Submitted:
09 January 2023
Posted:
12 January 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
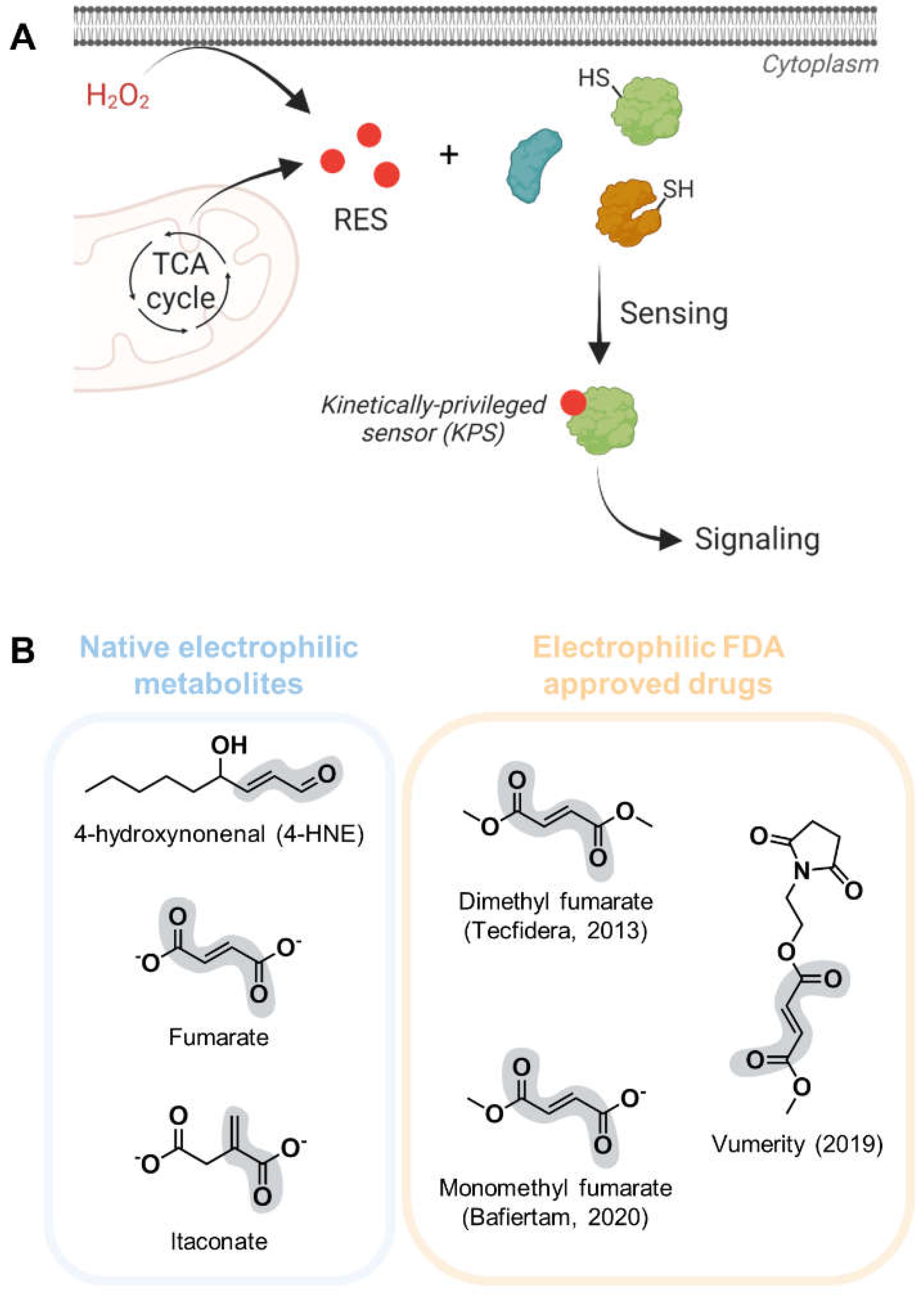
1. Introduction
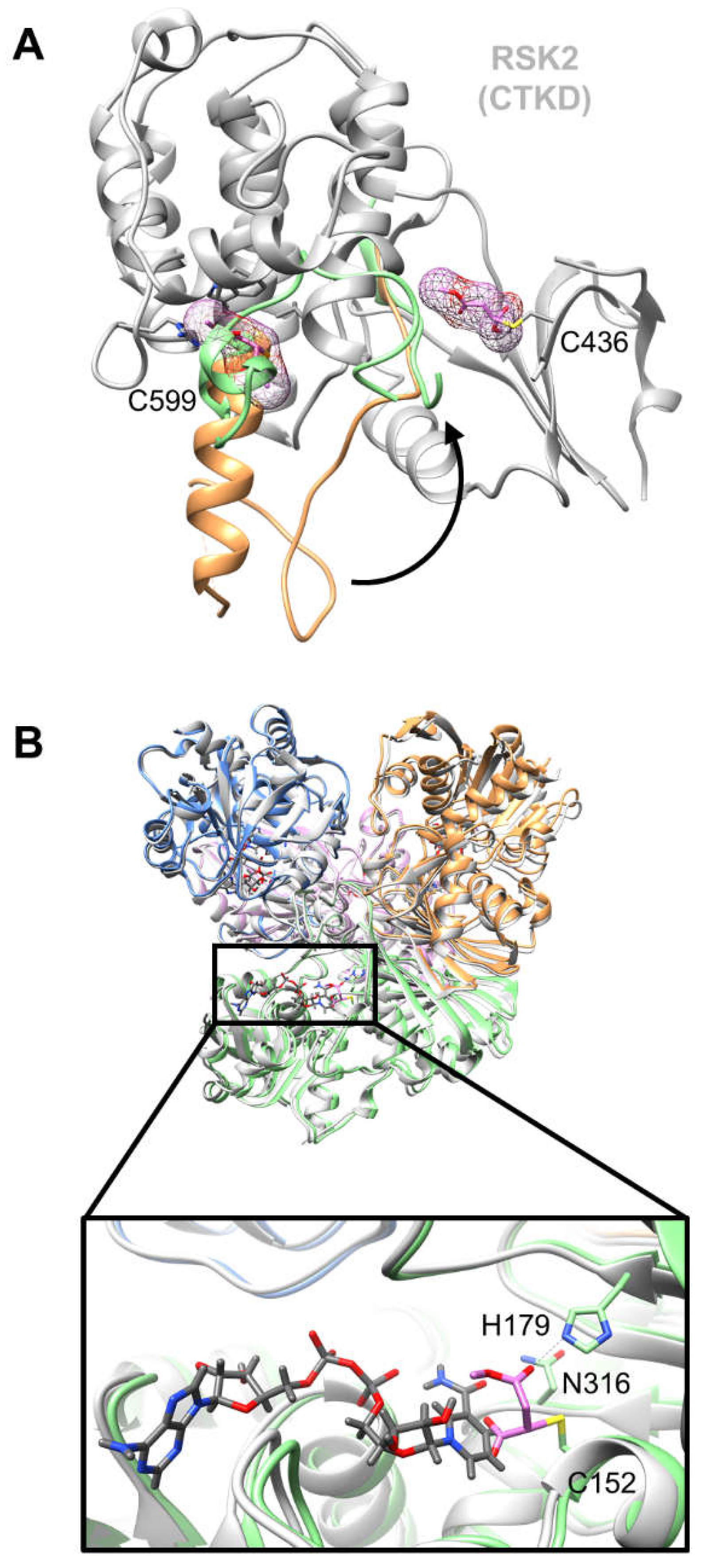
