Submitted:
12 January 2023
Posted:
12 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
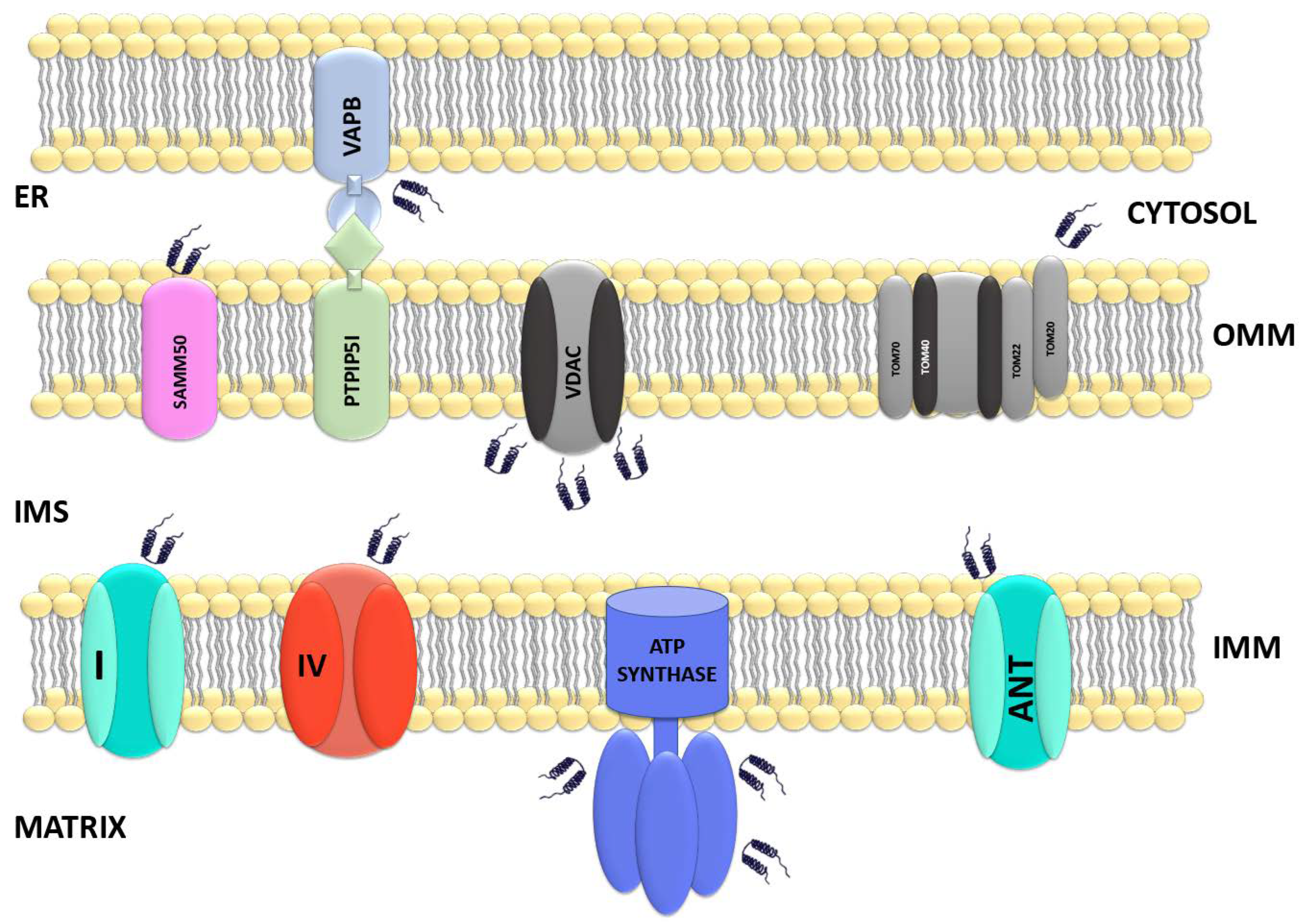
Mitochondria Dysregulation in MSA
Mitochondrial Reprogramming
Management of MSA
Alternative neuroprotective agents in MSA
Molecular Hydrogen (H2)
Magnesium
Low Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide
Conclusion and Future Directions
References
- Dickson, D.W.; Liu, W.-K.; Hardy, J.; Farrer, M.; Mehta, N.; Uitti, R.; Mark, M.; Zimmerman, T.; Golbe, L.; Sage, J.; Sima, A.; D'Amato, C.; Albin, R.; Gilman, S.; Yen, S.-H. Widespread alterations of α-synuclein in multiple system atrophy. The American Journal of Pathology 1999, 155, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Cellular pathology in multiple system atrophy. Neuropathology 2006, 26, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M. Multiple system atrophy: α-synuclein and neuronal degeneration. Neuropathology 2007, 27, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, G.K.; Shlomo, Y.B.; Magalhães, M.; Danie, S.E.; Quinn, N.P. Clinical features and natural history of multiple system atrophy. Brain 1994, 117, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Ikeda, K.; Budka, H. Diffuse type of Lewy body disease: progressive dementia with abundant cortical Lewy bodies and senile changes of varying degree--a new disease? . Clin Neuropathol. 1984, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, K. Diffuse lewy body disease in Japan. Journal of Neurology 1990, 237, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K. Lewy bodies in cerebral cortex. report of three cases. Acta Neuropathologica 1978, 42, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, S.; May, S.J.; Shults, C.W.; Tanner, C.M.; Kukull, W.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Masliah, E.; Low, P.; Sandroni, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Ozelius, L.; Foroud, T. The North American Multiple System Atrophy Study Group. Journal of Neural Transmission 2005, 112, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, DJ.; Jaros, E. ; Multiple system atrophy: cellular and molecular pathology. Mol Pathol. 2001, 54(6), 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, S.; Low, P.; Quinn, N.; Albanese, A.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Fowler, C.; Kaufmann, H.; Klockgether, T.; Lang, A.; Lantos, P.; Litvan, I.; Mathias, C.; Oliver, E.; Robertson, D.; Schatz, I.; Wenning, G. Consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Clinical Autonomic Research 1998, 8, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Overk, C.R.; Oueslati, A.; Masliah, E. The many faces of α-synuclein: From structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2013, 14, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, A.; Masliah, E.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ge, N.; Flanagan, L.; Rohan de Silva, H.A.; Kittel, A.; Saitoh, T. The precursor protein of non-Aβ component of alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 1995, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliezer, D.; Kutluay, E.; Bussell, R.; Browne, G. Conformational properties of α-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states 1 1edited by P. E. Wright. Journal of Molecular Biology 2001, 307, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uéda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cdna encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in alzheimer disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, E.; Monzio Compagnoni, G.; Masliah, E. Review: Novel treatment strategies targeting alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy as a model of synucleinopathy. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 2016, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmen, T.; Lynes, E.M.; Gesson, K.; Thomas, G. Oxidative protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum: Tight links to the mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2010, 1798, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottolini, D.; Cali, T.; Negro, A.; Brini, M. The parkinson disease-related protein DJ-1 counteracts mitochondrial impairment induced by the tumour suppressor protein p53 by enhancing endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering. Human Molecular Genetics 2013, 22, 2152–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calì, T.; Ottolini, D.; Negro, A.; Brini, M. α-Synuclein controls mitochondrial calcium homeostasis by enhancing endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interactions. J Biol Chem 2012, 287(22), 17914–17929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo Devoto, V.M.; Falzone, T.L. Mitochondrial dynamics in parkinson's disease: A role for α-synuclein? Disease Models & Mechanisms 2017, 10, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordás, G.; Hajnóczky, G. SR/ER–mitochondrial local communication: Calcium and Ros. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2009, 1787, 1352–1362. 21. Friedman, J. R.; Lackner, L. L.; West, M.; DiBenedetto, J. R.; Nunnari, J.; Voeltz, G. K. ER tubules mark sites of Mitochondrial Division. Science 2011, 334, 358–362. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Rizzuto, R.; Hajnoczky, G.; Su, T.