INTRODUCTION
Heart failure (HF) is a major public health problem and a leading cause of hospitalisation in Western countries. The prevalence of HF is approximately 2% in the adult population in Spain, rising to ≥10% among people >80 years of age.[
1] The most common cause of hospitalisation in HF patients is HF decompensation, which leads to a progressive deterioration of myocardial function and quality of life and also represents the most important determinant of HF associated costs in our country. [
2]
Despite improvements in HF therapy, the 12-month hospitalisation rates remain very high in this population, ranging from 32% to 44% for ambulatory and hospitalised patients, respectively.[
3]
Remote monitoring emerged as a viable way to overcome the long interval between office visits and to keep patients safe by identifying disease progression in time to prevent hospitalisation.[
4] The CardioMEMS HF System (St. Jude Medical, Inc., Atlanta, GA, USA) is the first system to provide real-time remote monitoring of pulmonary artery pressures (PAP), with the goal of maintaining this pressure within a therapeutic range by adjusting medications in response to pressure trends. Unlike other implantable devices, the CardioMEMS pressure sensor does not require a battery and therefore, continues to function indefinitely.
In a randomised controlled trial of 550 New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III HF patients with a previous HF hospitalisation, those whose treatment was guided by PAP measurements (treatment group) achieved a 33% reduction in HF-related hospitalisations over an average study duration of 15 months compared with the control arm, who had the device implanted but in whom the data were not used to guide management. The treatment group also had a higher reduction in mean PAP and a greater improvement in quality of life.[
5]
In 2014 CardioMEMS was approved for use in the United States of America by the Food and Drug Administration and in 2016 the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) included the system in the ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, indicating that the device may be considered for monitoring symptomatic patients with a previous HF hospitalisation in order to reduce the risk of recurrent hospitalisation (class IIb recommendation, level of evidence B).[
6]
A randomised controlled trial conducted in the Netherlands has recently confirmed that haemodynamic monitoring of pulmonary pressures improves quality of life and reduces HF hospitalisations and a previous cost-utility analysis suggested that the CardioMEMS HF system is also a cost-effective strategy for HF patients in the United Kingdom.[
7,
8] However, the value of CardioMEMS in Southern Europe, where hospitalizations costs are significantly lower, remains uncertain and this might lead to an underutilization of the device. The aim of this study was to estimate the cost and benefits of CardioMEMS in a healthcare centre from Spain.
METHODS
Study population and follow-up
The study was carried out in a HF clinic of a tertiary hospital in the Northern area of Barcelona. This hospital was a pioneer in the use of pulmonary pressure sensors in southern Europe and currently follows the largest number of patients with the CardioMEMS device implanted in the country.
All consecutive patients implanted with a CardioMEMS from June 2019 to November 2021 were included in the analysis.
The criteria for implementing the CardioMEMS HF System were the presence of symptomatic HF with a high risk of HF hospitalisation, regardless of the ejection fraction, in patients already receiving optimal medical treatment.
Since patients initiated follow-up at the HF Clinic, they were followed in regular follow-up visits, including a minimum of one visit with a nurse every 3 months and one visit with a physician (cardiologist or internist) every 6 months.
After CardioMEMS implantation, a range of optimal values of PAP was established considering the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and the transpulmonary gradient of each patient. These PAP thresholds were adjusted during the first week of follow-up. Subsequently, the HF specialist nurses reviewed the PAP values daily and when the established range was exceeded, the cardiologist assessed the possibility of adjusting the diuretic or vasodilator treatment.
During the baseline visit, patients provided written consent for the use of their clinical data for research purposes. Demographic, clinical, echocardiographic, and analytical data were recorded in a specific database (Ethical Committee number PI-18-037).
