1. Introduction
Climate change is a meaningful phenomenon which challenges the economic development and the prowess of our environment. It is severe in many parts of the world. Most areas in the world are vulnerable to its impacts such as sea-level rise, advanced sea, coastal erosion, biodiversity decreasing, lands salinity, disappearance of human establishments, ocean acidification, fishing reduction, and an unbalance between water offerings and water asking, etc. However, it would be accurate to say that due to their low adaptation capacities, developing countries are the most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Senegal is among the most vulnerable West African countries to the impacts of climate change. Coastal erosion is the most threatening disaster in Senegal apart from the flood. Therefore, the Dakar region, like most coastal cities in the world, is not safe from the impacts of coastal erosion. Advanced sea resulting from the rise in sea level affects the coasts (Pouye et al., 2022). Phenomena of exogenous and endogenous nature drive coastal dynamics. Therefore, defined as the boundary between land and water surface, the coastline is the most dynamic part of the seascape since its shape is affected by different parameters, such as hydrography, geology, climate, vegetation. These parameters change the coastline shape in a dynamic equilibrium (Guariglia et al., 2006) .
With the effects of climate change combined with the advanced sea resulting in sea level rise due to global warming, the natural coastal morpho dynamic is changed compared to a few decades ago. In this context, (Duxbury et al, (2002) stated that 'sea-level rise is one of the most critical manifestations of climate change over the coastal zone in many countries. Added to this rising sea- level (an increase between 0,09 and 0,88 meters of sea level by 2100), an increase in temperature is also expected. Sea-level has risen about 15 cm during the past century, but the rate of rise has recently increased, and it is thought that the sea level may gain another 30 cm in the next fifty years because of the melting land ice and warming ocean water. This increasing rate of sea-level rise has been primarily blamed on the greenhouse effect. If the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere doubles during the next 100 years, there are estimated that the ocean surface will warm an additional 2 to 4° C. The expansion of warming water will also affect the sea level by raising it an additional 60 cm for each degree of increase in the average ocean temperature. As a result, the coast's edge will move inland from hundreds to thousands of meters along low-lying coasts, and coastal erosion will be accelerated.'
In addition, the effects of climate change and rising sea levels are accentuated by wind velocity, height waves, height tides changes, and increases in temperature in coastal areas leading to coastal erosion. Consequently, coastal areas are subject to erosion. For example, in Senegal, most tourist facilities are endangered, and up to 180 000 people could lose their homes (Nicholls and Mimura, 1999).
Such impacts suggest that vulnerability to sea-level rise will increase substantially over the next few decades. At the local level, the coastal dynamics of the Dakar region show that there is indeed an advanced sea which probably is due to variations in oceanic waters aggravated by the effects of hydrodynamic agents such as wave, tide, wind, geomorphologic, topographic conditions. Therefore, a reduction of coastal areas, human displacement toward inland and disruption of economic activities (fishing, recreation, hotel and industrial activities) are noted. These threats are accentuated by humankind through sand mining, pollution and illegal settlements along the coast (Pouye et al., 2022).
The Dakar region contains the highest concentration of towns and industries along the coast, including 26 km of erodible coastline. Inundation and erosion are the significant visible consequences impact of sea-level rise. Dakar region itself is situated on a rocky headland, but much of the surrounding metropolitan area is vulnerable to erosion given sea-level rise. In addition, saltwater intrusion into Senegal's aquifers and surface waters is one of the damages of sea-level rise, threatening water resources unless offset by increased rainfall. This could damage agricultural production in several areas. Besides, sanitation and other changes are promoted by sea-level rise and climate change (Dennis, Niang-Diop and Nicholls, 1995).