2. Structural basis of and putative insights into dimethyl fumarate mode of action
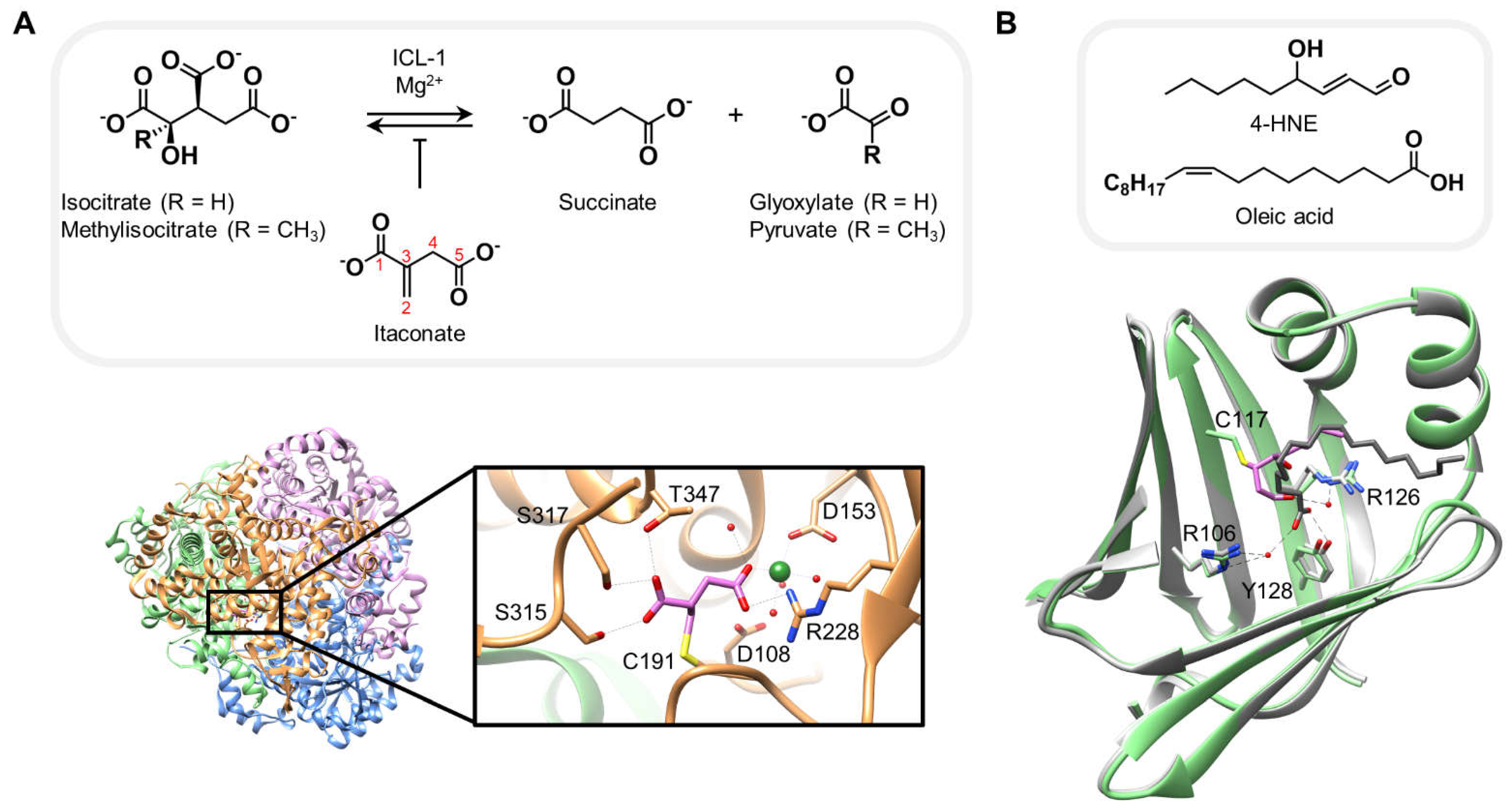
3. Structures of proteins covalently bound to native electrophiles