Submitted:
02 January 2023
Posted:
26 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Free Radical Stress and Antioxidants in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Diseases
Diet as Oxidant and Antioxidant Agent
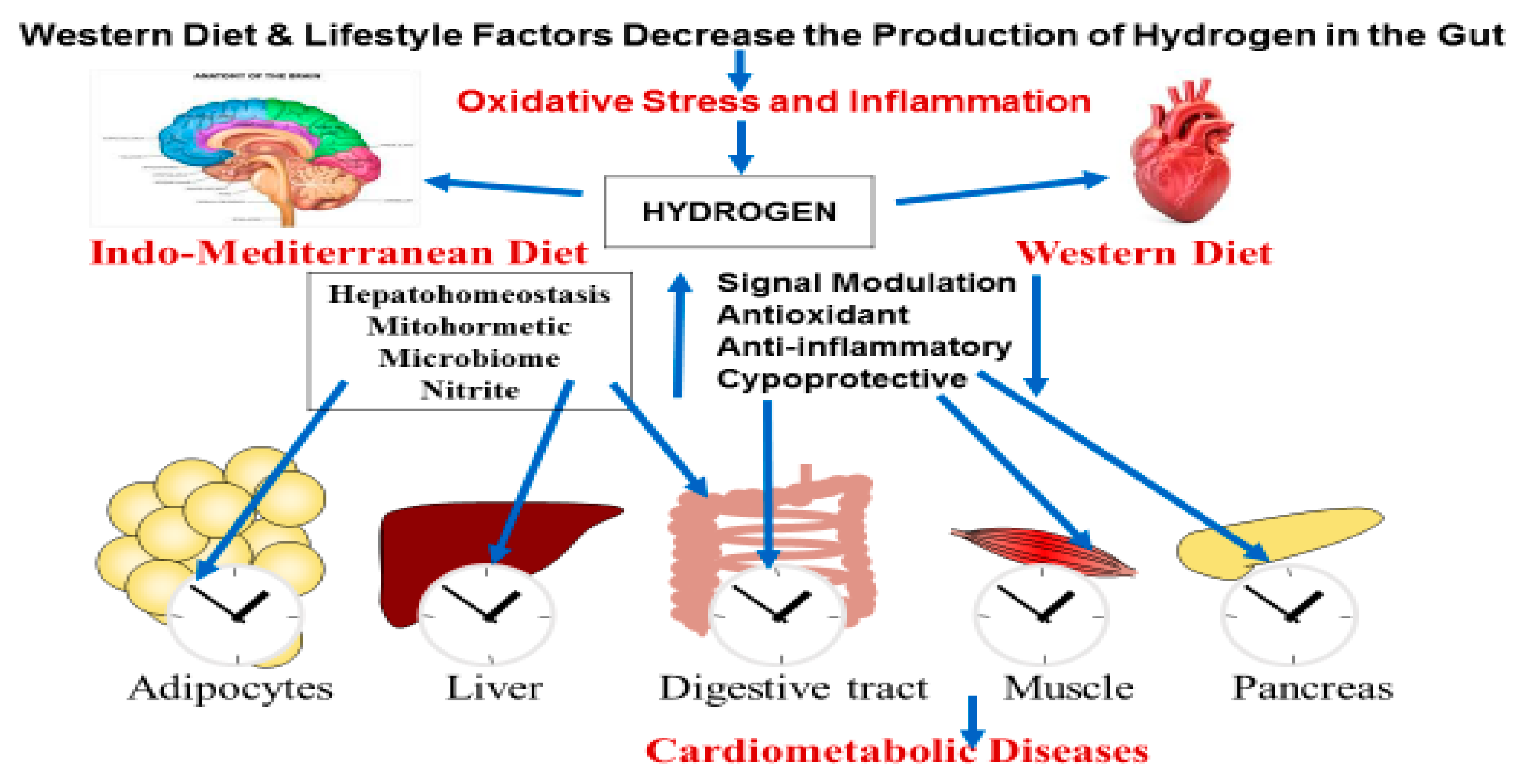
Production of Molecular Hydrogen in the Gut
Molecular Hydrogen Production by Gastrointestinal Microbiota
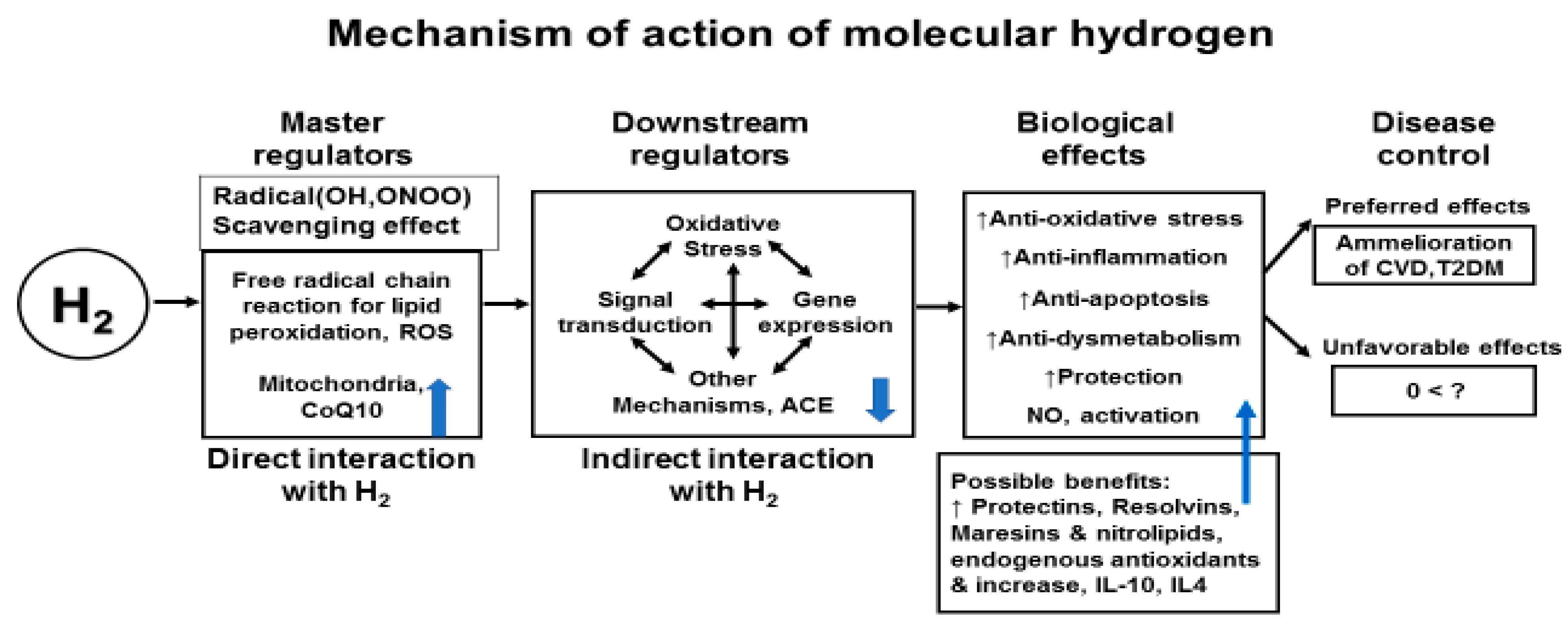
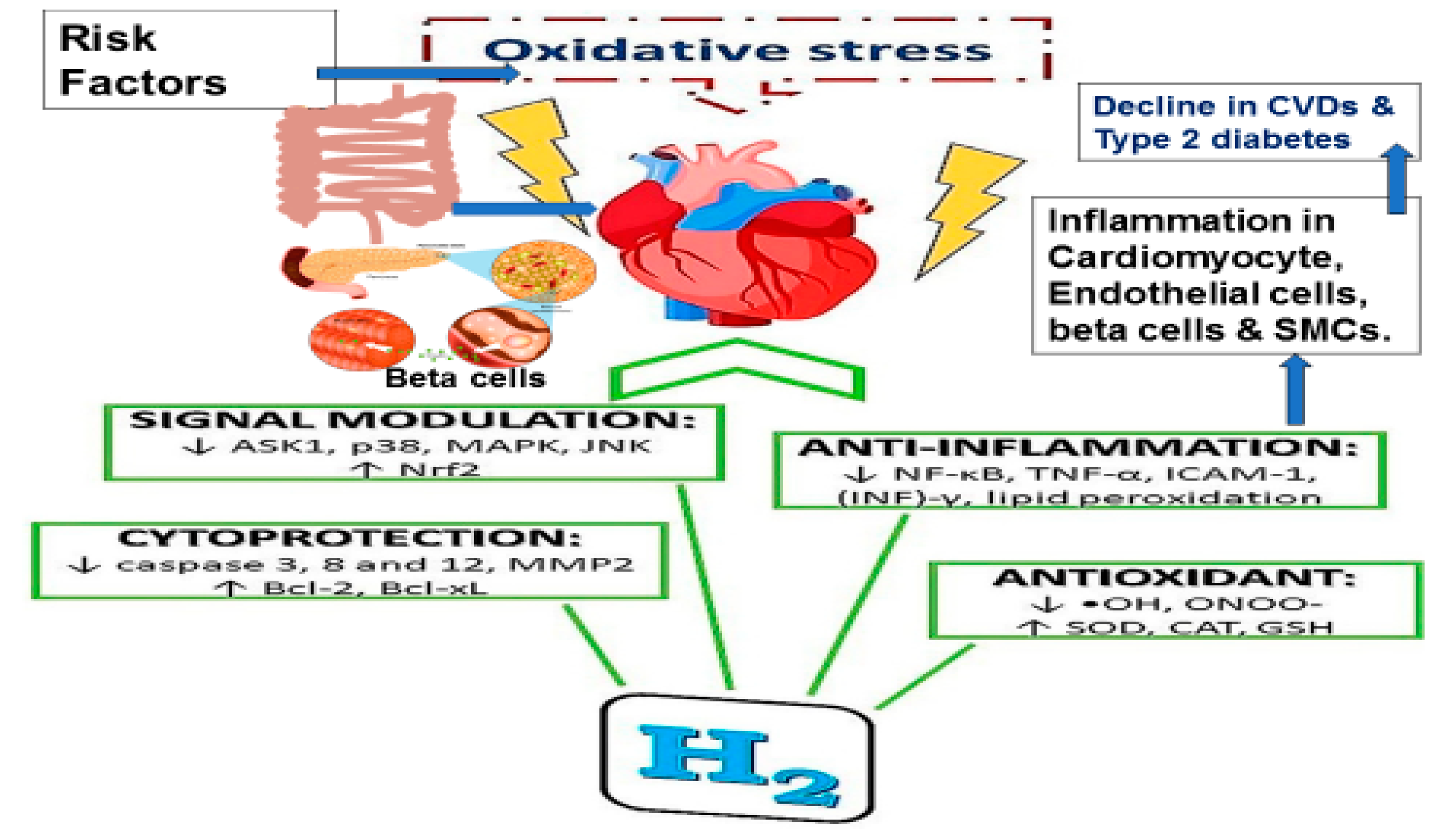
Molecular Hydrogen Therapy for Cardiovascular Diseases
Effects of Hydrogen in Stroke
Effects of Molecular Hydrogen on Blood Lipoproteins
Conclusions
Authors Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest
References
- Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76:2982–3021. [CrossRef]
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1736–88. [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan M, Mensah GA, Varieur Turco J, et al. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk: A Compass for Future Health. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 12 December 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jiang S, Liu H, Li C. Dietary regulation of oxidative stress in chronic metabolic diseases. Foods. 2021 Aug 11;10(8):1854. [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova K, Koelman L, Rodrigues CE. Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: A systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biology, 2021; 42:101869.
