Submitted:
19 January 2023
Posted:
27 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
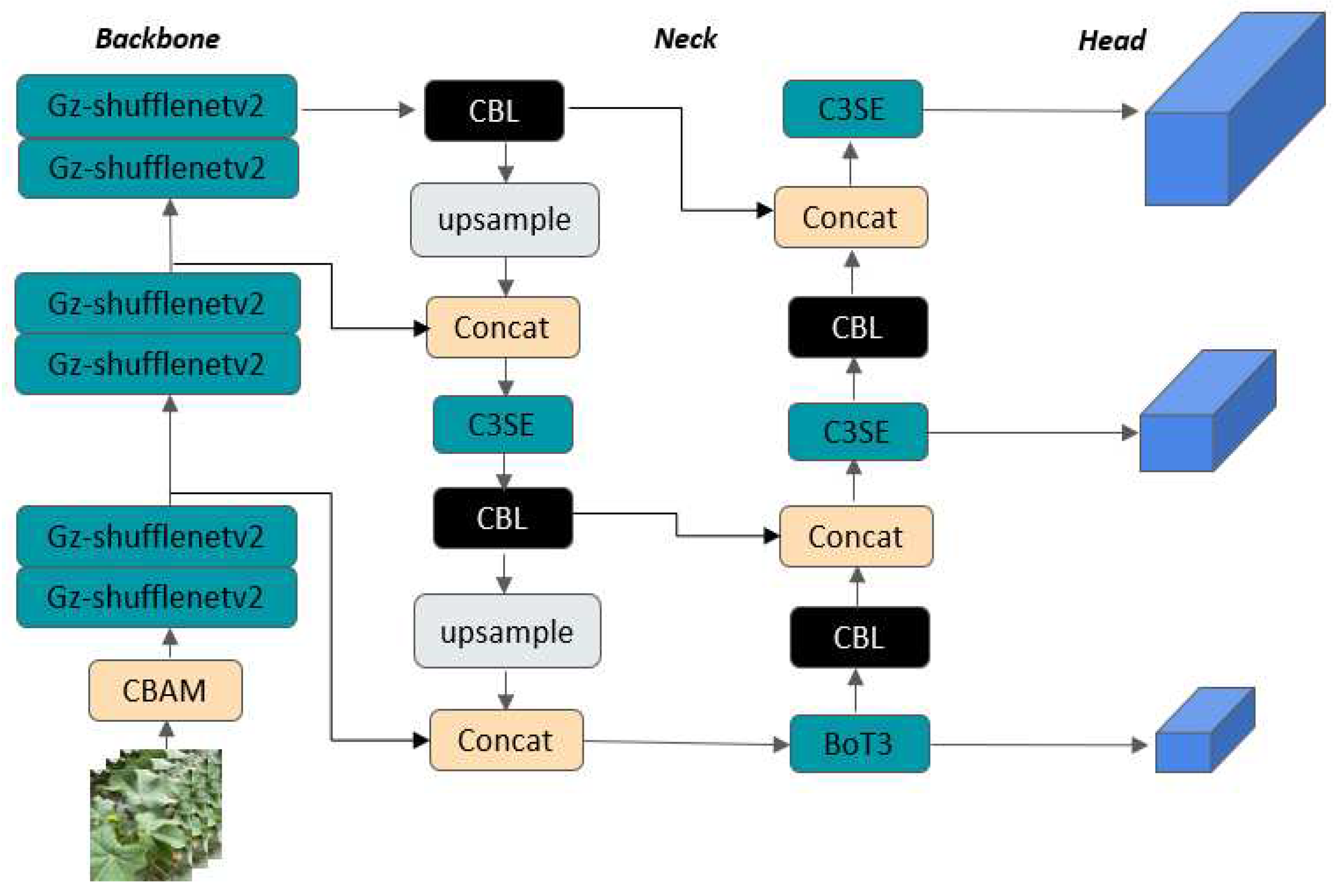
2. Improved YOLOv5S network
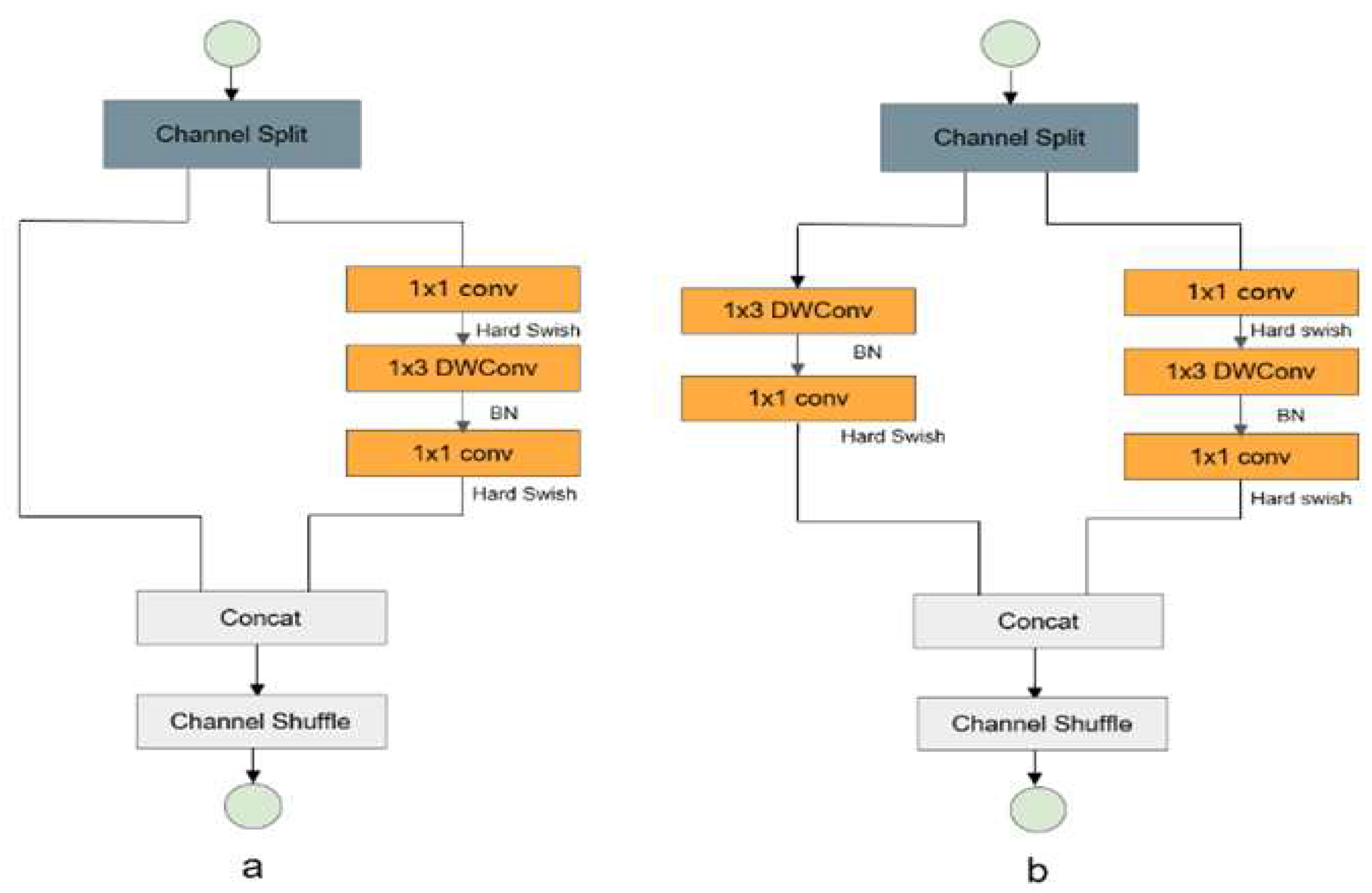
2.1. Gz-ShuffleNetv2 Network module
2.2. C3SE attention mechanism module
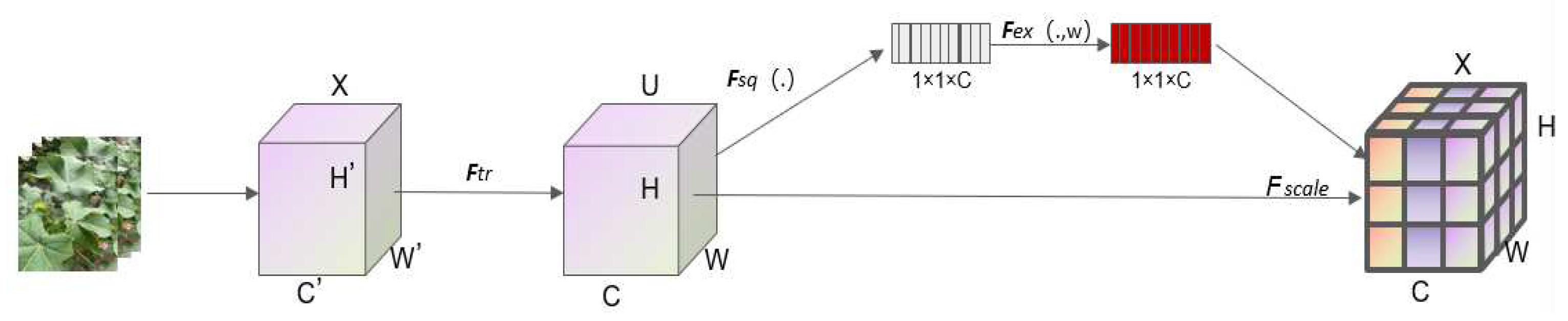
2.3. BotNet Attention mechanism module
2.4. Loss function improvement
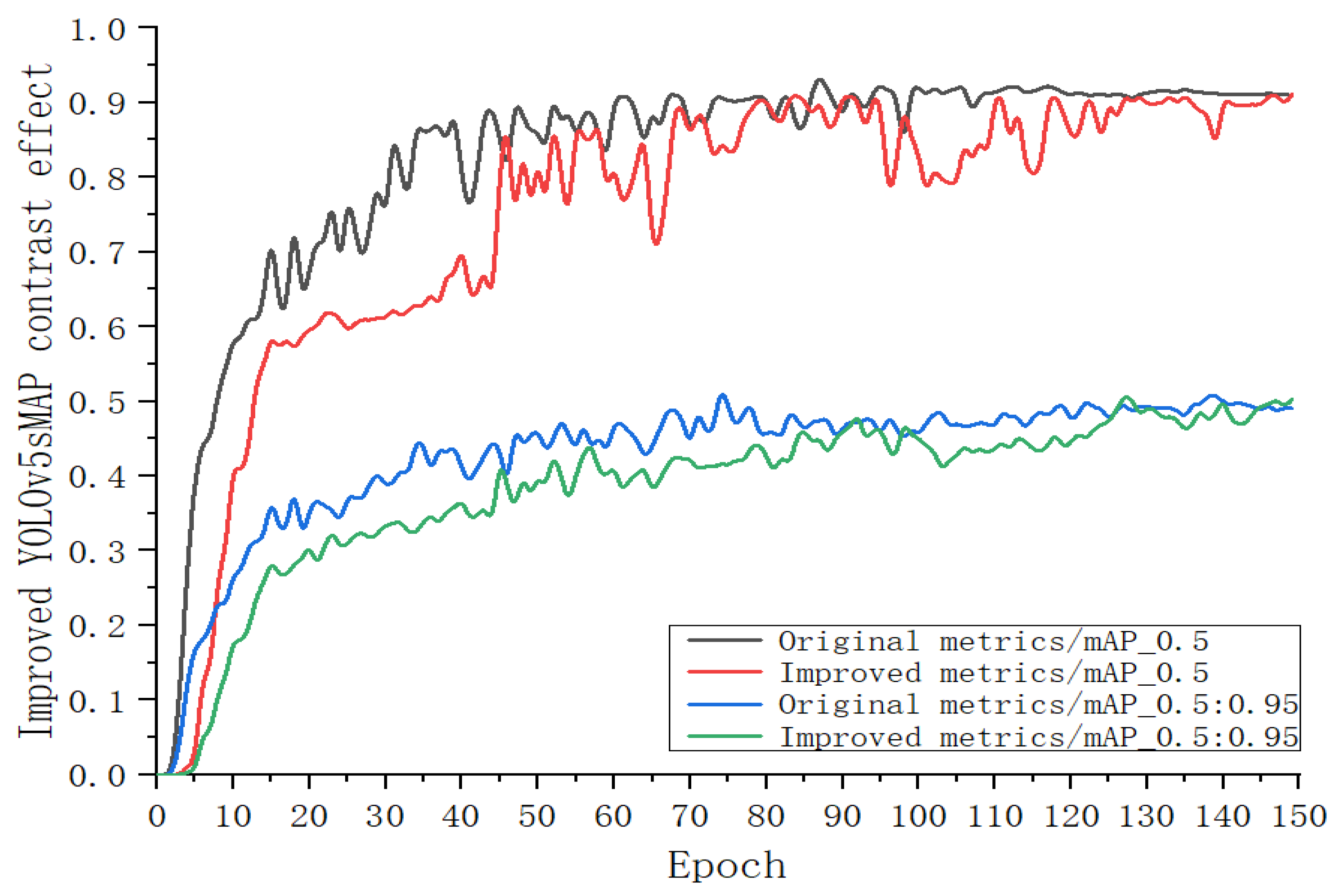
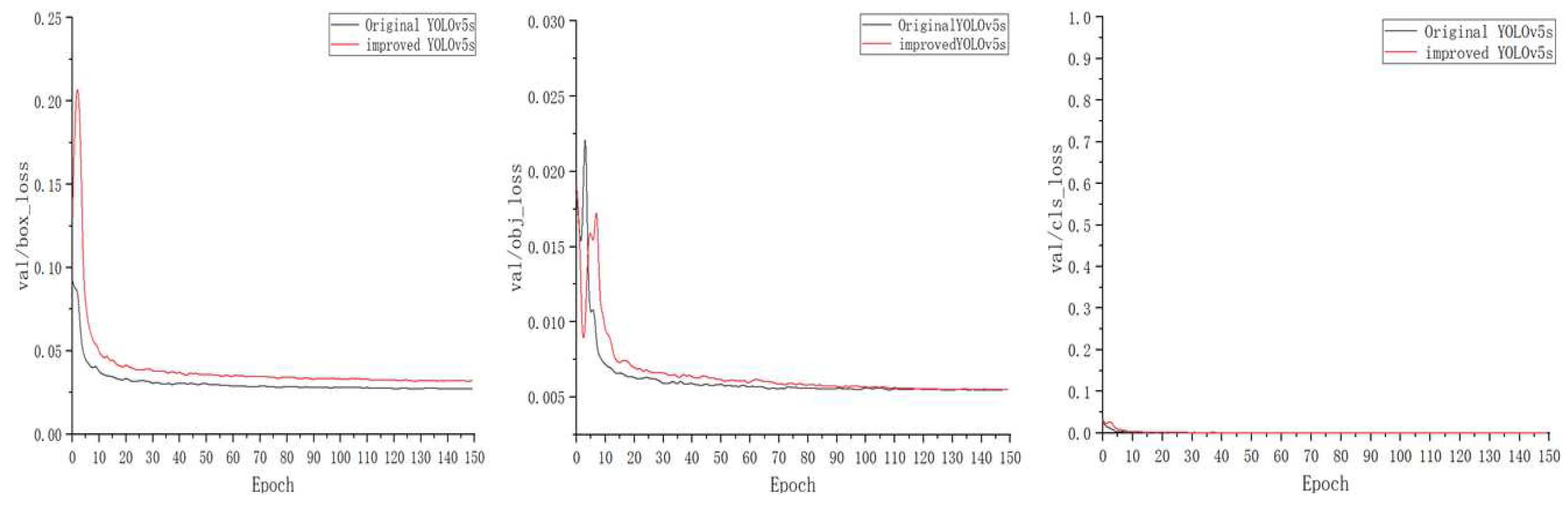
3. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Environment and its Configuration
3.2. Evaluation index
3.3. Object detection model detection compariso