resembling canonical substrates
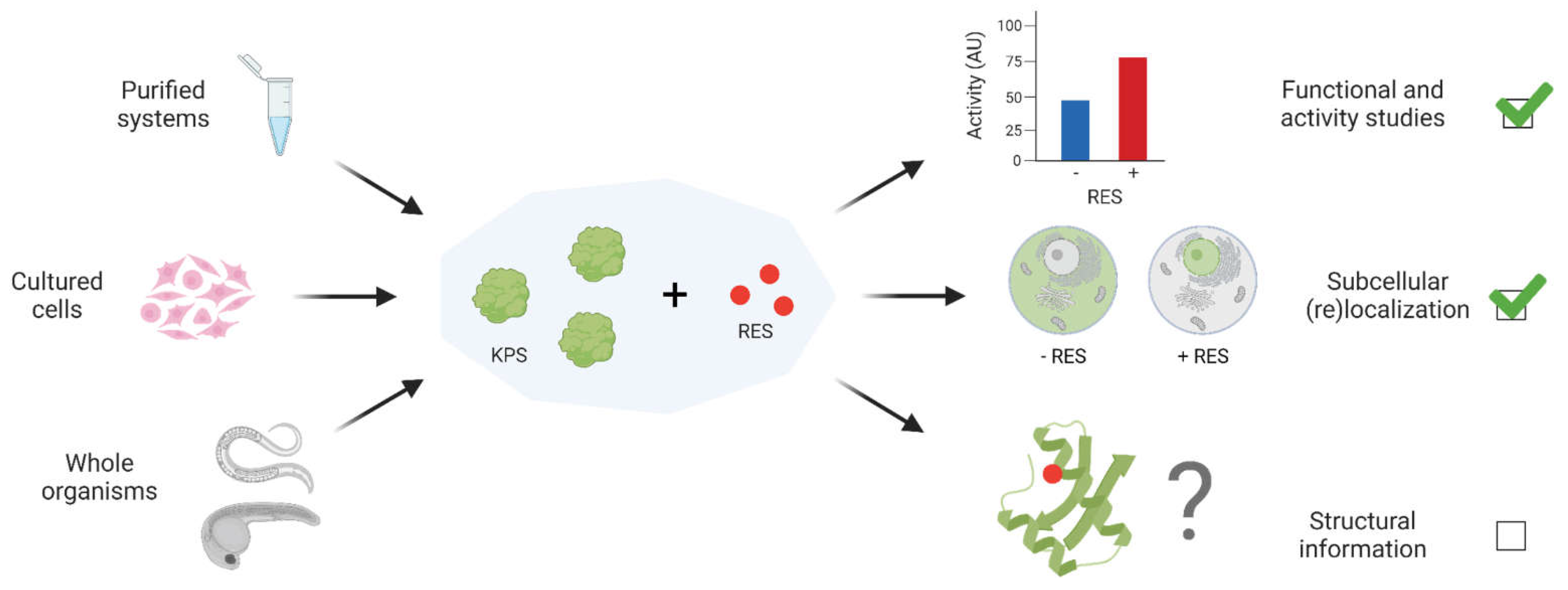
4. Capturing structural data on true kinetically-privileged electrophile-sensor proteins
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S. Parvez, M. J. C. Long, J. R. Poganik, Y. Aye, ‘Redox Signaling by Reactive Electrophiles and Oxidants’, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 8798–8888.