Despite all the endeavours of West African countries against coastal erosion, the coasts are still challenged by this phenomenon. Nevertheless, it would be important to note that the impacts of possible responses to sea-level rise vary at the local and regional scales due to variations in local and regional parameters. When combined with the coast's low-lying nature and low socioeconomic and institutional development, these parameters would suggest that West Africa is vulnerable to sea-level rise. Large areas of land could be lost, and most of the threatened land is wetland areas within deltas or around estuaries and lagoons (Nicholls and Mimura, 1999). According to Stewart et al.,( 2011), long-term coast management is an important and challenging task. Some challenges coastal managers face includes maintaining and protecting public access and natural character, protecting people and property from natural hazards, and sustainable planning and use of natural and physical resources.
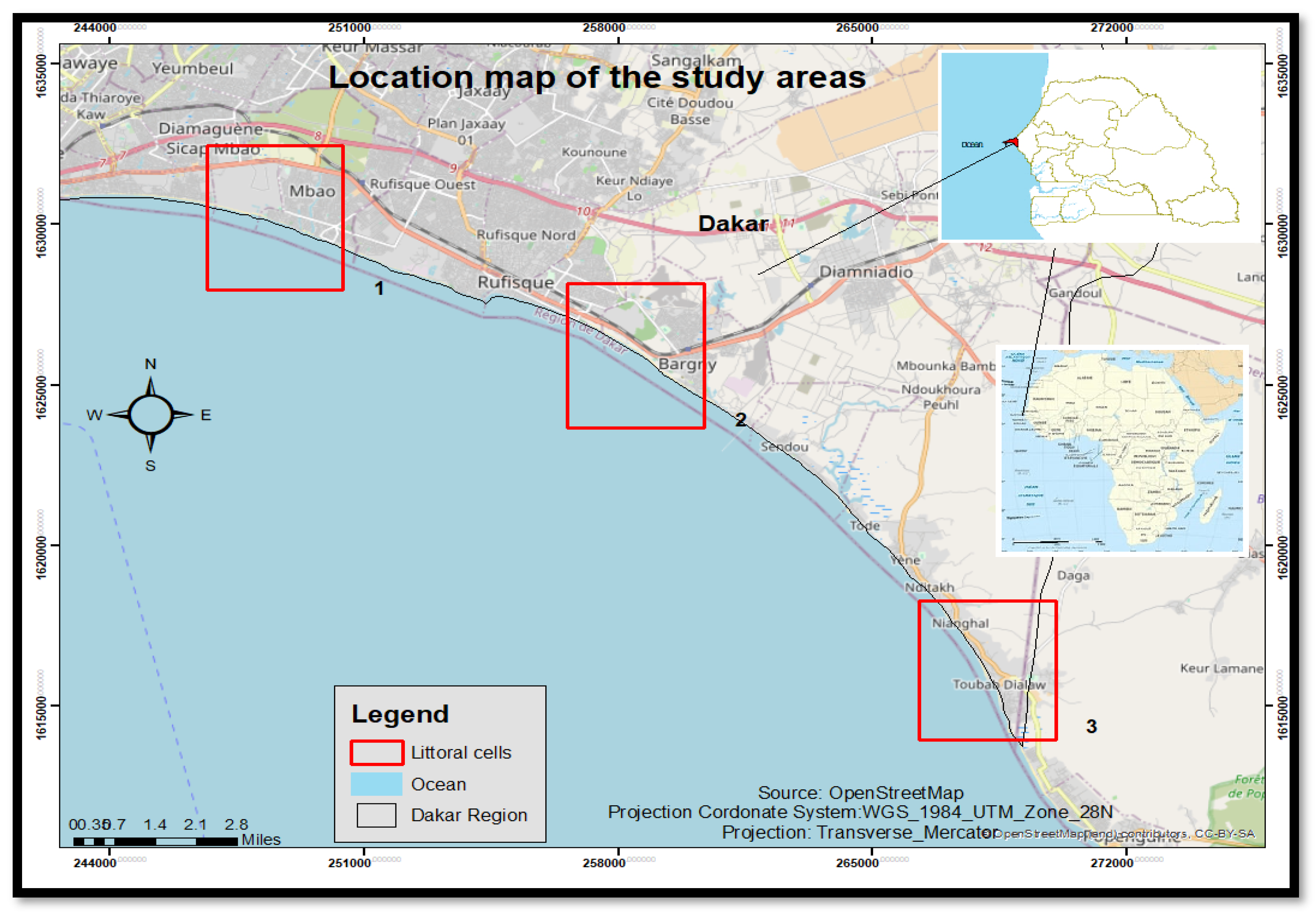
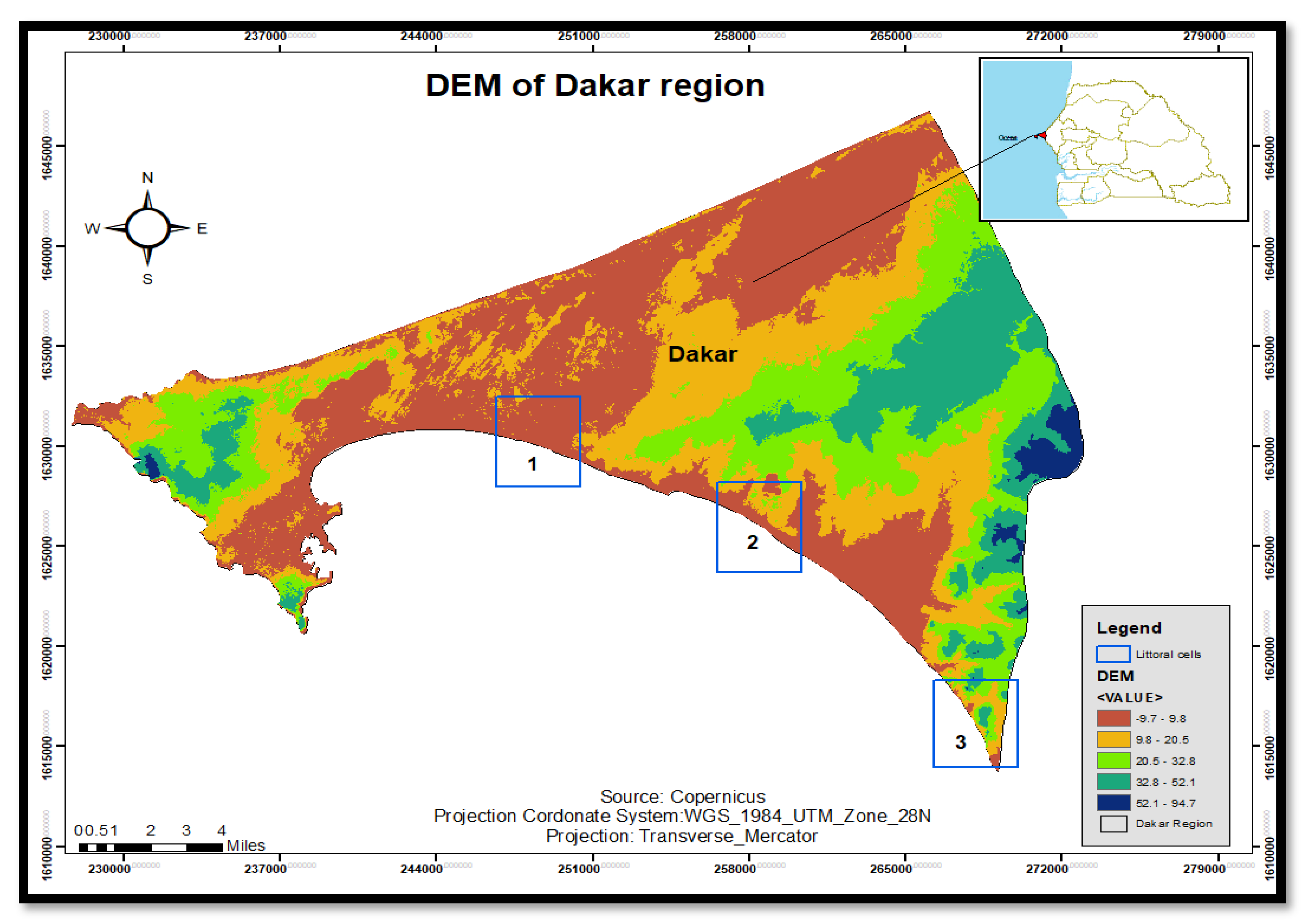
2. Study Area
The southern coast of Dakar region is located between 14°43′ North latitude and 17°16′ West longitude. Its coastal length is estimated at 41 kilometers. This study was conducted in three littoral cells (Mbao (3.9 km), Bargny (5.5 km) and Toubab Dialaw (4.9 km)) on the southern coast of the Dakar region. Approximately 500,000, or 17% of the regional population, live in the department of Rufisque (GRDR, 2017). The southern coast comprises two maritime facades to the north and south. The climate can be determined by airline conditions which a Canarian characterizes. Geographical and atmospheric conditions strongly influence climate. Three types of wind are noted: the trade wind maritime, harmattan and monsoon. The wind is among the critical factor in the coastal systems generating swell, sea currents and waves and plays an important role in coastal sediment transport. However, the perturbation of these airline conditions in coastal zones accentuates coastal erosion through an increase in storm surge frequency, coastal flooding, dune retreats, dune disappearances, etc. (Pouye
et al., 2022). It is subjected to a northwest swell whose energy is reduced due to refraction and diffraction around the Cape-vert peninsula and the southwest swell, which is more noticeable during the rainy season. Offshore, its energy is lower than the northwest swell (11 kW.m-1 vs 18 kW.m-1) (Barusseau, 1980; Sall, 1982, in Niang-Diop, 1996). Northwest swell reaches a depth of 13 meters with a minimum direction of N200°. Due to its low occurrence and low offshore energy, the importance of this type of swell could be minimised (Nardari, B, 1993 in Guerin, 2003). The geomorphologic and morpho-pedologic conditions are essential in the morphology and natural coastal erosion dynamic. The limestone plateau of the Bargny- Rufisque district, whose substratum is part of limestone and Marl of Eocene age, is found. Geomorphological units are portrayed by low topography, high porousness and less resistant materials. The characteristics of the geomorphological units in the graben are one of the primary drivers of the vulnerability of Dakar to coastal erosion (Sane and Yamagishi, 2004). The southern coast has infrastructures for industrial and artisanal and industrial fishing activities via ports and harbours. It remains the most vulnerable to erosion due to its high population and the industrial and tourist infrastructures along the coast (
Figure 1).
3. Materials and Methods
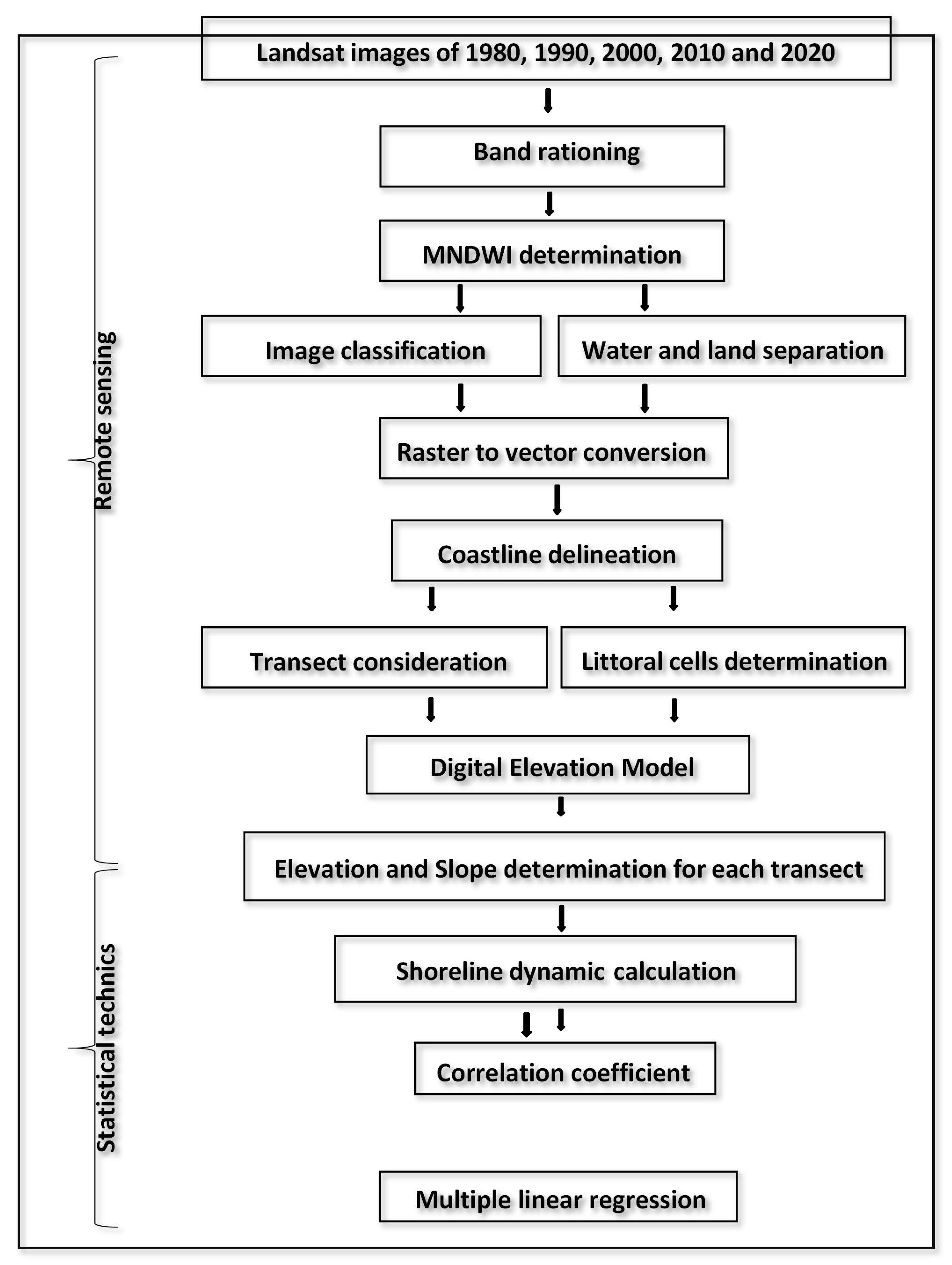
In this study, remote sensing and statistical technics were used to analyze the relationship between coastline dynamics and topography and slope conditions. Using the historical Landsat images, the Modified Normalised Different Water Index (MNDWI) was employed to delineate the coastlines before computing their evolution rate. After that, the relationship between the coastline dynamic rate, topographic and Slope conditions was analyzed through the correlation coefficient and linear regression model. The following flowchart resumes the methodology employed in this study (
Figure 2).