| Model | MAP(%) | Params/M | Model size /MB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Textual method | 91.3 | 2.90 | 6.70 |
| YOLOv6s | 90.4 | 37.8 | 38.02 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 83.5 | 6.0 | 12.2 |
3.4. Effect comparison of different loss function models
| Model | MAP@0.5(%) | MAP_0.5:0.95(%) | Params/M | Model size /MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shufflenetv2+XIOU | 91.2 | 46.2 | 3.7 | 7.97 |
| Shufflenetv2+DIOU | 90.9 | 47.6 | 3.7 | 7.97 |
| Shufflenetv2+EIOU | 89.1 | 49.1 | 3.7 | 7.97 |
| Shufflenetv2+CIOU | 90.4 | 44.3 | 3.7 | 7.97 |
| Textual method | 91.3 | 50.2 | 2.9 | 6.70 |
| Backbone+Neck | MAP@0.5(%) | MAP_0.5:0.95(%) | Params/M | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shufflenetv2+4C3SE | 90.6 | 46.2 | 3.29 | 45 |
| Shufflenetv2+BoT+3C3SE | 90.3 | 49.2 | 3.21 | 45 |
| Shufflenetv2+BoT+3C3SE | 90.3 | 49.2 | 3.21 | 45 |
| Shufflenetv2+C3SE+BoT+2C | 90.8 | 45.3 | 3.27 | 43 |
| Shufflenetv2+2C+BoT+C3SE | 91.1 | 43.5 | 3.21 | 47 |
| Textual method | 91.3 | 50.2 | 2.95 | 47 |
3.5. Evaluation index
| YOLOv5s | T-method | EIOU | Shuf-v2 | Ghostnet | Mo-V3 | XIOU | MAP@0.5(%) | MAP_0.5:0.95(%) | Params/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 90.8 | 45.9 | 7.01 | ||||||