- Micha R, Penalyo JL, Cidhea F, Imamura F, Rehm CD, Mozaffarian D. Association between dietary factors and mortality from heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes in the United States. JAMA 2017; 317 (9): 912-924. [CrossRef]
- Sacco RL, Roth GA, Reddy KS, Arnett DK, Bonita R, Gaziano TA, Heidenreich PA, Huffman MD, Mayosi BM, Mendis S, Murray CJL, Perel P, Piñeiro DJ, Smith SC Jr, Taubert KA, Wood DA, Zhao D, Zoghbi WA. The heart of 25 by 25: achieving the goal of reducing global and regional premature deaths from cardiovascular diseases and stroke: a modeling study from the American Heart Association and World Heart Federation. Circulation 2016; 133: e674-e690. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Fedacko, J.; Fatima, G.; Magomedova, A.; Watanabe, S.; Elkilany, G. Why and How the Indo-Mediterranean Diet May Be Superior to Other Diets: The Role of Antioxidants in the Diet. Nutrients 2022; 14, 898. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Fedacko, J.; Pella, D.; Fatima, G.; Elkilany, G.; Moshiri, M.; Hristova, K.; Jakabcin, P.; Vanova, N. High Exogenous Antioxidant, Restorative Treatment (Heart) for Prevention of the Six Stages of Heart Failure: The Heart Diet. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1464. [CrossRef]
- Mojto V, Singh RB, Gvozdjakova A, Pella D, Fedacko J, Pella D. Molecular hydrogen: a new approach for the management of cardiovascular diseases. World Heart J 2018;10: 83-93.
- Ichikawa Y, Yamamoto H, Hirano Si, Sato B, Takefuji Y, Satoh F. The overlooked benefits of hydrogen-producing bacteria. Med Gas Res 2022;12. [cited 2022 Dec 20]. Available from: https://www.medgasres.com/preprintarticle.asp?id=344977.
- Slezák, J.; Kura, B.; Frimmel, K.; Zálešák, M.; Ravingerová, T.; Viczenczová, C.; Okruhlicová, Ľ.; Tribulová, N. Preventive and therapeutic application of molecular hydrogen in situations with excessive production of free radicals. Physiol. Res. 2016; 65 (Suppl. 1): S11–S28.
- Sakai T, Sato B, Hara K, Hara Y, Naritomi Y, Koyanagi S, Hara H, Nagao T, Ishibashi T. Consumption of water containing over 3.5 mg of dissolved hydrogen could improve vascular endothelial function. Vascular Health and Risk Management 2014; 10: 591–597.
- Ichihara, M.; Sobue, S.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Beneficial biological effects and the underlying mechanisms of molecular hydrogen- Comprehensive review of 321 original articles. Med. Gas Res. 2015; 5: 1–21.
- Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy Reviews 2010; 4 (8): 118-126. [CrossRef]
- Takac I, Schroder K, Brandes RP. The Nox family of NADPH oxidases: friend or foe of the vascular system. Curr Hypertens Rep 2012; 14: 70–78.
- Montezano AC, Touyz RM. Reactive oxygen species and endothelial function role of nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and Nox family nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidases. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2012; 110: 87–94.
- Al Ghouleh I, Khoo NK, Knaus UG. Oxidases and peroxidases in cardiovascular and lung disease: new concepts in reactive oxygen species signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 2011; 51: 1271–1288.
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 245–313.