-P. MAM: More than just a housekeeper. Trends in Cell Biology 2009, 19, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzuto, R.; Pozzan, T. Microdomains of intracellular Ca2+: Molecular determinants and functional consequences. Physiological Reviews 2006, 86, 369–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillusson, S.; Gomez-Suaga, P.; Stoica, R.; Little, D.; Gissen, P.; Devine, M.J.; Noble, W.; Hanger, D.P.; Miller, C.C. A-synuclein binds to the ER–mitochondria tethering protein VAPB to disrupt ca2+ homeostasis and mitochondrial ATP production. Acta Neuropathologica 2017, 134, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. Novel subcellular localization for α-synuclein: Possible functional consequences. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvadchak, V.V.; Yushchenko, D.A.; Pievo, R.; Jovin, T.M. The mode of α-synuclein binding to membranes depends on lipid composition and lipid to protein ratio. FEBS Letters 2011, 585, 3513–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-W.; Yang, R.; Guo, J.-C.; Ren, H.-M.; Zha, X.-L.; Cheng, J.-S.; Cai, D.-F. Localization of α-synuclein to mitochondria within midbrain of mice. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, F.; Exner, N.; Lutz, A.K.; Wender, N.; Hegermann, J.; Brunner, B.; Nuscher, B.; Bartels, T.; Giese, A.; Beyer, K.; Eimer, S.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Haass, C. Inhibition of mitochondrial fusion by α-synuclein is rescued by Pink1, parkin and DJ-1. The EMBO Journal 2010, 29, 3571–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Du, T.; Wang, X.; Duan, C.; Gao, G.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, H. A-synuclein amino terminus regulates mitochondrial membrane permeability. Brain Research 2014, 1591, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robotta, M.; Gerding, H.R.; Vogel, A.; Hauser, K.; Schildknecht, S.; Karreman, C.; Leist, M.; Subramaniam, V.; Drescher, M. Alpha-synuclein binds to the inner membrane of mitochondria in an α-helical conformation. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Yin, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Uéda, K.; Chan, P.; Yu, S. A-synuclein is differentially expressed in mitochondria from different rat brain regions and dose-dependently down-regulates complex I activity. Neuroscience Letters 2009, 454, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.; Raghavendran, V.; Prabhu, B.M.; Avadhani, N.G.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of α-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and parkinson disease brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, 9089–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, M.A.; Ellis, C.E.; Markey, S.P.; Nussbaum, R.L. Proteomics analysis identifies phosphorylation-dependent α-synuclein protein interactions. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2008, 7, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Chan, P.; Uéda, K.; Yu, S.; Yang, H. Semi-quantitative analysis of α-synuclein in subcellular pools of rat brain neurons: An immunogold electron microscopic study using a C-terminal specific monoclonal antibody. Brain Research 2008, 1244, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K. A-synuclein and mitochondria: Partners in crime? Neurotherapeutics 2013, 10, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, A.Y.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Fedotova, E.I.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Dolgacheva, L.P. Interaction of misfolded proteins and mitochondria in neurodegenerative disorders. Biochemical Society Transactions 2017, 45, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuta, T.; Langer, T. Quality control of mitochondria: Protection against neurodegeneration and ageing. The EMBO Journal 2008, 27, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deas, E.; Plun-Favreau, H.; Wood, N.W. PINK1 function in health and disease. EMBO Molecular Medicine 2009, 1, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Vogel, H. drosophila models of neurodegenerative diseases. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 2009, 4, 315–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, S.A.; Hartl, F.U. Mitochondrial stress signaling: A pathway unfolds. Trends in Cell Biology 2008, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufi, R.; Gandhi, S.; de Castro, I.P.; Lehmann, S.; Angelova, P.R.; Dinsdale, D.; Deas, E.; Plun-Favreau, H.; Nicotera, P.; Abramov, A.Y.; Willis, A.E.; Mallucci, G.R.; Loh, S.H.; Martins, L.M. Enhancing nucleotide metabolism protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in a PINK1 model of parkinson’s disease. Nature Cell Biology 2014, 16, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, M.; Allaman, I.; Magistretti, P.J. Brain energy metabolism: Focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metabolism 2011, 14, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, A.; Arduíno, D.; Silva, D.F.F.; Martins Branco, D.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cardoso, S. Mitochondrial Metabolism in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Revisited. Nova Science Publishers, Inc: New York 2011, 187-244.
