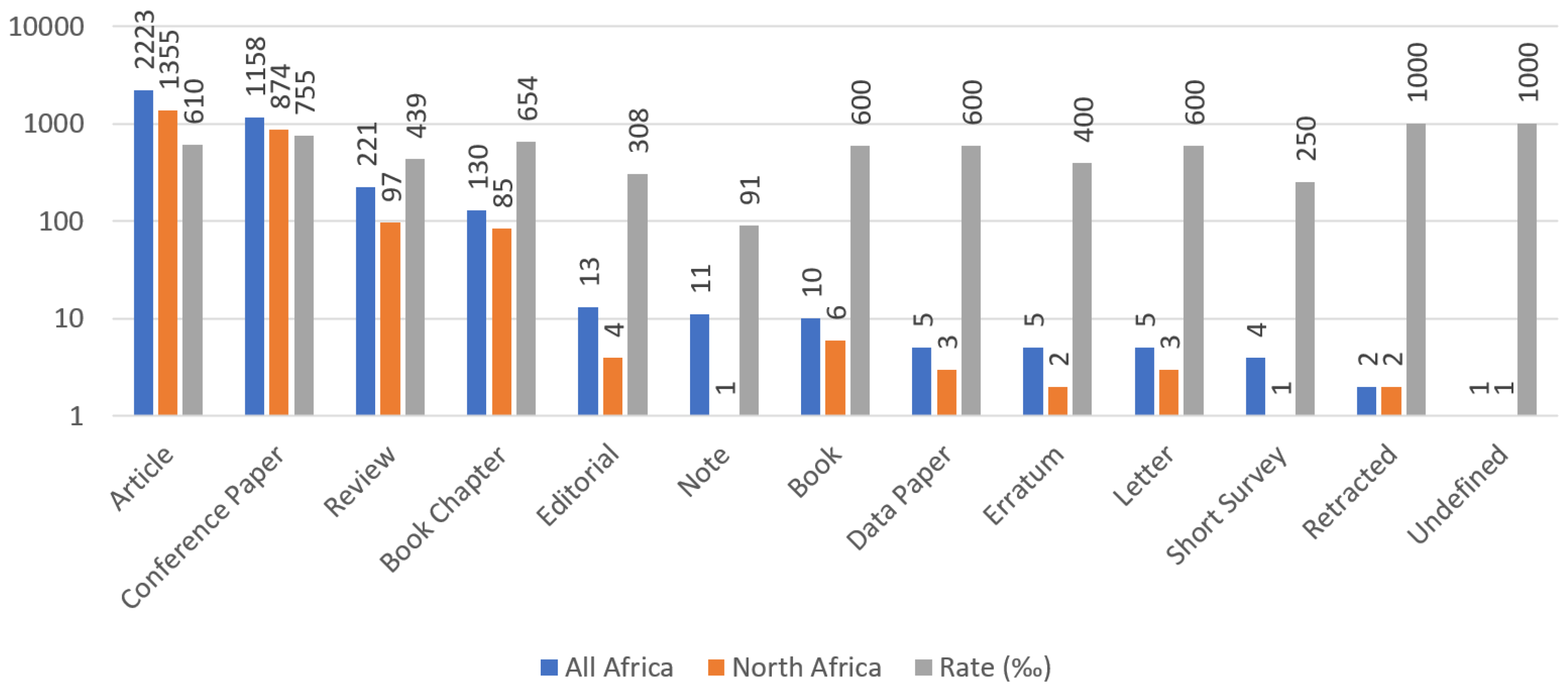
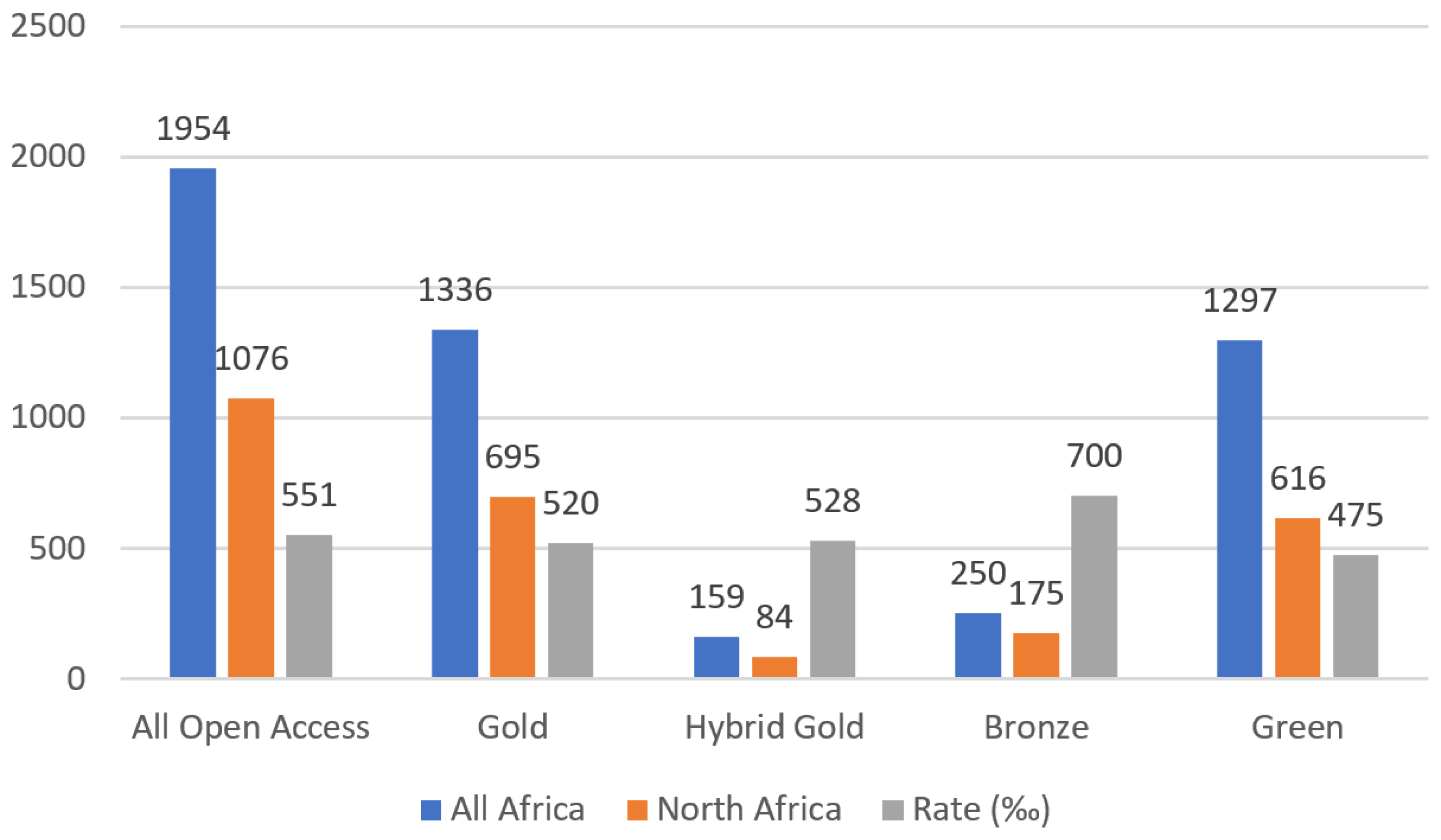
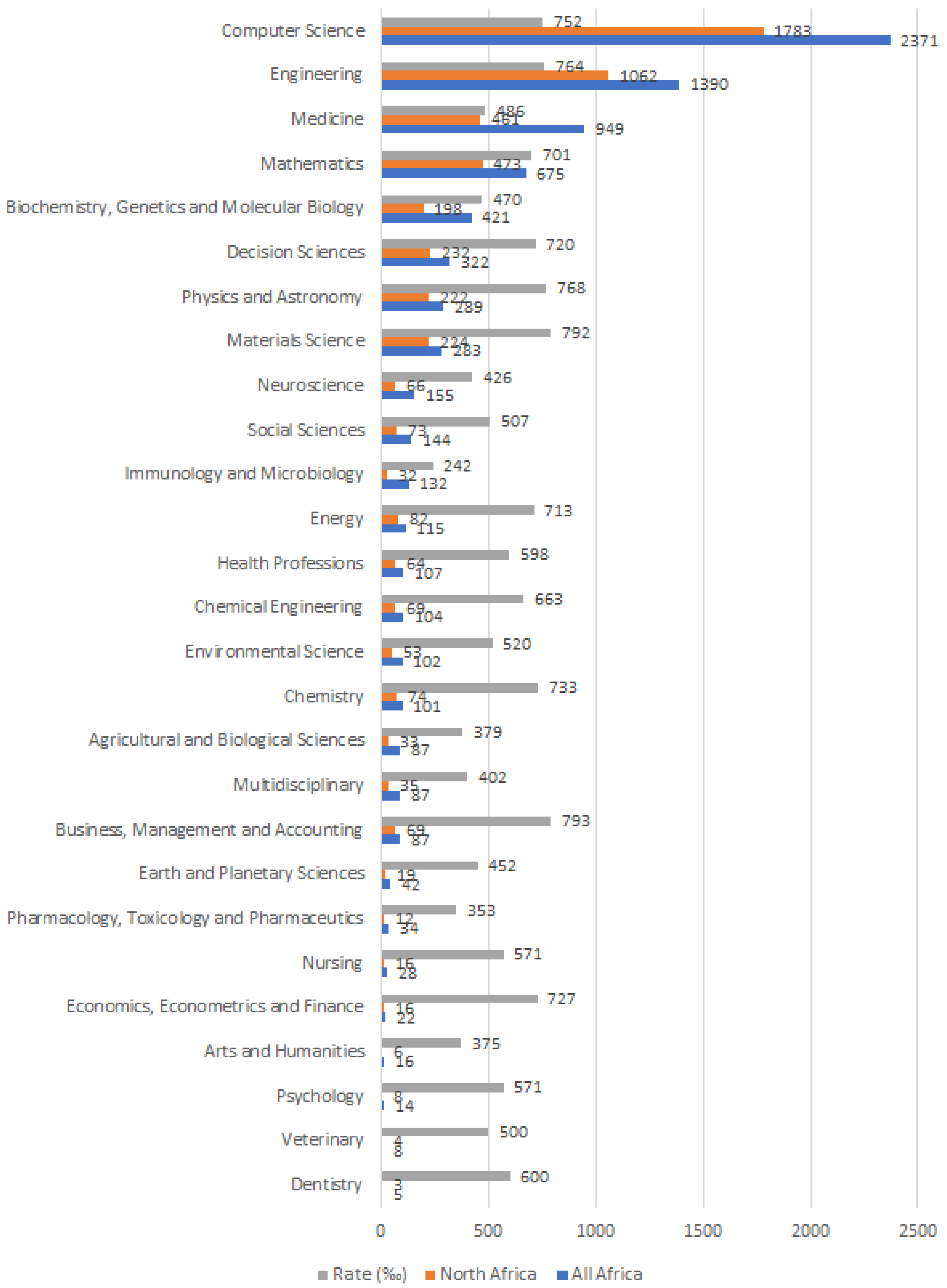
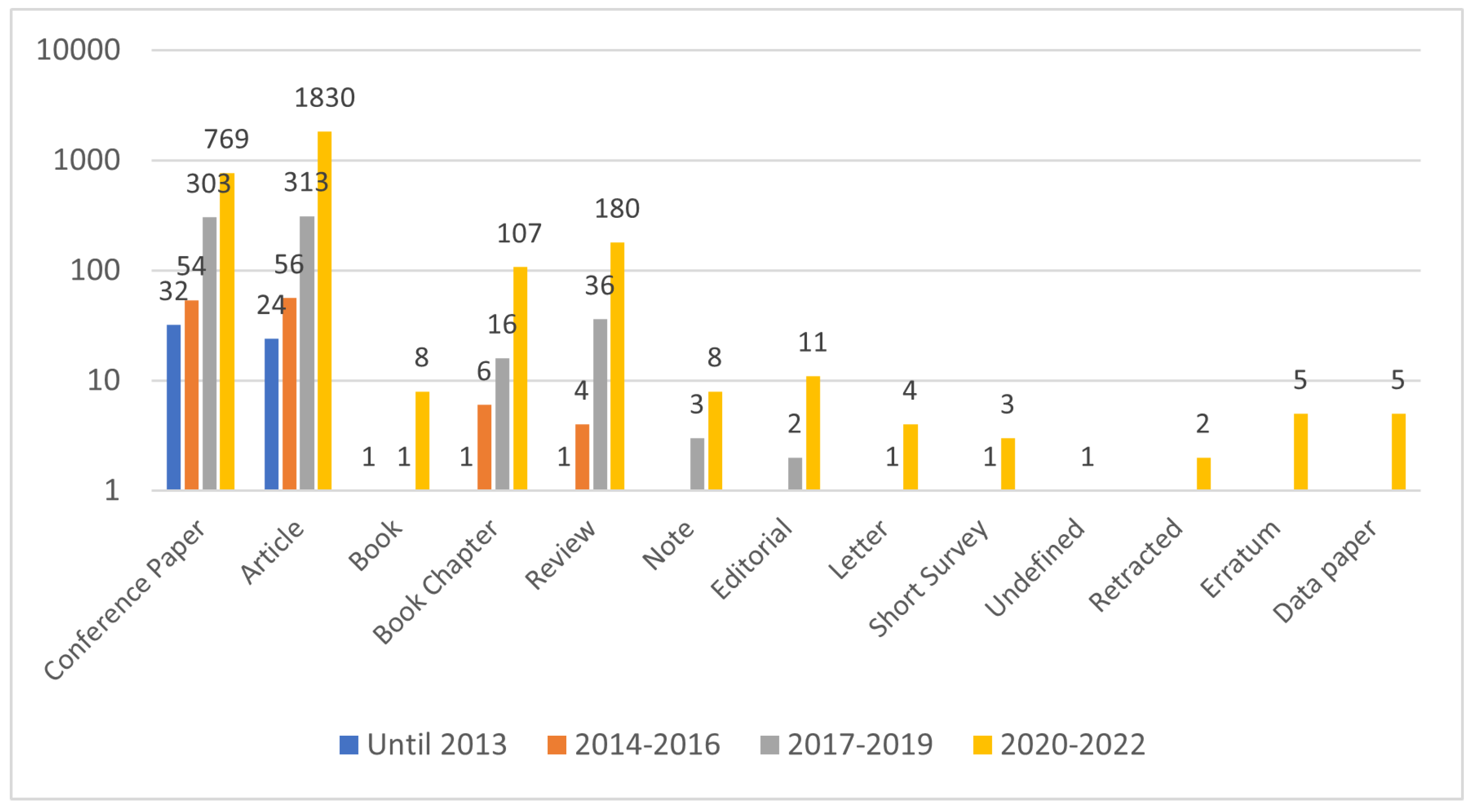
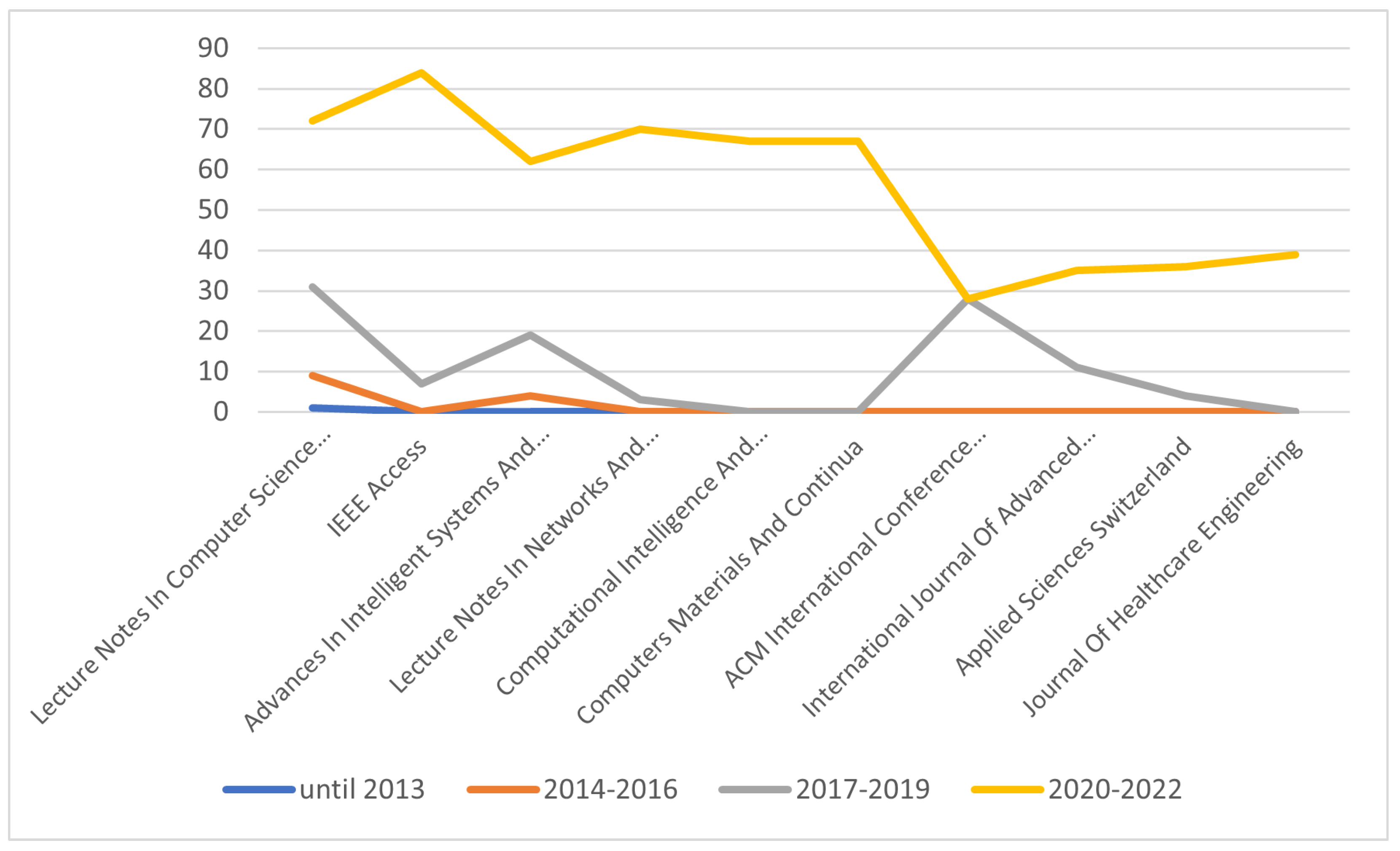
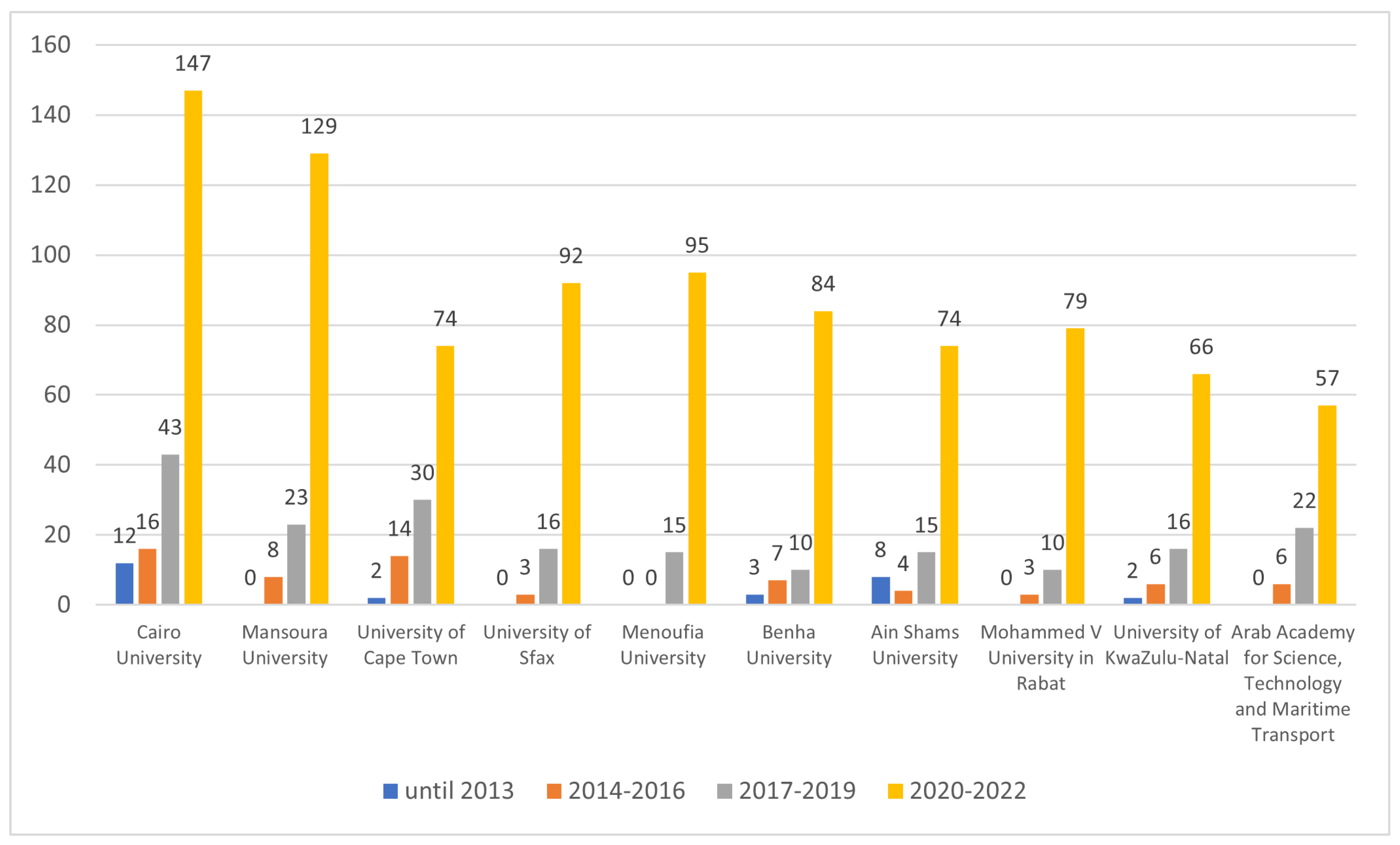
4.1. Publishing Patterns
- Decision Sciences stand for ML research about clinical decision support and recommendation system engineering.
- Chemical Engineering, Chemistry, and Materials Science mainly reveal research outputs linked to biochemistry, nanomedicine, device engineering, and drug discovery.