3.1. Data Source
The data used in this study are five different Landsat images from 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020. These images are characterised by the provided satellite, sensor, path and row, the number of bands, and the acquisition date. Topographic data from GLO-30 DEM and geomorphologic data from the website (
http://sphaera.cartographie.ird.fr/) also have been employed.
The following table resumes all helpful information related to the different Landsat images (
Table 1).
3.2. The Use of the Modified Normalised Difference Water Index (MNDWI)
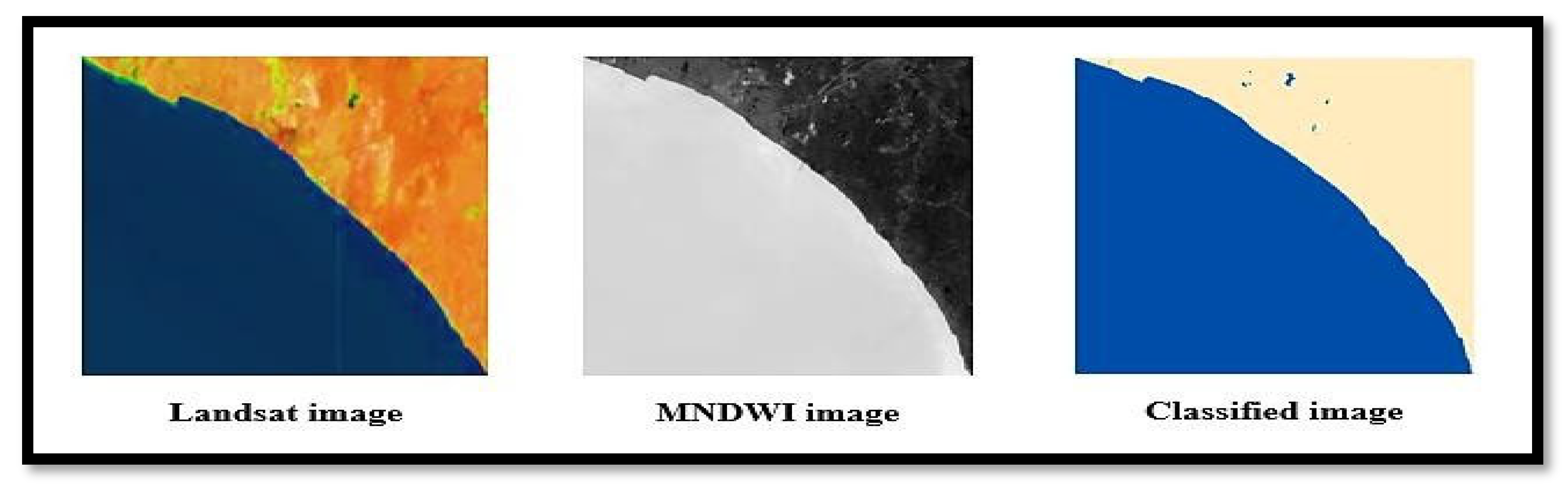
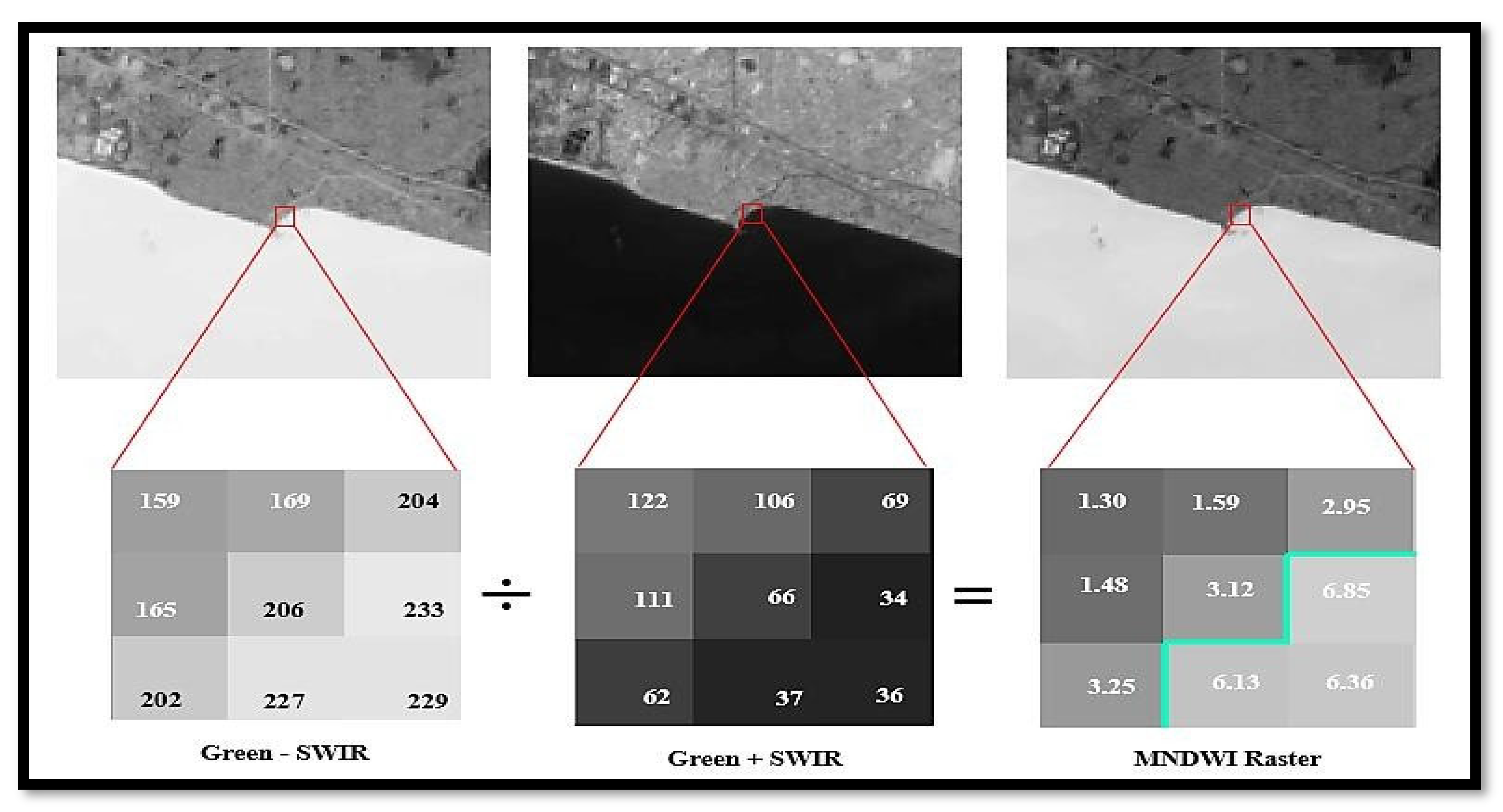
To better dissociate the land surface and sea, the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) has been used in this study (
Figure 3). For that, the band rationing technic was employed using the Near Infrared (NIR) and Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) (Munasinghe et al., 2021). The bands 2 and 5 for Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 7 were used. For Landsat 8, bands 3 and 6 were used. In MNDWI, the highest value is +1, and the lowest is -1. The threshold value for classification is 0.
The Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) originates from the Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI), which is calculated using two near-infrared channels. These two indices are enhancement technics through band rationing. According to (Gao, 1996), the NDWI is used for remote sensing vegetation liquid water interacting with solar radiation. In a study, McFeeters, (1996), stated that this NDWI takes benefits of the condition where the presence of features that have higher near-infrared reflectance and lower red-light reflectance, e.g., terrestrial vegetation will be enhanced, while those with low red-light reflectance and very low NIR reflectance (e.g., water) will be suppressed or eliminated. This NDWI is modified by substituting a middle infrared band such as Landsat TM band 5 for the near-infrared band used in the NDWI. To enhance and extract water information in the water regions where the background is dominated by build-up land area. It is more suitable than the NDWI because it reduces or even removes build-up land and vegetation noise (Xu, 2006).