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.-X. Decreased glucose transporters correlate to abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau in alzheimer disease. FEBS Letters 2008, 582, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R.H.N.; Harik, S.I. Reduced glucose transporter at the blood-brain barrier and in cerebral cortex in alzheimer disease. Journal of Neurochemistry 1989, 53, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, I.A.; Chundu, K.R.; Davies-Hill, T.; Honer, W.G.; Davies, P. Decreased concentrations of Glut1 and GLUT3 glucose transporters in the brains of patients with alzheimer's disease. Annals of Neurology 1994, 35, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harr, S.D.; Simonian, N.A.; Hyman, B.T. Functional alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: Decreased glucose transporter 3 immunoreactivity in the perforant pathway terminal zone. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 1995, 54, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, W.D.; Filley, C.M.; Parks, J.K. Cytochrome oxidase deficiency in alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1990, 40, 1302–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, R.H.; Kish, S.J. Mitochondria in alzheimer's disease. International Review of Neurobiology 2002, 341–385. [Google Scholar]
- Kish, S.J.; Bergeron, C.; Rajput, A.; Dozic, S.; Mastrogiacomo, F.; Chang, L.-J.; Wilson, J.M.; DiStefano, L.M.; Nobrega, J.N. Brain cytochrome oxidase in alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neurochemistry 1992, 59, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoffner, J.M. Oxidative phosphorylation defects and alzheimer's disease. neurogenetics 1997, 1, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Riley, M.; Antuono, P.; Ho, K.-C.; Egan, R.; Hevner, R.; Liebl, W.; Huang, Z.; Rachel, R.; Jones, J. Cytochrome oxidase in alzheimer's disease: Biochemical, histochemical, and immunohistochemical analyses of the visual and other systems. Vision Research 1997, 37, 3593–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.X.; Correia, S.C.; Wang, X.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Moreira, P.I.; Zhu, X. Alzheimer’s disease: Diverse aspects of mitochondrial malfunctioning. International journal of clinical and experimental pathology 2010, 3, 570–581. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, W.D.; Mahr, N.J.; Filley, C.M.; Parks, J.K.; Hughes, D.; Young, D.A.; Cullum, C.M. Reduced platelet cytochrome c oxidase activity in alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1994, 44, 1086–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Vlkolinsky, R.; Cairns, N.; Lubec*, G. Decreased levels of complex III core protein 1 and complex V β chain in brains from patients with alzheimer’s disease and Down Syndrome. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2000, 57, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, F. Cytochrome c oxidase and mitochondrial F1F0-atpase (ATP synthase) activities in platelets and brain from patients with alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2002, 23, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blass, J.P.; Sheu, R.K.; Gibson, G.E. Inherent abnormalities in energy metabolism in alzheimer disease: Interaction with cerebrovascular compromise. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2000, 903, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.M.; Proença, M.T.; Santos, S.; Santana, I.; Oliveira, C.R. Cytochrome c oxidase is decreased in alzheimer’s disease platelets. Neurobiology of Aging 2004, 25, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutisya, E.M.; Bowling, A.C.; Beal, M.F. Cortical cytochrome oxidase activity is reduced in alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neurochemistry 1994, 63, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valla, J.; Schneider, L.; Niedzielko, T.; Coon, K.D.; Caselli, R.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Ahern, G.L.; Baxter, L.; Alexander, G.; Walker, D.G.; Reiman, E.M. Impaired platelet mitochondrial activity in alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Mitochondrion 2006, 6, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.D.; BA, J.P.; Filley, C.M.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K. Electron transport chain defects in alzheimer's disease brain. Neurology 1994, 44, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, D.; Rognoni, F.; Gasparini, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Paolillo, M.; Racchi, M.; Zani, L.; Bianchetti, A.; Trabucchi, M.; Bergamaschi, S.; Govoni, S. Oxidative metabolism in cultured fibroblasts derived from sporadic alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. Neuroscience Letters 1997, 236, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Irwin, R.W.; Zhao, L.; Nilsen, J.; Hamilton, R.T.; Brinton, R.D. Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficit precedes alzheimer's pathology in female mouse model of alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, 14670–14675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, R.; Hatanpää, K.; Rapoport, S.I.; Chandrasekaran, K. Gene expression of ND4, a subunit of complex I of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, is decreased in temporal cortex of brains of alzheimer's disease patients. Brain Research 1996, 713, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.K.; Thomas, B.; Li, X.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Marsh, L.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates ubiquitination and compromises Parkin's protective function. Science 2004, 304, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghammer, P.; Chakravarty, M.; Jonsdottir, K.Y.; Sato, N.; Matsuda, H.; Ito, K.; Arahata, Y.; Kato, T.; Gjedde, A. Cortical hypometabolism and hypoperfusion in parkinson’s disease is extensive: Probably even at early disease stages. Brain Structure and Function 2010, 214, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.D.; Shults, C.W.; Sisk, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E. Enhanced substantia nigra mitochondrial pathology in human α-synuclein transgenic mice after treatment with MPTP. Experimental Neurology 2004, 186, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, L.; Caputo, V.; Bellacchio, E.; Atorino, L.; Dallapiccola, B.; Valente, E.M.; Casari, G. Mitochondrial import and enzymatic activity of PINK1 mutants associated to recessive parkinsonism. Human Molecular Genetics 2005, 14, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacino, J.J.; Sagi, D.; Goldberg, M.S.; Krauss, S.; Motz, C.; Wacker, M.; Klose, J.; Shen, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in parkin-deficient mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 18614–18622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, A.; Kawarai, T.; Paitel, E.; Sanjo, N.; Maj, M.; Scheid, M.; Chen, F.; Gu, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Salehi-Rad, S.; Wang, L.; Rogaeva, E.; Fraser, P.; Robinson, B.; St George-Hyslop, P.; Tandon, A. Wild-type pink1 prevents basal and induced neuronal apoptosis, a protective effect abrogated by parkinson disease-related mutations. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2005, 280, 34025–34032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gehrke, S.; Imai, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, J.-W.; Yang, L.; Beal, M.F.; Vogel, H.; Lu, B. Mitochondrial pathology and muscle and dopaminergic neuron degeneration caused by inactivation of drosophila PINK1 is rescued by Parkin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 10793–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.L.; Yan, X.; Hamamichi, S.; Ajjuri, R.R.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Zhang, M.W.; Daigle, J.G.; Zhang, S.; Borom, A.R.; Roberts, L.R.; Lee, S.K.; DeLeon, S.M.; Viollet-Djelassi, C.; Krainc, D.; O’Donnell, J.M.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. The glycolytic enzyme, GPI, is a functionally conserved modifier of dopaminergic neurodegeneration in parkinson’s models. Cell Metabolism 2014, 20, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesah, Y.; Pham, T.; Burgess, H.; Middlebrooks, B.; Verstreken, P.; Zhou, Y.; Harding, M.; Bellen, H.; Mardon, G. drosophila parkinmutants have decreased mass and cell size and increased sensitivity to oxygen radical stress. Development 2004, 131, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, L.; Allen, G.F.G.; Mamais, A.; Ling, H.; Li, A.; Duberley, K.E.; Hargreaves, I.P.; Pope, S.; Holton, J.L.; Lees, A.; Heales, S.J.; Bandopadhyay, R. Dysregulation of glucose metabolism is an early event in sporadic parkinson's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2014, 35, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, N.; Campos, Y.; Huertas, R.; Esteban, J.; Molina, J.A.; Alonso, A.; Gutierrez-Rivas, E.; Arenas, J. Respiratory chain enzyme activities in lymphocytes from untreated patients with parkinson disease. Clinical Chemistry 1993, 39, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, V.M.; Cooper, J.M.; Daniel, S.E.; Srai, K.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D.; Schapira, A.H. Complex I, iron, and ferritin in parkinson's disease substantia nigra. Annals of Neurology 1994, 36, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Araujo, G.; Nakagami, H.; Hayashi, H.; Mori, M.; Shiuchi, T.; Minokoshi, Y.; Nakaoka, Y.; Takami, Y.; Komuro, I.; Morishita, R.; Kaneda, Y. Alpha-synuclein elicits glucose uptake and utilization in adipocytes through the GAB1/PI3K/akt transduction pathway. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2013, 70, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Nappi, G.; Timothy Greenamyre, J. Quantitative study of Mitochondrial Complex I in platelets of Parkinsonian patients. Movement Disorders 1998, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H.; Nakagawa-Hattori, Y.; Kondo, T.; Mizuno, Y. Mitochondrial complex I and II activities of lymphocytes and platelets in parkinson's disease. Journal of Neural Transmission - Parkinson's Disease and Dementia Section 1992, 4, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.H.; Nasirian, F.; Nakano, K.; Ward, D.; Pay, M.; Hill, R.; Shults, C.W. Low platelet mitochondrial complex I and complex II/III activity in early untreated parkinson's disease. Annals of Neurology 1995, 37, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Schenck, H.; Hall, J.R.; Ross, S.E.; Kline, G.P.; Chen, S.; Mallet, R.T.; Chen, P. Intermittent hypoxia training for treating mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study. American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease & Other Dementias® 2020, 35, 153331751989672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrovska, Z.O.; Serebrovska, T.V.; Kholin, V.A.; Tumanovska, L.V.; Shysh, A.M.; Pashevin, D.A.; Goncharov, S.V.; Stroy, D.; Grib, O.N.; Shatylo, V.B.; Bachinskaya, N.Y.; Egorov, E.; Xi, L.; Dosenko, V.E. Intermittent hypoxia-hyperoxia training improves cognitive function and decreases circulating biomarkers of alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, U.; Likar, R.; Pinter, G.; Stettner, H.; Demschar, S.; Trummer, B.; Neuwersch, S.; Glazachev, O.; Burtscher, M. Intermittent hypoxic-hyperoxic training on cognitive performance in Geriatric Patients. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions 2017, 3, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, K.; Benhamron, S.; Valitsky, M.; Kesner, E.E.; Lichtenstein, M.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Ella, E.; Segalstein, Y.; Saada, A.; LorberboumGalski, H.; et al. Mitochondrial transfer ameliorates cognitive deficits, neuronal loss, and gliosis in Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2019, 72, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, M.; Fu, C.; Fu, A. Intravenous administration of mitochondria for treating experimental Parkinson’s disease. Mitochondrion 2017, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 86 Beale, G.H.; Knowles, J.K. Interspecies transfer of mitochondria in Paramecium aurelia. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1976, 143, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.A.; Shay, J.W. Mitochondrial transformation of mammalian cells. Nature 1982, 295, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flabeau, O.; Meissner, W.G.; Tison, F. Multiple system atrophy: Current and future approaches to management. Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders 2010, 3, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenning, G.K.; Colosimo, C.; Geser, F.; Poewe, W. Multiple system atrophy. The Lancet Neurology 2004, 3, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciulli, A.; Wenning, G.K. Multiple-system atrophy. New England Journal of Medicine 2015, 372, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajrut, A.H.; Uitti, R.J.; Fenton, M.E.; George, D. Amantadine effectiveness in multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 1997, 3, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllensperger, M.; Geser, F.; Ndayisaba, J.-P.; Boesch, S.; Seppi, K.; Ostergaard, K.; Dupont, E.; Cardozo, A.; Tolosa, E.; Abele, M.; Klockgether, T.; Yekhlef, F.; Tison, F.; Daniels, C.; Deuschl, G.; Coelho, M.; Sampaio, C.; Bozi, M.; Quinn, N.; Schrag, A.; Mathias, C.J.; Fowler, C.; Nilsson, C.F.; Widner, H.; Schimke, N.; Oertel, W.; del Sorbo, F.; Albanese, A.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Barone, P.; Djaldetti, R.; Colosimo, C.; Meco, G.; Gonzalez-Mandly, A.; Berciano, J.; Gurevich, T.; Giladi, N.; Galitzky, M.; Rascol, O.; Kamm, C.; Gasser, T.; Siebert, U.; Poewe, W.; Wenning, G.K. Presentation, diagnosis, and management of multiple system atrophy in Europe: Final analysis of the European Multiple System Atrophy Registry. Movement Disorders 2010, 25, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, G.K. Placebo-controlled trial of amantadine in multiple-system atrophy. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2005, 28, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thobois, S.; Broussolle, E.; Toureille, L.; Vial, C. Severe dysphagia after botulinum toxin injection for cervical dystonia in multiple system atrophy. Movement Disorders 2001, 16, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesch, S.M. Dystonia in multiple system atrophy. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2002, 72, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenning, G.K.; Tison, F.; ben Shlomo, Y.; Daniel, S.E.; Quinn, N.P. Multiple system atrophy: A review of 203 pathologically proven cases. Movement Disorders 1997, 12, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Wenning, G.K.; Wissel, J.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. Botulinum toxin treatment in atypical Parkinsonian disorders associated with disabling focal dystonia. Journal of Neurology 2002, 249, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colosimo, C.; Tiple, D.; Wenning, G.K. Management of Multiple System atrophy: State of the art. Journal of Neural Transmission 2005, 112, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilg, W.; Bastian, A.J.; Boesch, S.; Burciu, R.G.; Celnik, P.; Claaßen, J.; Feil, K.; Kalla, R.; Miyai, I.; Nachbauer, W.; Schöls, L.; Strupp, M.; Synofzik, M.; Teufel, J.; Timmann, D. Consensus paper: Management of degenerative cerebellar disorders. The Cerebellum 2013, 13, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedge, F. The impact of resistance training on balance and functional ability of a patient with multiple system atrophy. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2008, 31, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilg, W.; Synofzik, M.; Brotz, D.; Burkard, S.; Giese, M.A.; Schols, L. Intensive coordinative training improves motor performance in degenerative cerebellar disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, M.; Adams, M.; Acosta, K.; Fox, A. Challenge-oriented gait and balance training in sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy: A case study. Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy 2009, 33, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribá, J.; Hoyo, B. Alternatives to clonazepam in rem behavior disorder treatment. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2016, 12, 1193–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, A.; Santamaria, J.; Tolosa, E.; Vilaseca, I.; Valldeoriola, F.; Marti, M.J.; Munoz, E. Long-term effect of CPAP in the treatment of Nocturnal Stridor in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2004, 63, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, M.; Imai, T.; Shintani, T.; Kawamata, M.; Chiba, S.; Matsumoto, H. Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation for laryngeal contraction disorder during sleep in multiple system atrophy. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2006, 247, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorayeb, I.; Bioulac, B.; Tison, F. Sleep disorders in multiple system atrophy. Journal of Neural Transmission 2005, 112, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, G.; Höglinger, G.U.; Levin, J. Symptomatic therapy of Multiple System Atrophy. Autonomic Neuroscience 2018, 211, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensimon, G.; Ludolph, A.; Agid, Y.; Vidailhet, M.; Payan, C.; Leigh, P.N. RILUZOLE treatment, survival and diagnostic criteria in parkinson plus disorders: The NNIPPS study. Brain 2008, 132, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, J.; Koguchi, K.; Momose, T.; Takahashi, M.; Matsukawa, T.; Yasuda, T.; Tokushige, S.-ichi; Ishiura, H.; Goto, J.; Nakazaki, S.; Kondo, T.; Ito, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsuji, S. Three-year follow-up of high-dose ubiquinol supplementation in a case of familial multiple system atrophy with compound heterozygous COQ2 mutations. The Cerebellum 2017, 16, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.-S.; Song, S.K.; Lee, H.S.; Nam, H.S.; Cheong, J.-W.; Jeong, Y.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, D.J.; Nam, C.M.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.O.; Sohn, Y.H. A randomized trial of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple system atrophy. Annals of Neurology 2012, 72, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacca, F.; Marsili, A.; Quarantelli, M.; Brescia Morra, V.; Brunetti, A.; Carbone, R.; Pane, C.; Puorro, G.; Russo, C.V.; Salvatore, E.; Tucci, T.; Michele, G.; Filla, A. A randomized clinical trial of lithium in multiple system atrophy. Journal of Neurology 2013, 260, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras-Garvin, A.; Weckbecker, D.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Griesinger, C.; Giese, A.; Wenning, G.K.; Stefanova, N. ANLE138B modulates α-synuclein oligomerization and prevents motor decline and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Multiple System Atrophy. Movement Disorders 2019, 34, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, E.; Spencer, B.; Mott, J.; Trejo, M.; Adame, A.; Mante, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Troncoso, J.C.; Beach, T.G.; Masliah, E.; Desplats, P. MicroRNA-101 modulates autophagy and oligodendroglial alpha-synuclein accumulation in multiple system atrophy. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2017, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassil, F.; Canron, M.-H.; Vital, A.; Bezard, E.; Li, Y.; Greig, N.H.; Gulyani, S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Fernagut, P.-O.; Meissner, W.G. Insulin resistance and exendin-4 treatment for multiple system atrophy. Brain 2017, 140, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Vaquero, M.; Bouquio, D.; Kallab, M.; Biggs, K.; Nair, G.; Ochoa, J.; Heras-Garvin, A.; Heid, C.; Hadrovic, I.; Poewe, W.; Wenning, G.K.; Klärner, F.-G.; Schrader, T.; Bitan, G.; Stefanova, N. The Molecular Tweezer CLR01 reduces aggregated, pathologic, and seeding-competent α-synuclein in experimental multiple system atrophy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2019, 1865, 165513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassil, F.; Fernagut, P.