- F. J. Schopfer, C. Cipollina, B. A. Freeman, ‘Formation and Signaling Actions of Electrophilic Lipids’, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5997–6021. [CrossRef]
- V. Lampropoulou, A. Sergushichev, M. Bambouskova, S. Nair, E. E. Vincent, E. Loginicheva, L. Cervantes-Barragan, X. Ma, S. C.-C. Huang, T. Griss, C. J. Weinheimer, S. Khader, G. J. Randolph, E. J. Pearce, R. G. Jones, A. Diwan, M. S. Diamond, M. N. Artyomov, ‘Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation’, Cell Metabolism 2016, 24, 158–166. [CrossRef]
- M. Delmastro-Greenwood, B. A. Freeman, S. G. Wendell, ‘Redox-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Signaling Actions of Unsaturated Fatty Acids’, Annual Review of Physiology 2014, 76, 79–105. [CrossRef]
- J. Singh, R. C. Petter, T. A. Baillie, A. Whitty, ‘The resurgence of covalent drugs’, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 307–317. [CrossRef]
- H.-P. Shih, X. Zhang, A. M. Aronov, ‘Drug discovery effectiveness from the standpoint of therapeutic mechanisms and indications’, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2018, 17, 19–33. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Privileged Electrophile Sensors: A Resource for Covalent Drug Development’, Cell Chemical Biology 2017, 24, 787–800. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, A. Kulkarni, Y. Aye, ‘Can Precision Electrophile Signaling Make a Meaningful and Lasting Impression in Drug Design?’, ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202100051. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Poganik, K.-T. Huang, S. Parvez, Y. Zhao, S. Raja, M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Wdr1 and cofilin are necessary mediators of immune-cell-specific apoptosis triggered by Tecfidera’, Nat Commun 2021, 12, 5736. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu, M. J. C. Long, B. D. Hopkins, C. Luo, L. Wang, Y. Aye, ‘Precision Targeting of pten-Null Triple-Negative Breast Tumors Guided by Electrophilic Metabolite Sensing’, ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 892–902. 2020; 6, 892–902. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Niphakis, B. F. Cravatt, ‘Enzyme Inhibitor Discovery by Activity-Based Protein Profiling’, Annual Review of Biochemistry 2014, 83, 341–377. [CrossRef]
- A. J. Maurais, E. Weerapana, ‘Reactive-cysteine profiling for drug discovery’, Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2019, 50, 29–36. [CrossRef]
- S. Parvez, M. J. C. Long, H.-Y. Lin, Y. Zhao, J. A. Haegele, V. N. Pham, D. K. Lee, Y. Aye, ‘T-REX on-demand redox targeting in live cells’, Nature Protocols 2016, 11, 2328–2356. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, C. Rogg, Y. Aye, ‘An Oculus to Profile and Probe Target Engagement In Vivo: How T-REX Was Born and Its Evolution into G-REX’, Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 618–631. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘The Die Is Cast: Precision Electrophilic Modifications Contribute to Cellular Decision Making’, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1575–1582. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Poganik, M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Getting the Message? Native Reactive Electrophiles Pass Two Out of Three Thresholds to be Bona Fide Signaling Mediators’, BioEssays 2018, 40, 1700240. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu, M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Proteomics and Beyond: Cell Decision-Making Shaped by Reactive Electrophiles’, Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2019, 44, 75–89. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, H.-Y. Lin, S. Parvez, Y. Zhao, J. R. Poganik, P. Huang, Y. Aye, ‘β-TrCP1 Is a Vacillatory Regulator of Wnt Signaling’, Cell Chemical Biology 2017, 24, 944-957.e7.
- M. J. C. Long, D. A. Urul, S. Chawla, H.-Y. Lin, Y. Zhao, J. A. Haegele, Y. Wang, Y. Aye, ‘Precision Electrophile Tagging in Caenorhabditis elegans’, Biochemistry 2018, 57, 216–220.
- M. J. C. Long, S. Parvez, Y. Zhao, S. L. Surya, Y. Wang, S. Zhang, Y. Aye, ‘Akt3 is a privileged first responder in isozyme-specific electrophile response’, Nat Chem Biol 2017, 13, 333–338. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao, M. J. C. Long, Y. Wang, S. Zhang, Y. Aye, ‘Ube2V2 Is a Rosetta Stone Bridging Redox and Ubiquitin Codes, Coordinating DNA Damage Responses’, ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 246–259.
- S. Parvez, Y. Fu, J. Li, M. J. C. Long, H.-Y. Lin, D. K. Lee, G. S. Hu, Y. Aye, ‘Substoichiometric Hydroxynonenylation of a Single Protein Recapitulates Whole-Cell-Stimulated Antioxidant Response’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10–13. [CrossRef]
- S. L. Surya, M. J. C. Long, D. A. Urul, Y. Zhao, E. J. Mercer, I. M. EIsaid, T. Evans, Y. Aye, ‘Cardiovascular Small Heat Shock Protein HSPB7 Is a Kinetically Privileged Reactive Electrophilic Species (RES) Sensor’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1824–1831. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Poganik, M. J. C. Long, M. T. Disare, X. Liu, S.-H. Chang, T. Hla, Y. Aye, ‘Post-transcriptional regulation of Nrf2-mRNA by the mRNA-binding proteins HuR and AUF1’, The FASEB Journal 2019, 33, 14636–14652.