3.3. Classification, Digitalization and Coastline Delineations
Landsat images for each year (1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020) from the MNDWI calculation were used to analyze the coastline dynamics. The MNDWI images were classified to distinguish the land and sea boundary. After that, these classified raster images were converted to vector layers from which the coastline was delineated (
Figure 4).
3.4. Shoreline Dynamic Calculation
The shoreline velocity between 1980 and 2020 is evaluated. For that, the distance of shoreline movement is divided by the time elapsed between the oldest and the youngest shorelines using the Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) software which is an extension of Arc GIS 10.7. The advantage of this statistical method is that the dynamic rate is computed easily through the End Point Rate (EPR) (Himmelstoss
et al., 2018).
Where
EPR = End Point Rate (EPR) statistical method is computed by dividing the Net Shoreline Movement (NSM) by the time elapsed between the oldest and the youngest shorelines.
NSM = Net Shoreline Movement is the distance between the most recent shorelines and the oldest shorelines for each transect and is measured in meters (m).
ET = Elapsed time between 1980 and 2020 (Himmelstoss et al., 2018 in Pouye et al., 2022).
3.5. Littoral Cells and Transect Determinations
According to Inman (2005), 'A littoral cell is a coastal compartment containing a complete sedimentation cycle including sources, transport paths, and sinks. The cell boundaries delineate the geographical area within which the sediment budget is balanced, providing the framework for the quantitative analysis of coastal erosion and accretion. The sediment sources are commonly streams, sea cliff erosion, onshore migration of sandbanks, and material of biological origins such as shells, coral fragments and skeletons of tiny marine organisms. The usual transport path is along the coast by waves and currents (longshore transport, longshore drift, or littoral drift). Cross-shore (on/offshore) paths may include windblown sand, overwash, and ice-push. The sediment sinks are usually offshore losses at submarine canyons and shoals or onshore dune migration, rollover, and deposition in bays and estuaries. This study has considered three littoral cells: Mbao, Bargny and Toubab Dialaw on the southern coast of Dakar. In each littoral cell, over 80 transects were taken into account, and the distance between two transects is estimated at 50 meters. For each transect, the coastline dynamic rate, average topographic values of 5 intersects (1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020), and slope value was employed to analyse their relationship.
3.6. Determination of Elevation Value for each Transect using a DEM Copernicus Raster
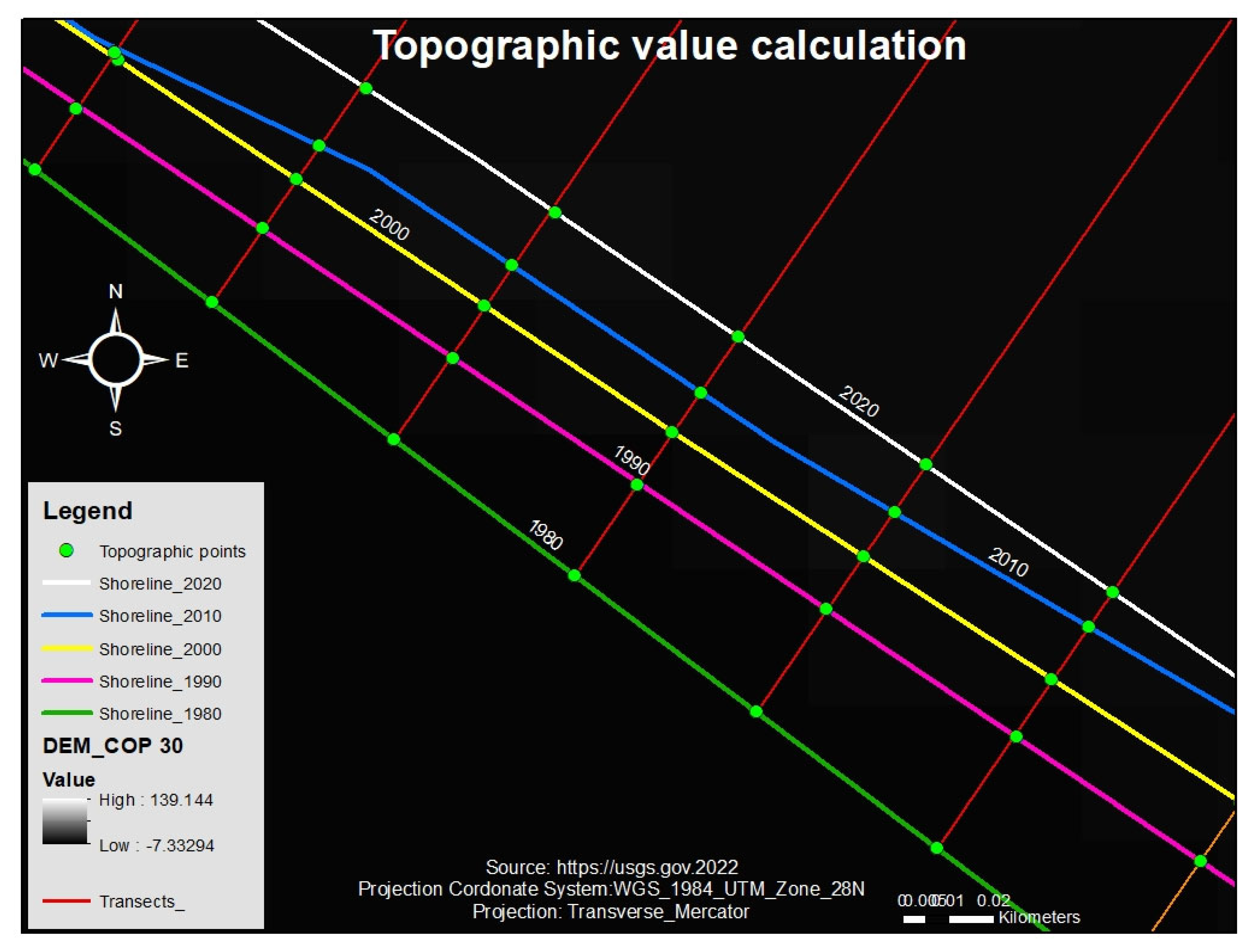
The elevation value was measured using each intersect point's X and Y coordinate points, a GLO-30 DEM raster and ArcGIS software. After the determination of each littoral cell, the coordinate points (X and Y) for each intersection are defined (
Figure 5).
3.7. Slope Determination
Coastal areas are the most dynamic part of the terrestrial sphere. Several factors and processes lead to this dynamism. Far from being negligible, Slope plays an essential role in shoreline dynamics. Most often, the lower it is, the faster the shoreline retreat. Low-lying areas are more exposed to submersion than coastal areas with high topographic values. In this study, the Slope is included in the relationship between the topography and shoreline dynamic to power the linear regression prediction. It was determined using a Digital Elevation Model Copernicus raster and the Spatial Analysis tool in ArcGIS (
Figure 6).