-O.; Bezard, E.; Pruvost, A.; Leste-Lasserre, T.; Hoang, Q.Q.; Ringe, D.; Petsko, G.A.; Meissner, W.G. Reducing C-terminal truncation mitigates synucleinopathy and neurodegeneration in a transgenic model of Multiple System Atrophy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, 9593–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenning, G.K.; Krismer, F.; Poewe, W. Rifampicin for Multiple System atrophy. The Lancet Neurology 2014, 13, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal, J.S.; Zhan, J.; Wang, Y.; Sugimoto, R.; Tsung, A.; McCurry, K.R.; Billiar, T.R.; Nakao, A. Oral hydrogen water prevents chronic allograft nephropathy in rats. Kidney International 2009, 77, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, K.; Sano, M.; Kamimura, N.; Yokota, T.; Suzuki, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Kawamura, A.; Abe, T.; Ohta, S.; Fukuda, K. ; Hori, S H 2 gas improves functional outcome after cardiac arrest to an extent comparable to therapeutic hypothermia in a rat model. Journal of the American Heart Association 2012, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-ichiro; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nature Medicine 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.-ichi; Asoh, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Inhalation of hydrogen gas suppresses hepatic injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion through reducing oxidative stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2007, 361, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Huang, C.-S.; Tochigi, N.; Lee, S.; Shigemura, N.; Billiar, T.R.; Okumura, M.; Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y. Inhaled hydrogen gas therapy for prevention of lung transplant-induced ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, S.; Hasegawa, G.; Asano, M.; Hosoda, H.; Fukui, M.; Nakamura, N.; Kitawaki, J.; Imai, S.; Nakano, K.; Ohta, M.; Adachi, T.; Obayashi, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutrition Research 2008, 28, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, N.; Nishimaki, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen improves obesity and diabetes by inducing hepatic FGF21 and stimulating energy metabolism in db/db mice. Obesity 2011, 19, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Recent progress toward hydrogen medicine: Potential of molecular hydrogen for preventive and therapeutic applications. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2011, 17, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, B.M.; Kaczorowski, D.J.; Sugimoto, R.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Billiar, T.R.; McCurry, K.R.; Bauer, A.J.; Nakao, A. Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates oxidative stress in transplantation induced intestinal graft injury. American Journal of Transplantation 2008, 8, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yamafuji, M.; Tachibana, T.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Noda, M.; Nakaya, H. Oral ‘Hydrogen Water’ induces neuroprotective ghrelin secretion in mice. Scientific Reports 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoritaka, A.; Takanashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nakahara, T.; Ohta, S.; Hattori, N. Pilot study of H2therapy in parkinson's disease: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2013, 28, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Imamura, R.; Koyama, Y.; Kondo, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Nonomura, N.; Shimada, S. Renoprotective and neuroprotective effects of enteric hydrogen generation from si-based agent. Scientific Reports 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Yamai, K.; Goto, S.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Ohno, K. Drinking hydrogen water and intermittent hydrogen gas exposure, but not lactulose or continuous hydrogen gas exposure, prevent 6-hydorxydopamine-induced parkinson’s disease in rats. Medical Gas Research 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, Y.; Inoue, T.; Uemura, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yada, T.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Noda, M. Complexity of stomach–brain interaction induced by molecular hydrogen in parkinson’s disease model mice. Neurochemical Research 2017, 42, 2658–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Seike, T.; Yutsudo, N.; Ohno, M.; Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sakumi, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Kido, M.A.; Takaki, A.; Katafuchi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Noda, M. Hydrogen in drinking water reduces dopaminergic neuronal loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of parkinson's disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Ito, M.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Masuda, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Maesawa, S.; Kajita, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S.; Ohno, K. Molecular hydrogen is protective against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nigrostriatal degeneration in a rat model of parkinson's disease. Neuroscience Letters 2009, 453, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, B.; Cai, S.; Hui, K.; Yu, G.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Duan, M.; Sun, X. Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen-rich saline in global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats: Up-regulated Tregs and down-regulated Mir-21, mir-210 and NF-ΚB Expression. Neurochemical Research 2016, 41, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.-Y.; Hu, Q.; Huang, J.-L.; Liu, W.-W.; Manaenko, A.; Sun, X.-J. Hydrogen inhibits microglial activation and regulates microglial phenotype in a mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Medical Gas Research 2019, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kinone, K.; Horikosi, T.; Tamaki, M.; Takeshita, H.; Futatuki, T.; Ohishi, W.; Ishiguro, T.; Okamoto, S.; Ishii, S.; Takanami, H. Hydrogen gas inhalation treatment in acute cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled clinical study on safety and neuroprotection. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2017, 26, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Gui, Q.; Jin, L.; Yu, P.; Wu, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, Q.; Duan, M. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates hippocampus endoplasmic reticulum stress after cardiac arrest in rats. Neuroscience Letters 2017, 640, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Shao, A.W.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.J.; McBride, D.W.; Wu, Q.; Sun, X.J.; Zhang, J.M. Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen-rich saline against neurologic damage and apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage: Possible role of the AKT/gsk3β signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, A.; Wu, H.; Hong, Y.; Tu, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuated subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced early brain injury in rats by suppressing inflammatory response: Possible involvement of NF-ΚB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Molecular Neurobiology 2016, 53, 3462–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang L, Zhao P, Yue C, Jin Z, Liu Q, Du X, et al. Sustained release of bioactive hydrogen by Pd hydride nanoparticles overcomes Alzheimer’s disease. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 393–404.