To conduct the cost-benefit analysis, annualised HF hospitalisations in the year before and the year after sensor implantation were taken into account, considering time at risk for each patient. Additional calculations were made in order to assess the accumulated costs over five years; for those calculations, a 3% discount rate was considered as per the recommendations for health economics in the Spanish healthcare system.[
9]
The study was performed in compliance with the laws that protect personal data, in accordance with the international guidelines on clinical investigations from the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki.
Resources and costs
The costs assessed in the study were chosen based on the description of costs from previous studies. To do so, a literature review of CardioMEMS cost-effectiveness analysis (ranging from 2011 to 2021) was conducted. Out of eleven results yielded, only six were actual economic evaluations. As shown in Supplementary Table S1, four of the six research papers found were conducted in the United States of America, one in different countries of the European Union (United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Belgium, Italy and Germany) and one in Argentina. The mean and median Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER), converting currency and adjusting for inflation, were of €34,432 and €23,236 respectively; as for the QALY gained after the implant of the CardioMEMS device, the mean and median values were 0.42 and 0.39 respectively.[
5,
8,
10,
11,
12,
13]
The perspective of the evaluation was conducted from the hospital centre in order to estimate the costs and impact of the CardioMEMS treatment in comparison to standard treatment.
Table 1 shows a valuation of the costs and resources. The cost of the device and its pillow, including taxes, totalled €12,650. The implant procedure totalled €1,528, counting the use and costs derived from the haemodynamics room (including the salary of the interventional cardiologist), according to public prices.[
14] Outpatient costs, including monitoring, regular visits and possible hospitalisations were taken into account. Monitoring costs were accounted for as a nurse's 30-minute salary, which is the daily time a nurse needs to consult the pulmonary pressures of CardioMEMS patients (this process is repeated 5 days a week). Such cost is accounted as €63 per patient per year, given the fact all patients are covered under that time.
Regular visits were appointed both with the HF Cardiologist (every 6 months) and the nurse (every 3 months). Both regular appointments were accounted for as an outpatient visit under public prices at €80 per visit.[
14,
15]
The hospitalisation per day price is an average of €674. No hospital admission costs were accounted for CardioMEMS implantation as patients were discharged on the same day of implantation.
We valuated the QALY at €25,000.[16-17] An effectiveness of 0,3 QALY was taken as reference as according to the CHAMPION trial.[
5]
The costs, resources and benefits of the study and its evaluation were valued in euros (€) as of 2022. The currencies were converted to 2022 euros per the price dates in each study. The reporting of this study follows the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) framework for economic evaluations.[
18]
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables are expressed as absolute numbers and percentages. Continuous variables are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation for normal distributions, or the median and interquartile range, for non-normal distribution. Normal distributions were assessed with normal Quantile-Quantile plots. Comparisons between groups were performed with paired t-test for continuous variables.
To compute the HF hospitalisation rate for pre- and post-sensor implantation, the risk exposure time (total follow-up time until death, minus days of hospitalisation) for each patient was taken into account. For the cost analysis, both the number of hospital admissions and the length of stay were taken into account.
RESULTS
From September 2019 to November 2021, 43 patients from the same HF clinic had a CardioMEMS device implanted, with a balanced representation of both male and female participants, aged 75.5±7.0 years, with both reduced and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (mean LVEF 49±14%). 67.4% of them were in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III and 32.6% in NYHA class II. Mean creatinine was 1.37±0.49mg/dL and median baseline NT-ProBNP 1919 pg/mL [IQR 1014-3339].
79,1% had been previously admitted due to HF decompensation at least once during the year before CardioMEMS implantation (53.5% two or more times). 7 patients died during the first year of follow-up (two of them due to cardiovascular causes, none of them due to HF), mean follow-up for those patients was 208.9±91.3 days. The final patient completed 1-year follow-up in November 2022.
Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics, and treatments of the included patients are shown in
Table 2.
