Submitted:
06 January 2023
Posted:
06 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Models
3. Results
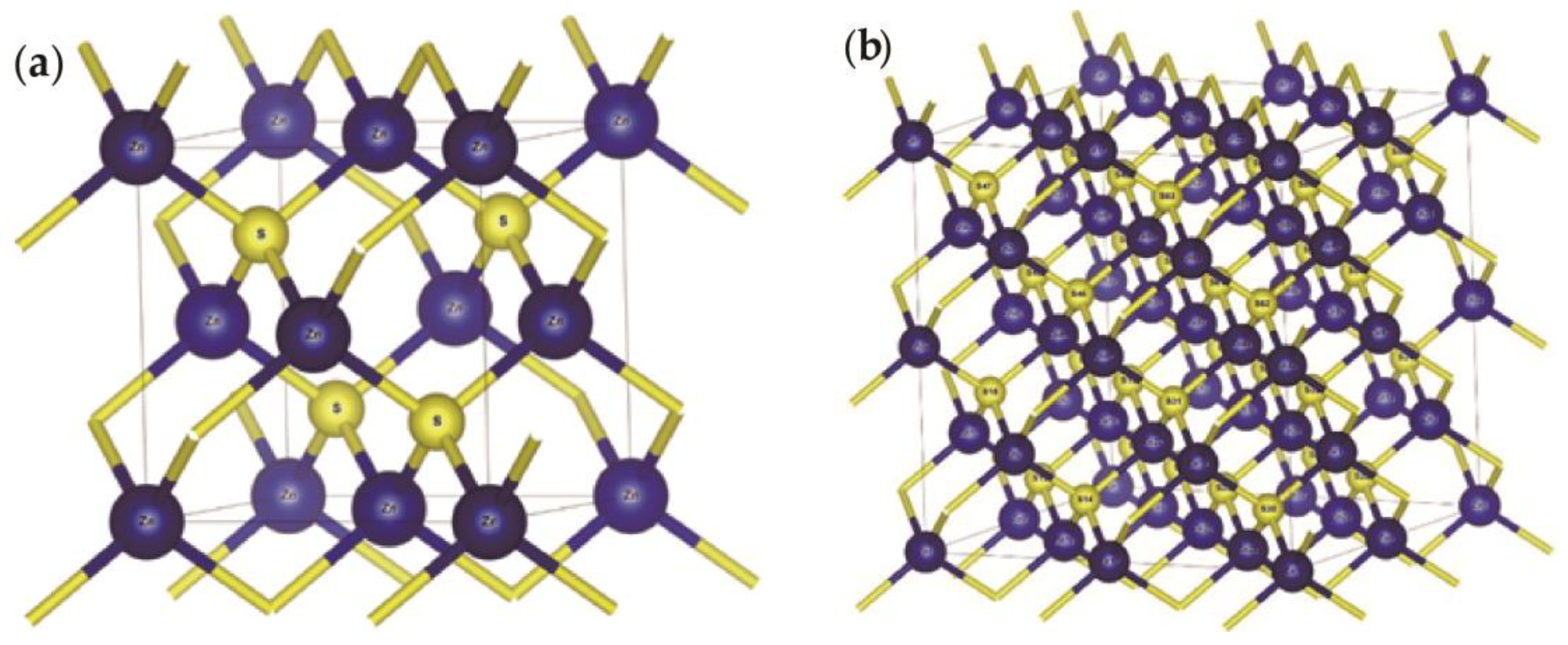
3.1. Sphalerite
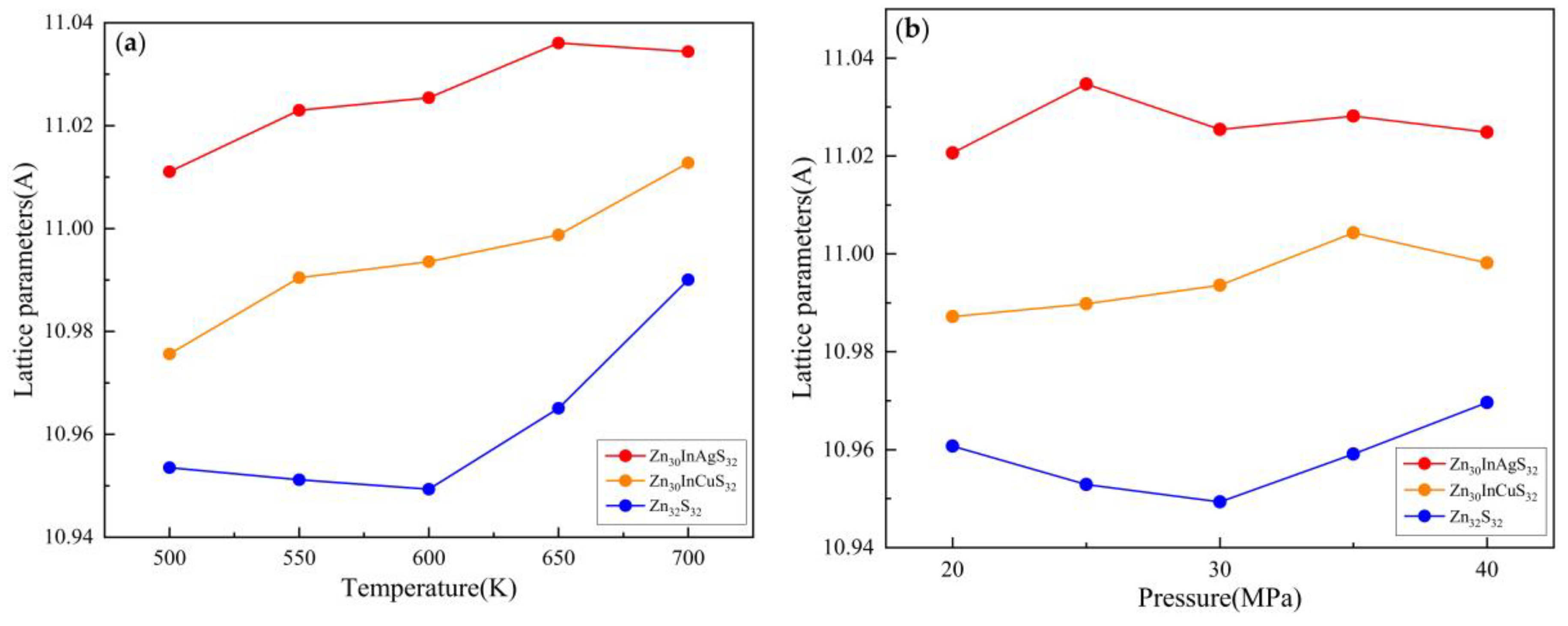
3.1.1. Lattice Parameter
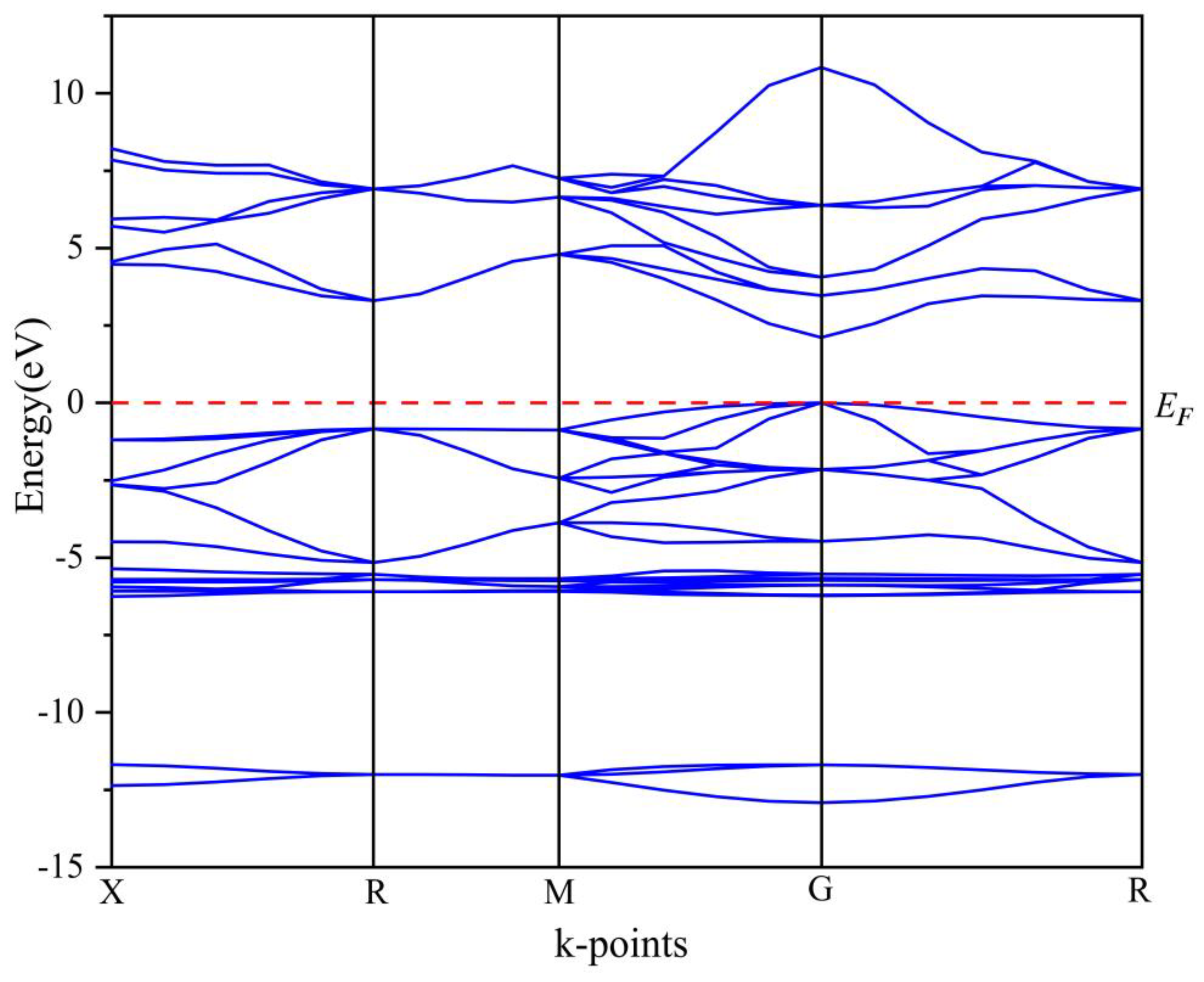
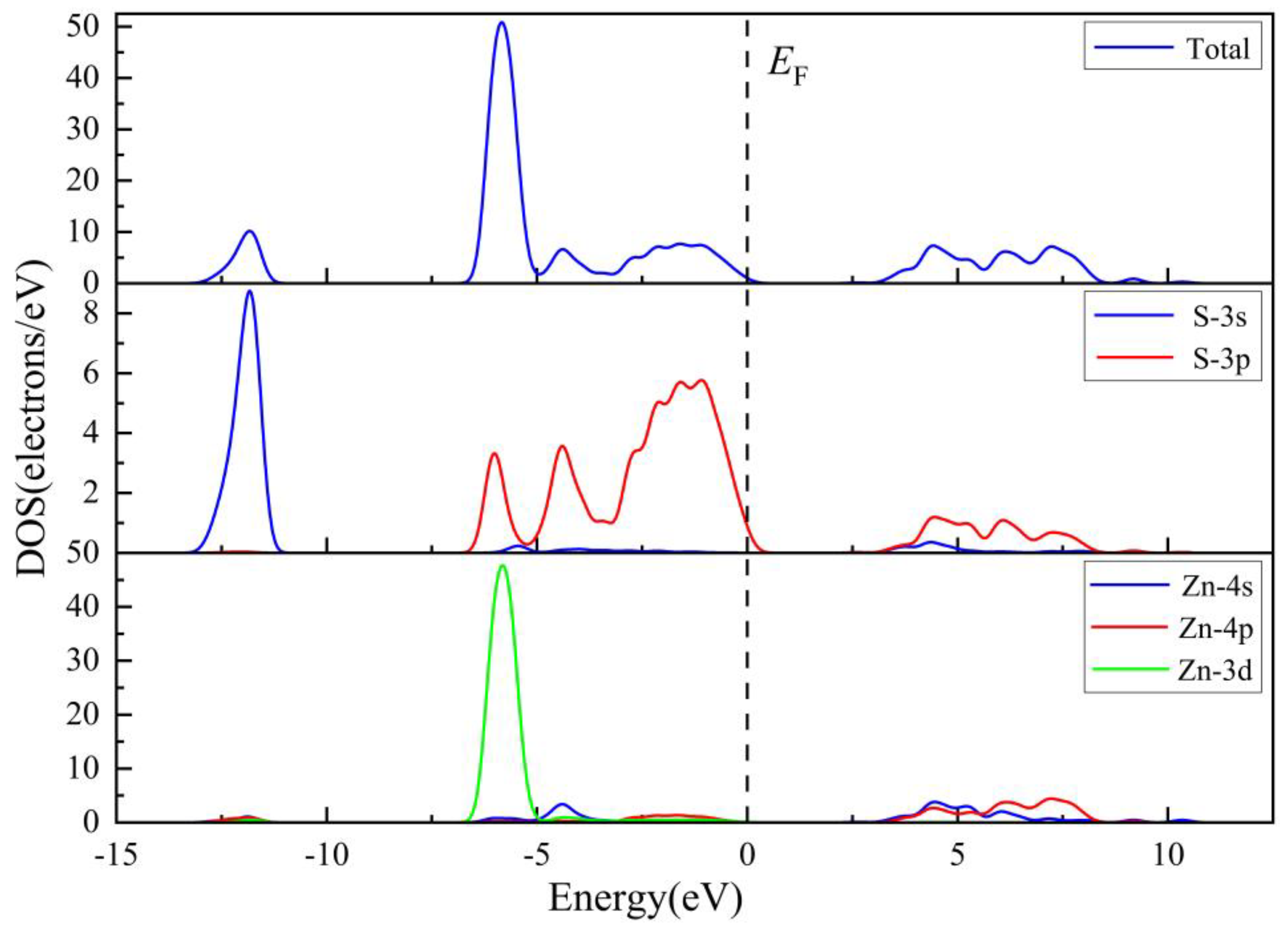
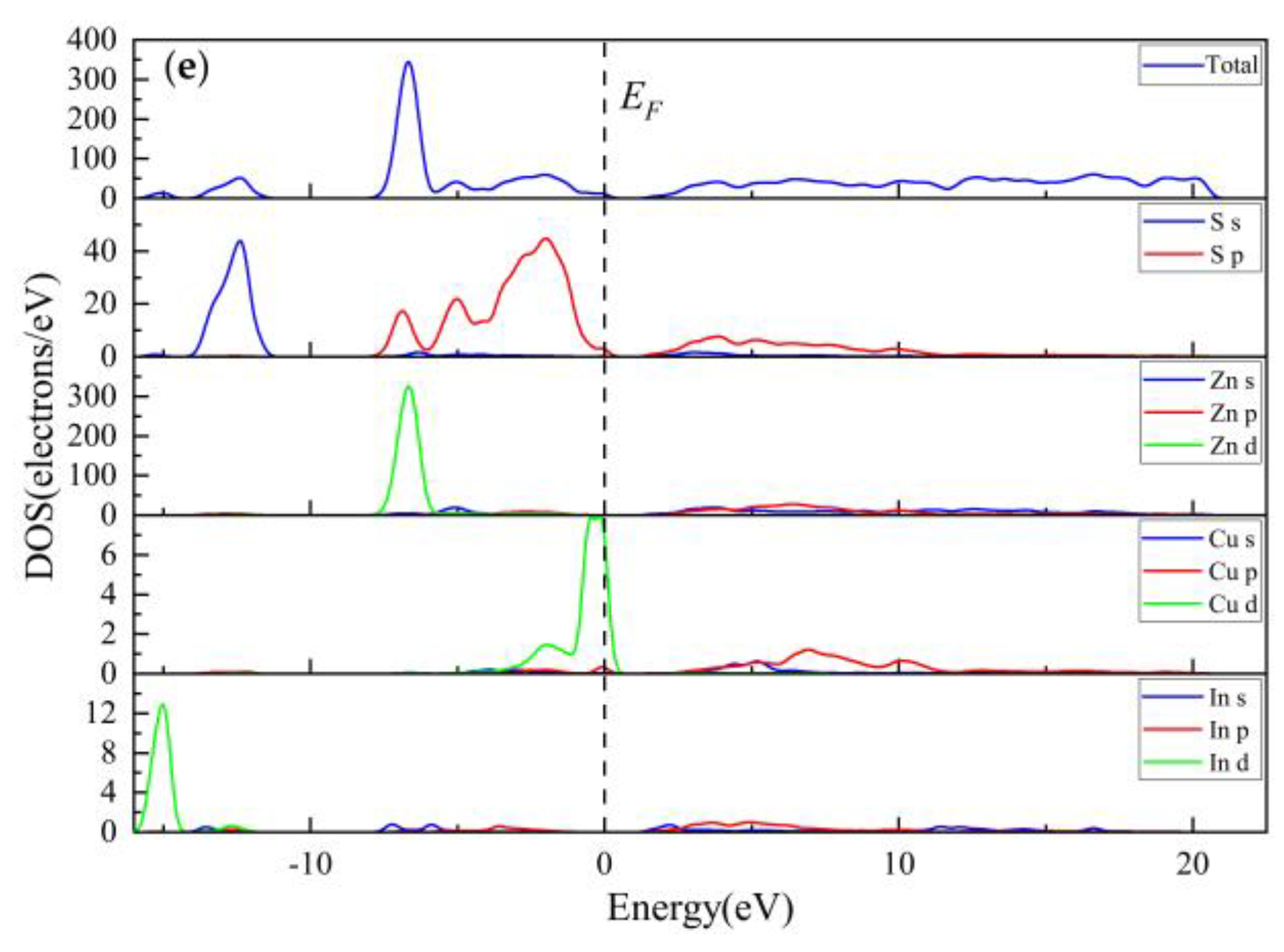
3.1.2. Electronic Properties
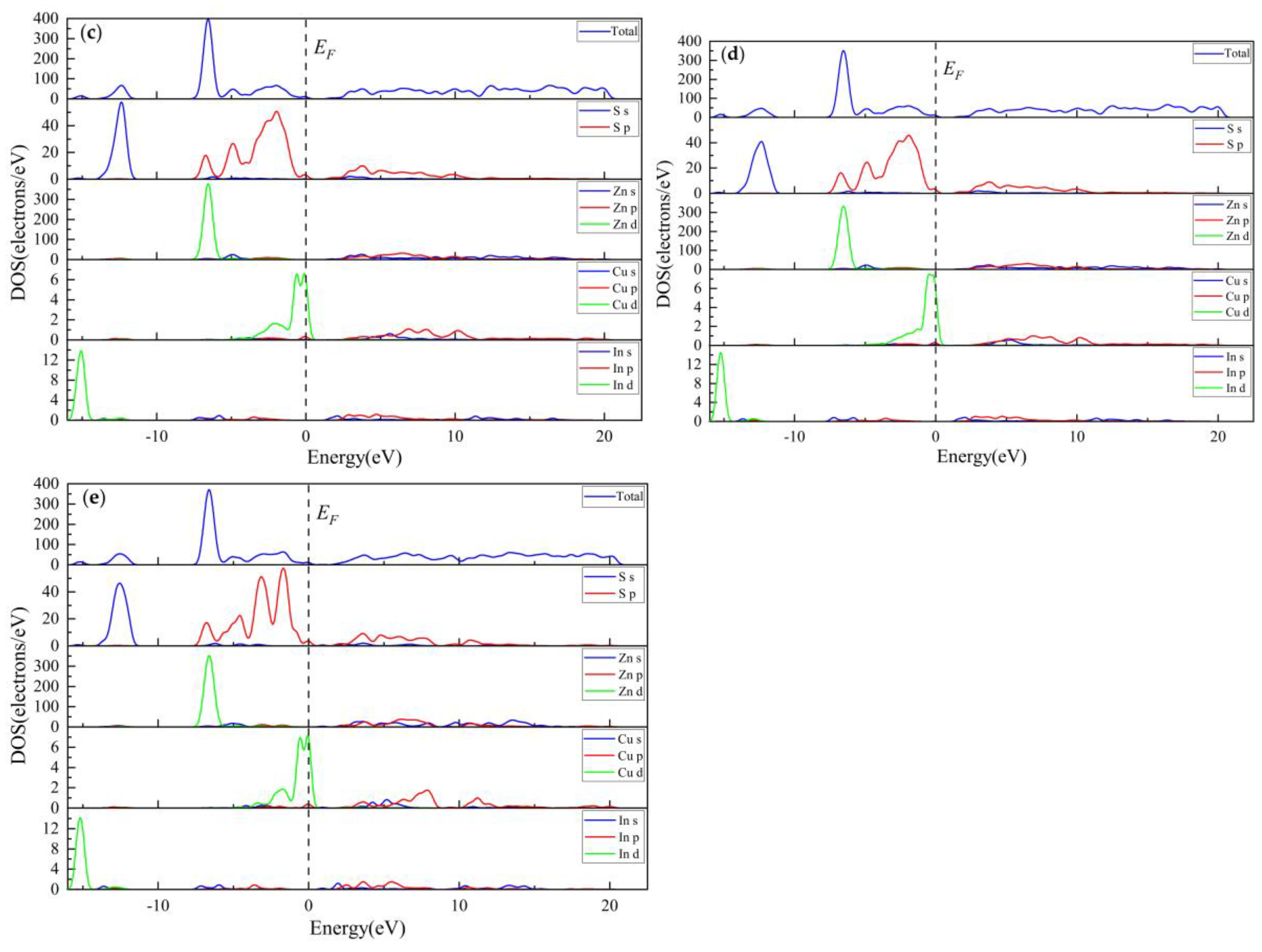
3.1.3. Population Analysis
3.2. Coupled Substitution Scheme
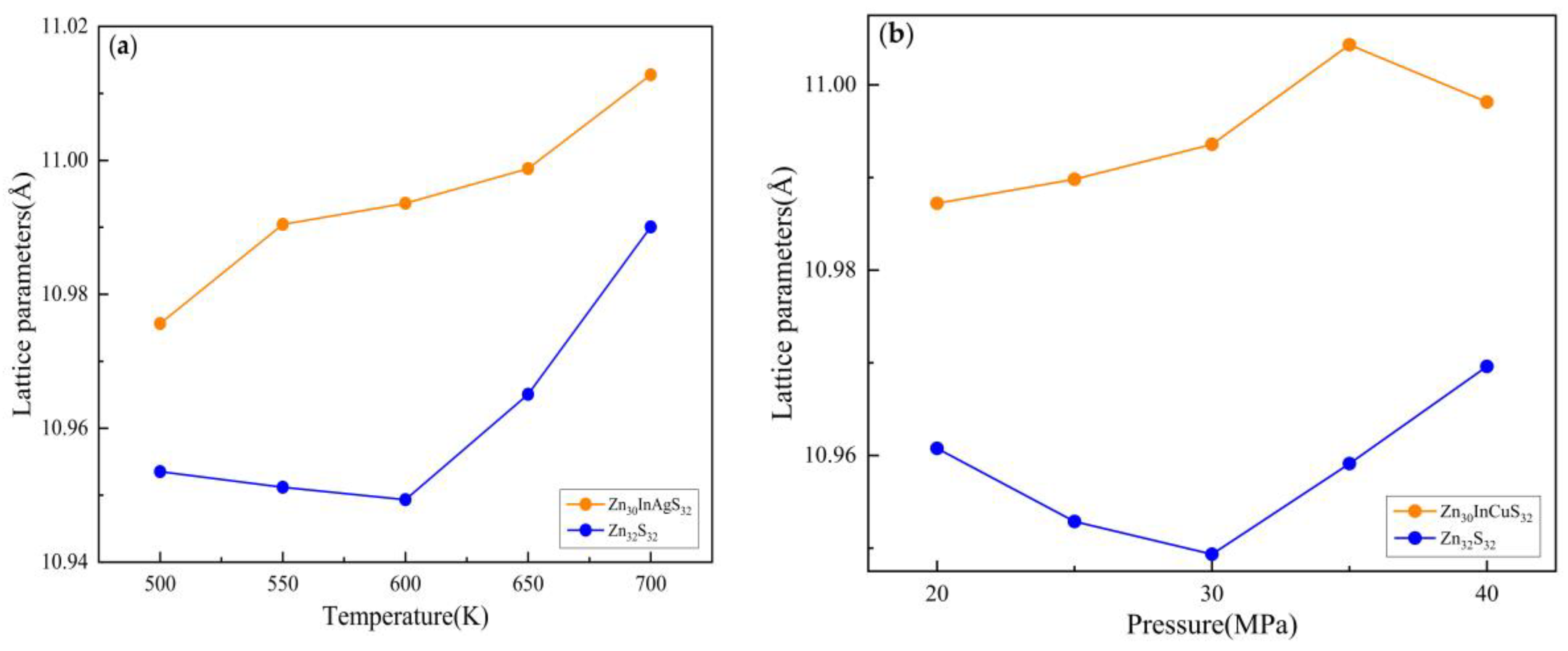
3.2.1. Lattice Parameter
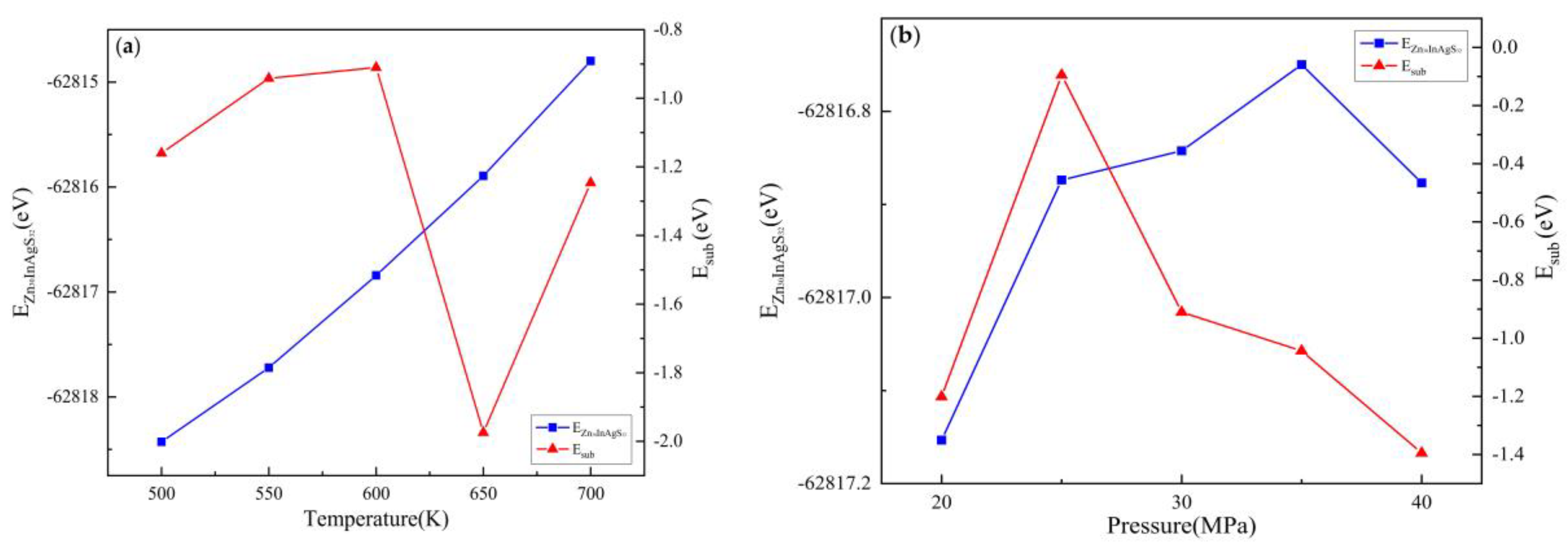
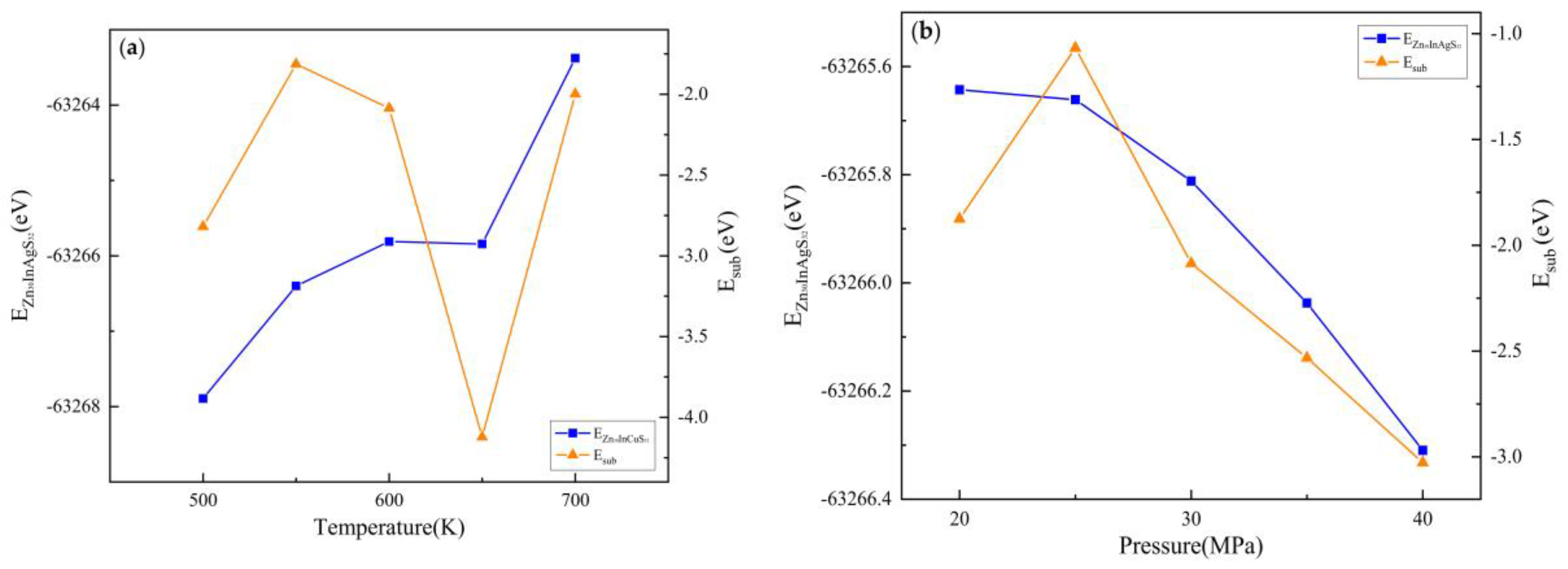
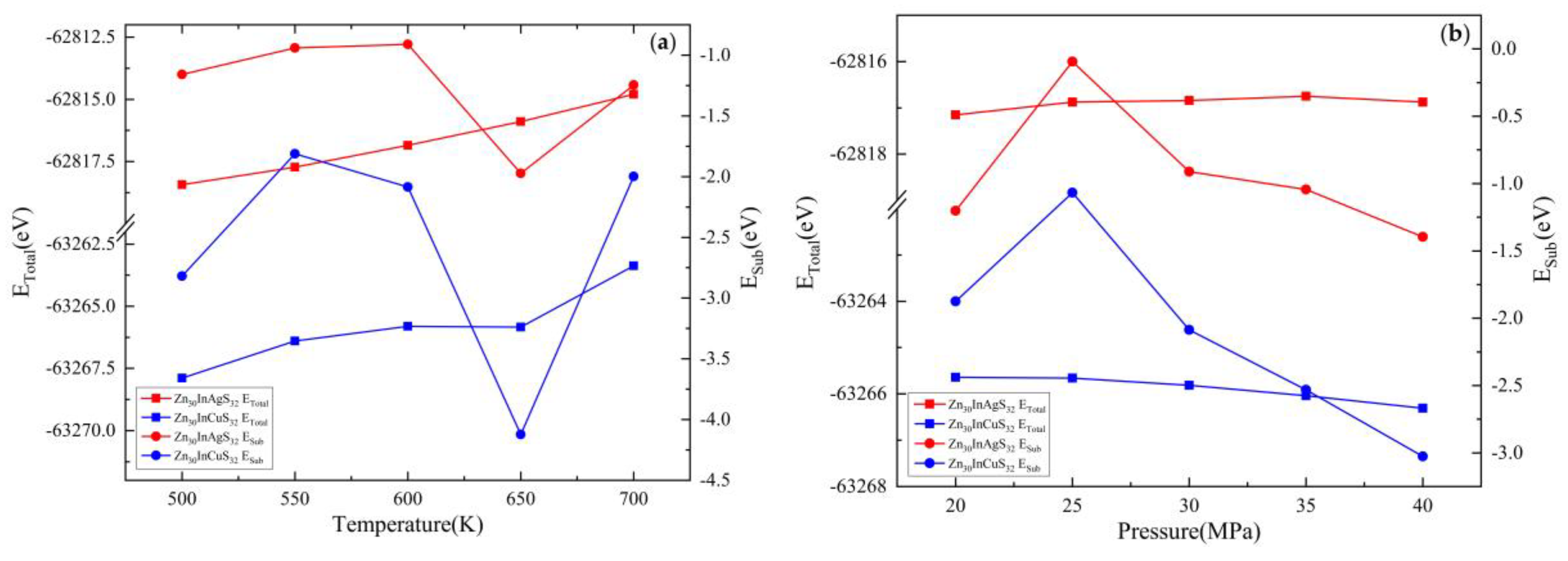
3.2.2. Substitution Energy
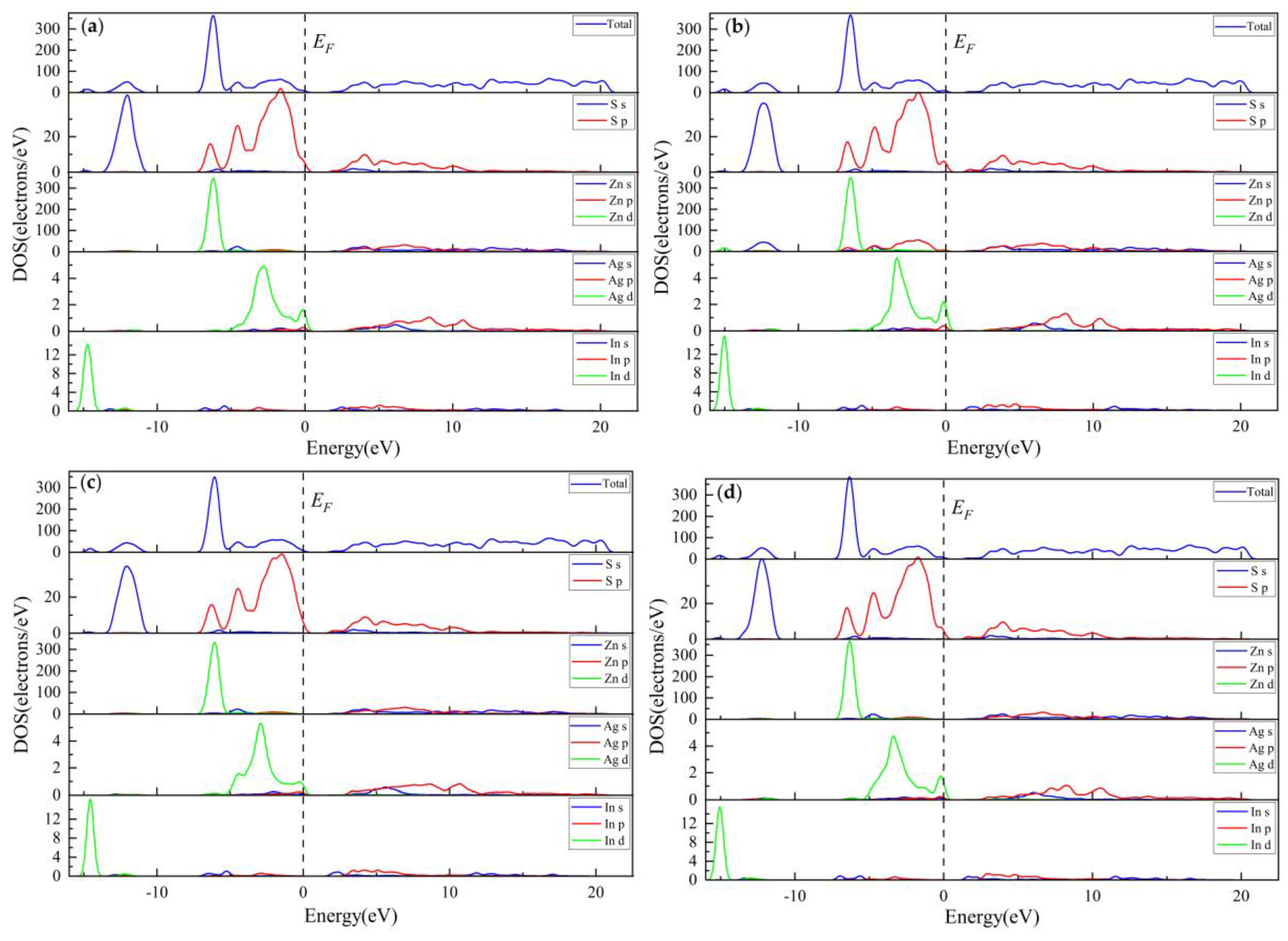
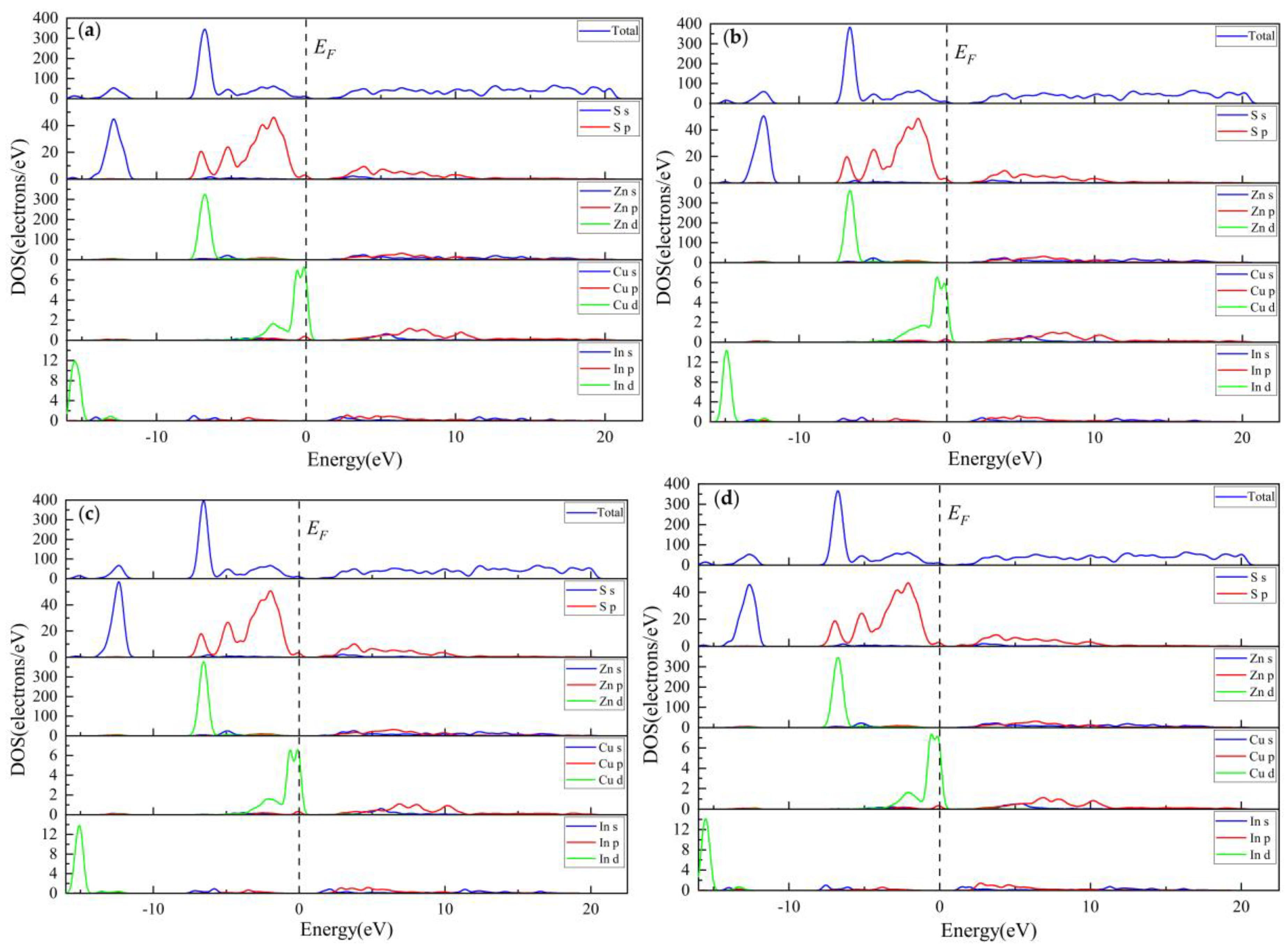
3.2.3. Electronic Properties
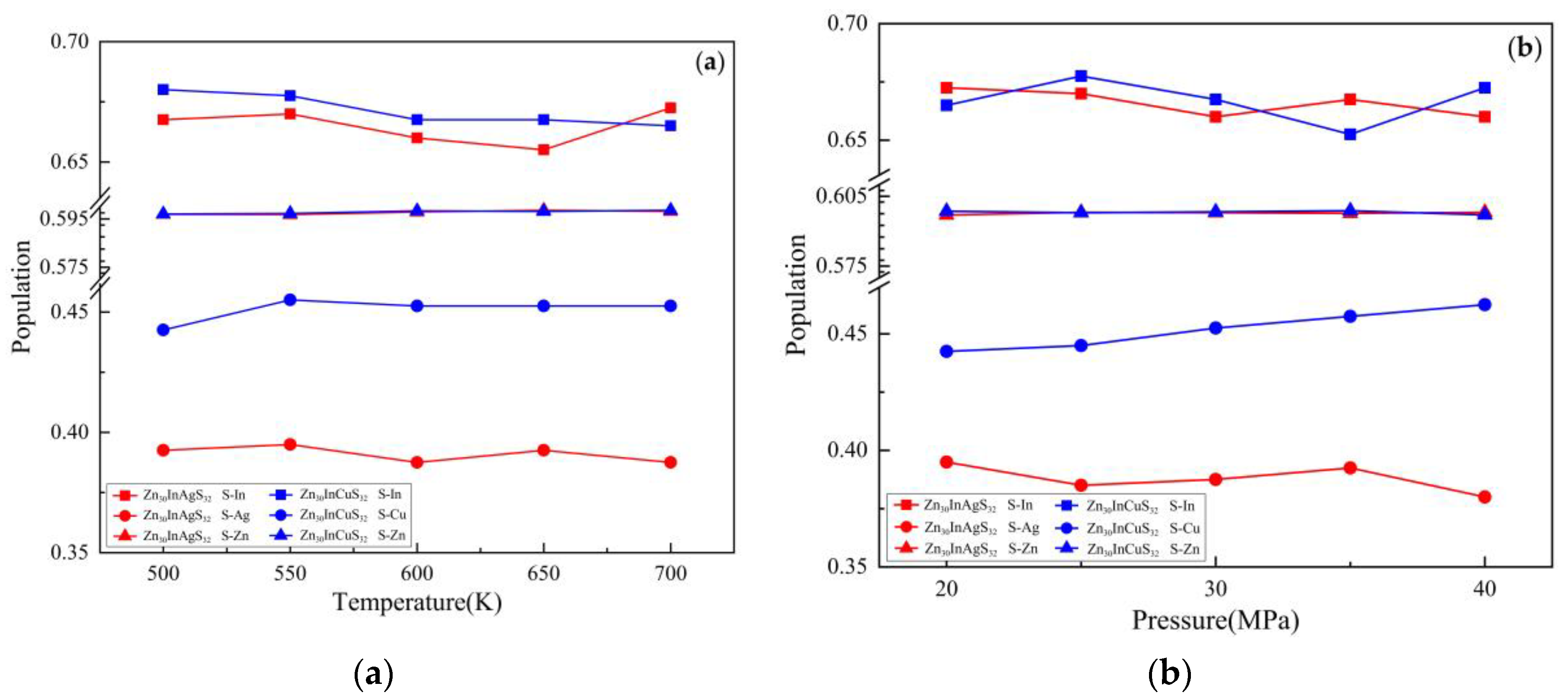
3.2.4. Population Analysis
3.3. Coupled Substitution Scheme
3.3.1. Lattice Parameter
3.3.2. Substitution Energy
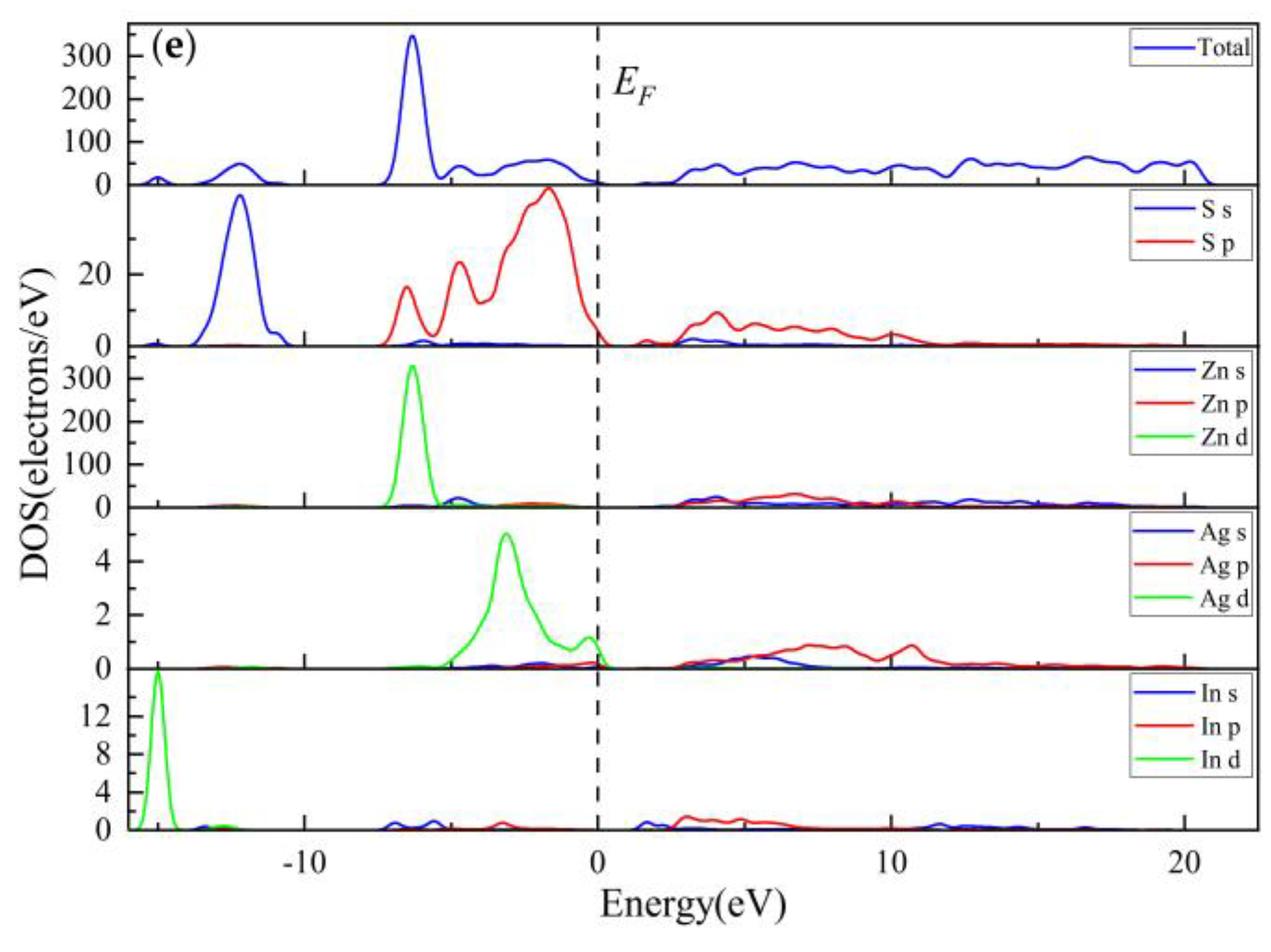
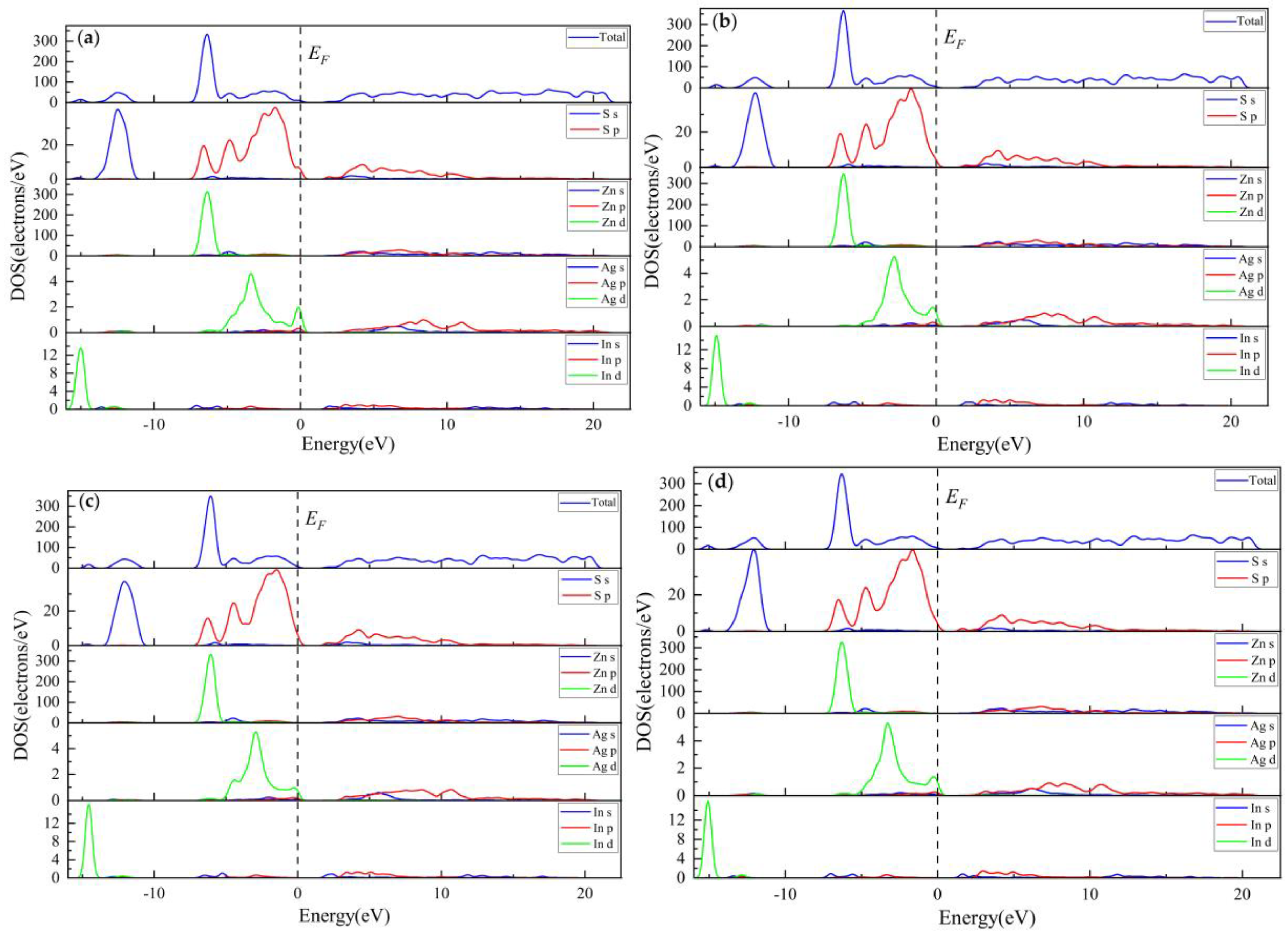
3.3.3. Electronic Properties
3.3.4. Population Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Xu, J.; Li, X. Spatial and temporal distributions, metallogenic backgrounds and processes of indium deposits. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 3611–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, M.; Wu, F.; Hu, R.; Jiang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Qi, T.; Qin, K.; Wen, H. Critical metal mineral resources: current research status and scientific issues. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Foun. China 2019, 33, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Wen, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Sun, W. Earth sphere cycling and enrichment chanimof critical metals: major scientific issues for future research. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Foun. China 2019, 33, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J. Indium as a critical mineral: A research progress report. CHINESE SCIENCE BULLETIN-CHINESE 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Yang, Z.; Xie, G.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, Z. Critical minerals: International trends and thinking. Miner. Deposits 2019, 38, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Study on critical mineral resources: significance of research, determination of types, attributes of resources, progress of prospecting, problems of utilization, and direction of exploitation. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 1189–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, T. T.; Mudd, G. M.; Jowitt, S. M. The world's by-product and critical metal resources part III: A global assessment of indium. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 86, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Daigo, I.; Matsuno, Y. Global Substance Flow Analysis of Indium. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Analysis of the development and the reserve of indium resources in China. China Min. Mag. 2018, 27, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R. L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In: Turekian, H.D., Holland, K.K. (Eds.), Treatise on Geochemistry. second ed. Elsevier, Oxford, pp. 1–51. 2014.
- European, C. Report on Critical Raw Materials for the EU: Report of the Ad hoc Working Group on defining critical raw materials.; 2014.
- Jowitt, S. M. Mineral Economics and Critical Metals: introduction to a multi-part thematic issue. Appl. Earth Sci. 2015, 124, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirrow, R. G.; Huston, D. L.; Mernagh, T. P.; Thorne, J. P.; Duffer, H.; Senior Anthony, B. , Critical commodities for a high-tech world: Australia's potential to supply global demand. In Canberra: Geoscience Australia.: 2013.
- Zepf, V.; Simmons, J.; Augsburg, U. , Materials critical to the energy industry: an introduction. In BP plc: 2014.
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, X.; Shao, S. Trace element geochemistry of Meng's Entaolegai Ag-Pb-Zn-In deposit, inner mongolia, China. Acta Minerl. Sin. 2004, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, G.; Gao, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, B. Dispersed element geochemistry and mineralization mechanisms. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 2004; p 430.
- Ishihara, S.; Murakami, H.; Marquez-Zavalia, M. F. Inferred Indium Resources of the Bolivian Tin-Polymetallic Deposits. Resour. Geol. 2011, 61, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Bu, G.; Wang, Y. A tentative discussion on geochemistry and genesis of indium in Dachang tin ore district‚, Guangxi. Miner. Deposits 2010, 29, 903–914. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, N. S.; Cabri, L. J.; Chauvin, W. J.; Laflamme, J. H. G. Secondary ion mass spectrometric study of dissolved silver and indium in sulfide minerals. Scan. Elec. Micros. 1984, 1984, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N. J.; Ciobanu, C. L.; Pring, A.; Skinner, W.; Shimizu, M.; Danyushevsky, L.; Saini-Eidukat, B.; Melcher, F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2009, 73, 4761–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, T. Metallogenesis of indium in magmatic hydrothermal system. Miner. Deposits 2021, 40, 206–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Yue, L.; Ma, D.; Ma, W.; Tang, B. Critical