- J. R. Poganik, A. K. Van Hall-Beauvais, M. J. C. Long, M. T. Disare, Y. Zhao, Y. Aye, ‘The mRNA-Binding Protein HuR Is a Kinetically-Privileged Electrophile Sensor’, Helvetica Chimica Acta 2020, 103, e2000041.
- Y. Zhao, P. A. Miranda Herrera, D. Chang, R. Hamelin, M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Function-guided proximity mapping unveils electrophilic-metabolite sensing by proteins not present in their canonical locales’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2022, 119, e2120687119. [CrossRef]
- A. Van Hall-Beauvais, J. R. Poganik, K.-T. Huang, S. Parvez, Y. Zhao, H.-Y. Lin, X. Liu, M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Z-REX uncovers a bifurcation in function of Keap1 paralogs’, eLife 2022, 11, e83373. [CrossRef]
- K.-T. Huang, J. R. Poganik, S. Parvez, S. Raja, B. Miller, M. J. C. Long, J. R. Fetcho, Y. Aye (in press), ‘Z-REX: Shepherding Reactive Electrophiles to Specific Proteins Expressed either Tissue-Specifically or Ubiquitously, and Recording the Resultant Functional Electrophile-Induced Redox Responses in Larval Fish’, Nat Protoc 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Hellberg, P. A. Grimsrud, A. C. Kruse, L. J. Banaszak, D. H. Ohlendorf, D. A. Bernlohr, ‘X-ray crystallographic analysis of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aP2) modified with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal’, Protein Science 2010, 19, 1480–1489. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Andersen, B. Gesser, E. D. Funder, C. J. F. Nielsen, H. Gotfred-Rasmussen, M. K. Rasmussen, R. Toth, K. V. Gothelf, J. S. C. Arthur, L. Iversen, P. Nissen, ‘Dimethyl fumarate is an allosteric covalent inhibitor of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinases’, Nat Commun 2018, 9, 4344. [CrossRef]
- J. B. Park, H. Park, J. Son, S.-J. Ha, H.-S. Cho, ‘Structural Study of Monomethyl Fumarate-Bound Human GAPDH’, Molecules and Cells 2019, 42, 597–603. [CrossRef]
- B. X. C. Kwai, A. J. Collins, M. J. Middleditch, J. Sperry, G. Bashiri, I. K. H. Leung, ‘Itaconate is a covalent inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyase’, RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 57–61. [CrossRef]
- X.-N. Guan, T. Zhang, T. Yang, Z. Dong, S. Yang, L. Lan, J. Gan, C.-G. Yang, ‘Covalent sortase A inhibitor ML346 prevents Staphylococcus aureus infection of Galleria mellonella’, RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 138–149. [CrossRef]
- ‘FDA Approves Tecfidera - a New Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis’, can be found under. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-tecfidera-new-multiple-sclerosis-3731.html, n.d.
- D. M. Balak, ‘Fumaric acid esters in the management of psoriasis’, PTT 2015, 5, 9–23. [CrossRef]
- H. A. Blair, ‘Dimethyl Fumarate: A Review in Relapsing-Remitting MS’, Drugs 2019, 79, 1965–1976. [CrossRef]
- ‘FDA Approves Vumerity (diroximel fumarate) for Multiple Sclerosis’, can be found under. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-vumerity-diroximel-fumarate-multiple-sclerosis-5096.html, n.d.
- ‘FDA Approves Bafiertam (monomethyl fumarate) for Multiple Sclerosis’, can be found under. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-bafiertam-monomethyl-fumarate-multiple-sclerosis-5252.html, n.d.