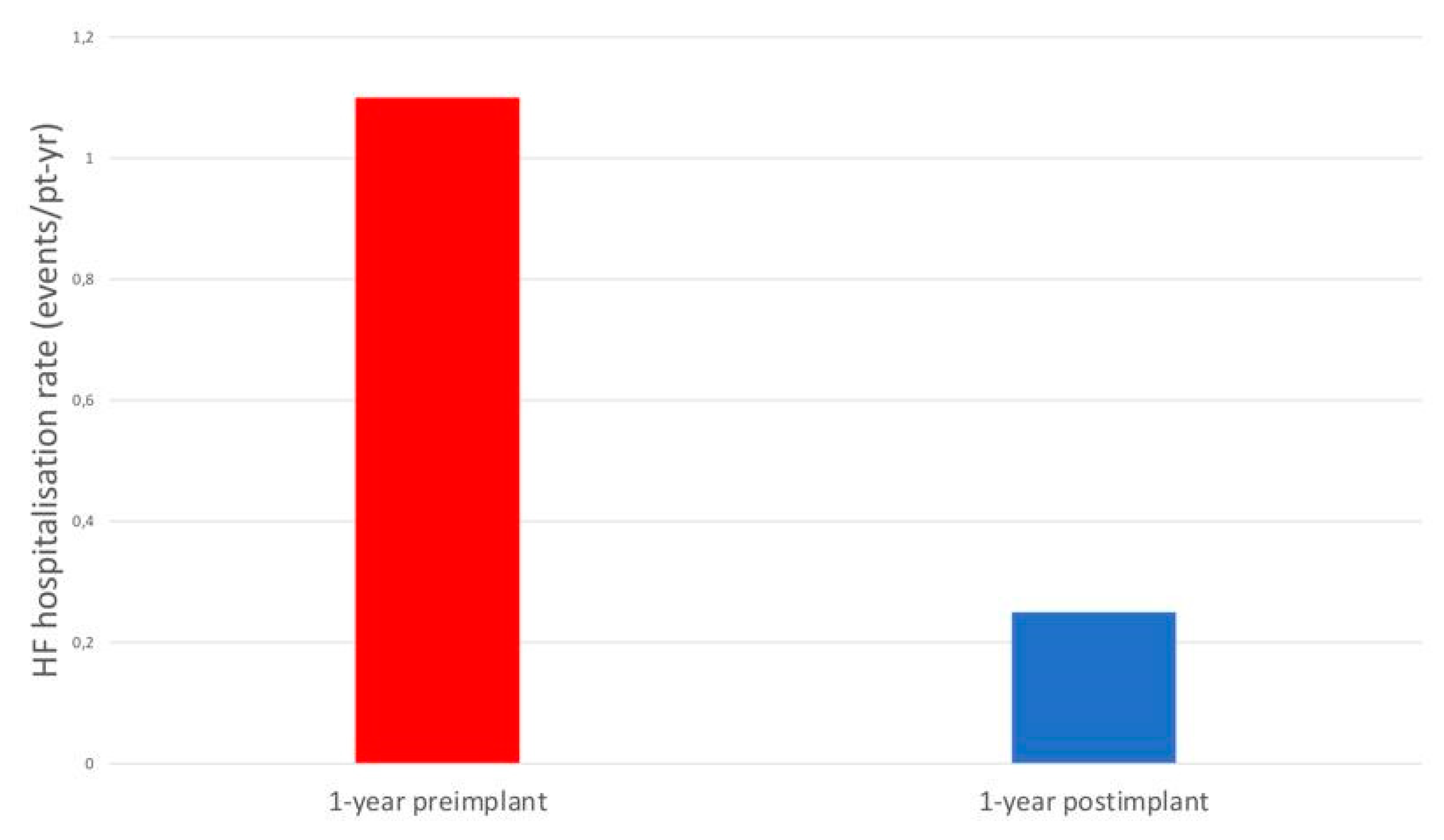
The rate of HF hospitalisations was significantly lower at 1 year compared with the year before CardioMEMS implantation (0.25 versus 1.10 events/patient-years, HR 0.22, P=0.001), with an absolute reduction of 0.85 events/patient-years.