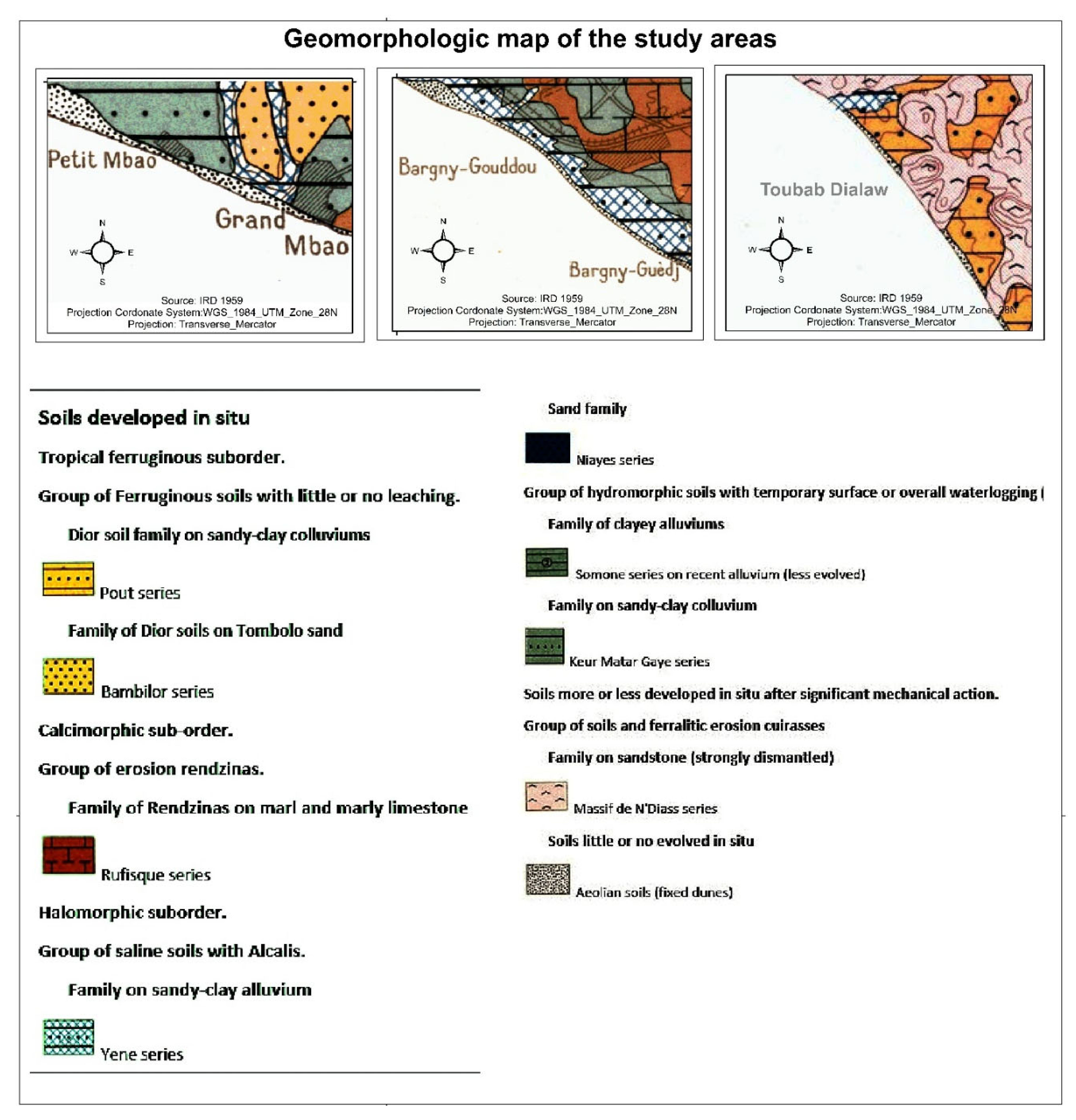
3.8. Geomorphologic Condition of the Southern Coast of Dakar
The morpho pedological conditions of the Dakar region are characterised by five formations: Recent volcanic formations. The Cape Verde peninsula in Senegal has been the site of significant magmatic activity. Outcrops of volcanic rocks are scattered over 7000 km
2 from Dakar to the East of Thiès (Barusseau
et al., 2009). In addition, the formation of Maastrichtian sandstone (Cretaceous), the formation of marl-limestone rocks (Paleocene-Eocene), and recent Ergs and littoral formations are noted. The recent volcanic formation is composed of a Basaltic spread, a low leaching tropical ferruginous soil on complex material in the head of the Dakar region. The formation of Maastrichtian sandstone (Cretaceous) can be found in trays and small valley zones and is composed of two types of sediment: Lithosols and ragosols
1, on cuirass dismantled on sandstone which can be found in the tray zones at the centre of Dakar and in the north close to the coastal dunes and tropical ferruginous soils with little or no leaching, on colluviums which appear in small valley zones. The formation of marl-limestone rocks (Paleocene-Eocene) can be found in a tray, alluvial plain, cliff zones and the edge of a plateau and is composed successively by the vertic hydromorphic soils, on clayey marly-limestone material, strongly tirsified; deep hydromorphic soils on sandy-clayey alluviums; hydromorphic soils, on various materials; erosion rendzina
2 on marl-limestone rocks and hydromorphic soils on limestone colluvium. The recent Ergs are composed of inland dunes and coastal dunes: Hydromorphic soils in the Niayes area and low leaching tropical ferruginous soils. Three sediments characterise the littoral formations: Sharp coastal dunes and marine beaches - Raw mineral soils; Semi-fixed coastal dunes - Raw mineral soils and Holomorphic soils
3 on clayey material - Hydromorphic soils on clayey material - Slightly evolved soils on exuding sands (USAID, 2021). In our study areas, the composition of the geomorphologic conditions is different regarding the nature of rocks and sediment, their permeability and porousness. Therefore, the geomorphologic conditions in the Mbao littoral cell are characterised by sandy-clay colluvium.
4 In the Bargny littoral cell Sandy-clay alluvium
5 and wind soil. The geomorphology in the Toubab Dialaw littoral cell is characterised by highly depleted sandstone, eolian soil, and Dior soil
6 on sandy-clay colluvium (
Figure 7).
3.9. Linear Regression between Coastline Dynamic, Slope and Topography
The following formula is used to point out the correlation between coastline dynamic, slope and topography.
Where
y = Predicted variable
= EPR; = Slope; = Topography
βi (1,2,3) =parameters to be estimated or model parameters
Ɛ = The error term;
3.10. Multicollinearity Test
In a study, Oke et al., (2022) stated that ‘Multicollinearity is a statistical phenomenon in which there exists a strong or perfect relationship between the predictor variables. The presence of multicollinearity can cause serious problems with the estimation of and the interpretation’. Therefore, much higher correlation between the explanatory variables means more risk in the statistical inference about the significance of the regression coefficients. Various tests and diagnostic measures of multicollinearity have been proposed in the econometric literature. Some measures are available for diagnosing multicollinearity, such as the variance inflation factor (
VIF), condition number (
CN), condition index (
CI), and variance decomposition (Belsley, Kuh and Welsch, 1980); Chi-square test statistic (Farrar & Glauber, 1967, Haitovsky, 1969); and an F-test by regressing each of the independent variables on the remaining independent variables. The VIF, a well-known measure of multicollinearity, is defined as
Where
: is the coefficient of determination of the regression of the i-th column of
X on the remaining columns of
X: Based on the VIF diagnostic measure, multicollinearity is severe whenever the
VIF is more than
10. There is no logical reasoning behind the value
10. There is no logical reasoning behind the value
10. (Mohammadi, 2020). In this study a multicollinearity was done to point out the dependence among independent variables (
Table 2).
The results from the multicollinearity test show that there is no collinearity among independents variables because the square roots of the VIF are lower than 5.
3.11. Specification of the Model
For the selection of the model used in this study, AIC, BIC and R2 are employed. In a study, Romero (2007) He stated that it is usual practice in econometrics to employ R2 in model selection. This goodness of fit measurement, along with others like the unadjusted R squared, the Akaike Information Criterion, and the Bayesian Information Criterion, are almost always available to researchers using econometric software.
Therefore, a prominent approach for selecting models is the Akaike information criterion (AIC). It is widely employed at parameter space singularities and borders to violate regularity conditions (Mitchell, Allman and Rhodes, 2022). Whereas, a helpful metric for comparing multilevel models is the Bayesian information criterion. The BIC has a number of benefits over conventional hypothesis-testing techniques. (Lorah and Womack, 2019). According to Yulistiani & Suliadi (2019), the good criteria for models selection can use the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). For model selection in linear mixed models, one may use Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) or Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). Distinct random effect specifications result in different covariance structures of observation because linear mixed models might provide specific structure of dependency among responses (Lee, 2015) (
Table 3).
Where:
M0 = Model without diagnostic; M1 = Model neither outlier nor influencer
The lower is the AIC, the better is the model. The higher is the R2, the better is the model. The lower is the BIC, the better is the model. Based on these later statements, the model M1 was chosen.
4. Results
Table 4.
Littoral cells and transect consideration and statistic values.
Table 4.
Littoral cells and transect consideration and statistic values.
