Submitted:
16 January 2023
Posted:
19 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Cholesterol-Membrane Interactions
1.2. GPCR-Cholesterol Interactions
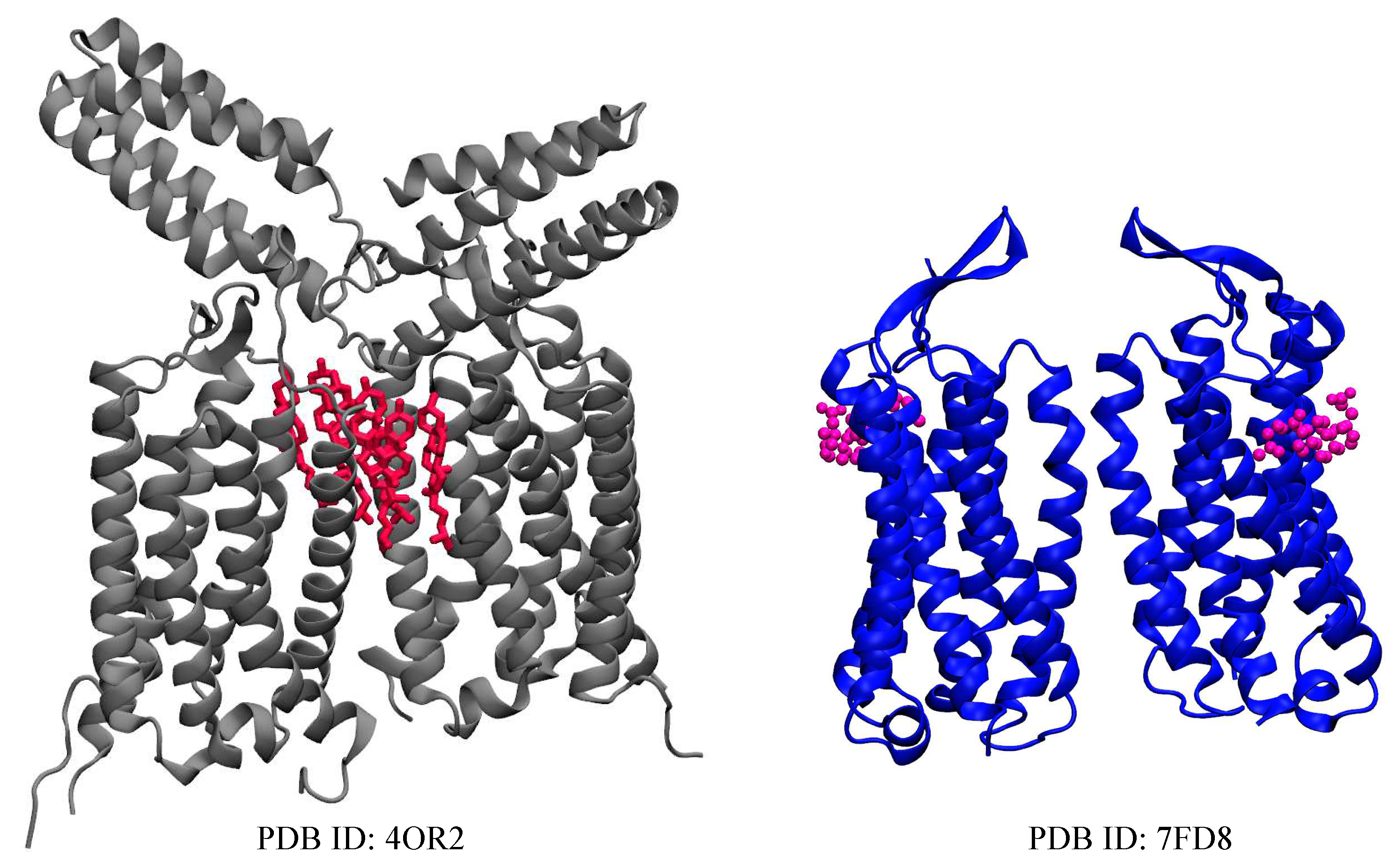
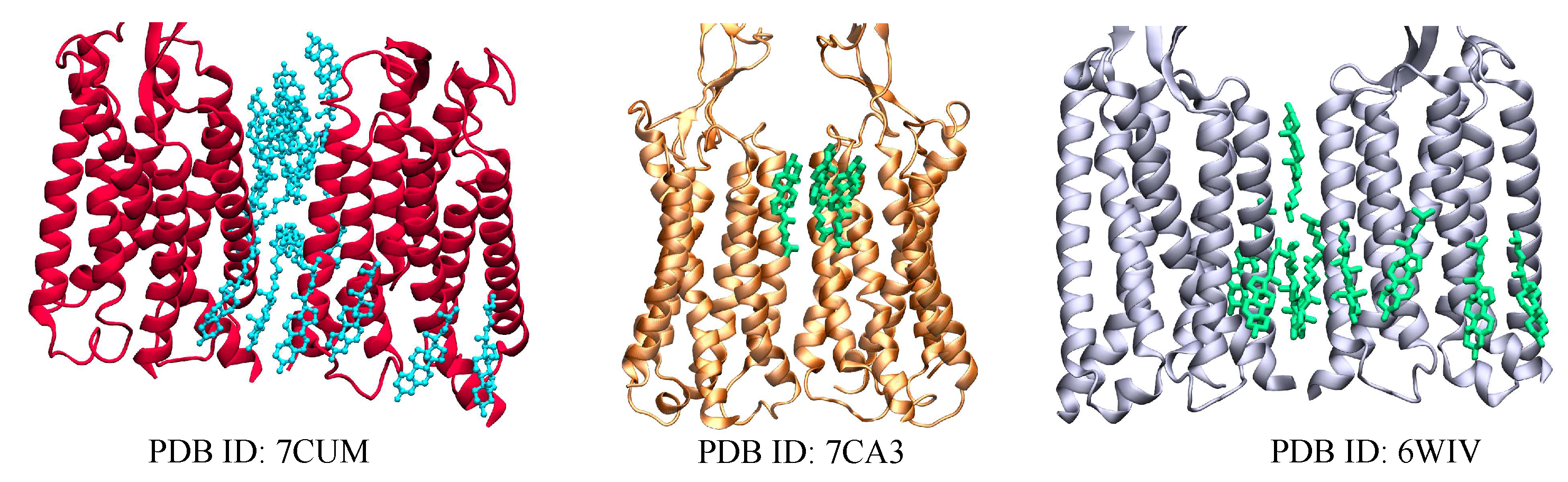
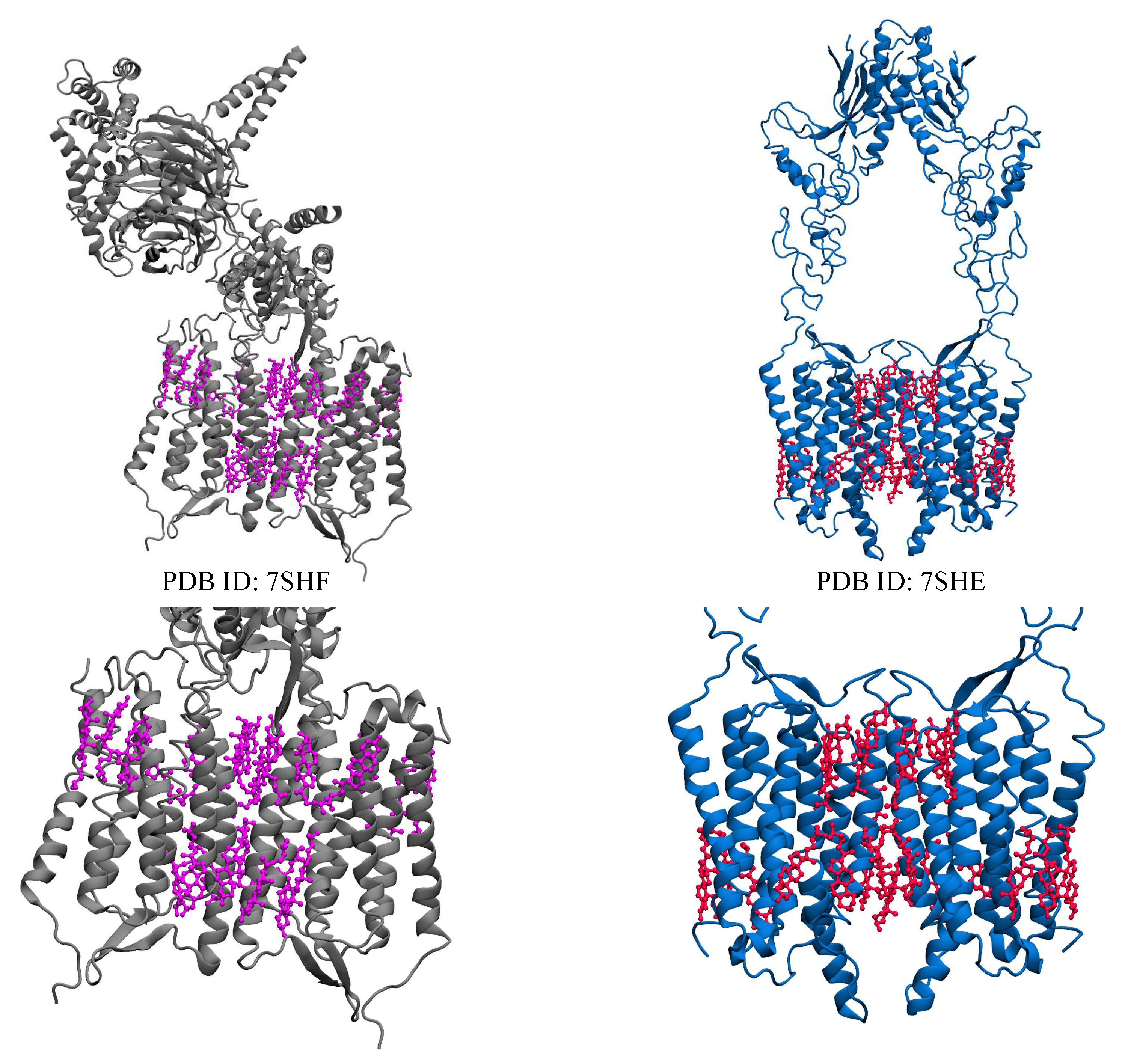
| Name | PDB ID* | # of Choleseterols in TM |
|---|---|---|
| mGluR1 | 4OR2 [17] | 6 CLR |
| mGluR5 | 7FD8 [16] | 2 CHS |
| () | 6WIV [75] | 10 CLR |
| 7CUM [76] | 16 CLR | |
| 7CA3 [76] | 3 CLR | |
| Orphan receptor (GPR158) | 7SHF [77] | 22 CLR |
| 7SHE [77] | 22 CLR** |
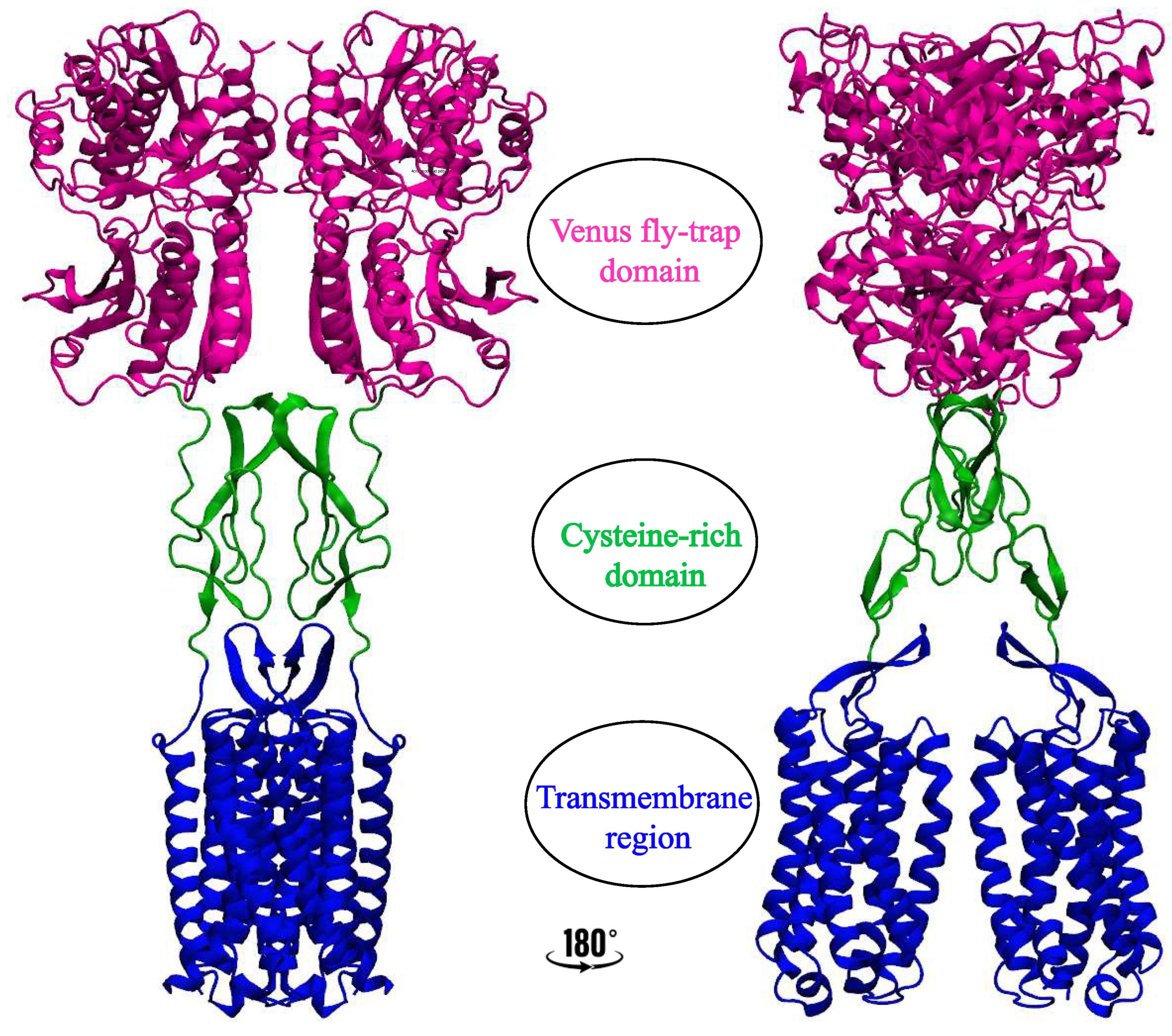
2. Significance and Interaction Sites of Cholesterol in Class C GPCRs
2.1. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRs)
2.2. GABAB Receptors
2.3. Taste Receptor
2.4. Calcium Sensing Receptor-Related Receptor
2.5. Orphan Receptor
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPCR | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| CHS | Cholesteryl hemisuccinate |
| CLR | Cholesterol |
| mGluR | Metabotropic glutamate receptors |
| CRAC | Cholesterol Recognition/Interaction Amino Acid Consensus (CRAC) |
| MD(S) | Molecular dynamics (simulation) |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric acid |
| TAS1R1 | Taste 1 receptor member 1 |
| TAS1R2 | Taste 1 receptor member 2 |
| TAS1R3 | Taste 1 receptor member 3 |
| RORs | Retinoid-related orphan receptors |
| CASR | calcium-sensing receptor |
| TM(D) | Transmembrane (domain) |
| NTD | N-terminal domain |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
| PLC | phospholipase C |
| MMP-2 | Matrix metalloproteinase-2 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
References
- Maurice, P.; Kamal, M.; Jockers, R. Asymmetry of GPCR oligomers supports their functional relevance. Trends in pharmacological sciences 2011, 32, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, A.D.; Watts, A. Regulation of G protein-coupled receptors by palmitoylation and cholesterol, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Cherezov, V.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Hanson, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kuhn, P.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K.; others. High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human β2-adrenergic G protein–coupled receptor. science 2007, 318, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffientini, U.; Graham, A. Intracellular cholesterol transport proteins: roles in health and disease. Clinical Science 2016, 130, 1843–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.G. Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Biophysical Journal 2019, 116, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakany, F.; Kovacs, T.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. Direct and indirect cholesterol effects on membrane proteins with special focus on potassium channels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2020, 1865, 158706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, M.; Zhang, C.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Kobilka, B.K.; Müller, D.J. Cholesterol increases kinetic, energetic,and mechanical stability of the human β2-adrenergic receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polasa, A.; Moradi, M. Deciphering the Inter-domain Decoupling in the Gram-negative Bacterial Membrane Insertase. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind Kumar, V.; Polasa, A.; Agrawal, S.; Kumar, T.K.S.; Moradi, M. Binding affinity estimation from restrained umbrella sampling simulations. Nature Computational Science 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasa, A.; Mosleh, I.; Losey, J.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Beitle, R.; Moradi, M. Developing a rational approach to designing recombinant proteins for peptide-directed nanoparticle synthesis. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 3161–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind Kumar, V.; Ogden, D.S.; Isu, U.H.; Polasa, A.; Losey, J.; Moradi, M. Prefusion spike protein conformational changes are slower in SARS-CoV-2 than in SARS-CoV-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2022, 298, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasa, A.; Hettige, J.; Kalyan, I.; Moradi, M. An investigation of the YidC-mediated membrane insertion of Pf3 coat protein using molecular dynamics simulations. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immadisetty, K.; Moradi, M. Mechanistic Picture for Chemomechanical Coupling in a Bacterial Proton-Coupled Oligopeptide Transporter from Streptococcus Thermophilus. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2021, 125, 9738–9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Kim, T.K.; Hobrath, J.V.; Oak, A.S.W.; Tang, E.K.Y.; Tieu, E.W.; Li, W.; Tuckey, R.C.; Jetten, A.M. Endogenously produced nonclassical vitamin D hydroxy-metabolites act as “biased” agonists on VDR and inverse agonists on RORα and RORγ. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2017, 173, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2010, 50, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, C.; Cannone, G.; Briot, J.; Rottier, K.; Berizzi, A.E.; Huang, C.Y.; Quast, R.B.; Hoh, F.; Banères, J.L.; Malhaire, F.; Berto, L.; Dumazer, A.; Font-Ingles, J.; Gómez-Santacana, X.; Catena, J.; Kniazeff, J.; Goudet, C.; Llebaria, A.; Pin, J.P.; Vinothkumar, K.R.; Lebon, G. Agonists and allosteric modulators promote signaling from different metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 conformations. Cell Reports 2021, 36, 109648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Gregory, K.J.; Han, G.W.; Cho, H.P.; Xia, Y.; Niswender, C.M.; Katritch, V.; Meiler, J.; Cherezov, V.; Conn, P.J.; Stevens, R.C. Structure of a class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 bound to an allosteric modulator. Science 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzitelli, M.; Palazzo, E.; Maione, S.; Neugebauer, V. Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Role in Pain Mechanisms and Pain Modulation. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaye, H.; Ishchenko, A.; Lam, J.H.; Han, G.W.; Xue, L.; Rondard, P.; Pin, J.P.; Katritch, V.; Gati, C.; Cherezov, V. Structural basis of the activation of a metabotropic GABA receptor. Nature 2020, 584, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafabakhsh, R.; Levitz, J.; Isacoff, E.Y. Conformational dynamics of a class C G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 2015, 524, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.; Zhang, W.h.; Liu, J.f. Structure and ligand recognition of class C GPCRs. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2012, 33, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishima, N.; Shimada, Y.; Tsuji, Y.; Sato, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kumasaka, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Jingami, H.; Morikawa, K. Structural basis of glutamate recognition by a dimeric metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, T.; Tsuchiya, D.; Morikawa, K.; Jingami, H. Structures of the extracellular regions of the group II/III metabotropic glutamate receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, T.C.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Pin, J.P.; Kniazeff, J. Class CG protein-coupled receptors: reviving old couples with new partners. Biophysics reports 2017, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salon, J.A.; Lodowski, D.T.; Palczewski, K. The Significance of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Crystallography for Drug Discovery. Pharmacological Reviews 2011, 63, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerström, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schiöth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Molecular Pharmacology. [CrossRef]
- Harkey, T.; Govind Kumar, V.; Hettige, J.; Tabari, S.H.; Immadisetty, K.; Moradi, M. The Role of a Crystallographically Unresolved Cytoplasmic Loop in Stabilizing the Bacterial Membrane Insertase YidC2. Scientific Reports 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Barrantes, F. How cholesterol interacts with membrane proteins: An exploration of cholesterol-binding sites including CRAC, CARC, and tilted domains. Frontiers in physiology 2013, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohvo-Rekilä, H.; Ramstedt, B.; Leppimäki, P.; Peter Slotte, J. Cholesterol interactions with phospholipids in membranes, 2002. [CrossRef]
- McMullen, T.P.W.; Lewis, R.N.A.H.; McElhaney, R.N. Cholesterol–phospholipid interactions, the liquid-ordered phase and lipid rafts in model and biological membranes. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2004, 8, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.W.; Jacobson, K. A Role for Lipid Shells in Targeting Proteins to Caveolae, Rafts, and Other Lipid Domains. Science 2002, 296, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Yahi, N. Molecular insights into amyloid regulation by membrane cholesterol and sphingolipids: common mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 2010, 12, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Garmy, N.; Mahfoud, R.; Yahi, N. Lipid rafts: structure, function and role in HIV, Alzheimer’s and prion diseases. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 2002, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeagle, P.L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Biomembranes 1985, 822, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P.L. Modulation of membrane function by cholesterol. Biochimie 1991, 73, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Peränen, J.; Schreiner, R.; Wieland, F.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Simons, K. VIP21/caveolin is a cholesterol-binding protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1995, 92, 10339–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.A.; Young, K.E.; Beachy, P.A. Cholesterol Modification of Hedgehog Signaling Proteins in Animal Development. Science 1996, 274, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.A.; Ericsson, J. Signaling molecules derived from the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway: mechanisms of action and possible roles in human disease. Current Opinion in Lipidology 1998, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paila, Y.D.; Chattopadhyay, A. The function of G-protein coupled receptors and membrane cholesterol: Specific or general interaction? Glycoconjugate Journal, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Paila, Y.D.; Tiwari, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Are specific nonannular cholesterol binding sites present in G-protein coupled receptors?, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Paila, Y.D.; Chattopadhyay, A. Membrane cholesterol in the function and organization of g-protein coupled receptors. Sub-Cellular Biochemistry, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M. Cholesterol and the interaction of proteins with membrane domains. Progress in Lipid Research 2006, 45, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, M.L.; Console, L.; Fahner, A.F.; Samodelov, S.L.; Gai, Z.; Ciarimboli, G.; Indiveri, C.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Visentin, M. The role of cholesterol recognition (CARC/CRAC) mirror codes in the allosterism of the human organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2, SLC22A2). Biochemical Pharmacology 2021, 194, 114840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, P.E.; Labouesse, M. The sterol-sensing domain: multiple families, a unique role? Trends in Genetics 2002, 18, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, V.; Carrillo, G.; Torroja, C.; Guerrero, I. The sterol-sensing domain of Patched protein seems to control Smoothened activity through Patched vesicular trafficking. Current biology : CB 2001, 11, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafurulla, M.; Tiwari, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Identification of cholesterol recognition amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif in G-protein coupled receptors. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2011, 404, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol in GPCR Structures: Prevalence and Relevance. The Journal of Membrane Biology 2022, 255, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Z.x.; Degenhardt, B.; Teper, G.; Papadopoulos, V. Cholesterol binding at the cholesterol recognition/ interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor and inhibition of steroidogenesis by an HIV TAT-CRAC peptide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2001, 98, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Mozumder, S.; Bej, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta, J.; Chattopadhyay, A. Structure, dynamics and lipid interactions of serotonin receptors: excitements and challenges. Biophysical Reviews 2021, 13, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Paila, Y.D.; Jafurulla, M.; Chattopadhyay, A. Membrane cholesterol depletion from live cells enhances the function of human serotonin1A receptors. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2009, 389, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, N.; Genin, C.; Malvoisin, E. Identification of a conserved domain of the HIV-1 transmembrane protein gp41 which interacts with cholesteryl groups. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2002, 1567, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolari, S.; Müller, K.; Bittman, R.; Herrmann, A.; Müller, P. Interaction of Mammalian Seminal Plasma Protein PDC-109 with Cholesterol: Implications for a Putative CRAC Domain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9027–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Di Scala, C.; Evans, L.S.; Williamson, P.T.F.; Barrantes, F.J. A mirror code for protein-cholesterol interactions in the two leaflets of biological membranes. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 21907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Scala, C.; Baier, C.; Evans, L.; Williamson, P.; Fantini, J.; Barrantes, F. Relevance of CARC and CRAC Cholesterol-Recognition Motifs in the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Other Membrane-Bound Receptors. Current Topics in Membranes 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Chattopadhyay, A. Molecular dynamics simulations of GPCR-cholesterol interaction: An emerging paradigm, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Azzaz, F.; Chahinian, H.; Yahi, N.; Di Scala, C.; Baier, C.J.; Barrantes, F.J.; Fantini, J. Chapter 7 - Cholesterol-recognizing amino acid consensus motifs in transmembrane proteins: Comparative analysis of in silico studies and structural data. In Cholesterol; Bukiya, A.N.; Dopico, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; pp. 127–145. [CrossRef]
- Bukiya, A.N.; Dopico, A.M. Common structural features of cholesterol binding sites in crystallized soluble proteins. Journal of Lipid Research 2017, 58, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rone, M.B.; Fan, J.; Papadopoulos, V. Cholesterol transport in steroid biosynthesis: Role of protein–protein interactions and implications in disease states. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2009, 1791, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Hua, T.; Liu, Z.J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, S. MD Simulations Revealing Special Activation Mechanism of Cannabinoid Receptor 1. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto Gutierrez, A.; McDonald, P.H. GPCRs: Emerging anti-cancer drug targets. Cellular Signalling 2018, 41, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. GPCRs as targets for approved drugs: How many targets and how many drugs? Molecular Pharmacology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, D.; Prasanna, X.; Mohole, M.; Chattopadhyay, A. exploring GPCR-lipid interactions by Molecular dynamic simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, X.; Mohole, M.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sengupta, D. Role of cholesterol-mediated effects in GPCR heterodimers. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2020, 227, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niswender, C.M.; Jones, C.K.; Lin, X.; Bubser, M.; Thompson Gray, A.; Blobaum, A.L.; Engers, D.W.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Loch, M.T.; Daniels, J.S.; others. Development and antiparkinsonian activity of VU0418506, a selective positive allosteric modulator of metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 homomers without activity at mGlu2/4 heteromers. ACS chemical neuroscience 2016, 7, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, C.J.; Audic, G.; Lemel, L.; García-Fernández, M.D.; Nieścierowicz, K. Interactions of cholesterol molecules with GPCRs in different states: A comparative analysis of GPCRs’ structures. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2023, 1865, 184100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubík, J.; El-Fakahany, E.E. Allosteric Modulation of GPCRs of Class A by Cholesterol, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Taghon, G.; Rowe, J.; Kapolka, N.; Isom, D. Predictable cholesterol binding sites in GPCRs lack consensus motifs. Structure 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyn, B.; Stepien, P.; Poojari, C.; Mobarak, E.; Polit, A.; Wisniewska-Becker, A.; Róg, T. Cholesteryl Hemisuccinate Is Not a Good Replacement for Cholesterol in Lipid Nanodiscs. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2019, 123, 9839–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulig, W.; Tynkkynen, J.; Javanainen, M.; Manna, M.; Rog, T.; Vattulainen, I.; Jungwirth, P. How well does cholesteryl hemisuccinate mimic cholesterol in saturated phospholipid bilayers? Journal of Molecular Modeling 2014, 20, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulig, W.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Olżyńska, A.; Tynkkynen, J.; Javanainen, M.; Manna, M.; Rog, T.; Hof, M.; Vattulainen, I.; Jungwirth, P. Experimental determination and computational interpretation of biophysical properties of lipid bilayers enriched by cholesteryl hemisuccinate. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2015, 1848, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddi, S.; Dainese, E.; Sandiford, S.; Fezza, F.; Lanuti, M.; Chiurchiù, V.; Totaro, A.; Catanzaro, G.; Barcaroli, D.; De Laurenzi, V.; Centonze, D.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Selent, J.; Howlett, A.; Maccarrone, M. Effects of palmitoylation of Cys 415 in helix 8 of the CB 1 cannabinoid receptor on membrane localization and signalling. British Journal of Pharmacology 2012, 165, 2635–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol interaction motifs in G protein-coupled receptors: Slippery hot spots? Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Fu, Z.; Frangaj, A.; Liu, J.; Mosyak, L.; Shen, T.; Slavkovich, V.N.; Ray, K.M.; Taura, J.; Cao, B.; Geng, Y.; Zuo, H.; Kou, Y.; Grassucci, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Williams, J.P.; Rice, W.J.; Eng, E.T.; Huang, R.K.; Soni, R.K.; Kloss, B.; Yu, Z.; Javitch, J.A.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Slesinger, P.A.; Quick, M.; Graziano, J.; Yu, H.; Fiehn, O.; Clarke, O.B.; Frank, J.; Fan, Q.R. Structure of human GABAB receptor in an inactive state. Nature 2020, 584, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jeong, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Cho, Y. Structural Basis for Activation of the Heterodimeric GABAB Receptor. Journal of Molecular Biology 2020, 432, 5966–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, D.N.; Singh, S.; Laboute, T.; Strutzenberg, T.S.; Qiu, X.; Wu, D.; Novick, S.J.; Robinson, C.V.; Griffin, P.R.; Hunt, J.F.; Izard, T.; Singh, A.K.; Martemyanov, K.A. Cryo-EM structure of human GPR158 receptor coupled to the RGS7-Gβ5 signaling complex. Science 2022, 375, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pin, J.P.; De Colle, C.; Bessis, A.S.; Acher, F. New perspectives for the development of selective metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands. European journal of pharmacology 1999, 375, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejdiu, B.I.; Tieleman, D.P. Lipid-protein interactions are a unique property and defining feature of G protein-coupled receptors. Biophysical journal 2020, 118, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, M.; Lolicato, F.; Sandoval, A.; Amaya-Espinosa, H.; Teslenko, A.; Sinning, I.; Beck, R.; Brügger, B.; Aponte-Santamaria, C. Cholesterol Localization Around the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2020, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liauw, B.W.H.; Foroutan, A.; Schamber, M.R.; Lu, W.; Samareh Afsari, H.; Vafabakhsh, R. Conformational fingerprinting of allosteric modulators in metabotropic glutamate receptor 2. eLife 2022, 11, e78982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, F.; Ugolini, A. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: implications for brain diseases. Progress in neurobiology 1999, 59, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liauw, B.W.H.; Afsari, H.S.; Vafabakhsh, R. Conformational rearrangement during activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature Chemical Biology 2021, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P. The biophysics and cell biology of cholesterol: an hypothesis for the essential role of cholesterol in mammalian cells. Cholesterol in Membrane Models, 1993; 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sooksawate, T.; Simmonds, M. Influence of membrane cholesterol on modulation of the GABAA receptor by neuroactive steroids and other potentiators. British journal of pharmacology 2001, 134, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, F.; Jefferson, J.R.; Kier, A.B.; Knittel, J.; Scallen, T.J.; Wood, W.G.; Hapala, I. Membrane cholesterol dynamics: cholesterol domains and kinetic pools. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 1991, 196, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, B.; Kuenze, G.; Li, B.; Sanders, C.R.; Meiler, J. Structural determinants of cholesterol recognition in helical integral membrane proteins. Biophysical Journal 2021, 120, 1592–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Castillo, C.; Francesconi, A. Agonist-dependent signaling by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors is regulated by association with lipid domains. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2013, 288, 32004–32019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Hu, Z.; Ding, R.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Pu, X.; Zhao, N. Exploring the Activation Mechanism of a Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Homodimer via Molecular Dynamics Simulation. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2020, 11, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibado, J.K.; Tano, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Salas-Estrada, L.; Provasi, D.; Strauss, A.; Marcelo Lamim Ribeiro, J.; Xiang, G.; Broichhagen, J.; Filizola, M.; Lohse, M.J.; Levitz, J. Differences in interactions between transmembrane domains tune the activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors. eLife 2021, 10, e67027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, A.; Kumari, R.; Zukin, R.S. Regulation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor trafficking and signaling by the caveolar/lipid raft pathway. Journal of Neuroscience 2009, 29, 3590–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraci, F.; Nicoletti, F.; Copani, A. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: the potential for therapeutic applications in Alzheimer’s disease. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2018, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Bruno, V.; Ngomba, R.T.; Gradini, R.; Battaglia, G. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as drug targets: what’s new? Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2015, 20, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, J.Y.; Wall, B.A.; Wangari-Talbot, J.; Chen, S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in cancer. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Immadisetty, K.; Hettige, J.; Moradi, M. What Can and Cannot Be Learned from Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Bacterial Proton-Coupled Oligopeptide Transporter GkPOT? The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2017, 121, 3644–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Babin, V.; Roland, C.; Sagui, C. The Adaptively Biased Molecular Dynamics method revisited: New capabilities and an application. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2015, 640, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind Kumar, V.; Agrawal, S.; Kumar, T.K.S.; Moradi, M. Mechanistic Picture for Monomeric Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 Stabilization by Heparin Binding. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2021, 125, 12690–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, C.J.; Fantini, J.; Barrantes, F.J. Disclosure of cholesterol recognition motifs in transmembrane domains of the human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Scientific reports 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Costantino, G.; de Fabritiis, G.; Pastor, M.; Selent, J. Membrane-sensitive conformational states of helix 8 in the metabotropic Glu2 receptor, a class C GPCR. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, D.J.; Malizia, A.L. New insights into the role of the GABAA–benzodiazepine receptor in psychiatric disorder. The British Journal of Psychiatry 2001, 179, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaye, H.; Stauch, B.; Gati, C.; Cherezov, V. Molecular mechanisms of metabotropic GABAB receptor function. Science Advances 2021, 7, eabg3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconochie, D.J.; Zempel, J.M.; Steinbach, J.H. How quickly can GABAA receptors open? Neuron 1994, 12, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W. Structure, pharmacology, and function of GABAA receptor subtypes. Advances in pharmacology 2006, 54, 231–263. [Google Scholar]
- Soltesz, I.; Mody, I. Patch-clamp recordings reveal powerful GABAergic inhibition in dentate hilar neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 1994, 14, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otis, T.S.; De Koninck, Y.; Mody, I. Characterization of synaptically elicited GABAB responses using patch-clamp recordings in rat hippocampal slices. The Journal of physiology 1993, 463, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmakina, S.; Geng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Q.R. Heterodimeric coiled-coil interactions of human GABAB receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, 6958–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Bush, M.; Mosyak, L.; Wang, F.; Fan, Q.R. Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human GABAB receptor. Nature 2013, 504, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, D. Keeping the Balance: GABAB Receptors in the Developing Brain and Beyond. Brain Sciences 2022, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooksawate, T.; Simmonds, M. Effects of membrane cholesterol on the sensitivity of the GABAA receptor to GABA in acutely dissociated rat hippocampal neurones. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon, M.A.; Adler, E.; Lindemeier, J.; Battey, J.F.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. Putative mammalian taste receptors: a class of taste-specific GPCRs with distinct topographic selectivity. Cell 1999, 96, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigues, S.; Dotson, C.D.; Munger, S.D. The receptor basis of sweet taste in mammals. Results and problems in cell differentiation 2009, 47, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad Pydi, S.; Singh, N.; Upadhyaya, J.; Pal Bhullar, R.; Chelikani, P. The third intracellular loop plays a critical role in bitter taste receptor activation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2014, 1838, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Dalziel, J.E. G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Taste Physiology and Pharmacology. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2020, 11, 587664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pydi, S.P.; Jafurulla, M.; Wai, L.; Bhullar, R.P.; Chelikani, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol modulates bitter taste receptor function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2016, 1858, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilegems, E.; Iwatsuki, K.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Benard, O.; Ninomiya, Y.; Margolskee, R.F. REEP2 Enhances Sweet Receptor Function by Recruitment to Lipid Rafts. The Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 30, 13774LP–13783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Hoon, M.A.; Adler, E.; Feng, L.; Guo, W.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J. T2Rs function as bitter taste receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamin, N.; Neumann, J.M.; Ostuni, M.A.; Vu, T.K.N.; Yao, Z.X.; Murail, S.; Robert, J.C.; Giatzakis, C.; Papadopoulos, V.; Lacapere, J.J. Characterization of the cholesterol recognition amino acid consensus sequence of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. Molecular endocrinology 2005, 19, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epand, R.F.; Thomas, A.; Brasseur, R.; Vishwanathan, S.A.; Hunter, E.; Epand, R.M. Juxtamembrane protein segments that contribute to recruitment of cholesterol into domains. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, F.A.; Medapati, M.R.; Chelikani, P. Cholesterol modulates the signaling of chemosensory bitter taste receptor T2R14 in human airway cells. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2019, 316, L45–L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; MacLeod, R.J. Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiological reviews 2001, 81, 239–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, F.M.; Kallay, E.; Chang, W.; Brandi, M.L.; Thakker, R.V. The calcium-sensing receptor in physiology and in calcitropic and noncalcitropic diseases. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2019, 15, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schamber, M.R.; Vafabakhsh, R. Mechanism of sensitivity modulation in the calcium-sensing receptor via electrostatic tuning. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendy, G.N.; Guarnieri, V.; Canaff, L. Calcium-sensing receptor and associated diseases. Progress in molecular biology and translational science 2009, 89, 31–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kifor, O.; Diaz, R.; Butters, R.; Kifor, I.; Brown, E.M. The calcium-sensing receptor is localized in caveolin-rich plasma membrane domains of bovine parathyroid cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1998, 273, 21708–21713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augé, N.; Maupas-Schwalm, F.; Elbaz, M.; Thiers, J.C.; Waysbort, A.; Itohara, S.; Krell, H.W.; Salvayre, R.; Nègre-Salvayre, A. Role for matrix metalloproteinase-2 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein–induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway and smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 2004, 110, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Azuma, H.; Nagashima, G.; Niimi, Y.; Tamaki, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Yamamoto, K. Immunolocalization of matrix metalloproteinases in rabbit carotid arteries after balloon denudation. Histochemistry and cell biology 1998, 109, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaman, S.S.; van der Vorst, E.P. Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR), Its Impact on Inflammation and the Consequences on Cardiovascular Health. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zielke, H.R.; Cheng, L.; Xiao, R.; Crow, M.T.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Froehlich, J.; Lakatta, E.G. Increased expression of 72-kd type IV collagenase (MMP-2) in human aortic atherosclerotic lesions. The American journal of pathology 1996, 148, 121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molostvov, G.; Fletcher, S.; Bland, R.; Zehnder, D. Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor mediated signalling is involved in human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2008, 22, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Kong, F.J.; Bai, S.Z.; He, W.; Xing, W.J.; Xi, Y.H.; Li, G.W.; Guo, J.; Li, H.Z.; Wu, L.Y.; others. Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in oxLDL-induced MMP-2 production in vascular smooth muscle cells via PI3K/Akt pathway. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2012, 362, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, M.; Kangawa, K. Orphan GPCRs and methods for identifying their ligands. Methods in enzymology 2012, 514, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mullican, S.E.; DiSpirito, J.R.; Lazar, M.A. The orphan nuclear receptors at their 25-year reunion. Journal of molecular endocrinology 2013, 51, T115–T140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, E.M.; Ford, M.G.J.; Burtey, A.; Praefcke, G.J.K.; Peak-Chew, S.Y.; Mills, I.G.; Benmerah, A.; McMahon, H.T. Role of the AP2 β-appendage hub in recruiting partners for clathrin-coated vesicle assembly. PLoS biology 2006, 4, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.l.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.l.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.y. Orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): biological functions and potential drug targets. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2012, 33, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Labroska, V.; Qin, S.; Darbalaei, S.; Wu, Y.; Yuliantie, E.; Xie, L.; Tao, H.; Cheng, J.; others. G protein-coupled receptors: Structure-and function-based drug discovery. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2021, 6, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanduri, R.; Bhutani, I.; Somavarapu, A.K.; Mahajan, S.; Parkesh, R.; Gupta, P. ONRLDB—manually curated database of experimentally validated ligands for orphan nuclear receptors: insights into new drug discovery. Database 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocrine reviews 1999, 20, 689–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mani, S. Orphan Nuclear Receptors as Targets for Drug Development. Pharmaceutical Research 2010, 27, 1439–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vera, I.M.S. Advances in orphan nuclear receptor pharmacology: a new era in drug discovery, 2018.
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, S.; Chan, F.L. Orphan nuclear receptors as regulators of intratumoral androgen biosynthesis in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.A.; Kennedy, M.A.; Mak, P.A. LXRs;: Oxysterol-activated nuclear receptors that regulate genes controlling lipid homeostasis. Vascular pharmacology 2002, 38, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, L.Z.; Devarakonda, S.; Harp, J.M.; Han, Q.; Pellicciari, R.; Willson, T.M.; Khorasanizadeh, S.; Rastinejad, F. Structural basis for bile acid binding and activation of the nuclear receptor FXR. Molecular cell 2003, 11, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, A.M. Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism. Nuclear receptor signaling 2009, 7, nrs–07003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solt, L.A.; Burris, T.P. Action of RORs and their ligands in (patho) physiology. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 2012, 23, 619–627. [Google Scholar]
- Jetten, A.M.; Kang, H.S.; Takeda, Y. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors α and γ: key regulators of lipid/glucose metabolism, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. Frontiers in endocrinology 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguere, V.; McBroom, L.; Flock, G. Determinants of target gene specificity for ROR alpha 1: monomeric DNA binding by an orphan nuclear receptor. Molecular and Cellular Biology 1995, 15, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, A.M.; Takeda, Y.; Slominski, A.; Kang, H.S. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ (RORγ): Connecting sterol metabolism to regulation of the immune system and autoimmune disease. Current Opinion in Toxicology 2018, 8, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, A.; Yan, Z.H.; Hirose, T.; Giguère, V.; Jetten, A.M. Cloning of a cDNA encoding the murine orphan receptor RZR/RORγ and characterization of its response element. Gene 1996, 181, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.N.; Kang, H.S.; Jetten, A.M. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors (RORs): regulatory functions in immunity, development, circadian rhythm, and metabolism. Nuclear receptor research 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, J.; Schlaeppi, J.M.; Bitsch, F.; Delhon, I.; Fournier, B. Crystal structure of the human RORα ligand binding domain in complex with cholesterol sulfate at 2.2 Å. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 14033–14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahoei, S.H.; Nelson, E.R. Nuclear receptors, cholesterol homeostasis and the immune system. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2019, 191, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