- Wei, R.; Zhang, R.; Xie, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, F. Hydrogen suppresses hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death in hippocampal neurons through reducing oxidative stress. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2015, 36, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Peng, Y.; Qin, C.; Fan, F.; Liu, J.; Long, J. Hydrogen-rich water improves cognitive impairment gender-dependently in App/PS1 mice without affecting AΒ clearance. Free Radical Research 2018, 52, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.H.; Cai, J.-M.; Cao, Y.-P.; Sun, X.-J. Hydrogen-rich saline improves memory function in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced alzheimer's disease by reduction of oxidative stress. Brain Research 2010, 1328, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-L.; Huang, W.-N.; Li, H.-H.; Huang, C.-N.; Hsieh, S.; Lai, C.; Lu, F.-J. Hydrogen-rich water attenuates amyloid β-induced cytotoxicity through upregulation of SIRT1-FOXO3A by stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase in SK-N-MC Cells. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2015, 240, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, Y.-P.; Sun, X.-J. Hydrogen-rich saline reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by inhibit of JNK and NF-ΚB activation in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience Letters 2011, 491, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-xiang; Wang, J.-long; Zhang, Q.-shan; Zhu, K.-di; Sun, J.-feng; Zhang, Z.-peng; Sun, J.-. wen Hydrogen-rich saline injection into the subarachnoid cavity within 2 weeks promotes recovery after acute spinal cord injury. Neural Regeneration Research 2015, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohi, K.; Kraemer, B.C.; Erickson, M.A.; McMillan, P.J.; Kovac, A.; Flachbartova, Z.; Hansen, K.M.; Shah, G.N.; Sheibani, N.; Salameh, T.; Banks, W.A. Molecular hydrogen in drinking water protects against neurodegenerative changes induced by traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Tian, Y.; Xie, K.; Liu, W.; Qu, Y.; Fei, Z. Protective effects of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat model of traumatic brain injury via reducing oxidative stress. Journal of Surgical Research 2012, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhi, X.; Weng, W.; Pan, P.; Cao, L.; Ji, F.; Wang, Z.; Su, J. Inhalation of hydrogen of different concentrations ameliorates spinal cord injury in mice by protecting spinal cord neurons from apoptosis, oxidative injury and mitochondrial structure damages. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2018, 47, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-T.; Xu, S.-M.; Xiang, Z.-H.; Li, X.-N.; Li, J.; Yuan, H.-B.; Sun, X.-J. Molecular hydrogen suppresses reactive astrogliosis related to oxidative injury during spinal cord injury in rats. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 2014, 20, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-ichiro; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nature Medicine 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, B.; Hanna, S.; Abdallahi, O.M.S.; Lepidi, H.; Gardette, B.; De Reggi, M. Anti-inflammatory properties of molecular hydrogen: Investigation on parasite-induced liver inflammation. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences - Series III - Sciences de la Vie 2001, 324, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Adachi, N.; Sakamoto, M.; Kudo, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Nakao, A.; Imaoka, T. A basic study on molecular hydrogen (H2) inhalation in acute cerebral ischemia patients for safety check with physiological parameters and measurement of blood H2 level. Medical Gas Research 2012, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, M.-liang; You, W.-chun; Zhu, L.; Ma, C.-yuan; Sun, X.-jun; Shi, J.-. xin Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates early brain injury via reducing oxidative stress and brain edema following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in Rabbits. BMC Neuroscience 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Maki, T.; Shindo, A.; Egawa, N.; Liang, A.C.; Itoh, N.; Lo, E.H.; Lok, J.; Arai, K. Magnesium sulfate protects oligodendrocyte lineage cells in a rat cell-culture model of hypoxic–ischemic injury. Neuroscience Research 2016, 106, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. A method for distinguishing ionized, complexed and protein-bound MG in normal and diseased subjects. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 1994, 54, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowaltowski, A.J.; Naia-da-Silva, E.S.; Castilho, R.F.; Vercesi, A.E. Ca2+-stimulated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and permeability transition are inhibited by Dibucaine or mg2+. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 1998, 359, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Meloni, B.P.; Knuckey, N.W. Combined magnesium and mild hypothermia (35 °C) treatment reduces infarct volumes after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat at 2 and 4, but not 6 h. Brain Research 2008, 1230, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, Y.; Roussel, S.; Pinard, E.; Seylaz, J. Reduction of infarct volume by magnesium after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 1991, 11, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-J.; Ayoub, I.A.; Harris, F.B.; Hassan, M.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Maynard, K.I. Mexiletine and magnesium independently, but not combined, protect against permanent focal cerebral ischemia in wistar rats. Journal of Neuroscience Research 1999, 58, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Chen, G. ; Effects of magnesium sulfate on neuron apoptosis and expression of caspase-3, bax and bcl-2 after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chinese medical journal 2003, 116, 1532–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.-J.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chang, G.-L.; Chen, L.-H.; Hu, Y.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wu, T.-S. Delayed treatment with magnesium: Reduction of brain infarction and improvement of electrophysiological recovery following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Journal of Neurosurgery 2005, 102, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabey, C.; Sahin, S.; Kahraman, S.; Bulakbasi, N. Can magnesium Sulphate prevent cerebral ischemic injury? An experimental study and Neuroradiological evidence. Journal of Neurological Sciences 2013, 30, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Irani K, Finkel T. Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science. 1995, 270, 296–299.
- Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free radicals, other reactive species and disease. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (eds). Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Clarendon Press: Oxford. 1999, pp.617–783.