metals in sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 67, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H. G.; Garrido, M. M.; Melcher, F.; Gomez, M. C.; Weber, B.; Luna, L. I.; Bahr, A. Sulfidic and non-sulfidic indium mineralization of the epithermal Au–Cu–Zn–Pb–Ag deposit San Roque (Provincia Rio Negro, SE Argentina) — with special reference to the "indium window" in zinc sulfide. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 51, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Hu, R.; Tang, Y.; Ye, L.; Qi, H.; Fan, H. Types of dispersed elements bearing ore-deposits and their enrichment regularity in Southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 1210–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lǚ, Y. Critical minerals of indium: Major ore types and scientific issues. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cook, N. J.; Ciobanu, C. L.; Li, X.; Kontonikas-Charos, A.; Gilbert, S.; Lv, Y. Indium distribution in sphalerite from sulfide–oxide–silicate skarn assemblages: a case study of the Dulong Zn–Sn–In deposit, Southwest China. Miner. Deposita 2021, 56, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Liao, M.; Xiong, F.; Deng, X. Distribution and existing state of indium in the Gejiu Tin polymetallic deposit, Yunnan Province, SW China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. P.; Rong, Y. N.; Zhang, S. G.; Liu, Z. F.; Chen, W. K. Indium Mineralization in the Xianghualing Sn-Polymetallic Orefield in Southern Hunan, SouthernChina. Minerals 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Murakami, H.; Li, X. Indium concentration in zinc ores in plutonic and volcanic environments: examples at the Dulong and Dachang mines, South China. BULLETIN OF THE GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF JAPAN 2011, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Ishihara, S. Trace elements of Indium-bearing sphalerite from tin-polymetallic deposits in Bolivia, China and Japan: A femto-second LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 53, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M. A.; Botelho, N. F.; de Mendonca, F. C. The Indum-rich sulfides and rare arsenates of the Sn-In-mineralized mangabeira A-Type granite, central Brazil. Canad. Mineral. 2007, 45, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schampera, U. S.; Herzig, P. M. Indium: Geology, Mineralogy, and Economics-A Review. 2002; p 164-169.
- Ye, L.; Cook, N. J.; Ciobanu, C. L.; Yuping, L.; Qian, Z.; Tiegeng, L.; Wei, G.; Yulong, Y.; Danyushevskiy, L. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: A LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, Z. Indium and germanium in the structure of sphalerite: an example of coupled substitution with Copper. Mineralogy and Petrology 1988, 39, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N. J.; Ciobanu, C. L.; Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Howard, D. L.; de Jonge, M. D.; Ryan, C.; Paterson, D. Determination of the oxidation state of Cu in substituted Cu-In-Fe-bearing sphalerite via -XANES spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonova, O. N.; Trigub, A. L.; Tonkacheev, D. E.; Nickolsky, M. S.; Kvashnina, K. O.; Chareev, D. A.; Chaplygin, I. V.; Kovalchuk, E. V.; Lafuerza, S.; Tagirov, B. R. Substitution mechanisms in In-, Au-, and Cu-bearing sphalerites studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy of synthetic compounds and natural minerals. Mineral. Mag. 2019, 83, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wen, H. A magmatic-hydrothermal indium-bearing