| √ | √ | 89.1 | 49.1 | 3.79 | |||||
| √ | 91.0 | 47.3 | 3.68 | ||||||
| √ | √ | 90.3 | 47.4 | 3.68 | |||||
| √ | √ | 89.1 | 49.2 | 3.54 | |||||
| √ | 90.4 | 47.1 | 3.79 | ||||||
| √ | √ | 91.2 | 49.0 | 3.79 | |||||
| √ | 91.3 | 50.2 | 2.91 |
3.6. Experimental analysis of target detection
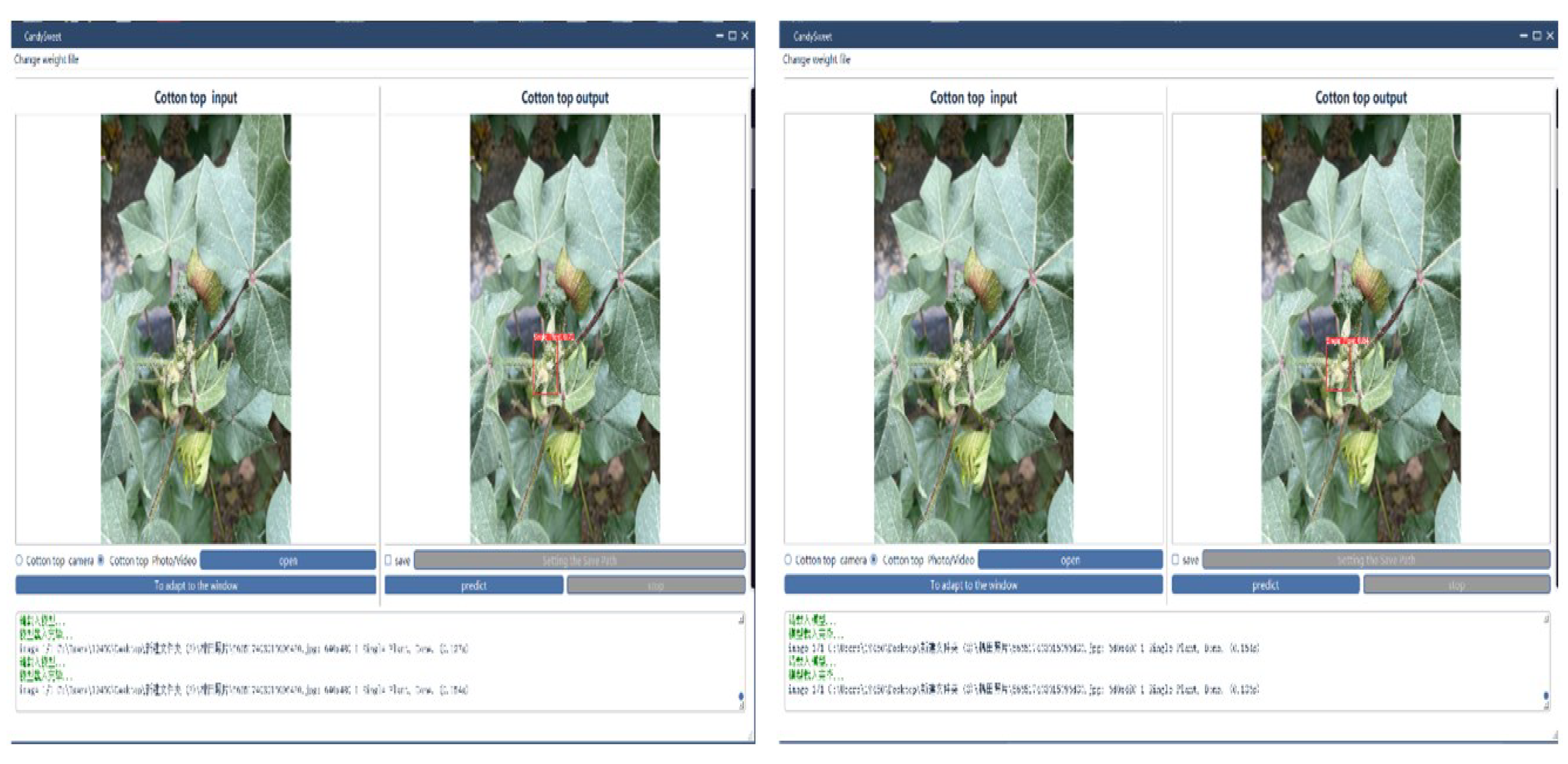
3.7. Different models test the effect of the image
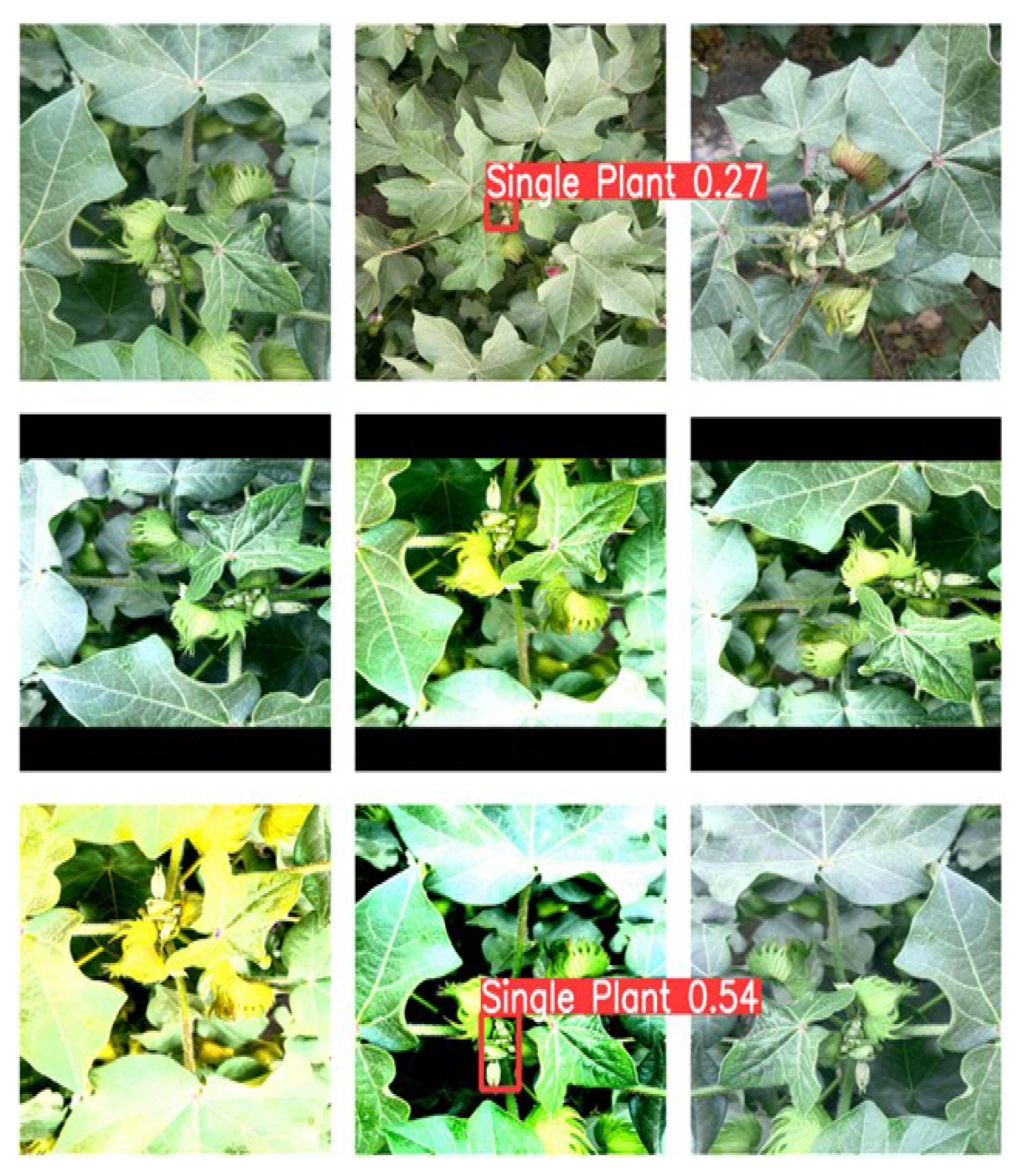
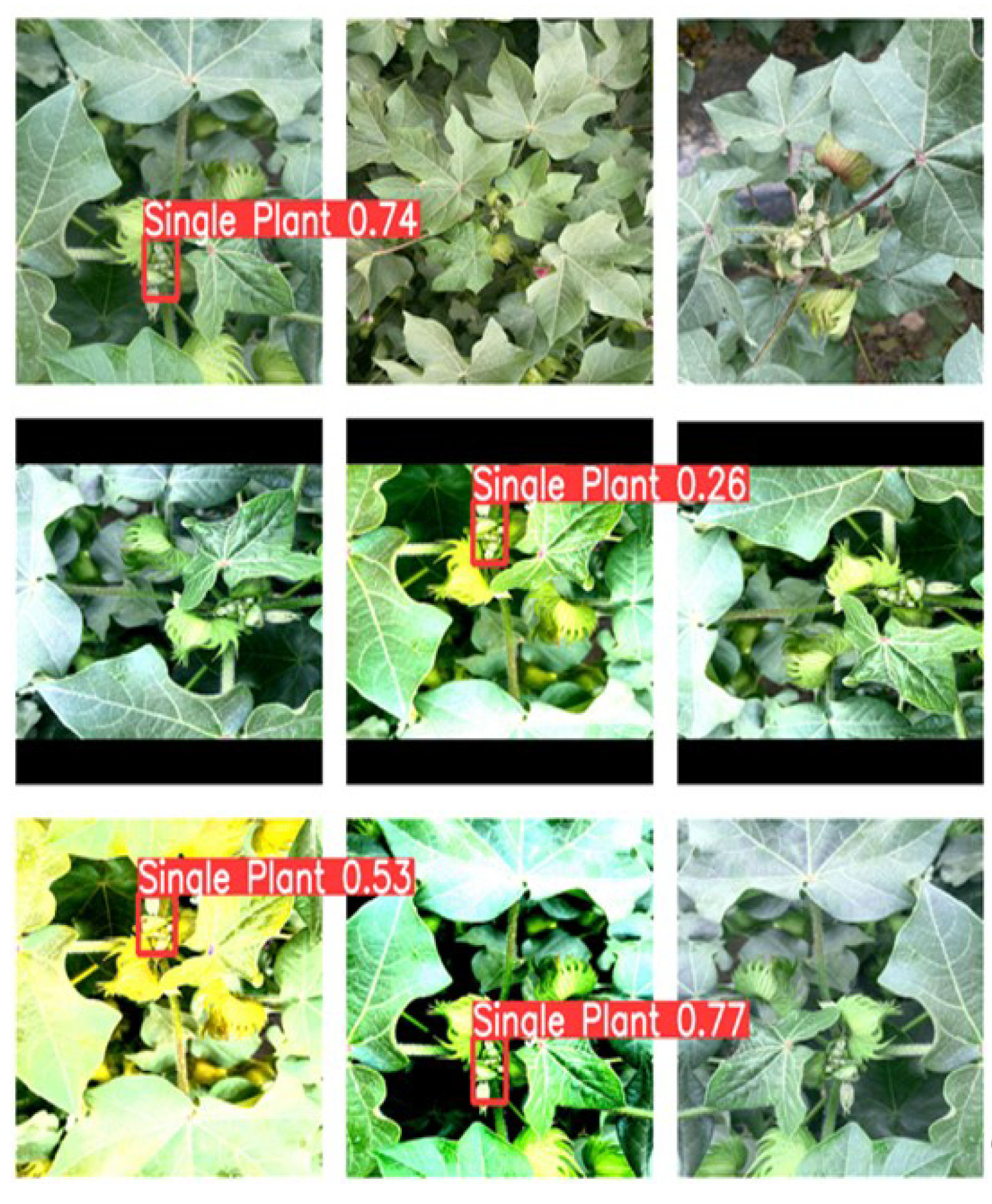


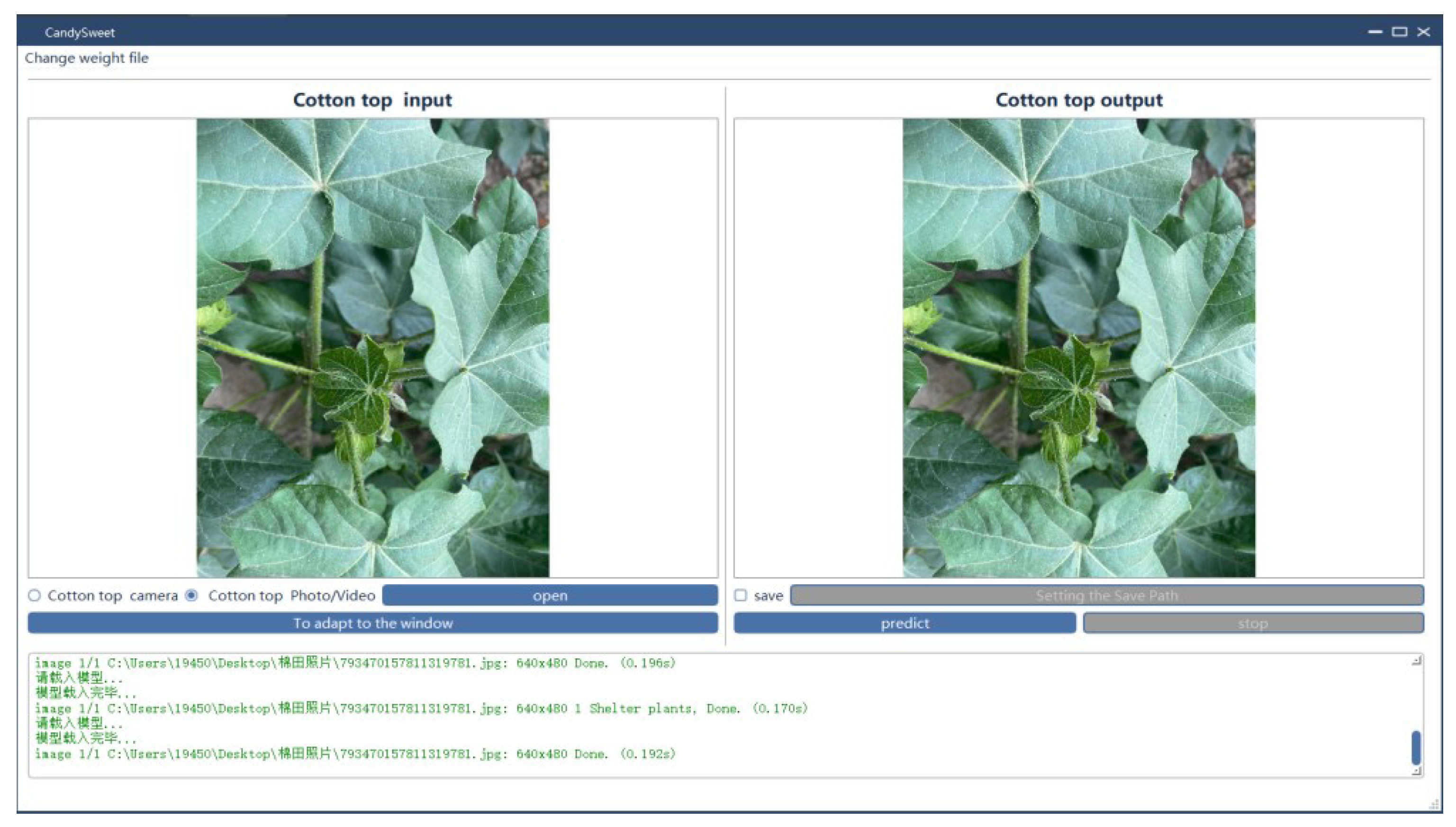
4. Experimental analysis of interface system
4.1. Interface system introduction