- Physics and Astronomy and Energy identify research related to Biophysics, Nuclear Medicine, Oncology, and Radiology.
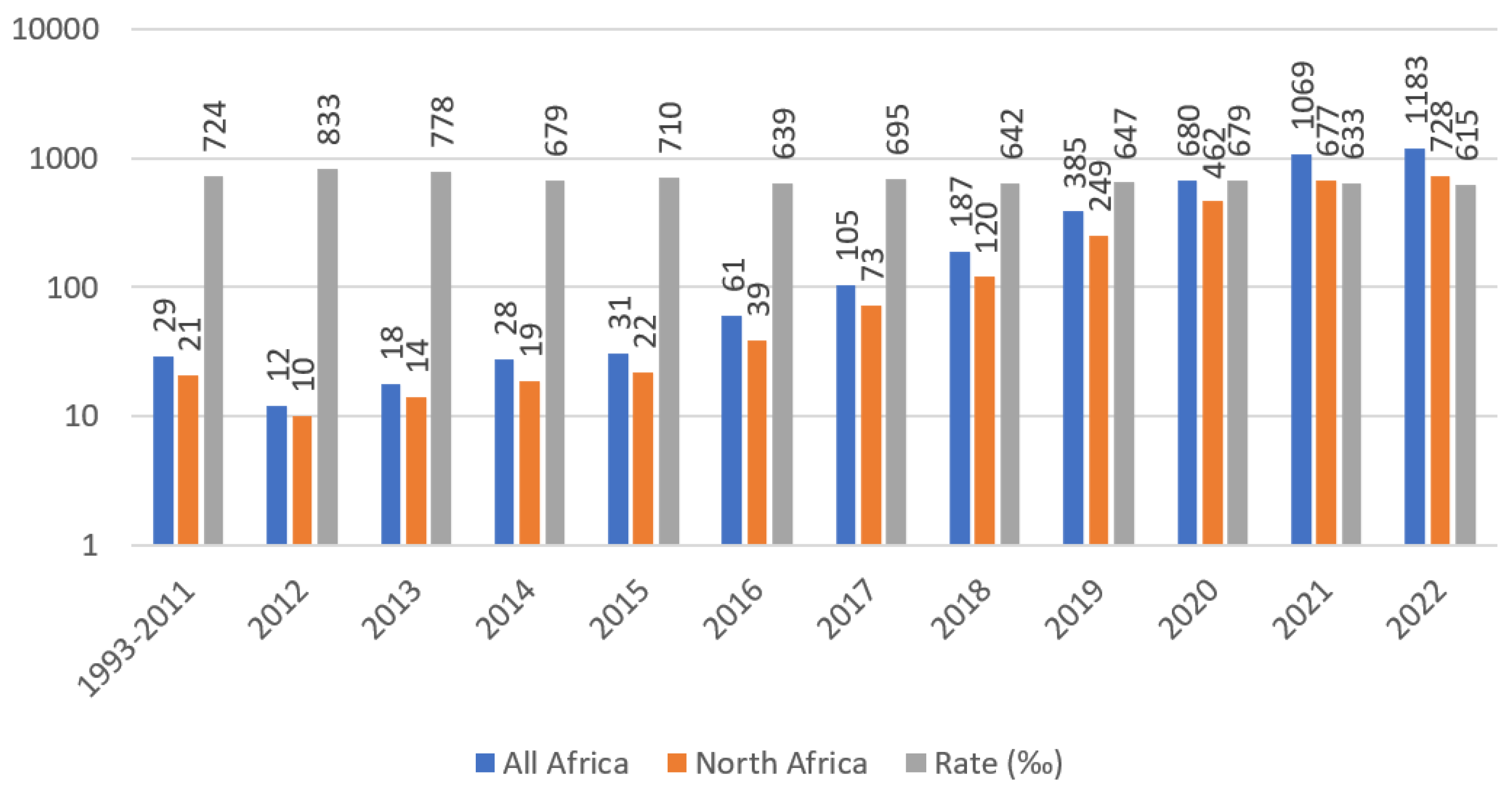
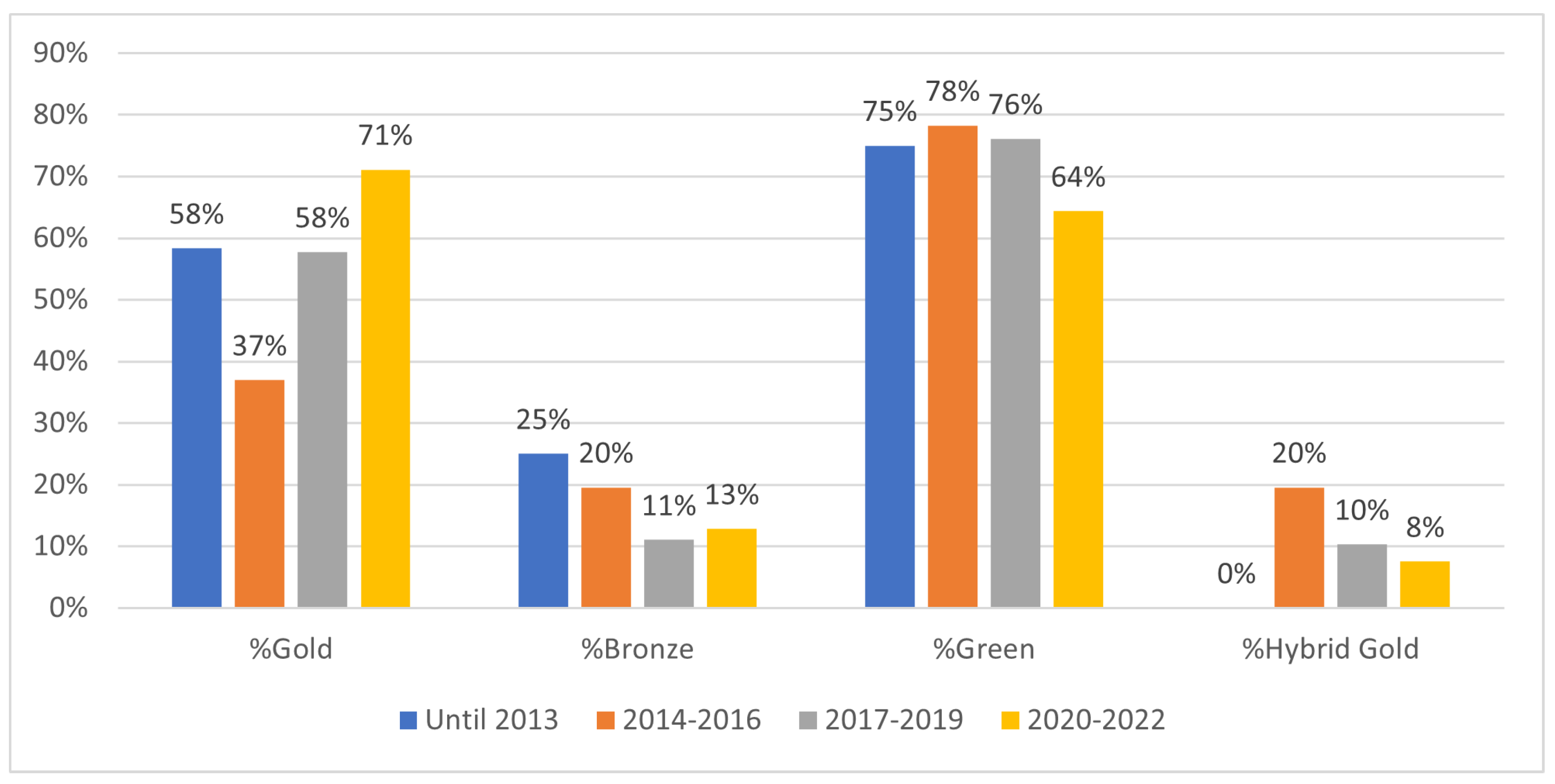
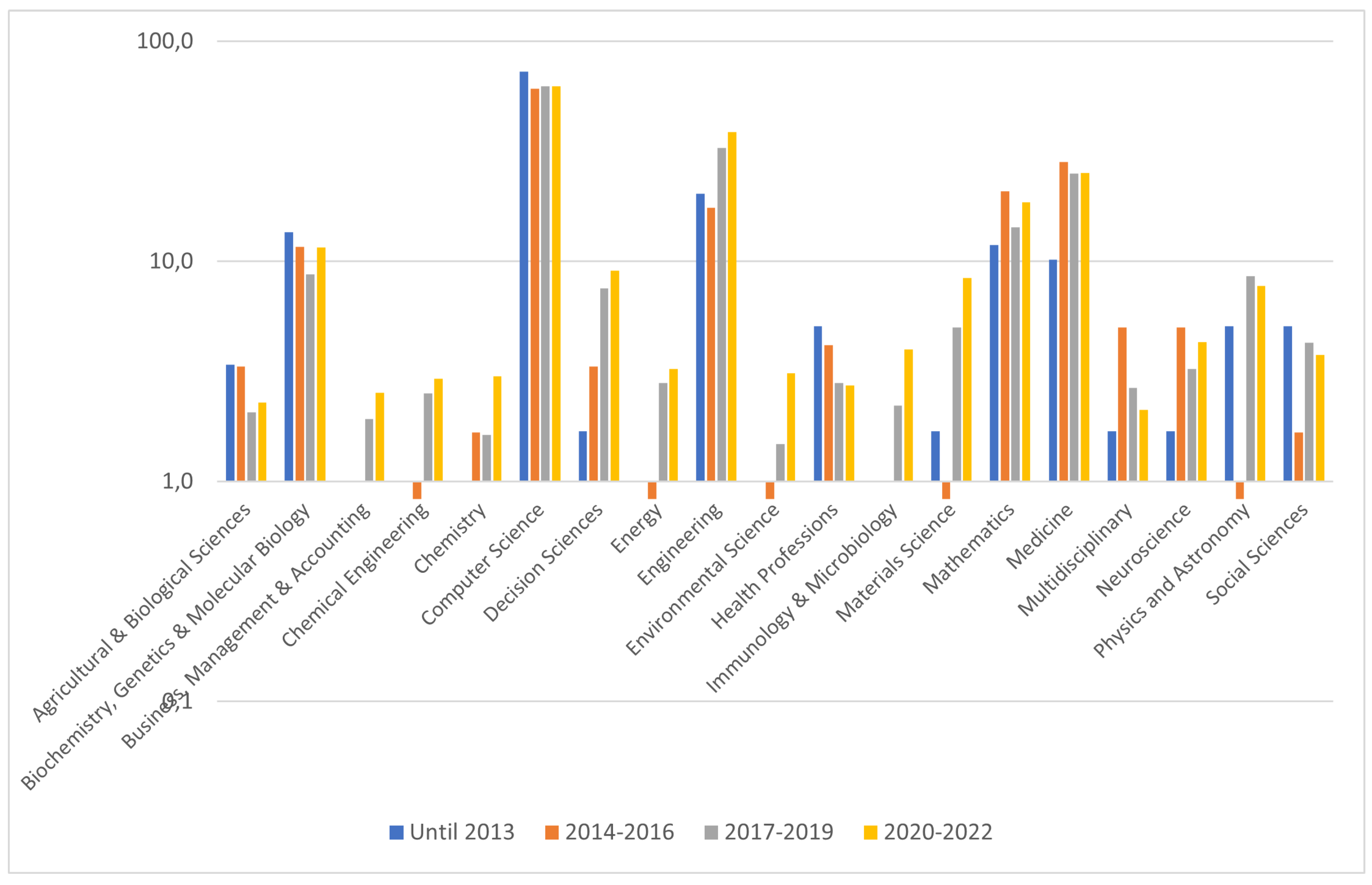
4.2. Time-Aware Analysis
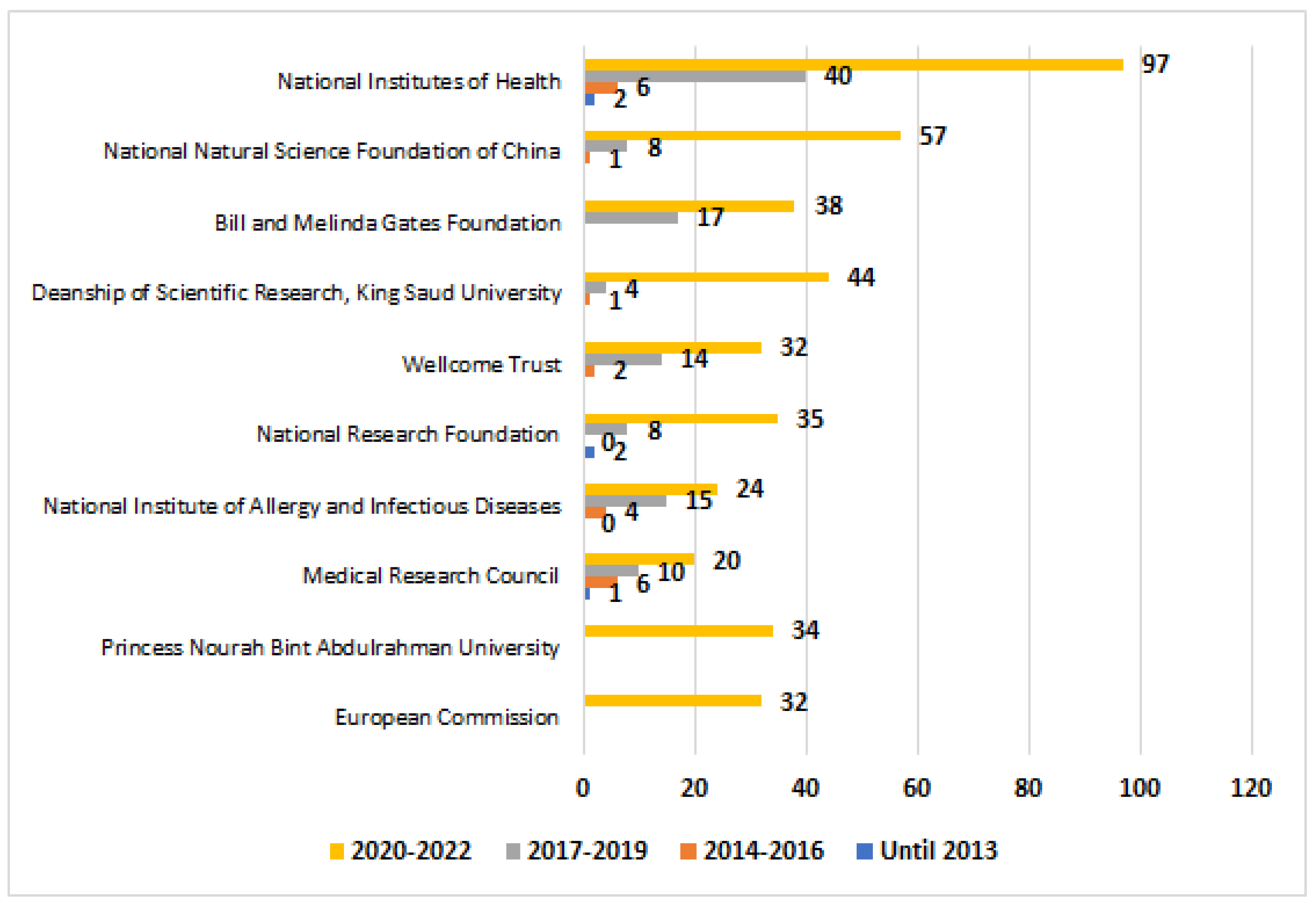
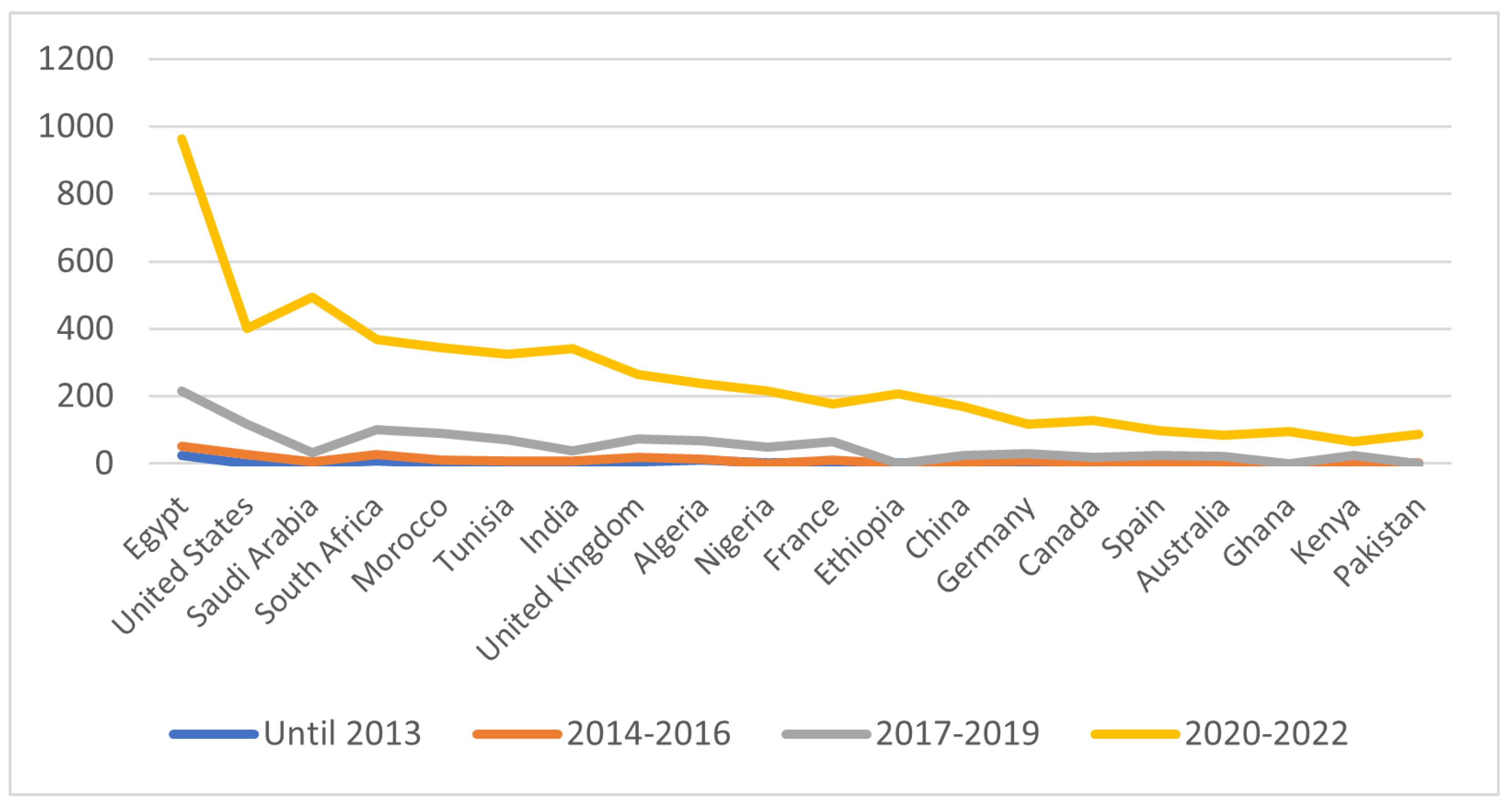
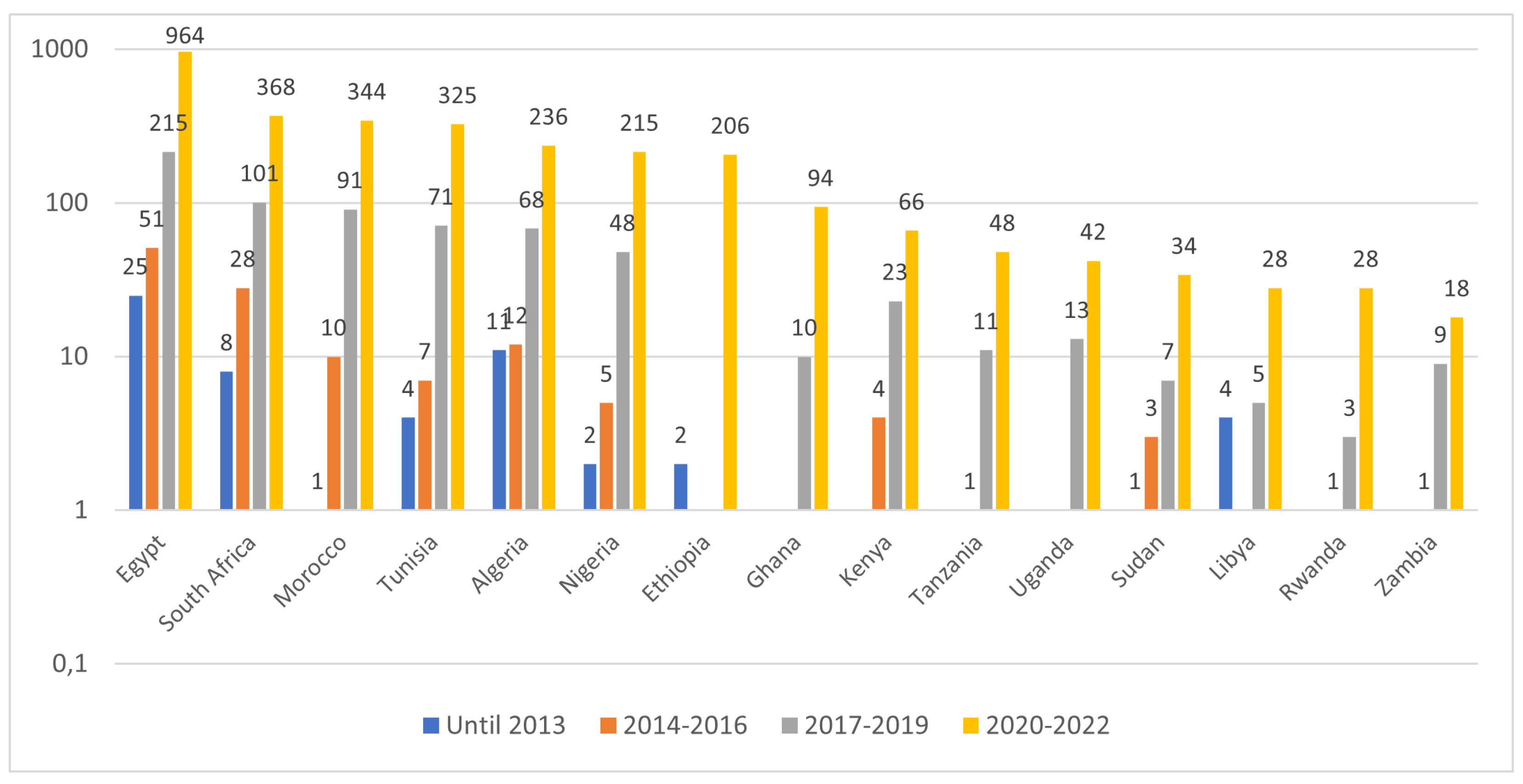
5. Conclusion
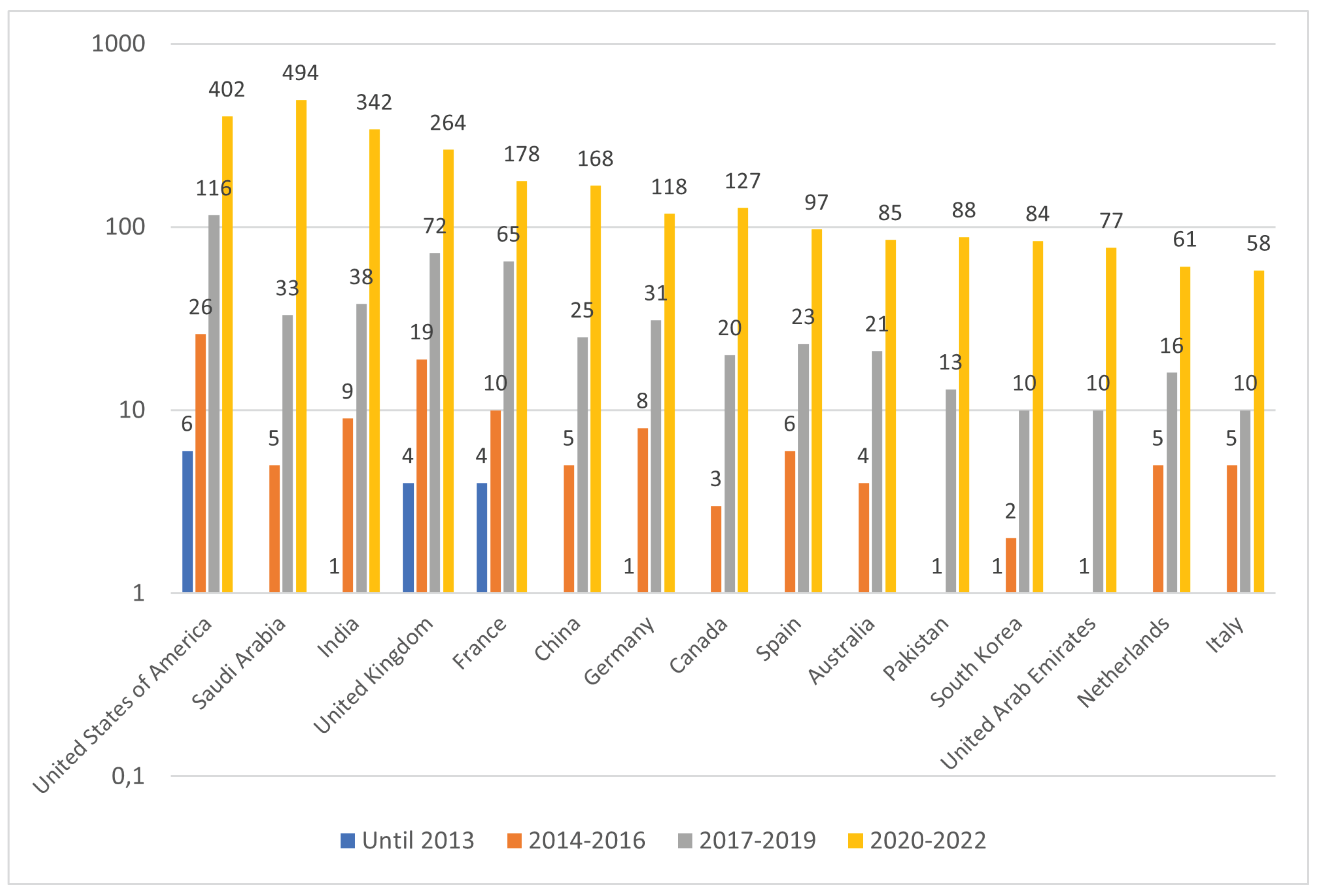
5.1. Key findings
5.2. Limitations and future work
Author Contributions
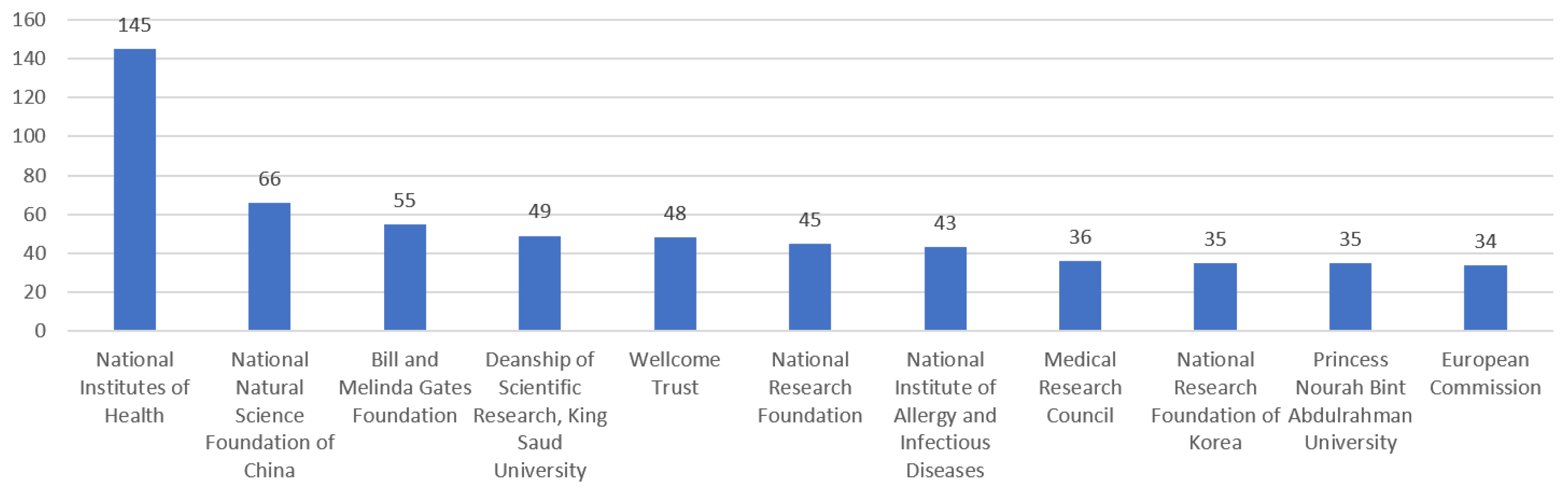
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currin, C.B.; Khoza, P.N.; Antrobus, A.D.; Latham, P.E.; Vogels, T.P.; Raimondo, J.V. Think: Theory for Africa. PLOS Computational Biology 2019, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shailaja, K.; Seetharamulu, B.; Jabbar, M.A. Machine Learning in Healthcare: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), 2018, p. 910–914. [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Qadir, J.; Bilal, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Secure and Robust Machine Learning for Healthcare: A Survey. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 2021, 14, 156–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke and Vascular Neurology 2017, 2, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidströmer, N.; Ashrafian, H. (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Springer International Publishing, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, E. 5 takeaways from the FDA’s list of AI-enabled medical devices. https://www.medtechdive.com/news/FDA-AI-ML-medical-devices-5-takeaways/635908/, 2022.
- Sculley, D.; Holt, G.; Golovin, D.; Davydov, E.; Phillips, T.; Ebner, D.; Chaudhary, V.; Young, M.; Crespo, J.F.; Dennison, D. Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems. In Proceedings of the NIPS, 2015.