- U. Schulze-Topphoff, M. Varrin-Doyer, K. Pekarek, C. M. Spencer, A. Shetty, S. A. Sagan, B. A. C. Cree, R. A. Sobel, B. T. Wipke, L. Steinman, R. H. Scannevin, S. S. Zamvil, ‘Dimethyl fumarate treatment induces adaptive and innate immune modulation independent of Nrf2’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, 4777–4782. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Poganik, Y. Aye, ‘Electrophile Signaling and Emerging Immuno- and Neuro-modulatory Electrophilic Pharmaceuticals’, Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12.
- B. Gesser, M. K. Rasmussen, L. Raaby, C. Rosada, C. Johansen, R. B. Kjellerup, K. Kragballe, L. Iversen, ‘Dimethylfumarate inhibits MIF-induced proliferation of keratinocytes by inhibiting MSK1 and RSK1 activation and by inducing nuclear p-c-Jun (S63) and p-p53 (S15) expression’, Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 643–653. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Blewett, J. Xie, B. W. Zaro, K. M. Backus, A. Altman, J. R. Teijaro, B. F. Cravatt, ‘Chemical proteomic map of dimethyl fumarate–sensitive cysteines in primary human T cells’, Science Signaling 2016, 9, rs10–rs10. [CrossRef]
- E. Kotelnikova, N. A. Kiani, D. Messinis, I. Pertsovskaya, V. Pliaka, M. Bernardo-Faura, M. Rinas, G. Vila, I. Zubizarreta, I. Pulido-Valdeolivas, T. Sakellaropoulos, W. Faigle, G. Silberberg, M. Masso, P. Stridh, J. Behrens, T. Olsson, R. Martin, F. Paul, L. G. Alexopoulos, J. Saez-Rodriguez, J. Tegner, P. Villoslada, ‘MAPK pathway and B cells overactivation in multiple sclerosis revealed by phosphoproteomics and genomic analysis’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 9671–9676. [CrossRef]
- K. Uchida, E. R. Stadtman, ‘Covalent attachment of 4-hydroxynonenal to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. A possible involvement of intra- and intermolecular cross-linking reaction.’, Journal of Biological Chemistry 1993, 268, 6388–6393.
- M. Blatnik, N. Frizzell, S. R. Thorpe, J. W. Baynes, ‘Inactivation of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase by Fumarate in Diabetes: Formation of S-(2-Succinyl)Cysteine, a Novel Chemical Modification of Protein and Possible Biomarker of Mitochondrial Stress’, Diabetes 2008, 57, 41–49.
- M. D. Kornberg, P. Bhargava, P. M. Kim, V. Putluri, A. M. Snowman, N. Putluri, P. A. Calabresi, S. H. Snyder, ‘Dimethyl fumarate targets GAPDH and aerobic glycolysis to modulate immunity’, Science 2018, 360, 449–453. [CrossRef]
- D. Werdenberg, R. Joshi, S. Wolffram, H. p. Merkle, P. Langguth, ‘Presystemic metabolism and intestinal absorption of antipsoriatic fumaric acid esters’, Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 2003, 24, 259–273. [CrossRef]
- N. H. Litjens, E. van Strijen, C. van Gulpen, H. Mattie, J. T. van Dissel, H. B. Thio, P. H. Nibbering, ‘In vitro pharmacokinetics of anti-psoriatic fumaric acid esters’, BMC Pharmacology 2004, 4, 22.
- H.-Y. Lin, J. A. Haegele, M. T. Disare, Q. Lin, Y. Aye, ‘A Generalizable Platform for Interrogating Target- and Signal-Specific Consequences of Electrophilic Modifications in Redox-Dependent Cell Signaling’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6232–6244. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, Y. Aye, ‘Keap 1: The new Janus word on the block’, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2022, 71, 128766.