| Littoral cells |
Net Shoreline Movement (m) |
Average of shoreline dynamic from 1980 to 2020 (m/year) |
Average of topographic value (m) |
Average of Slope (Degree) |
The correlation coefficient of the shoreline change rate, topography and Slope |
Geomorphologic characteristics |
| Mbao |
-41.3 |
-1.04 |
1.85 |
4.98 |
0.63 |
sandy-clay colluvium and wind soil |
| Bargny |
-46.9 |
-1.17 |
1.37 |
3.45 |
0.87 |
Sandy-clay alluvium and wind soil |
| Toubab Dialaw |
-3.8 |
-0.06 |
5.27 |
17.92 |
0.15 |
Depleted sandstone, eolian soil, Dior soil on sandy-clay colluvium |
| General |
-30.6 |
-0.75 |
2.86 |
8.78 |
0.55 |
sandy-clay colluvium, wind soil, Sandy-clay alluvium, Depleted sandstone, eolian soil, Dior soil on sandy-clay colluvium. |
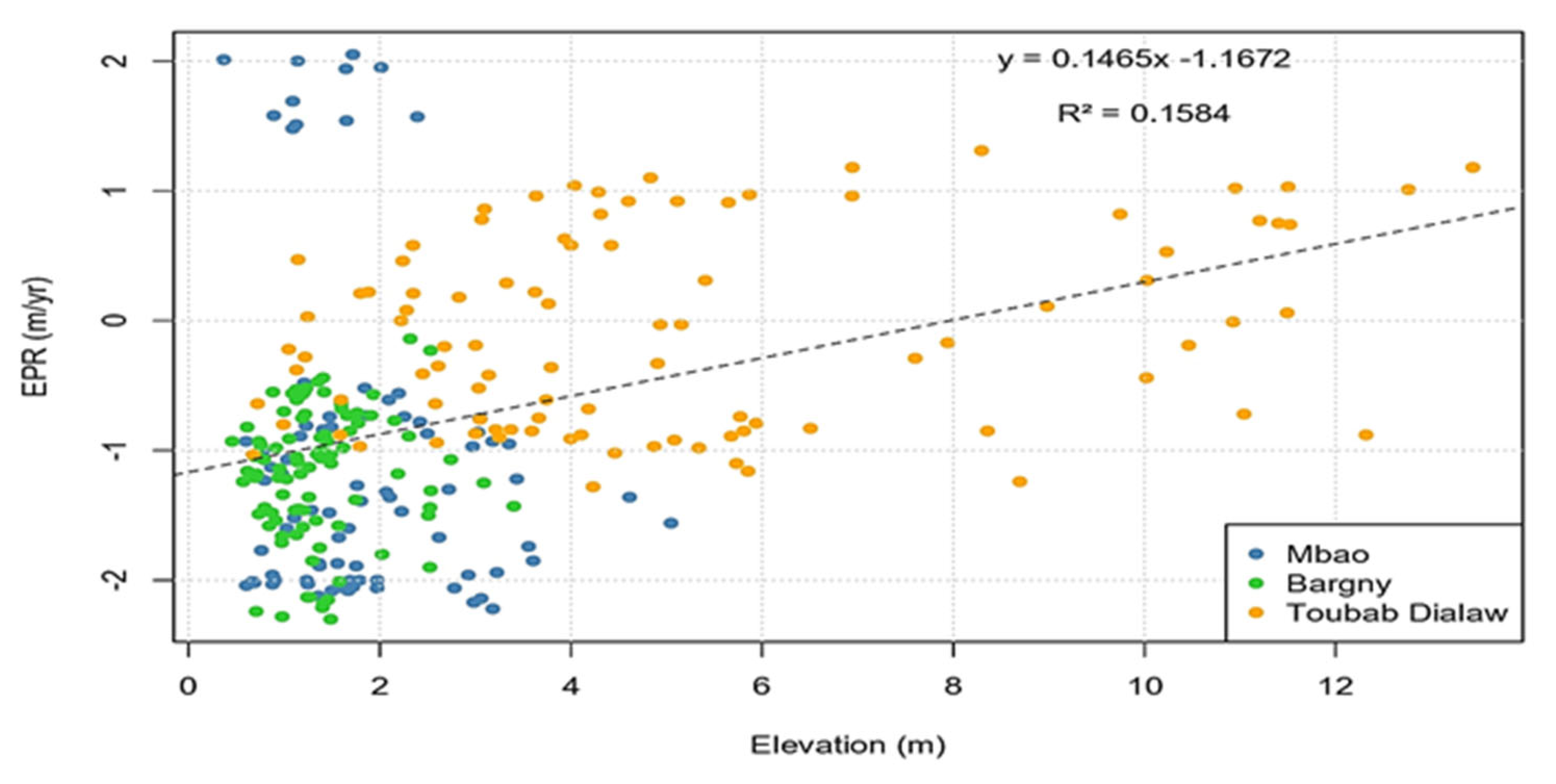
4.1. Linear Regression between Coastline Dynamic and Topography
In a study, Uyanık, G K & Güler (2013), states that 'regression analysis is a statistical technique for estimating the relationship among variables which have reason and result relation. The mean focus of univariate regression is to analyse the relationship between a dependent and one independent variable and formulates the linear relationship equation between the dependent and independent variable'. The following figures are about the linear regression of the topography (Elevation) and dynamic shoreline rate (EPR) in different littoral cells of the study area (
Figure 8).
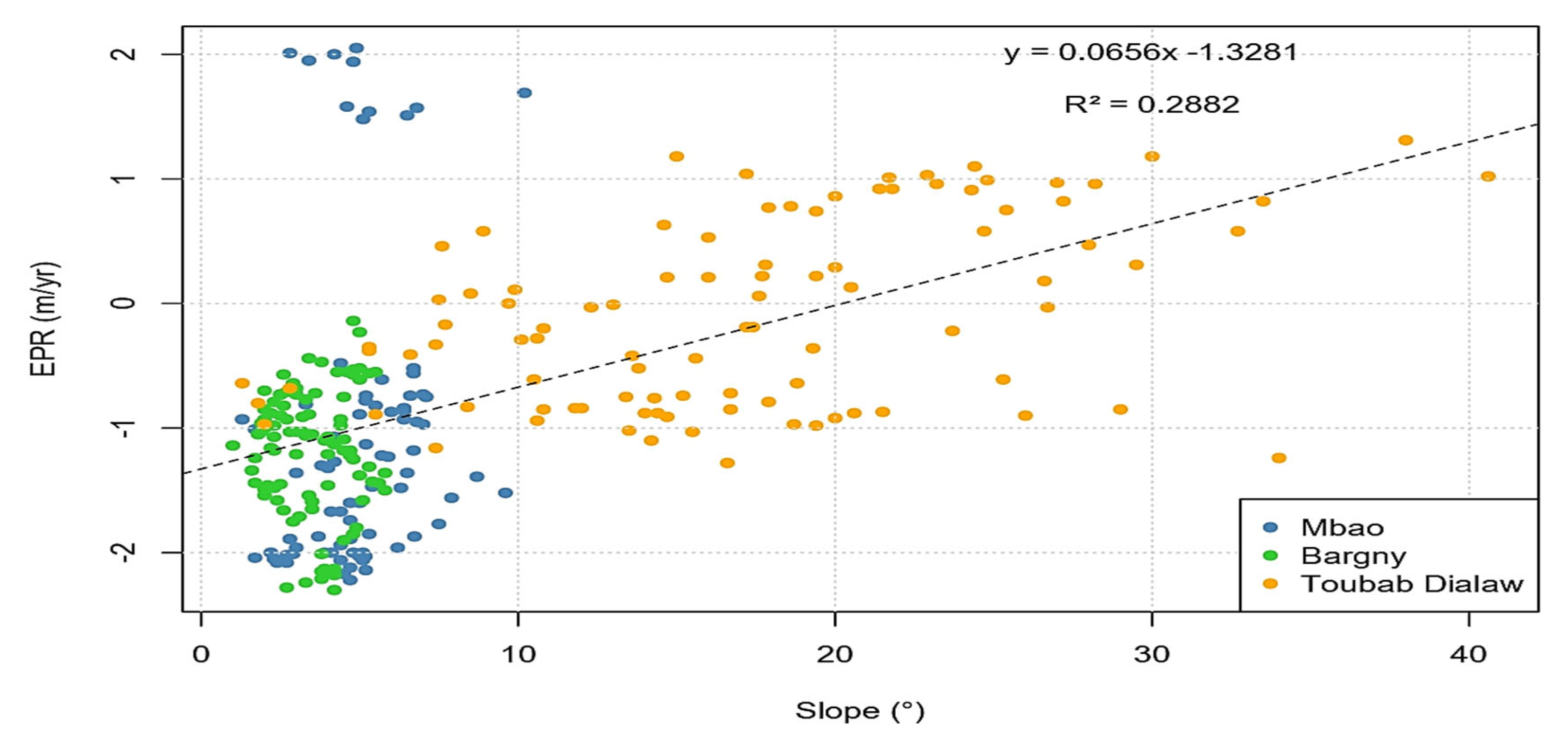
4.2. Linear Regression between Coastline Dynamic and Slope
The coefficient of correlation between the coastline dynamic and Slope is estimated at 0.56 in Mbao and 0.87 in Bargny. Whereas, in the littoral cell of Toubab Dialaw, the coefficient is lower than those recorded in Mbao and Bargny (0.06) because of high slope values with an average of about 17.92
o and a low dynamic rate of -0.06 m/year (
Figure 9).