- Chen, I.Y.; Pierson, E.; Rose, S.; Joshi, S.; Ferryman, K.; Ghassemi, M. Secure and Robust Ethical machine learning in healthcare. Annual review of biomedical data science 2021, 4, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldring, L.; Robinson, J.A. Colonialism and economic development in Africa. Technical report, National Bureau of Economic Research, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Ocheni, S.; Nwankwo, B.C. Analysis of colonialism and its impact in Africa. Cross-Cultural Communication 2012, 8, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziltener, P.; Künzler, D. Impacts of colonialism—a research survey. Journal of World-Systems Research 2013, 19, 290–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowi, J.; Ong’ondo, C.O.; Nega, M.; Sehoole, C.; Alabi, G.; Dimé, M.; Barasa, P.; Akudolu, L. Building phd capacity in subsaharan africa. International high education. accessed on 26th/102021 from www. daad. de 2018.
- Pouris, A.; Ho, Y.S. Research emphasis and collaboration in Africa. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichbaum, Quentin G., L.V.A.J.E.M.J.H.I.A.S.; van Schalkwyk, S.C. Decolonizing global health education: rethinking institutional partnerships and approaches. Academic Medicine 2021, 96.3. [CrossRef]
- Sooryamoorthy, R. Science in Africa: Contemporary Trends in Research. Journal of Scientometric Research 2022, 10, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, A.; Lan, G.; Adil, M. Sub-Saharan African Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Research: A Decade of Development; Washington, DC: World Bank, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouris, A. Bibliometric Analyses on EU-Africa Research Co-publications in Health; CAAST-NET and Department of Science and Innovation, Pretoria, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Owoyemi, A.; Owoyemi, J.; Osiyemi, A.; Boyd, A. Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare in Africa. Frontiers in Digital Health 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.; Cookson, J.; Wyatt, J., Eds. AIME 89: Second European Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, London, August 29th–31st 1989; Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1989. [CrossRef]
- Kastner, J.K.; Dawson, C.R.; Weiss, S.M.; Kern, K.B.; Kulikowski, C.A. An expert consultation system for frontline health workers in primary eye care. Journal of Medical Systems 1984, 8, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byass, P. Computers in Africa: Appropriate Technology? Comput. Bull. 1987, 3, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, D. Expert systems in health for developing countries: practice, problems, and potential; IDRC: Ottawa, ON, CA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, S.; Doan, T.N.; Yun, J.A.; Tshuma, N. Application of machine learning models in predicting length of stay among healthcare workers in underserved communities in South Africa. Human Resources for Health 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onu, C.C.; Lebensold, J.; Hamilton,W.L.; Precup, D. Neural Transfer Learning for Cry-Based Diagnosis of Perinatal Asphyxia. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019. ISCA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Bellemo, V.; Lim, Z.W.; Lim, G.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Xie, Y.; Yip, M.Y.T.; Hamzah, H.; Ho, J.; Lee, X.Q.; Hsu, W.; et al. Artificial intelligence using deep learning to screen for referable and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in Africa: a clinical validation study. The Lancet Digital Health 2019, 1, e35–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busari, S.; Adebayo, B. Nigerian Girls Win Silicon Valley Contest for App that Spots Fake Drugs. CNN.