- S. Unni, P. Deshmukh, G. Krishnappa, P. Kommu, B. Padmanabhan, ‘Structural insights into the multiple binding modes of Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF) and its analogs to the Kelch domain of Keap1’, The FEBS Journal 2021, 288, 1599–1613. [CrossRef]
- E. Crisman, P. Duarte, E. Dauden, A. Cuadrado, M. I. Rodríguez-Franco, M. G. López, R. León, ‘KEAP1-NRF2 protein–protein interaction inhibitors: Design, pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential’, Medicinal Research Reviews 2022, n/a, DOI 10.1002/med.21925. [CrossRef]
- L. Baird, M. Yamamoto, ‘The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway’, Molecular and Cellular Biology 2020, 40, e00099-20. [CrossRef]
- J. Lin, J. Ren, D. S. Gao, Y. Dai, L. Yu, ‘The Emerging Application of Itaconate: Promising Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Opportunities’, Frontiers in Chemistry 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- T. Cordes, A. Michelucci, K. Hiller, ‘Itaconic Acid: The Surprising Role of an Industrial Compound as a Mammalian Antimicrobial Metabolite’, Annual Review of Nutrition 2015, 35, 451–473. [CrossRef]
- L. A. J. O’Neill, M. N. Artyomov, ‘Itaconate: the poster child of metabolic reprogramming in macrophage function’, Nat Rev Immunol 2019, 19, 273–281. [CrossRef]
- J. D. McKinney, K. H. zu Bentrup, E. J. Muñoz-Elías, A. Miczak, B. Chen, W.-T. Chan, D. Swenson, J. C. Sacchettini, W. R. Jacobs, D. G. Russell, ‘Persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages and mice requires the glyoxylate shunt enzyme isocitrate lyase’, Nature 2000, 406, 735–738. [CrossRef]
- E. J. Muñoz-Elías, A. M. Upton, J. Cherian, J. D. McKinney, ‘Role of the methylcitrate cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis metabolism, intracellular growth, and virulence’, Molecular Microbiology 2006, 60, 1109–1122.
- P. A. Grimsrud, M. J. Picklo, T. J. Griffin, D. A. Bernlohr, ‘Carbonylation of Adipose Proteins in Obesity and Insulin Resistance: Identification of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-binding Protein as a Cellular Target of 4-Hydroxynonenal*’, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2007, 6, 624–637.
- A. Bennaars-Eiden, L. Higgins, A. V. Hertzel, R. J. Kapphahn, D. A. Ferrington, D. A. Bernlohr, ‘Covalent Modification of Epithelial Fatty Acid-binding Protein by 4-Hydroxynonenal in Vitro and in Vivo: EVIDENCE FOR A ROLE IN ANTIOXIDANT BIOLOGY*’, Journal of Biological Chemistry 2002, 277, 50693–50702.
- V. Matarese, M. K. Buelt, L. L. Chinander, D. A. Bernlohr, in Methods in Enzymology, Academic Press, 1990, pp. 363–369.
- G. S. Hotamisligil, R. S. Johnson, R. J. Distel, R. Ellis, V. E. Papaioannou, B. M. Spiegelman, ‘Uncoupling of Obesity from Insulin Resistance Through a Targeted Mutation in aP2, the Adipocyte Fatty Acid Binding Protein’, Science 1996, 274, 1377–1379.
- A. V. Hertzel, L. A. Smith, A. H. Berg, G. W. Cline, G. I. Shulman, P. E. Scherer, D. A. Bernlohr, ‘Lipid metabolism and adipokine levels in fatty acid-binding protein null and transgenic mice’, American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2006, 290, E814–E823. [CrossRef]
- M. J. C. Long, X. Liu, Y. Aye, ‘Genie in a bottle: controlled release helps tame natural polypharmacology?’, Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2019, 51, 48–56. [CrossRef]
| PDB code | Electrophile | Protein | Binding site | Resolution (Å) |
| 6XPP | Itaconate (e) | ICL-1 | Cys191 (c) | 1.55 |
| 3JS1 | 4-hydroxynonenal (e) | AFABP | Cys117 (b) | 1.81 |
| 6IQ6 | Monomethyl fumarate (d) | GAPDH | Cys152 (c) | 2.29 |
| 5O1S | Dimethyl fumarate (d) | RSK2 | Cys599 (a), Cys436 (a) |
1.90 |
| (e) endogenous electrophile, (d) approved drug, (c) catalytic site, (b) endogenous ligand binding site, (a) allosteric site. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