4.2. Interface system test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Carolis, B.; Ladogana, F.; Macchiarulo, N. Yolo trashnet: Garbage detection in video streams[C]//2020 IEEE Conference on Evolving and Adaptive Intelligent Systems (EAIS). IEEE 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016.
- Anguelov, D.; Liu Erhan, D.; et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. Springer, Cham, 2016.
- Girshick, R.; Jeff, D.; Trevor, D. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. IEEE Conference on computer vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014, pp. 2-6.
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Shen, S.M.; et al. Scale-aware fast r-cnn for pedestrian detection. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 2015, PP, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Scale-aware fast r-cnn for pedestrian detection. Computer Science 2015.
- Liu, J. Research on Cotton plant top identification system. Shihezi University. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Han, X.; Lan, Y.; Yi, L.; Wang, B.; Cui, L. Precision identification of cotton terminal bud based on YOLOv4 network. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology of China 2022, 24, 99–108 (In Chinese). (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao HY, M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Qian, H.; Guo, J. Lightweight target detection algorithm based on M-yolov4 model. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology 2022, 41, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, Q.; Bai, H. Light Weight Target detection algorithm for warehouse goods. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Song, T.; Liu, J. Remote Sensing military target detection algorithm based on lightweight Yolov3. Computer Engineering and Applications 2021, 57, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018, pp. 4510-4520.