- Akpanudo, S. Application of Artificial Intelligence Systems to Improve Healthcare Delivery in Africa. Primary Health Care: Open Access 2022, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, Mats Stage, A.W.M.L.T.M.; Evans., J. Machine learning in a time of COVID-19-Can machine learning support Community Health Workers (CHWs) in low and middle income countries (LMICs) in the new normal? Journal of Global Health 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, Christopher J., A.K.M.S.G.C.; King., D. Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence. BMC medicine 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Irene Y., E.P.S.R.S.J.K.F.; Ghassemi, M. Ethical machine learning in healthcare. Annual review of biomedical data science 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. A bibliometric analysis on deep learning during 2007–2019. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics 2020, 11, 2807–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, B.S.; Arns Steiner, M.T.; Trojan Fenerich, A.; Palma Lima, R.H. Data mining and machine learning techniques applied to public health problems: A bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2019, 138, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, N.; Abimiku, A.; Adebamowo, S.N.; de Vries, J.; Matimba, A.; Olowoyo, P.; Ramsay, M.; Skelton, M.; Stein, D.J. H3Africa: current perspectives. Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine 2018, 11, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larbi, D.; Sarheim Anthun, K.; Nah Asah, F.; Debrah, O.; Antypas, K. Assessing Strategic Priority Factors in eHealth Policies of Four African Countries. In Proceedings of the 2022 IST-Africa Conference (IST-Africa). IEEE, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tchuitcheu, G.K.; Mostert, N.; Ndlovu, K.; Oluoch, T.; da Costa Vroom, F.; Wanyee, S.; Nanann, I.; Wright, G. Pan African Health Informatics Association (HELINA). Yearbook of Medical Informatics 2020, 29, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, D.; Almerares, A.; Mayan, J.C.; de Quirós, F.G.B.; Otero, C. Health Informatics in Developing Countries: Going beyond Pilot Practices to Sustainable Implementations: A Review of the Current Challenges. Healthcare Informatics Research 2014, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. How has academia responded to the urgent needs created by COVID-19? A multi-level global, regional and national analysis. Journal of Information Science 2022, 01655515221084646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoudhi, L.; Sassi, N.; Jaziri, W. How Latest Computer Science Research Copes with COVID-19? In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems Design and Applications; Abraham, A., Gandhi, N., Hanne, T., Hong, T.P., Nogueira Rios, T., Ding, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; To, K.K.; Tse, H.; Hung, I.F.; Yuen, K.Y. Two Years after Pandemic Influenza A/2009/H1N1: What Have We Learned? Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2012, 25, 223–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, H.; Hadj Taieb, M.A.; Ben Aouicha, M.; Pouris, A. Infectious epidemics and the research output of nations: A data-driven analysis. Journal of Information Science 2021, 0, 01655515211006605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Kalfa, N.; Beckers, G.; Kaefer, M.; Nieuwhof-Leppink, A.J.; Fossum, M.; Herbst, K.; Bagli, D. The impact of COVID-19 on research. Journal of Pediatric Urology 2020, 16, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yin, Y.; Myers, K.R.; Lakhani, K.R.; Wang, D. Potentially long-lasting effects of the pandemic on scientists. Nature Communications 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapera, R.; Singh, Y. A Bibliometric Analysis of Medical Informatics and Telemedicine in Sub-Saharan Africa and BRICS Nations. Journal of Public Health Research 2021, 10, jphr.2021.1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, J.G.; Mather, F.J.; Wele, M.; Li, J.; Tangara, C.O.; Kassogue, Y.; Srivastav, S.K.; Thiero, O.; Diakite, M.; Sangare, M.; et al. Expanding Research Capacity in Sub-Saharan Africa Through Informatics, Bioinformatics, and Data Science Training Programs in Mali. Frontiers in Genetics 2019, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodoo, J.E.; Al-Samarraie, H.; Alzahrani, A.I. Telemedicine use in Sub-Saharan Africa: Barriers and policy recommendations for Covid-19 and beyond. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2021, 151, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonkam, A. Sequence three million genomes across Africa. Nature 2021, 590, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, J.R.; Todd, J.; Baisley, K.; Bradley, J.; Tumwesigye, N.M.; Musonda, P.; Chirwa, T. Training and capacity building in medical statistics in Sub-Saharan Africa: Impact of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine MSc in Medical Statistics, 1969 to 2021. Statistics in Medicine 2022, 41, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estreguil, C.; Buschke, F. The evolving role of the European Commission in research on Africa; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlelmola, F.M.; Zass, L.; Chaouch, M.; Samtal, C.; Ras, V.; Kumuthini, J.; Panji, S.; Mulder, N. Data Management Plans in the genomics research revolution of Africa: Challenges and recommendations. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2021, 122, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauci, A.S.; Touchette, N.A.; Folkers, G.K. Emerging Infectious Diseases: a 10-Year Perspective from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2005, 11, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, H.; Ben Aouicha, M.; Hadj Taieb, M.A. Discussing Arab Spring’s effect on scientific productivity and research performance in Arab countries. Scientometrics 2019, 120, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Cai, X.; Lyu, X. An in-depth analysis of government funding and international collaboration in scientific research. Scientometrics 2020, 125, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitis, R.; Mouton, J.; Néron, A. Funding Research in Africa: Landscapes of Re-institutionalisation. Science, Technology and Society 2022, 27, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tian, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, X. Mapping research collaborations in different countries and regions: 1980–2019. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landini, F.; Malerba, F.; Mavilia, R. The structure and dynamics of networks of scientific collaborations in Northern Africa. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1787–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.; Vu, G.; Ha, G.; Vuong, Q.H.; Ho, M.T.; Vuong, T.T.; La, V.P.; Ho, M.T.; Nghiem, K.C.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Global Evolution of Research in Artificial Intelligence in Health and Medicine: A Bibliometric Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2019, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.L.; Puricelli Perin, D.M.; Lu, Y.L.; Taplin, S.H. Understanding the Value of International Research Networks: An Evaluation of the International Cancer Screening Network of the US National Cancer Institute. Journal of Global Oncology 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, R.; Hassan, S.U. A bibliometric assessment of scientific productivity and international collaboration of the Islamic World in science and technology (S&T) areas. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1059–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivanen, H.; Ponomariov, B. African regional innovation systems: bibliometric analysis of research collaboration patterns 2005–2009. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H. The Arab region’s contribution to global COVID-19 research: Bibliometric and visualization analysis. Globalization and Health 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie-Alder, B.; Arvanitis, R.; Hanafi, S. Research in Arabic-speaking countries: Funding competitions, international collaboration, and career incentives. Science and Public Policy 2017, 45, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Nerima, B.; Bagaya, B.; Kambugu, A.; Joloba, M.; Cose, S.; Pantaleo, G.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Mabey, D.; Dunne, D.; et al. Capacity for science in sub-Saharan Africa. The Lancet 2015, 385, 2435–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Statistical Yearbook, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Fukui, T. Factors Related to Biomedical Research Productivity in Asian Countries. Journal of Epidemiology 2001, 11, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwizeye, D.; Karimi, F.; Thiong’o, C.; Syonguvi, J.; Ochieng, V.; Kiroro, F.; Gateri, A.; Khisa, A.M.; Wao, H. Factors associated with research productivity in higher education institutions in Africa: a systematic review. AAS Open Research 2022, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniol, M.; Kunjumen, T.; Nair, T.S.; Siyam, A.; Campbell, J.; Diallo, K. The global health workforce stock and distribution in 2020 and 2030: a threat to equity and ‘universal’ health coverage? BMJ Global Health 2022, 7, e009316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, D. Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Africa [Regional]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine 2019, 26, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeneme, S.; Okeibunor, J.; Muneene, D.; Husain, I.; Bento, P.; Gaju, C.; Housseynou, B.; Chibi, M.; Karamagi, H.; Makubalo, L. Data revolution, health status transformation and the role of artificial intelligence for health and pandemic preparedness in the African context. BMC Proceedings 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwagwa, A.; Kraemer-Mbula, E.; Rizk, N.; Rutenberg, I.; de Beer, J. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Deployments in Africa: Benefits, Challenges and Policy Dimensions. The African Journal of Information and Communication 2020, 26, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Lei, J. Trends and characteristics of global medical informatics conferences from 2007 to 2017: A bibliometric comparison of conference publications from Chinese, American, European and the Global Conferences. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2018, 166, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiek, M. The European research elite: a cross-national study of highly productive academics in 11 countries. Higher Education 2015, 71, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Klavans, R.; Boyack, K.W. Thousands of scientists publish a paper every five days. Nature 2018, 561, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramo, G.; Cicero, T.; D’Angelo, C.A. Are the authors of highly cited articles also the most productive ones? Journal of Informetrics 2014, 8, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scellato, G.; Franzoni, C.; Stephan, P. Migrant scientists and international networks. Research Policy 2015, 44, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confraria, H.; Blanckenberg, J.; Swart, C. Which Factors Influence International Research Collaboration in Africa? In Sustainable Development Goals Series; Springer International Publishing, 2019; pp. 243–255. [CrossRef]
- Korbel, J.O.; Stegle, O. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on life scientists. Genome Biology 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, B.; Hu, K.; Yuan, B.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Tang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Evidence-based biomaterials research. Bioactive Materials 2022, 15, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, H.; Hadj Taieb, M.A.; Ben Aouicha, M. The value of letters to the editor. Scientometrics 2018, 117, 1285–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquin, J.J.; Tan, R.R. The lost art of short communications in academia. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 9633–9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, L.; Castelli, D.; Manghi, P.; Tani, A. Data journals: A survey. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology 2015, 66, 1747–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xing, X.; Qi, F.; Grácio, M.C.C. Comparison of academic book impact from a disciplinary perspective: an analysis of citations and altmetric indicators. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 1101–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokol, M.; Ozbay, F.; Rodriguez-Esteban, R. Retraction rates are on the rise. EMBO reports 2008, 9, 2–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondari-Okemwa, E. Scholarly publishing in sub-Saharan Africa in the twenty-first century: Challenges and opportunities. First Monday 2007, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesooriya, N.R.; Mishra, V.; Brand, P.L.; Rubin, B.K. COVID-19 and telehealth, education, and research adaptations. Paediatric Respiratory Reviews 2020, 35, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, J. The need for accelerated change in diversity, equity and inclusion in publishing and learned societies. Learned Publishing 2022, 35, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Bekele, B.; Griessel, H.; de Korte, T.; Authier, S.; Grobler, A.F.; Markgraf, C.G.; Curtis, M.J. Twenty years of safety pharmacology model validation and the wider implications of this to drug discovery. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods 2020, 105, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaswa, R.; Nair, A.; Murphy, S.; Pressentin, K.B.V. Artificial intelligence: A strategic opportunity for enhancing primary care in South Africa. South African Family Practice 2022, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmatier, R.W.; Houston, M.B.; Hulland, J. Review articles: purpose, process, and structure. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 2017, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, D.; Marshall, D.M. Bite-size research: BMC Research Notes goes back to its roots. BMC Research Notes 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larivière, V.; Haustein, S.; Mongeon, P. The Oligopoly of Academic Publishers in the Digital Era. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0127502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCImago. SCImago Journal Country Rank [Portal], 2022.