polymetallic vein mineralization belt in the western Jiangnan Orogen: Evidence from zinc and cadmium isotopes of sphalerite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 131, 103843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzari, N.; Ferretti, A.; Wolverton, C. Electronic-structure methods for materials design. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, J.; Liu, W.; Etschmann, B.; Mei, Y.; Sherman, D. M.; Testemale, D. A review of the coordination chemistry of hydrothermal systems, or do coordination changes make ore deposits? Chem. Geol. 2016, 447, 219–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Deng, Y.; Wang, D.; Ji, W.; Li, E. Photoelectric properties of InxGa1-xAs: A first-principles study. Micro and Nanostructures 2019, 128, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Zhou, H.; Deng, J.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, J.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, F.; Chong, X.; Feng, J.; Schaller, R. D.; Zhu, K.; Padture, N. P.; Zhou, Y. Sub-1.4eV bandgap inorganic perovskite solar cells with long-term stability. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Fan, Z.; Liu, J. Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C. F. Adsorption of Ag on M-doped graphene: First principle calculations. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J. P.; Chevary, J. A.; Vosko, S. H.; Jackson, K. A.; Pederson, M. R.; Singh, D. J.; Fiolhais, C. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1992, 46, 6671–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. In Generalized gradient approximation made simple, United States, 1996, 1996; Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA (United States): United States, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism; 1990.