Figure 1.
Hospital admissions were considerably longer for the post-CardioMEMS period (30.5 days) in comparison with the pre-CardioMEMS period (12.53 days).
Table 3 shows the comparison between costs and benefits for patients before and after having the CardioMEMS HF System for the first year. For the post-treatment group, the device and its implant account for the majority of the costs, while in the pre-treatment group the hospitalisation costs comprised most of the costs. As for the outpatient costs, both groups had regular appointments with nurses and the cardiologist. The benefit-cost ratio was €7,500/€19,688 for the post-treatment group at 1 year.
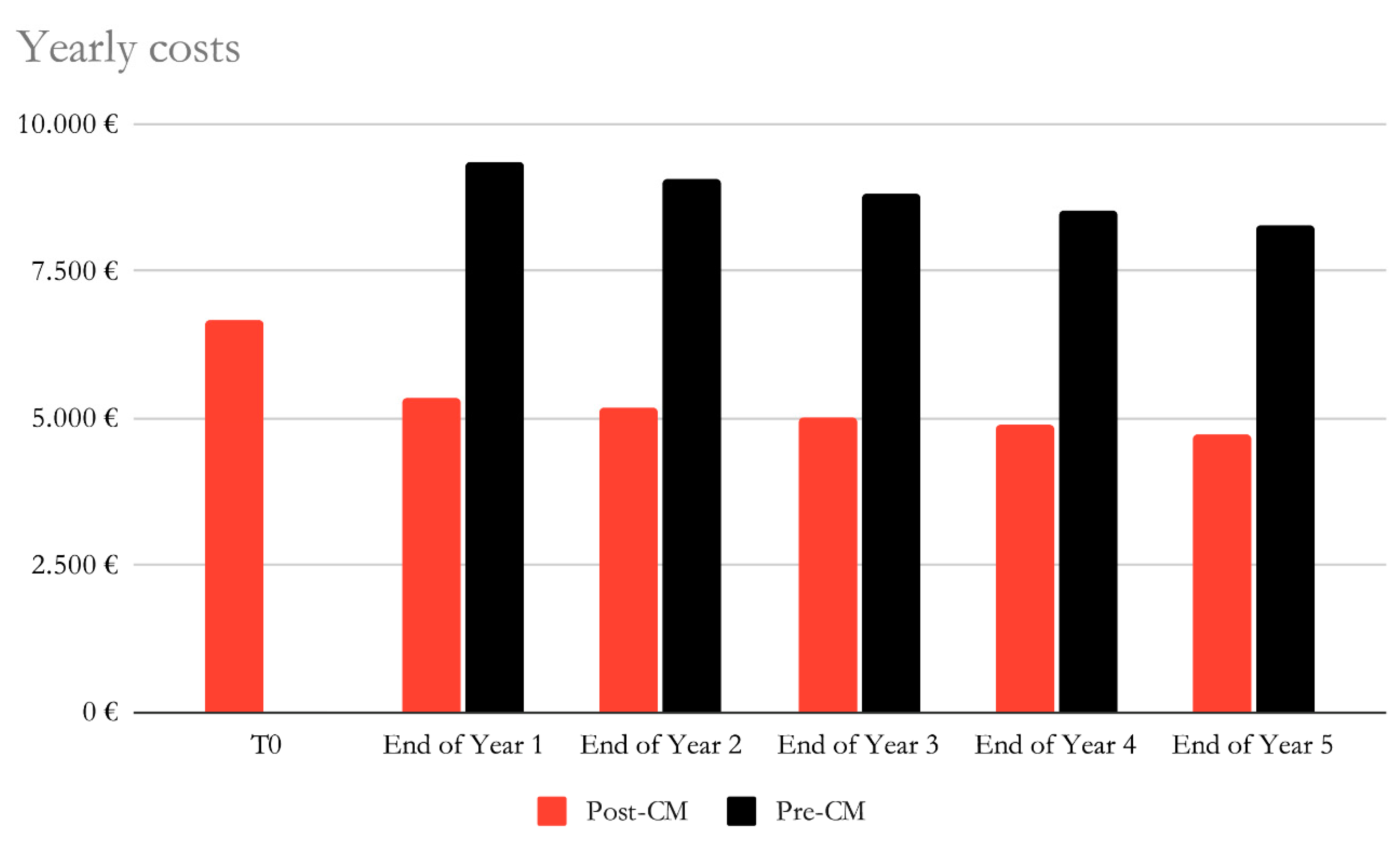
Considering the QALY gained (applied by the beginning of the first year of the study) as a benefit, a constant cost of hospitalisation for all groups and a 3% discount rate, the initial costs are higher for the post-CardioMEMS group due to the high costs of the device, however they are rapidly outgrown by the costs of the pre-CardioMEMS period, which are mainly driven by higher hospitalisation costs, as shown in
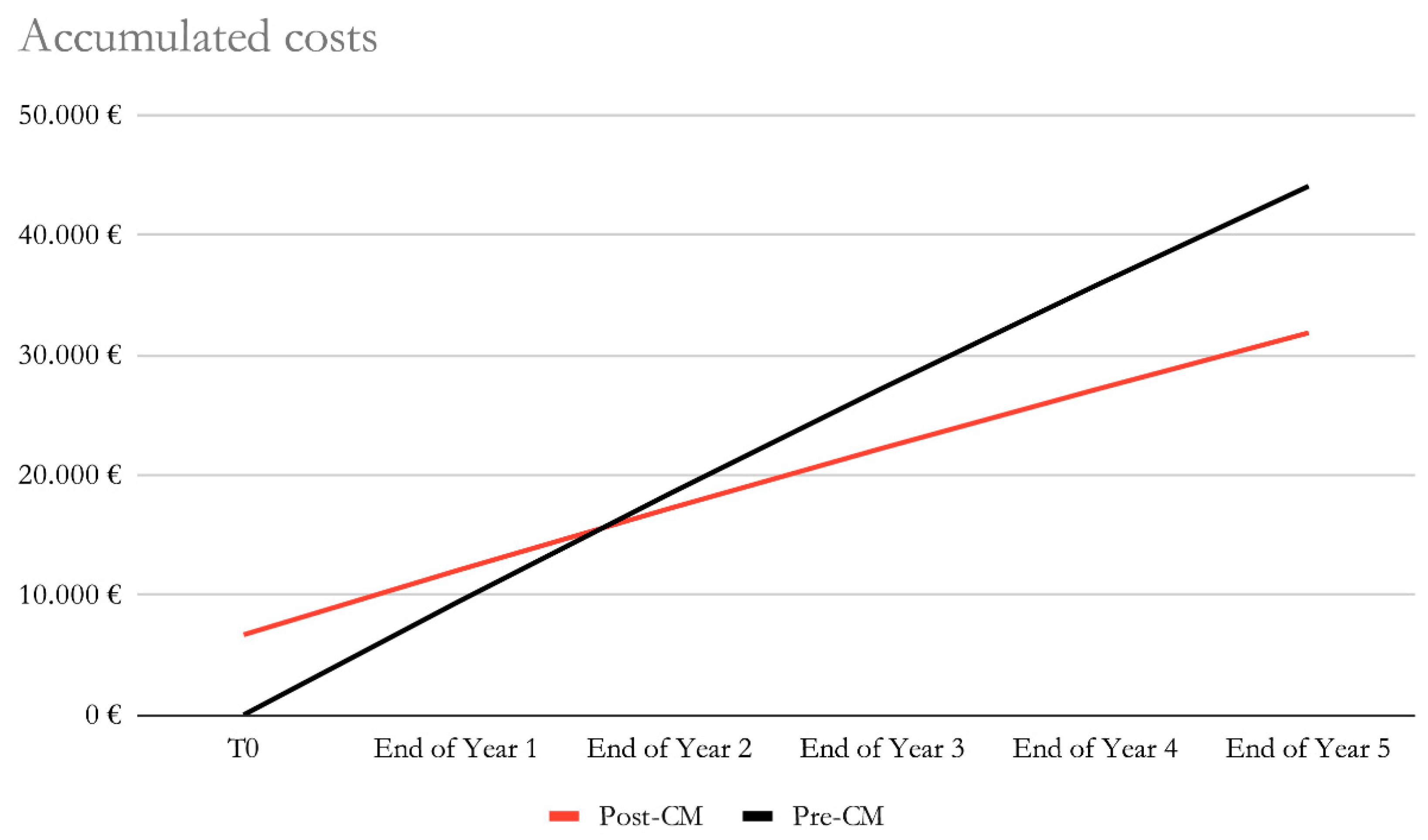
Figure 2. By the end of year 2, the costs of the post-CardioMEMS and pre-CardioMEMS groups would be of €18,435 and €17,207, with a reduction in accumulated costs of €1,228 in favour of the post-CardioMEMS group. By the end of year 5, the accumulated estimated costs for the post-CardioMEMS and pre-CardioMEMS groups would be of €31.846 and €44.066, respectively. (