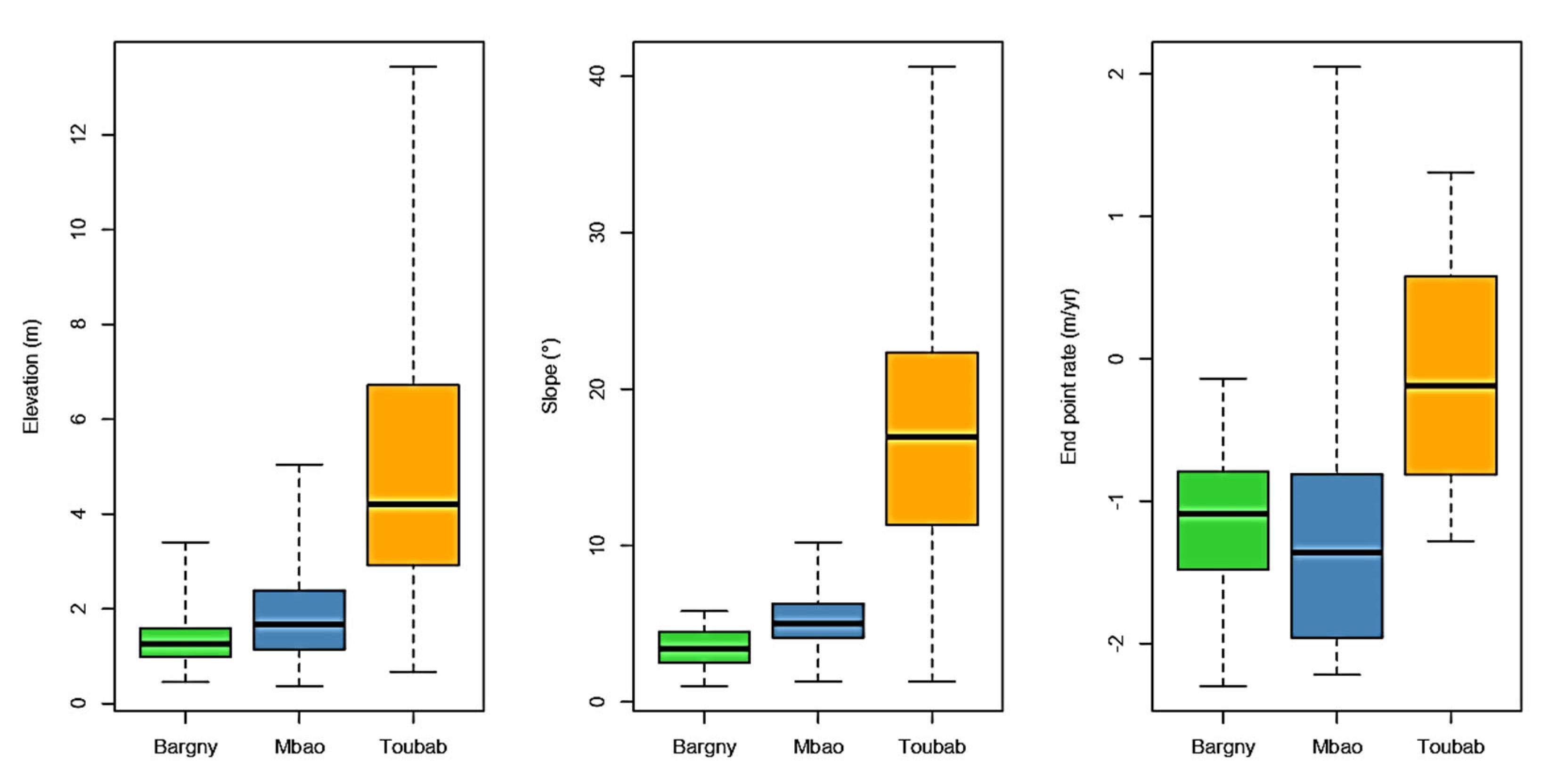
The following figure is the Box-plot of the Topography, Slope and EPR in the three littoral cells. It helps to understand the distributional characteristics of topography, slope and coastline dynamic value in each littoral cell. For the topography, the upper quartiles in Mbao and Bargny are lower than 2.5 meters whereas, in Toubab Dialaw 50% of observed values exceed 4 meters. In terms of slope, all quartiles are lower than 10.5
o. in Toubab Dialaw, 75% of observations are higher than 10
o. In Mbao and Bargny, 75% of quartiles regarding the coastline dynamic rate, are lower than 0.8 m/year whereas, in Toubab Dialaw 75% of quartiles are higher than 0.8 m/year (
Figure 10).
5. Discussion
In the context of climate change, the recorded temperatures in the world show an increase in the global trend. Consequently, global warming is noted. The effects of this global warming on the hydrosphere and cryosphere cause ice melting and dilating seawater, leading in most coastal areas in the world to a coastline retreat resulting from sea-level rise. The effects of this rising sea level combined with human activities such as sand mining and abnormal settlement lead to coastal erosion, which is accentuated by the effects of hydrodynamic agents. In addition, geologic and geomorphologic conditions along the coasts play an important role in this coastline dynamic. According to Adjoussi (2001), three different activities determine the geological history of the Dakar region: volcanic activities, marine transgressions, and regressions which were observed from the pre-quaternary period up to the quaternary period in the Dakar region, and the geomorphological structure is the result of the evolutionary dynamics of these geological formations. The coastal shapes observed in the Dakar region give evidence that there is a difference in terms of geomorphologic composition and topographic and slope conditions. Therefore, due to its geographical position in the sea and low-lying areas, the Dakar region is vulnerable to coastal erosion, the most threatening disaster that challenges communities. Most of its coastal areas are subjected to coastline retreat. In this study, the average shoreline dynamic in Mbao, Bargny and Toubab Dialaw littoral cells from 1980 to 2020 are estimated respectively at -1.04, -1.17 and -0.06 m/year. Shoreline retreat was already a problem, with recession rates at Rufisque between 0.45 and 2.46 m/year (1959 to 1980) (Dennis, Niang-Diop and Nicholls, 1995).
Therefore, the results of this study show that, in the littoral cells characterised by low topography and Slope, there is a positive relationship with a coefficient of correlation exceeding 0.50. The district Mbao and Bargny littoral cells record an average of topography of about 1.85 and 1.37. The average slopes in these coastal areas were estimated at 4.98 and 3.45o. In contrast, the Toubab Dialaw littoral cell records high topographic values with an average of about 5.27 meters and an average slope of about 17.92o. The morphology of Rufisque shows high topographic levels forming two plateaus in the North-West (Cap des Biches) and the South-East (Kolobane, Arafat), separated by a depression in the centre (Keury Souf) (Fall, Meissa and Niang, 2016).
Even if the topography and Slope are among the key parameters defining the level of exposure of coastal zones to erosion, coastal geology and geomorphology are far from negligible. In a study, Bird (2008) stipulated that the feature of a coastline may vary due to large-scale geology factors, surface processes and the effects of recent changes in the relative level of the sea and land. The results of this study show that the geomorphologic conditions intervene in the relationship between the coastline dynamic rate, topography and Slope. For example, in the Mbao littoral cell, there is a significant relationship between the topographic and Slope conditions and coastline dynamic with a coefficient of correlation of about 0.63. The geomorphology in the Mbao littoral cell is characterised by sandy-clay colluvium and wind soil with high porosity and water infiltration and is generally subjected to erosion. In the Bargny littoral cell, where the geomorphologic conditions are characterised by Sandy-clay alluvium and wind soil, the coefficient of correlation between the topography and the coastline dynamic is high. The coefficient of correlation is estimated at 0.87, meaning that the geomorphologic conditions contribute highly to the coastline retreat. Contrary to the Toubab Dialaw littoral cell, where the geomorphology is marked by highly depleted sandstone, eolian soil, and Dior soil on sandy-clay colluvium, it is less exposed to erosion due to its less porous characteristic and high compacity of soil. The relationship is not significant, with a correlation coefficient of about 0.15, assuming that the average of the topography (5.27 m) and Slope (17.92o) do not favour high shoreline dynamic rates and the geomorphologic conditions do not allow rapid erosion because of its compacity and impermeability of geomorphological structures. Some efforts were made in order to fight against coastal erosion in Senegal. Pouye (2016), stated that faced with this coastal erosion, the Senegalese governments adopted adaptation measures depending on the means at their disposal: Protective walls, reforestation, protective dykes, rock fill, beach nourishment, dune replenishment, beach drainage systems, breakwaters, etc. Among these protective measures, some are more effective depending on their quality, their duration of resistance against hydrodynamic parameters and the type of coastline where they are installed. However, it should be noted that these protective infrastructures constitute a significant constraint on sedimentary exchanges between continents and oceans. To better manage coastal erosion and pollution, 26 additional developments and preservation projects have been inventoried for an estimated budget of more than 30 billion francs CFA (Quensière et al., 2013). Despite all the endeavor that the Senegalese government made, coastal erosion still remains a challenge for communities living along the coasts.