- Broyden, C. G. The convergence of a class of double-rank minimization algorithms 1. general considerations. Ima J. Appl. Math. 1970, 6, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R. A new approach to variable metric algorithms. Comput. J. 1970, 13, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, D. A family of variable-metric methods derived by variational means. Math. Comput. 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanno, D. F. Conditioning of Quasi-Newton methods for function minimization. Math. Comput. 1970, 24, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadi, D. J. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. The metallogenesis research of Yaojialing Zn-Au polymetallic deposit in Tongling, Anhui Province. C. U. G. Beijing, 2012.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Yan, P.; Feng, J. Chemical composition characteristics and geological significance of sphalerite in Bangbule skarn Pb-Zn deposit, Tibet. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Yu, D.; Dong, G.; Ning, J.; Kang, B.; Peng, E. Trace element characteristics of sphalerite in the Lishan Pb-Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit in Hunan Province and the metallogenic implications. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 66–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Study on the mineralization of skarn-vein type lead-zinc deposits in the Northern of De'rbugan metallogenic belt, the Great Xing'an Range. Jilin U., 2021.
- Wei, W. Genetic mineralogy and metallogenesis of Shuangjianzishan Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia. C. U. G. Wuhan, 2021.
- Liu, J. Typical minerals chemical characteristics and discussion on genesis of the Mengxing Zn-Pb deposit, western Yunnan (SW China). Kunming U. Sci. Techno., 2020.
- Hu, P.; Cai, M.; He, G.; Gan, N.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, M.; Lv, T. Characteristics of trace elements, rare earth elements and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of sphalerite in Dachang Tongkeng deposit, Guangxi. Sci. Techno. Eng. 2022, 22, 10857–10866. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Huang, S.; Dou, P.; Hu, W. Source of ore-forming metals in Changba-Lijiagou super-large Pb-Zn deposit, Gansu Province: Evidence from in-situ S-Pb and Zn isotopic compositions of sphalerite. Miner. Deposits 2022, 41, 722–740. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of cassiterite and sphalerite in the Tongkeng tin polymetallic deposit, Northwestern Guangxi. Guangxi U., 2022.
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, T.; Yan, P. A discussion on the genesis of the Wulanbaiqi Pb-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia: Evidence from fluid inclusions, S-Pb isotopes and trace elements of ore minerals. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2020, 36, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, X. Optical absorption enhancement of Hg-doped ZnX (X= S, Se) for hydrogen production from water splitting driven by solar energy. Vacuum 2018, 157, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

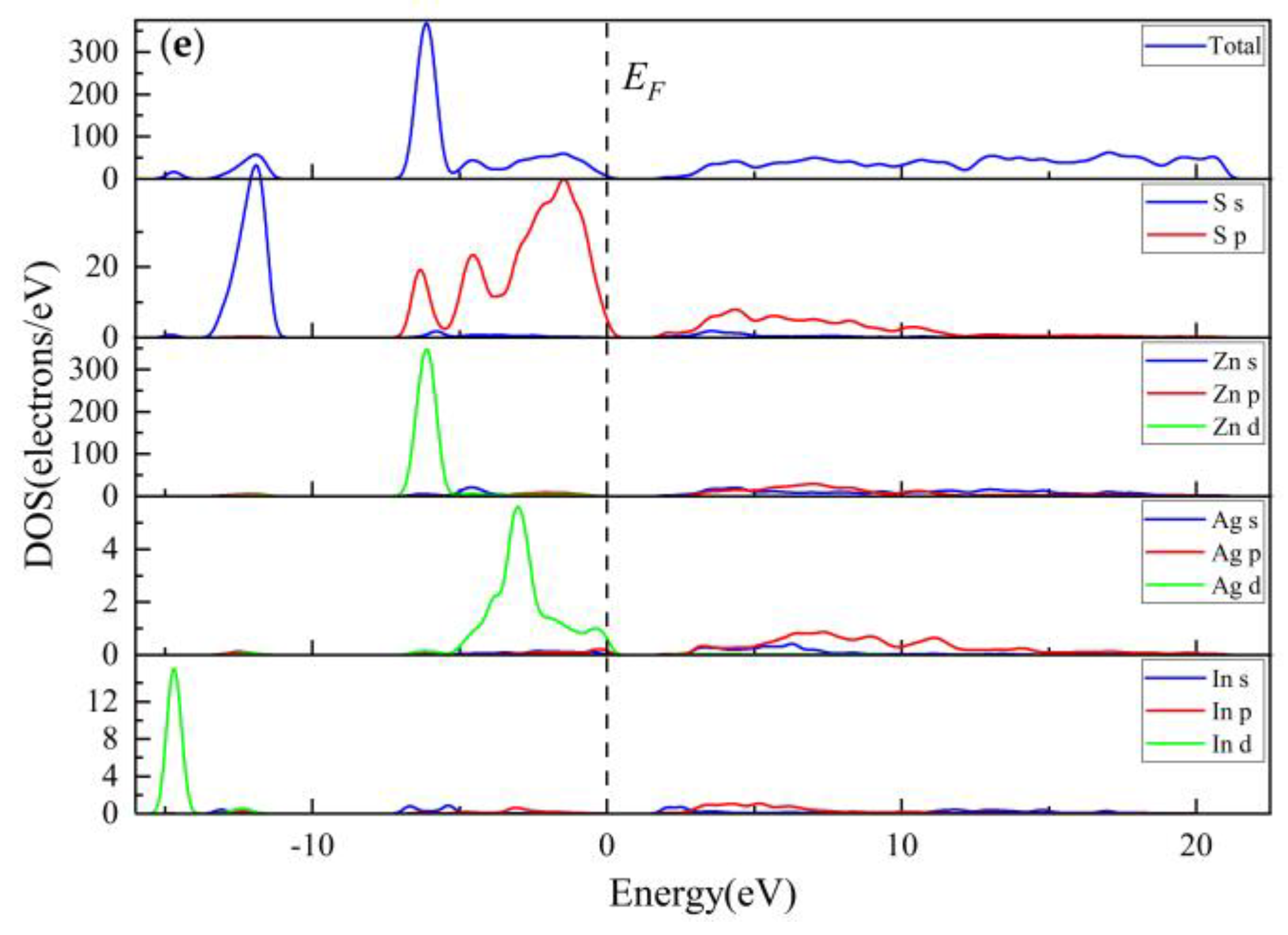
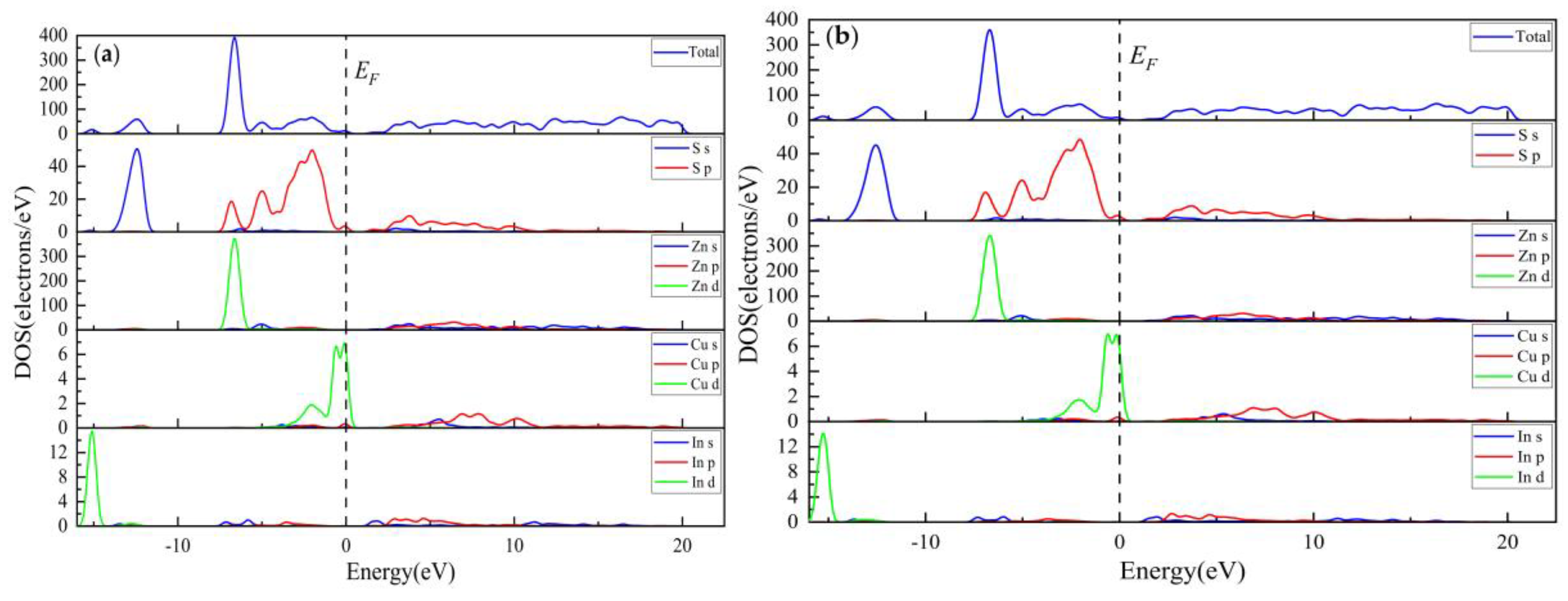
| Compound | Charge spilling | Species | Muliken atomic populations | Mulikencharge | Formal ionic charge | Effective valence | Hirshfeld charge | Effective valence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | p | d | Total | ||||||||
| Zn4S4 | 0.14 | Zn | 0.57 | 0.98 | 9.98 | 11.53 | 0.47 | 2 | 1.53 | 0.23 | 1.77 |
| S | 1.82 | 4.65 | - | 6.47 | -0.47 | -2 | 1.53 | -0.23 | 1.77 | ||
| Compound | Bond | nμ | pμ | dμ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn4S4 | Zn-S | 16 | 0.46 | 2.35501 |
| Zn-Zn | 6 | -2.5 | 3.84572 | |
| S-S | 6 | -0.17 | 3.84572 |
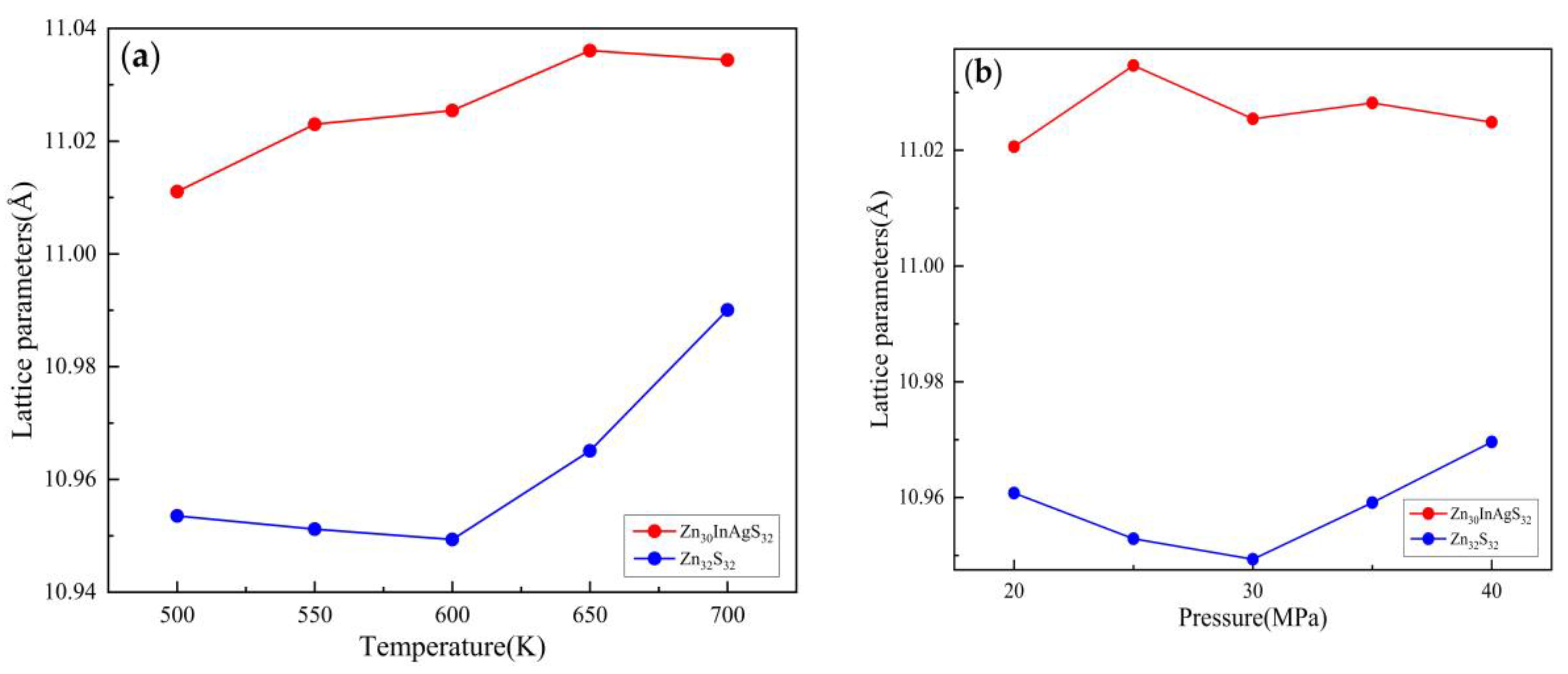
| Temperature(K) | Pressure (MPa) | Zn30InAgS32 cell length(Å) | Zn32S32 cell length(Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 30 | 11.011051 | 10.953515 |
| 550 | 11.023002 | 10.951177 | |
| 600 | 11.025429 | 10.949337 | |
| 650 | 11.036065 | 10.965068 | |
| 700 | 11.034404 | 10.990049 | |
| 600 | 20 | 11.020628 | 10.960759 |
| 25 | 11.034657 | 10.952866 | |