- Deryugina AV, Danilova DA, Brichkin YD, Taranov EV, Nazarov EI, Pichugin VV, Medvedev AP, Riazanov MV, Fedorov SA, Andrej YS, Makarov EV. Molecular hydrogen exposure improves functional state of red blood cells in the early postoperative period: a randomized clinical study.Med Gas Res. 2023 Apr-Jun;13(2):59-66. [CrossRef]
- Yang M, Dong Y, He Q, et al. Hydrogen: a novel option in human disease treatment. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8384742. [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13(6):688-694. [CrossRef]
- Yu Y, Feng J, Lian N, et al. Hydrogen gas alleviates blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive dysfunction of septic mice in an Nrf2-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106585.
- Nie C, Zou R, Pan S, A R, Gao Y, Yang H, Bai J, Xi S, Wang X, Hong X, Yang W. Hydrogen gas inhalation ameliorates cardiac remodelling and fibrosis by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome in myocardial infarction rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(18):8997-9010. [CrossRef]
- LeBaron T, Singh RB, Fatima G, Kartikey K, Sharma JP, Ostojic SM, Gvozdjakova A, Kura B, Noda M, Mojto V, Niaz MA, Slezak J.The Effects of 24-Week, High-ConcentrationHydrogen-Rich Water on Body Composition, Blood Lipid Profiles and Inflammation Biomarkers in Men and Women with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020;13:889-896.
- Singh RB, Halabi G, Fatima G, Rai RH, Tarnava AT, LeBaron TW. Molecular hydrogen as an adjuvant therapy may be associated with increased oxygen saturation and improved exercise tolerance in a COVID-19 patient. Clin Case Reports 9: e05039. 1 of 6. [CrossRef]
- Akita Y, Higashiyama M, Kurihara C, Ito S, Nishii S, Mizoguchi A, Inaba K, Tanemoto R, Sugihara N, Hanawa Y, Wada A, Horiuchi K, Okada Y, Narimatsu K, Komoto S, Tomita K, Takei F, Satoh Y, Saruta M, Hokari R. Ameliorating Role of Hydrogen-Rich Water Against NSAID-Induced Enteropathy via Reduction of ROS and Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids.
- Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Dec 7:1-11. [CrossRef]
- Koyama Y, Harada S, Sato T, Kobayashi Y, Yanagawa H, Iwahashi T, Tanaka H, Ohata K, Imai T, Ohta Y, Kamakura T, Kobayashi H, Inohara H, Shimada S. Therapeutic strategy for facial paralysis based on the combined application of Si-based agent and methylcobalamin.
- Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Nov 21;32:101388. [CrossRef]
- Hong Y, Dong G, Li Q, Wang V, Liu M, Jiang G, Bao D, Zhou J. Effects of pre-exercise H2 inhalation on physical fatigue and related prefrontal cortex activation during and after high-intensity exercise. Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 2;13:988028. eCollection 2022. [CrossRef]
- Eda, N.; Tsuno, S.;Nakamura, N.; Sone, R.; Akama, T.;Matsumoto, M. Effects of Intestinal Bacterial Hydrogen Gas Production on Muscle Recovery following Intense Exercise in Adult Men: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4875. [CrossRef]
- Perry RJ, Peng L, Barry NA, Cline GW, Zhang D, Cardone RL, Petersen KF, Kibbey RG, Goodman AL, Shulman GI. Acetate mediates a microbiome–brain–β- cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature 2016; 534: 213-217. [CrossRef]
- De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Goncalves D, Vinera J, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Bäckhed F, Mithieux G. Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 2014; 156: 84-96. [CrossRef]
- Levitt MD. Excretion of hydrogen gas in man. N Engl J Med 1969; 281: 122-127. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196907172810303.
- Hajishengallis G, Darveau RP, Curtis MA. The keystone-pathogen hypothesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 2012; 10 (10): 717–725. [CrossRef]
- Lupp C, Robertson ML, Wickham ME, Sekirov I, Champion OL, Gaynor EC, Finlay BB. Host-mediated inflammation disrupts the intestinal microbiota and promotes the overgrowth of Enterobacteriaceae. Cell Host Microbe 2007; 2: 119–129.