6. Conclusion
In summary, this study is undertaken to investigate if there is a relationship between the coastline dynamic, topographic and slope and the contribution of the geomorphology along the southern coast of Dakar. It helps to understand better the role which plays the topography, Slope and geomorphology in coastal dynamics using remote sensing, cartographic tools and statistical methods. It also allows having an idea about the most vulnerable coastal areas in terms of topography, slope and geomorphology. In the littoral cells of Mbao and Bargny, where the topography and Slope are low, the average shoreline dynamics are estimated respectively at -1.04 and -1.17 m/year. In contrast to the littoral cell of Toubab Dialaw, where the topography and Slope are more important, the average shoreline dynamic rate is about -0.06 m/year. Therefore, the geomorphologic structure plays an essential role in the relationship between the topography, slope and shoreline dynamic. For example, in the Mbao littoral cell, where porous and erodible structures characterise the geomorphologic condition, there is a positive relationship between the topography and coastline dynamic (0.63). In the littoral cell of Bargny, the relationship between the topography and coastline dynamic is positive with a coefficient of about 0.87, whereas, in the Toubab Dialaw littoral cell, the coefficient of correlation (0.15) is not significant. This is because of the domination of compact and impermeable structures in this coastal zone. Nevertheless, the topography and the geomorphology play a vital role in the coastline dynamic; it should be important to search for an answer to the following question: What about the contribution of the population to the shoreline dynamic?
Notes
| 1 |
Regosol in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is very weakly developed mineral soil in unconsolidated
materials. Regosols are extensively eroded lands, particularly in arid and semi‐arid areas and mountain regions (FAO/WRB,
2014). |
| 2 |
Rendzina soils typically develop from solid or unconsolidated rocky material that is carbonate- or sulphate-rich. Limestone is the most common, but others include dolomite, gypsum, marble, chalk and marlstone (Soil classification system of England and Wales). |
| 3 |
The pedogenic process of salinisation forms holomorphic soils. The areas where silts and clays make up a large proportion of the soil-body are called holomorphic soil (Musa, 2016). |
| 4 |
Colluvium can be defined as produced by mass-gravity-driven transport on steep slopes, and alluvium as produced by water-driven transport on floodplains and wind soil (Miller and Juilleret, 2020). |
| 5 |
The alluvium is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or similar settings (Miller and Juilleret, 2020). |
| 6 |
These soils, called Dior soils, constitute the wealth of Senegal; the dunes they form are highly favourable to peanut cultivation, whereas the soils between the dunes are suitable for other food crops, such as sorghum (Senegal - Land | Britannica). |
References
- Adjoussi, P. (2001) Impacts du prélèvement du sable marin sur l’évolution du trait de côte a Yoff: essai d’étude de vulnérabilité, (Presqu’île du Cap Vert, Sénégal). UCAD. (Accessed: 11 June 2021).
- Barusseau, J.P. et al. (2009) Notice explicative de la carte géologique du Sénégal à 1/500000, feuilles nord-ouest, nord-est et sud-ouest.
- Belsley, D. , Kuh, E. and Welsch, R. (1980) ‘Regression Diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity’, Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics, New York: Wiley, 1980, 144. [CrossRef]
- Dennis, K.C. , Niang-Diop, I. and Nicholls, R.J. (1995) ‘Sea-Level Rise and Senegal: Potential Impacts and Consequences’, Journal of Coastal Research, (14), pp. 243–261. Available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25735711.
- Duxbury, A.B. , Duxbury, A.C. and Sverdrup, K.A. (2002) Fundamentals of Oceanography. 4th edn. Mc Graw Hill.
- Fall, Meissa, M.N. and Niang, I. (2016) ‘Geological and Geotechnical Investigation of the Residual swelling Soils of Rufisque (Senegal)’. Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, p. 19. Available at: https://www.scienpress.com/journal_focus.asp?main_id=59&Sub_id=IV&Issue=1695.
- FAO/WRB (2014) ‘International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends For Soil Maps’, World Soil Resources Report No 106, p. 106. Available at: http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:World+reference+base+for+soil+resources+2006#0 (Accessed: 29 May 2022).
- Farrar, D. and Glauber, R. (1967) ‘Multicollinearity in Regression Analysis: The Problem Revisited’, The Review of Economics and Statistics, 49. [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. (1996) ‘NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space’, Elsevier, 58(3), pp. 257–266. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0034425796000673 (Accessed: 20 June 2021).
- GRDR (2017) Rapport sur le système alimentaire du département de Rufisque.
- Guariglia, A. et al. (2006) ‘A multisource approach for coastline mapping and identification of shoreline changes’, Annals of Geophysics, 49(1), pp. 295–304. [CrossRef]
- Guerin, K. (2003) Dynamique du littoral sableux de Tiaroye à Bargny (Baie de Gorée – Sénégal). Université de Paris 1 - Sorbonne-Panthéon.
- Haitovsky, Y. (1969) ‘Multicollinearity in Regression Analysis: Comment’, The Review of Economics and Statistics, 51(4), pp. 486–489. [CrossRef]
- Himmelstoss, E.A. et al. (2018) Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 5.0 user guide, Open-File Report. Reston, VA. [CrossRef]
- Inman, D.L. (2005) ‘Littoral Cells BT - Encyclopedia of Coastal Science’, in Schwartz, M.L. (ed.). Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 594–599. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Avinash, Deepika, B. and Jayappa, K.D. (2010) ‘Shoreline changes and morphology of spits along southern Karnataka, west coast of India: A remote sensing and statistics-based approach’, Elsevier, 120, pp. 133–152. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. (2015) ‘A Note on Performance of Conditional Akaike Information Criteria in Linear Mixed Models’, Communications for Statistical Applications and Methods, 22, pp. 507–518. [CrossRef]
- Lorah, J. and Womack, A. (2019) ‘Value of sample size for computation of the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) in multilevel modeling’, Behavior Research Methods, 51. [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. (1996) ‘The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features’, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(7), pp. 1425–1432. [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.A. and Juilleret, J. (2020) ‘The colluvium and alluvium problem: Historical review and current state of definitions’, Earth-Science Reviews, 209, p. 103316. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. , Allman, E. and Rhodes, J. (2022) A generalized AIC for models with singularities and boundaries.
- Mohammadi, S. (2020) ‘A test of harmful multicollinearity: A generalized ridge regression approach’, Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods, 51, pp. 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Musa, D. (2016) ‘A Study of Holomorphic Soil in SuleTankarkar Local Government Area of Jigawa State Using Remote Sensed Data’, Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 6, pp. 132–140.
- Niang-Diop, I. (1996) L’érosion côtière sur la petite côte du Sénégal à partir de l’ensemble de Rufisque : passé, présent et futur. Université d’Angers. [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J. and Mimura, N. (1999) ‘Regional issues raised by sea-level rise and their policy implications’, Climate Research, 11(1), pp. 5–18. [CrossRef]
- Oke, J. , Akinkunmi, W. and Etebefia, S. (2022) ‘USE OF CORRELATION, TOLERANCE AND VARIANCE INFLATION FACTOR FOR MULTICOLLINEARITY TEST’, VOLUME 7.
- Pouye, I. (2016) Modification des conditions climatiques et avancée de la mer au niveau de la côte nord de la presqu’île du Cap-Vert (De Yoff à Guédiawaye) de 1984 à 2014 : Enjeux et Perspectives. Universié Cheikh Anta Diop de Dakar.
- Pouye, I. et al. (2022) ‘Coastline Dynamics Analysis in Dakar Region, Senegal from 1990 to 2040’, American Journal of Climate Change, 11(2), pp. 23–36. [CrossRef]
- Quensière, J. et al. (2013) ‘Vulnérabilités de la région de Dakar au changement climatique : PCTI - Dakar’.
- Romero, A. (2007) ‘A Note on the Use of R-squared in Model Selection’, Department of Economics, College of William and Mary, Working Papers [Preprint].
- Sane, M. and Yamagishi, H. (2004) ‘Coastal Erosion in Dakar, Western of Senegal, West Africa. The coast has been re- cently damaged by serious erosion, which has various causes resulting from human activities and natural processes. It is related to a number of among which the geologic’, 44(6), pp. 360–366.
-
Senegal - Land | Britannica (no date). Available at: https://www.britannica.com/place/Senegal/Land (Accessed: 29 May 2022).
-
Soil classification system of England and Wales (no date). Cranfield University, UK, National Soil Resources Institute. Available at: http://www.soilsworldwide.net/index.php/Soil_classification_system_of_England_and_Wales (Accessed: 29 May 2022).
- Stewart, C. , Becker, J. and Coomer, M. (2011) ‘Community Perceptions of Coastal Processes and Management Options for Coastal Erosion - REPORT’, 4355, p. 116.
- USAID (2021) USAID project/ RSI N 685 - 0233. (Accessed: 20 June 2021).
- Uyanık, G K & Güler, N. (2013) ‘A study on multiple linear regression analysis’, Elsevier, p. 7. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. (2006) ‘Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery’, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(14), pp. 3025–3033. [CrossRef]
- Yulistiani, S. and Suliadi, S. (2019) ‘Deteksi Pencilan pada Model ARIMA dengan Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) Termodifikasi’, STATISTIKA: Journal of Theoretical Statistics and Its Applications, 19, pp. 29–37. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).