- Auerbach JM, Segal M. Peroxide modulation of slow onset potentiation in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8695–8701.
- Klann E, Thiels E. Modulation of protein kinases and proteins phosphatases by reactive oxygen species: implications for hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1999, 23, 359–376.
- Topper JN, Cai J, Falb D, Gimbrone MA Jr. Identification of vascular endothelial genes differentially responsive to fluid mechanical stimuli: cyclooxygenase-2, manganese superoxide dismutase, and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase are selectively up-regulated by steady laminar shear stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996, 93, 10417–10422.
- Rhee, SG. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science. 2006, 312, 1882–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Autréaux B, Toledano MB. ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 813–824.
- Stone JR, Yang S. Hydrogen peroxide: a signaling messenger. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 243–270.
- Xiao-Qing T, Jun-Li Z, Yu C, Jian-Qiang F, Pei-Xi C. Hydrogen peroxide preconditioning protects PC12 cells against apoptosis induced by dopamine.
- Wibowo S, Sumitro SB, Widyarti S. Computational Study of Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+ and Mn3+ binding sites identification on HSA 4K2C. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2020, 833, 012052. [CrossRef]
- WIBOWO SYAHPUTRA, WIDYARTI SRI, SABARUDIN AKHMAD, SOEATMADJI DJOKOWAHONO, SUMITRO SUTIMANBAMBANG. The role of astaxanthin compared with metformin in preventing glycated human serum albumin from possible unfolding: A molecular dynamic study. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2019, 276-282. [CrossRef]
- Wibowo S, Widyarti S, Sabarudin A, Soeatmadji DW, Sumitro SB. DFT and molecular dynamics studies of astaxanthin-metal ions (cu2+ and zn2+) complex to prevent glycated human serum albumin from possible unfolding. Heliyon. 2021, 7(3). [CrossRef]
- Wibowo S, Costa J, Baratto MC, Pogni R, Widyarti S, Sabarudin A, Matsuo K, Sumitro SB. Quantification and Improvement of the Dynamics of Human Serum Albumin and Glycated Human Serum Albumin with Astaxanthin/Astaxanthin-Metal Ion Complexes: Physico-Chemical and Computational Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23, 4771. [CrossRef]
| Neurodegenerative Diseases | Neuronal Glucose and Glucose metabolism (Decrease Uptake) | Dysfunctional in Mitochondria | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | ↓ Expression of glucose transporter | Imbalance in mitochondrial fission and fusion | [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| ↑ Metabolism of ketone body | ↓ Axonal transport | ||
| ↓ Metabolic complex activity | ↓ Mitochondria in a cell | ||
| ↑ Aerobic Glycolysis | |||
| ↑ Pyruvate dehydrogenase in inactive form | |||
| Parkinson’s Disease | ↓ NADH dehydrogenase | Mutations in Leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) | [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] |
| ↓ 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase | Mutations in PTEN induced kinase 1 (PINK1) | ||
| ↓ G6P dehydrogenase | Mutations in Htr A serine peptide 2 (HTRA2) |
| Mechanism | Therapeutic drug | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroprotection | Riluzole | No effect on progression of MSA (Phase III) | [108] |
| Mitochondrial Function | CoQ10 | Ongoing (Phase II) | [109] |
| Neuroprotection | Mesenchymal stem cells | Delayed progression of MSA (Phase II) | [110] |
| α-Synuclein (Inhibition of aggregation process) |
Lithium | Drug trial is terminated (severe side effect such as death, daytime sleepiness and tremor) | [111] |
| α-Synuclein (Modulates of oligomerization process) | Anle138b | Ongoing (Phase I) | [112] |
| α-Synuclein (Inhibition of aggregation process) |
Anti-miR-101 | Decreased GCIs and increased autophagy (Pre-clinic) | [113] |
| Neuroprotection | Exendin-4 | Decreased α-synuclein oligomers, cell death and insulin resistance (Phase II) | [114] |
| α-Synuclein (Inhibition of aggregation process) |
CLR01 | Decreased synuclein oligomers, GCIs, microglial activation and motor impairment (Pre-clinic) | [115] |
| Belnacasan (VX-765) | Decreased synuclein oligomers, GCIs, microglial activation (Pre-clinic) | [116] | |
| Rifampicin | No offect on progression of MSA (Phase II) | [117] |
| Hydrogen administration | Neurodegenerative Disease | Mechanism of Neuroprotective Effects | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral and inhalation | Parkinson’s disease | Activation of gastric ghrelin system, minimizing the loss of dopaminergic cells, and reducing oxidative stress | [127,128,129,130,131,132,133] |
| Oral, inhalation, intravenous and intraperitoneal injection | Ischemia | Stabilization of mitochondrial function, blood-brain barrier maintenance, reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative and inflammatory stress | [134,135,136,137] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | Subarachnoid hemorrhage | Anti apoptosis and inhibiton of oxidative stress | [138,139] |
| Oral, intracerebral and intraperitoneal injection | Alzheimer’s disease | Up regulation of Sirt1-FoxO3a axis, stimulating AMPK, inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 and JNK | [140,141,142,143,144,145] |
| Intraperitoneal injection and inhalation | Brain injury | Blood-brain barrier maintenance and stabilization of mitochondrial function | [146,147,148,149,150] |
| Magnesium Administration | Magnesium Type and Dose | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous injection | MgSO4 (360 μmol/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume if combined with mild hypothermia | [158] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | MgCl2 (1 mmol/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume | [159] |
| Inraarterial injection | MgSO4 (90 mg/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume | [160] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | MgSO4 (2 g/kg) | Reduction of neuronal apoptosis | [161] |
| Inraarterial injection | MgSO4 (750 μmol/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume | [162] |
| Intravenous injection | MgSO4 (90 mg/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume | [163] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | MgSO4 (250 mg/kg) | Reduction of infarct volume | [164] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