- Donovan SM. Introduction to the special focus issue on the impact of diet on gut microbiota composition and function and future opportunities for nutritional modulation of the gut microbiome to improve human health. Gut Microbes 2017; 8 (2): 75-81.
- LeBaron TW, Kura B, Kalocayova B, Tribulova N, Slezak J. A New Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders. Molecular Hydrogen Significantly Reduces the Effects of Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019; 24(11): 276. [CrossRef]
- LeBaron TW, Sharpe R, Ohno K. Electrolyzed-Reduced Water: Review I. Molecular Hydrogen Is the Exclusive Agent Responsible for the Therapeutic Effects. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23 (23):14750. [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Recent Progress Toward Hydrogen Medicine: Potential of Molecular Hydrogen for Preventive and Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011; 17:2241-52.
- Carr AC, McCall MR, Frei B. Oxidation of LDL by myeloperoxidase and reactive nitrogen species: reaction pathways and antioxidant protection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000;20: 1716–1723.
- Yoshida H, Kisugi R. Mechanisms of LDL oxidation. Clin Chim Acta 2010; 411: 1875–1882.
- Chia S, Qadan M, Newton R, Ludlam CA, Fox KA, Newby DE. Intra-arterial tumor necrosis factor-alpha impairs endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and stimulates local tissue plasminogen activator release in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 695–701.
- Szekanecz Z, Kerekes G, Soltesz P. Vascular effects of biologic agents in RA and spondyloarthropathies. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2009; 5: 677–684.
- Zálešák M, Kura B, Graban J, Farkašová V, Slezák J, Ravingerová T. Molecular hydrogen potentiates beneficial anti-infarct effect of hypoxic postconditioning in isolated rat hearts: Novel cardioprotective intervention. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017; 95 (8): 888-893. [CrossRef]
- Slezak J, Kura B, Babal P, Barancik M, Ferko M, Frimmel K, Kalocayova B, Kukreja RC, Lazou A, Mezesova L, Okruhlicova L, Ravingerova T, Singal PK, Szeiffova Bacova B, Viczenczova C, Vrbjar N, Tribulova N. Potential markers and metabolic processes involved in mechanism of radiation-induced heart injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017; 95 (10): 1190-1203. [CrossRef]
- Kura B, Bagchi AK, Akolkar G, Singal P, Slezák J. Myocardial changes after mediastinal irradiation in rats: molecular mechanisms and potential targets to minimize the adverse effects. In: Adaptation Biology and Medicine, Volume 8: Current Trends. New Delhi: Narosa Publishing House; 2017. pp. 93-122. ISBN 978-81-8487-567-6.
- Viczenczova C, Kura B, Chaudagar KK, Szeiffova Bacova B, Egan Benova T, Barancik M, Knezl V, Ravingerova T, Tribulova N, Slezak J. Myocardial connexin-43 is up-regulated in response to acute cardiac injury in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017; 95 (10): 1190-1203. [CrossRef]
- Kura B, Babal P, Slezak J. Implication of microRNAs in the development and potential treatment of radiation-induced heart disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017; 95 (10): 1236-1244. [CrossRef]
- Kura B, Yin C, Frimmel K, Krizak J, Okruhlicova L, Kukreja RC, Slezak J. Changes of microRNA-1, -15b and -21 levels in irradiated rat hearts after treatment with potentially radioprotective drugs. Physiological Research 2016; 65 (Suppl. 1): S129-S137.
- Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S, Ohta S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 2007; 13 (6): 688-694.
- Ishibashi T. Molecular hydrogen: New antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and related diseases. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2013; 19: 6375-6381. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi T, Sato B, Shibata S, Sakata T, Hara Y, Naritomi Y, Koyanagi S, Hara H, Nagao T. Therapeutic efficacy of infused molecular hydrogen in saline on rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Int Immunopharmacol 2014; 21: 468-473.