- Collazo-Reyes, F. Growth of the number of indexed journals of Latin America and the Caribbean: the effect on the impact of each country. Scientometrics 2013, 98, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz Rodrigues, R.; Abadal, E.; Kricheldorf Hermes de Araújo, B. Open access publishers: The new players. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0233432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, D.; Tutoky, G. Computer Science Papers in Web of Science: A Bibliometric Analysis. Publications 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainer, J.; Xavier, E.C.; Bezerra, F. Scientific production in Computer Science: A comparative study of Brazil and other countries. Scientometrics 2009, 81, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Salhab, J.; Calvé-Genest, A.; Horava, T. Open Access Article Processing Charges: DOAJ Survey May 2014. Publications 2015, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, F.; Frehywot, S.; Omaswa, F.; Buch, E.; Chen, C.; Greysen, S.R.; Wassermann, T.; Abubakr, D.E.E.; Awases, M.; Boelen, C.; et al. Medical schools in sub-Saharan Africa. The Lancet 2011, 377, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortliffe, E.H. Biomedical Informatics in the Education of Physicians. JAMA 2010, 304, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, S. Informatics is a critical strategy in combating the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2020, 27, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.A.; Ghiasi, G.; Mongeon, P.; Larivière, V. National differences in dissemination and use of open access literature. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0272730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, R.; Singh, P.; Singh, V.K.; Vinuesa, R.; Nedungadi, P. Understanding the Bibliometric Patterns of Publications in IEEE Access. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 35561–35577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Haupt, J.P. Scientific globalism during a global crisis: research collaboration and open access publications on COVID-19. Higher Education 2020, 81, 949–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Piryani, R.; Srichandan, S.S. The case of significant variations in gold–green and black open access: evidence from Indian research output. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, B.C. The hybrid model for open access publication of scholarly articles: A failed experiment? Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 2012, 63, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M. Green open access policies of scholarly journal publishers: a study of what, when, and where self-archiving is allowed. Scientometrics 2013, 99, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstam, E.V.; Smith, J.W.; Johnson, T.R. What is biomedical informatics? Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2010, 43, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithakin, K.; Bearden, C.; Pittenger, S.; Bernstam, E. Toward a veterinary informatics research agenda: An analysis of the PubMed-indexed literature. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2007, 76, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, R.; Strudwick, G.; McMurray, J.; Chan, R.; Cotton, K.; Cooke, S. The Future of Nursing Informatics in a Digitally-Enabled World. In Health Informatics; Springer International Publishing, 2021; pp. 395–417. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Joglekar, G.; Jain, A.; Venkatasubramanian, V.; Reklaitis, G. Pharmaceutical informatics: A novel paradigm for pharmaceutical product development and manufacture. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier, 2005; pp. 1561–1566. [CrossRef]
- London, S.D.; Fontelo, P.; Boroumand, S.; Dye, B.A. COVID-19 provides an opportunity for integration of dentistry into the health informatics system. The Journal of the American Dental Association 2022, 153, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, A. Human–computer interaction, foundations and new paradigms. Journal of Visual Languages & Computing 2017, 42, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, E. Machine Learning for Mental Health in Social Media: Bibliometric Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2021, 23, e24870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoobane, P.; Masinde, M.; Mabhaudhi, T. Predicting Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Review on Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Dolias, G.; Berruto, R.; Kateris, D.; Bochtis, D. Machine Learning in Agriculture: A Comprehensive Updated Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, K.Y.; Chuang, Y.C.; Ho, M.; Ho, Y.S. Bibliometric analysis of public health research in Africa: The overall trend and regional comparisons. South African Journal of Science 2011, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, N.J.; Adebiyi, E.; Alami, R.; Benkahla, A.; Brandful, J.; Doumbia, S.; Everett, D.; Fadlelmola, F.M.; Gaboun, F.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; et al. H3ABioNet, a sustainable pan-African bioinformatics network for human heredity and health in Africa. Genome Research 2015, 26, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, M.B.; Ahmad, U.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Hamidu, S.K.; Nasr, F.E.; Salihu, A.T.; Abushouk, A.I.; Abdurrazak, M.; Awadelkareem, M.A.; Amin, A.; et al. Two decades of neuroscience publication trends in Africa. Nature Communications 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, N.L. Nanomedicine: Insights from a Bibliometrics-Based Analysis of Emerging Publishing and Research Trends. Medicina 2019, 55, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adunlin, G.; Diaby, V.; Xiao, H. Application of multicriteria decision analysis in health care: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Health Expectations 2014, 18, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, S.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Chien, C.H.; Chin, Y.P.; Yoon, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Yang, H.C.; Li, Y.C.J. Alerts in Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): A Bibliometric Review and Content Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winks, S.; Woodland, J.G.; Pillai, G.C.; Chibale, K. Fostering drug discovery and development in Africa. Nature Medicine 2022, 28, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutebi, M.; Lewison, G.; Aggarwal, A.; Alatise, O.; Booth, C.; Cira, M.; Grover, S.; Ginsburg, O.; Gralow, J.; Gueye, S.M.; et al. Cancer research across Africa: a comparative bibliometric analysis. The Lancet Global health 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Kielar, A.Z.; Hong, J. A Comprehensive Analysis of Authorship in Radiology Journals. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0139005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sooryamoorthy, R. The production of science in Africa: an analysis of publications in the science disciplines, 2000–2015. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 317–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensly, P.J.; Hodges, P.E.; Davenport, S.A. Acceptance Rates and Journal Quality: An Analysis of Journals in Economics and Finance. Journal of Business & Finance Librarianship 2008, 14, 2–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, R. Accept Me, Accept Me Not: What Do Journal Acceptance Rates Really Mean? SSRN Electronic Journal 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, F.; Polimeni, A. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Machine Learning Bibliometric Analysis. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garousi, V.; Fernandes, J.M. Highly-cited papers in software engineering: The top-100. Information and Software Technology 2016, 71, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabre, R. ACL Rolling Review: A New Format For Centralized Peer Review. Journal of Natural Language Processing 2022, 29, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahamtan, I.; Afshar, A.S.; Ahamdzadeh, K. Factors affecting number of citations: a comprehensive review of the literature. Scientometrics 2016, 107, 1195–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Query: TITLE-ABS-KEY(""Machine Learning"" OR ""Deep Learning"") AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(Medic* OR Clinic* OR Biomed* OR Health*). |
| 2 | Examples: https://cutt.ly/fB0l9Ie and https://cutt.ly/TB0l6hb. |
| 3 | |
| 4 | Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations: https://iclr.cc/Conferences/2023
|
| 5 | 27th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention: http://www.miccai.org/news/2020/12/31/and-the-location-of-miccai-2024-is
|
| 6 | Only 2 out of 104 Scopus-indexed health informatics journals are published by Taylor & Francis: Health systems and reform and Health Systems. Even these two journals are not fully related to the field and deal with it as a part of Public, Environmental and Occupational Health [93]. |
| 7 | Also co-published by Hindawi. |
| 8 | Further information are available at https://www.hindawi.com/publish-research/authors/. |
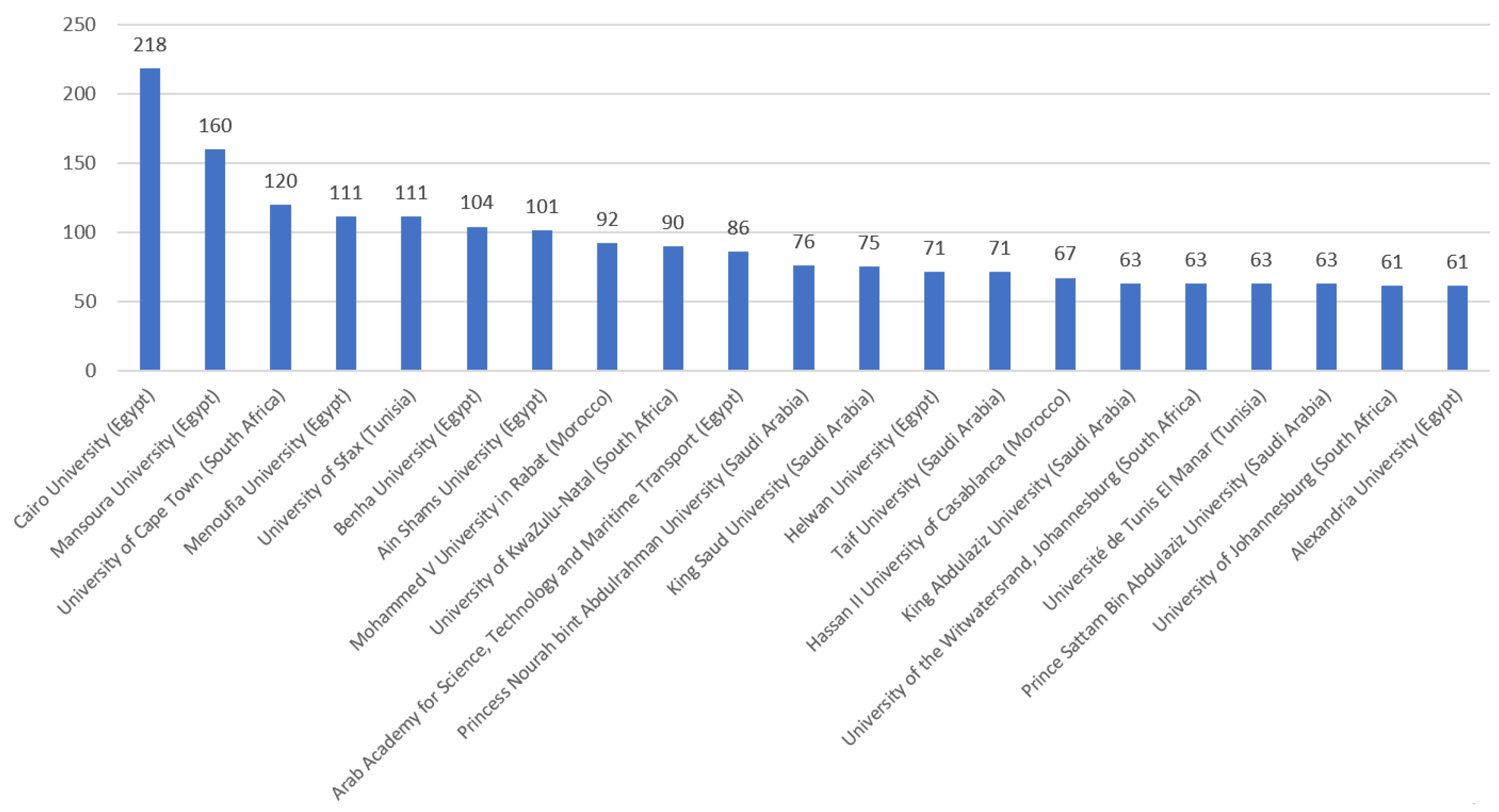
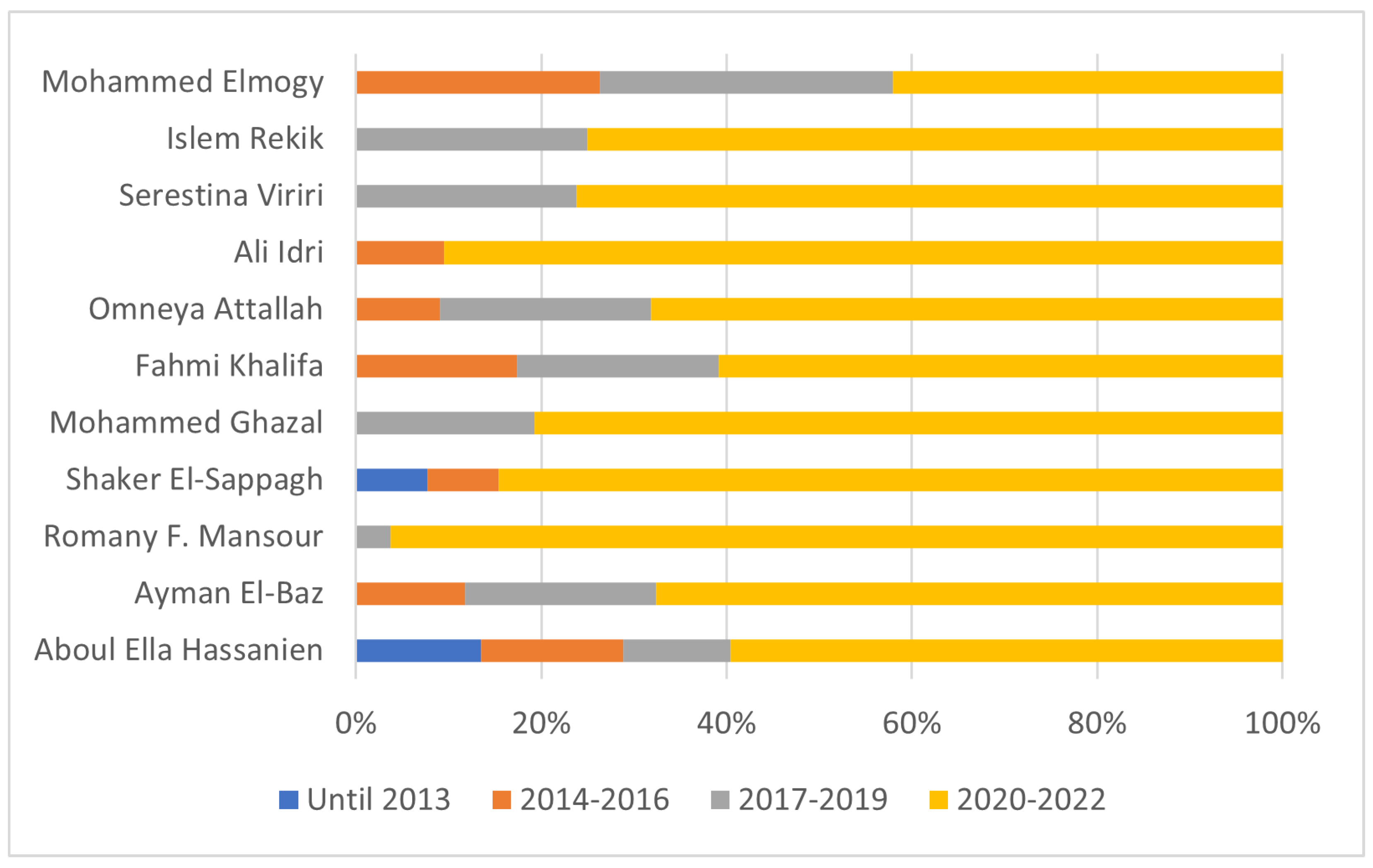
| Rank | Scientist | Affiliation | Publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aboul Ella Hassanien | Cairo University (Egypt) | 52 |
| 2 | Ayman El-Baz | University of Louisville (United States of America) | 34 |
| 3 | Romany F. Mansour | New Valley University (Egypt) | 27 |
| 4 | Shaker El-Sappagh | Benha University (Egypt) | 26 |
| 4 | Mohammed Ghazal | Abu Dhabi University (United Arab Emirates) | 26 |
| 6 | Fahmi Khalifa | Mansoura University (Egypt) | 23 |
| 7 | Omneya Attallah | Arab Academy for Science, Technology, and Maritime Transport (Egypt) | 22 |
| 8 | Ali Idri | Mohamed V University of Rabat (Morocco) | 21 |
| 8 | Serestina Viriri | University of KwaZulu-Natal (South Africa) | 21 |
| 10 | Islem Rekik | Istanbul Technical University (Turkey) | 20 |
| 11 | Mohammed Elmogy | Mansoura University (Egypt) | 19 |
| 12 | Mohamed Elhoseny | University of Sharjah (United Arab Emirates) | 18 |
| 12 | Sanjay Misra | Østfold University College (Norway) | 18 |
| 14 | Abdelmgeid A. Ali | Minia University (Egypt) | 17 |
| 14 | Essam H. Houssein | Minia University (Egypt) | 17 |
| 14 | Ahmed Soliman | University of Louisville (United States of America) | 17 |
| 14 | Dan J. Stein | University of Cape Town (South Africa) | 17 |
| 18 | Ahmad Taher Azar | Benha University (Egypt) | 16 |
| 18 | Bouchaib Cherradi | Hassan II University of Casablanca (Morocco) | 16 |
| 18 | Ashraf Darwish | Helwan University (Egypt) | 16 |
| 18 | Abdel-Badeeh M. Salem | Ain Shams University (Egypt) | 16 |
| 22 | Fathi E. Abd El-Samie | Menoufia University (Egypt) | 15 |
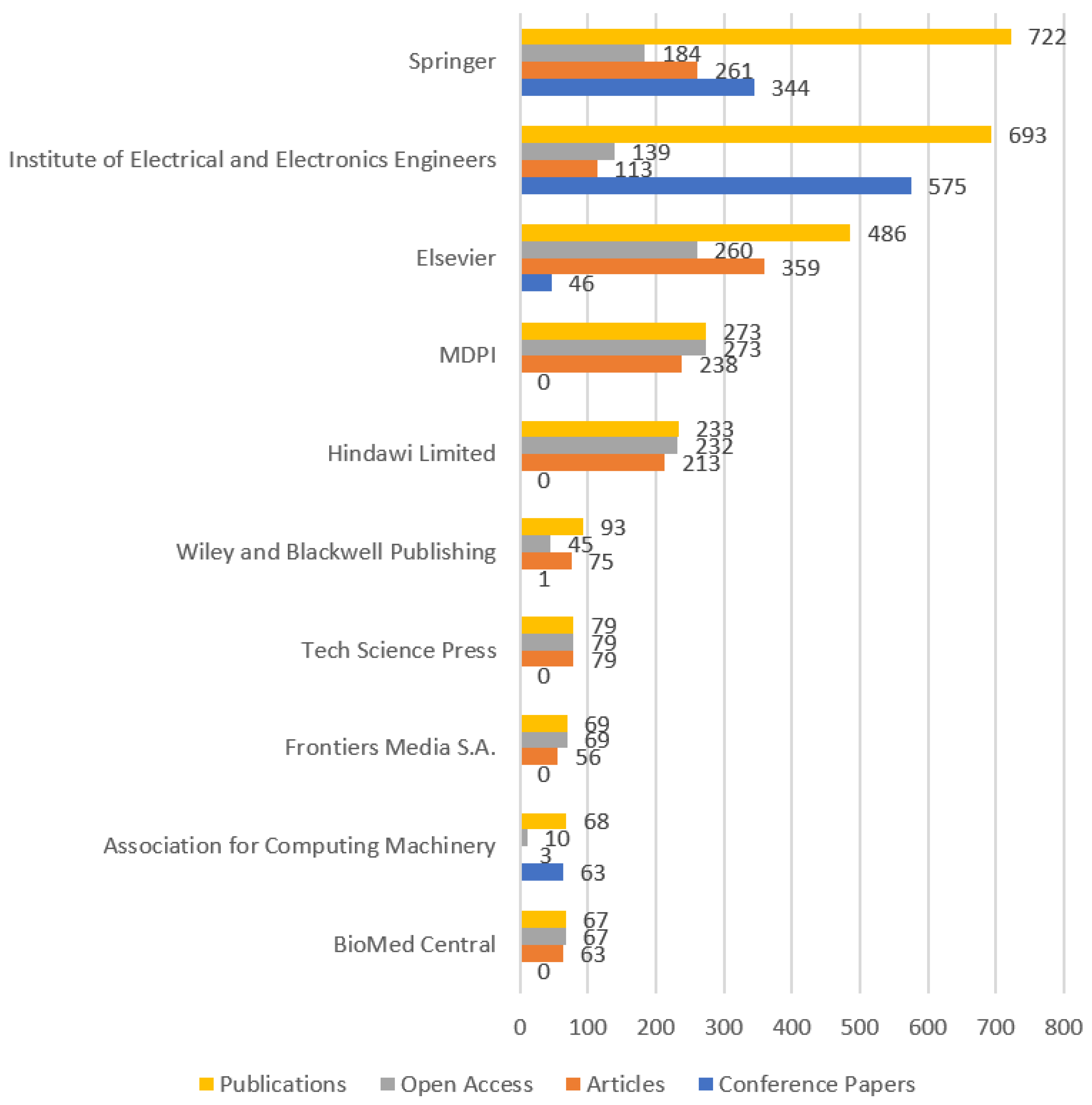
| Source Title | Publisher | All Africa | North Africa | Rate (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lecture Notes In Computer Science Including Subseries Lecture Notes In Artificial Intelligence And Lecture Notes In Bioinformatics | Springer | 113 | 81 | 717 |
| IEEE Access | IEEE | 91 | 68 | 747 |
| Advances In Intelligent Systems And Computing | Springer | 85 | 76 | 894 |
| Lecture Notes In Networks And Systems | Springer | 73 | 59 | 808 |
| Computational Intelligence And Neuroscience | Hindawi | 68 | 22 | 324 |
| Computers Materials And Continua | Tech Science Press | 67 | 65 | 970 |
| ACM International Conference Proceeding Series | ACM | 56 | 42 | 750 |
| International Journal Of Advanced Computer Science And Applications | Science and Information Organization | 46 | 36 | 783 |
| Applied Sciences Switzerland | MDPI | 40 | 36 | 900 |
| Journal Of Healthcare Engineering | Hindawi | 40 | 13 | 325 |
| Communications In Computer And Information Science | Springer | 37 | 30 | 811 |
| Procedia Computer Science | Elsevier | 35 | 32 | 914 |
| Sensors | MDPI | 34 | 30 | 882 |
| Computers In Biology And Medicine | Elsevier | 31 | 20 | 645 |
| Biomedical Signal Processing And Control | Elsevier | 30 | 26 | 867 |
| Neural Computing And Applications | Springer | 30 | 28 | 933 |
| Biomed Research International | BioMed Central | 28 | 4 | 143 |
| Scientific Reports | Nature Publishing Group | 28 | 10 | 357 |
| Electronics Switzerland | MDPI | 27 | 18 | 667 |
| Informatics In Medicine Unlocked | Elsevier | 26 | 12 | 462 |
| First Author (Year) | Title | Source | Citations | Publisher | Open Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hao Y. (2021) | Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data | Cell | 706 | Elsevier | Yes |
| El-Dahshan E.A.-S. (2014) | Computer-aided diagnosis of human brain tumor through MRI: A survey and a new algorithm | Expert Systems with Applications | 443 | Elsevier | No |
| Nweke H.F. (2018) | Deep learning algorithms for human activity recognition using mobile and wearable sensor networks: State of the art and research challenges | Expert Systems with Applications | 418 | Elsevier | No |
| Abdel-Zaher A.M. (2016) | Breast cancer classification using deep belief networks | Expert Systems with Applications | 318 | Elsevier | No |
| Asri H. (2016) | Using ML Algorithms for Breast Cancer Risk Prediction and Diagnosis | Procedia Computer Science | 307 | Elsevier | Yes |
| Loey M. (2021) | A hybrid deep transfer learning model with ML methods for face mask detection in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic | Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation | 291 | Elsevier | Yes |
| Shrock E. (2020) | Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity | Science | 264 | American Association for the Advancement of Science | Yes |
| Loey M. (2020) | Within the lack of chest COVID-19 X-ray dataset: A novel detection model based on GAN and deep transfer learning | Symmetry | 246 | MDPI AG | Yes |
| Chougrad H. (2018) | Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for breast cancer screening | Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine | 238 | Elsevier | No |
| Inbarani H.H. (2014) | Supervised hybrid feature selection based on PSO and rough sets for medical diagnosis | Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine | 229 | Elsevier | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