| 30 | 11.025429 | 10.949337 | |
| 35 | 11.028178 | 10.959118 | |
| 40 | 11.024839 | 10.969608 |
| Doped system | Temperature(K) | Pressure(MPa) | EZnS+In+Ag/eV | EZn/eV | EZnS/eV | EIn/eV | EAg/eV | Esub/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn30InAgS32 | 500 | 30 | -62818.43 | -1708.92 | -63651.81 | -1558.28 | -1025.02 | -1.16 |
| 550 | -62817.72 | -1708.91 | -63651.32 | -1558.26 | -1025.02 | -0.94 | ||
| 600 | -62816.84 | -1708.90 | -63650.46 | -1558.25 | -1025.02 | -0.91 | ||
| 650 | -62815.89 | -1708.89 | -63648.43 | -1558.25 | -1025.01 | -1.97 | ||
| 700 | -62814.80 | -1708.85 | -63648.02 | -1558.24 | -1024.99 | -1.25 | ||
| 600 | 20 | -62817.15 | -1708.92 | -63650.54 | -1558.26 | -1025.00 | -1.20 | |
| 25 | -62816.87 | -1708.94 | -63651.39 | -1558.26 | -1025.01 | -0.09 | ||
| 30 | -62816.84 | -1708.90 | -63650.46 | -1558.25 | -1025.02 | -0.91 | ||
| 35 | -62816.75 | -1708.97 | -63650.38 | -1558.26 | -1025.02 | -1.04 | ||
| 40 | -62816.88 | -1708.95 | -63650.11 | -1558.27 | -1025.02 | -1.40 |
| Doped system | Temperature(K) | Pressure (MPa) | S-In bond | S-Ag bond | S-Zn bond | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| population | length | population | length | population | length | |||
| Zn30InAgS32 | 500 | 30 | 0.668 | 2.37642 | 0.393 | 2.37218 | 0.597 | 2.36707 |
| 550 | 0.670 | 2.37870 | 0.395 | 2.35881 | 0.597 | 2.36555 | ||
| 600 | 0.660 | 2.38988 | 0.388 | 2.37972 | 0.598 | 2.36288 | ||
| 650 | 0.655 | 2.40507 | 0.393 | 2.36310 | 0.599 | 2.36160 | ||
| 700 | 0.673 | 2.36874 | 0.388 | 2.38320 | 0.598 | 2.36117 | ||
| 600 | 20 | 0.673 | 2.37213 | 0.395 | 2.35916 | 0.597 | 2.36435 | |
| 25 | 0.670 | 2.37078 | 0.385 | 2.39321 | 0.598 | 2.36326 | ||
| 30 | 0.660 | 2.38988 | 0.388 | 2.37972 | 0.598 | 2.36288 | ||
| 35 | 0.668 | 2.37831 | 0.393 | 2.37982 | 0.598 | 2.36334 | ||
| 40 | 0.660 | 2.39155 | 0.380 | 2.39766 | 0.598 | 2.36206 | ||
| Temperature(K) | Pressure (MPa) | Zn30InCuS32 cell length(Å) | Zn32S32 cell length(Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 30 | 10.975624 | 10.953515 |
| 550 | 10.99044 | 10.951177 | |
| 600 | 10.993576 | 10.949337 | |
| 650 | 10.998761 | 10.965068 | |
| 700 | 11.012782 | 10.990049 | |
| 600 | 20 | 10.987211 | 10.960759 |
| 25 | 10.989812 | 10.952866 | |
| 30 | 10.993576 | 10.949337 | |
| 35 | 11.004323 | 10.959118 | |
| 40 | 10.99814 | 10.969608 |
| Doped system | Temperature(K) | Pressure (MPa) | EZnS+In+Cu/eV | EZn/eV | EZnS/eV | EIn/eV | ECu/eV | Esub/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn30InCuS32 | 500 | 30 | -63267.89 | -1708.92 | -63651.81 | -1558.28 | -1472.83 | -2.82 |
| 550 | -63266.40 | -1708.91 | -63651.32 | -1558.26 | -1472.83 | -1.81 | ||
| 600 | -63265.81 | -1708.90 | -63650.46 | -1558.25 | -1472.82 | -2.09 | ||
| 650 | -63265.84 | -1708.89 | -63648.43 | -1558.25 | -1472.81 | -4.12 | ||
| 700 | -63263.38 | -1708.85 | -63648.02 | -1558.24 | -1472.82 | -2.00 | ||
| 600 | 20 | -63265.64 | -1708.92 | -63650.54 | -1558.26 | -1472.82 | -1.88 | |
| 25 | -63265.66 | -1708.94 | -63651.39 | -1558.26 | -1472.82 | -1.07 | ||
| 30 | -63265.81 | -1708.90 | -63650.46 | -1558.25 | -1472.82 | -2.09 | ||
| 35 | -63266.04 | -1708.97 | -63650.38 | -1558.26 | -1472.81 | -2.53 | ||
| 40 | -63266.31 | -1708.95 | -63650.11 | -1558.27 | -1472.82 | -3.03 |
| Doped system | Temperature(K) | Pressure(MPa) | S-In bond | S-Cu bond | S-Zn bond | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| population | length | population | length | population | length | |||
| Zn30InCuS32 | 500 | 30 | 0.680 | 2.35078 | 0.443 | 2.38279 | 0.597 | 2.36187 |
| 550 | 0.678 | 2.35704 | 0.455 | 2.35427 | 0.597 | 2.36085 | ||
| 600 | 0.668 | 2.38333 | 0.453 | 2.35995 | 0.598 | 2.35903 | ||
| 650 | 0.668 | 2.37992 | 0.453 | 2.36192 | 0.598 | 2.35781 | ||
| 700 | 0.665 | 2.38084 | 0.453 | 2.35974 | 0.599 | 2.35735 | ||
| 600 | 20 | 0.665 | 2.38164 | 0.443 | 2.38702 | 0.599 | 2.35821 | |
| 25 | 0.678 | 2.36125 | 0.445 | 2.38010 | 0.598 | 2.35868 | ||
| 30 | 0.668 | 2.38333 | 0.453 | 2.35995 | 0.598 | 2.35903 | ||
| 35 | 0.653 | 2.40277 | 0.458 | 2.35400 | 0.599 | 2.35842 | ||
| 40 | 0.673 | 2.36891 | 0.463 | 2.34061 | 0.597 | 2.35974 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