- Korovljev D, Trivic T, Drid P, Ostojic SM. Molecular hydrogen affects body composition, metabolic profiles, and mitochondrial function in middle-aged overweight women. Ir J Med Sci 2018; 187 (1): 85-89. [CrossRef]
- Song G, Li M, Sang H, Zhang L, Li X, Yao S, Yu Y, Zong C, Xue Y, Qin S. Hydrogen-rich water decrease serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and improves high density lipoprotein function in patients with potential metabolic syndrome. J Lipid Res 2013; 54: 1884-1893.
- Song G, Lin Q, Zhao H, Liu M, Ye F, Sun Y, Yu Y, Guo S, Jiao P, Wu Y, Ding G, Xiao Q, Qin S. Hydrogen activates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-dependent efflux ex vivo and improves high-density lipoprotein function in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A double-blinded, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100 (7): 2724-2733. Epub 2015 May 15. [CrossRef]
- Liu CL, Zhang K, Chen G. Hydrogen therapy: from mechanism to cerebral diseases. Med Gas Res 2016; 6 (1): 48-54.
- Nagatani K, Wada K, Takeuchi S, Kobayashi H, Uozumi Y, Otani N, Fujita M, Tachibana S, Nawashiro H. Effect of hydrogen gas on the survival rate of mice following global cerebral ischemia. Shock (Augusta, Ga) 2012; 37: 645–652.
- Zhang Y, Sun Q, He B, Xiao J, Wang Z, Sun X. Anti-inflammatory effect of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Int J Cardiol 2011; 148: 91–95.
- Chen CH, Manaenko A, Zhan Y, Liu WW, Ostrowki RP, Tang J, Zhang JH. Hydrogen gas reduced acute hyperglycemia-enhanced hemorrhagic transformation in a focal ischemia rat model. Neuroscience 2010; 169: 402–414.
- Chen S, Yang Q, Chen G, Zhang JH. An update on inflammation in the acute phase of intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res 2015; 6: 4–8.
- Engelhardt B, Sorokin L. The blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: function and dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol 2009; 31: 497–511.
- Manaenko A, Lekic T, Ma Q, Ostrowski RP, Zhang JH, Tang J. Hydrogen inhalation is neuroprotective and improves functional outcomes in mice after intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011; 111: 179–183.
- Munakata A, Ohkuma H, Shimamura N. Effect of a free radical scavenger, edaravone, on free radical reactions: related signal transduction and cerebral vasospasm in the rabbit subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011; 110: 17–22.
- Nakao A, Toyoda Y, Sharma P, Evans M, Guthrie N. Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome—an open label pilot study. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition 2010; 46 (2): 140-149. [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama S, Hasegawa G, Asano M, Hosoda H, Fukui M, Nakamura N, Kitawaki J, Imai S, Nakano K, Ohta M, Adachi T, Obayashi H, Yoshikawa T. Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutr Res 2008; 28 (3): 137-143. [CrossRef]
- Kamimura N, Ichimiya H, Iuchi K, Ohta S. Molecular hydrogen stimulates the gene expression of transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α to enhance fatty acid metabolism. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2016 Apr 28;2:16008. eCollection 2016. [CrossRef]
- Sobue S, Inoue C, Hori F, Qiao S, Murate T, Ichihara M. Molecular hydrogen modulates gene expression via histone modification and induces the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Nov 4;493(1):318-324. Epub 2017 Sep 7. [CrossRef]
- Singh RB, Fedacko J, Saboo B, Niaz MA, Maheshwari A, Verma N, Bharadwaj K. Association of higher omega-6/omega-3 fatty acids in the diet with higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome in North India. MOJ Public Health. 2017; 6 (6): 00193. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Nabavizadeh, F.; Fedacko, J.; Pella, D.; Vanova, N.; Jakabcin, P.; Fatima, G.; Horuichi, R.;Takahashi, T.; Mojto, V.; et al. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension viaIndo-Mediterranean Foods, May Be Superior to DASH Diet Intervention.Nutrients 2023, 15, 46. [CrossRef]
- Gvozdjáková A, Kucharská J, Kura B, Vančová O, Rausová Z, Sumbalová Z, Uličná O, Slezák J. A new insight into the molecular hydrogen effect on coenzyme Q and mitochondrial function of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;98(1):29-34. [CrossRef]
- Kucharská J, Gvozdjáková A, Kura B, et al. Effect of molecular hydrogen on coenzyme Q in plasma, myocardial tissue and mitochondria of rats. J Nutr Health Food Eng. 2018;8(5): 362‒364. [CrossRef]
- Christl SU, Murgatroyd PR, Gibson GR, Cummings JH. Production, metabolism, and excretion of hydrogen in the large intestine. Gastroenterology. 1992,102(4 Pt 1):1269-77.