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; et al. ShuffleNet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. European Conference on Computer Vision 2018.
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao HY, M.; Wu, Y.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 2020. 390–391.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; et al. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z. Focal and efficient iouloss for accurate bounding box regression. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. YOLOv6: a single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv arXiv:2209.02976, 2022.
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv arXiv:2207.02696, 2022.
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; et al. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G. Searching for mobilenetv3. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2019. 1314; 1314–132. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; et al. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020, pp. 1580-1589.

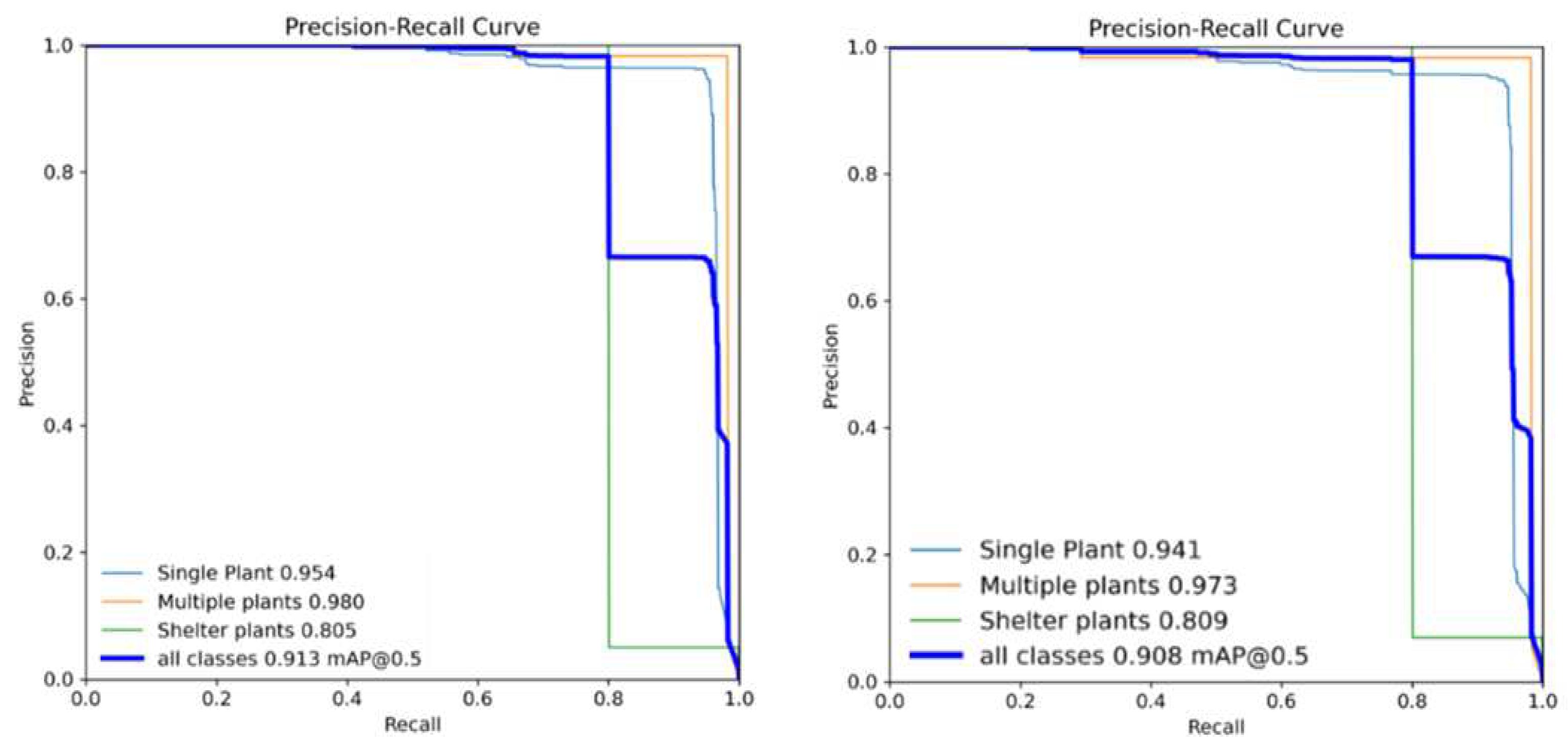
| Model | Single Plant | Multiple plants | Shelter plants |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 0.958 | 0.978 | 0.811 |
| Shufflenetv2+XIOU | 0.937 | 0.978 | 0.821 |
| MobileNetV3+EIOU | 0.948 | 0.984 | 0.764 |
| Ghostnet | 0.947 | 0.954 | 0.806 |
| Ghostnet+EIOU | 0.937 | 0.969 | 0.804 |
| Shufflenetv2 | 0.937 | 0.979 | 0.802 |
| Textual method | 0.954 | 0.980 | 0.805 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