- Suzuki A, Ito M, Hamaguchi T, Mori H, Takeda Y, Baba R, Watanabe T, Kurokawa K, Asakawa S, Hirayama M, Ohno K. Quantification of hydrogen production by intestinal bacteria that are specifically dysregulated in Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 2018, 13(12):e0208313. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi T. Therapeutic Efficacy of Molecular Hydrogen: A New Mechanistic Insight. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(9):946-955. [CrossRef]

| Data | Hydrogen rich water (n-30) | Placebo (n=30) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data, mg/dl | Baseline | After 24 weeks | Baseline | After 24 weeks |
| Cholesterol | 187.7 ± 32.4 | 169.2 ± 26.1*** | 184.3 ± 37.4 | 184.4 ± 38.6 |
| LDL-Cholesterol | 109.0 ± 34.4 | 102.5 ± 28.0 | 105.5 ± 42.0 | 106.0 ± 43.3 |
| HDL cholesterol | 41.7 ± 4.2 | 40.4 ± 1.8 | 41.8 ± 2.3 | 42.3 ± 2.4 |
| VLDL cholesterol | 37.3 ± 17.9 | 28.0 ± 11.3** | 36.8 ± 20.6 | 37.3 ± 20.5 |
| Triglycerides | 189.8 ± 93.3 | 142.4 ± 65.0** | 184.4 ± 102.8 | 185.6 ± 101.3 |
| C-reactive proteins | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1* | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.5 |
| Hydrogen rich water(n=30) | Placebo (n=30) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data, mg/dl | Baseline | After 24 weeks | Baseline | After 24 weeks |
| Fasting blood glucose | 121.5 ± 61.0 | 103.1 ± 33.0* | 123.9 ± 43.4 | 126.4 ± 42.3 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.8 ± 0.9 | 5.1 ± 0.2*** | 6.2 ± 1.2 | 6.1 ± 1.2 |
| TNF-α | 4.8 ± 1.2 | 3.9 ± 0.6*** | 4.8 ± 1.3 | 4.8 ± 1.3 |
| IL-6 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.2** | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.7±0.6 |
| TBARS | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3* | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| Melondialdehyde | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.2*** | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 0.2 |
| Diene conjugates | 27.8 ± 1.0 | 26.7 ± 0.5*** | 28.3 ± 0.8 | 28.3 ± 0.8 |
| Vitamin E | 23.0 ± 2.3 | 26.8 ± 1.9*** | 23.0 ± 1.5 | 23.1 ± 1.1 |
| Vitamin C | 20.7 ± 2.5 | 24.2 ± 1.8*** | 20.7 ± 2.5 | 20.8 ± 2.4 |
| Nitrite | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 0.68 ± 0.06*** | 0.66 ± 0.04 | 0.65 ± 0.03 |
| Angiotensin converting enzyme | 85.2 ± 7.8 | 80.7 ± 5.8*** | 84.5 ± 8.8 | 83.8 ± 8.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