Figure 3). Several sensitivity analyses were performed in order to evaluate how the results could be affected by changes in key assumptions or variables (Supplementary Tables S2 and S3).
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first study to perform a cost-benefit analysis of the CardioMEMS system in a HF clinic from Southern Europe. Remote monitoring of PAP with CardioMEMS was associated with a strong reduction in HF hospitalisations at 1 year.
Hospitalisation costs in Spain are lower in relation to the United Kingdom and the United States of America. Therefore, one could think the potential savings by avoiding HF admissions with remote PAP monitoring are also lower. This belief currently leads to an underutilization of this invasive remote monitoring strategy in Southern Europe in comparison to other countries.
In this study, considering the QALY gained as a benefit, a constant cost of hospitalisation for all groups and a 3% discount rate, the initial costs are higher for the post-CardioMEMS group due to the high costs of the device, however they are rapidly outgrown by the costs of the pre-CardioMEMS period, which are mainly driven by higher hospitalisation costs (
Figure 2).
Hospital admissions for the post-CardioMEMS period were considerably longer than those of the pre-CardioMEMS and matched control groups. A possible explanation is that patients who are admitted despite hemodynamic-guided treatment are more complex and require longer admissions.
The fact that the CardioMEMS system requires no batteries or replacements, along with patients having a lifespan exceeding two years, makes invasive remote monitoring not only a more effective but also a more cost-effective long-term strategy.
Table 4 shows the cost structure along that of the six other studies conducted since the CHAMPION trial. The actual cost shown in this article is similar to the studies by Schmier et al., Cowie et al. and Alcaraz et al., all published after 2017 and all very similar in their cost structure: device, implantation, complications, monitoring, usual cost of heart failure treatment and possible hospitalisations. This work has considered all these costs except for complications (due to their small number in our cohort, as only one patient had a vascular complication) and introduced costs related to regular visits with the nurse and HF cardiologist. Regarding the valuation of costs, ours were most similar to those described in Cowie et al, probably due to a similar context in terms of healthcare.
The CHAMPION trial found that the CardioMEMS implant had a benefit of 0.3 QALY for the patient; we used it as an effectiveness benchmark for our study. However, it could be considered a low-range benefit compared to the mean and median of other published articles, at a benefit of 0,42 and 0,39 QALY respectively (
supplementary Table S1). This could mean that the actual benefit is higher than what we have considered, making the benefit-cost ratio higher.
Study limitations
These results should be interpreted in the context of several potential limitations. First, despite having more implants than any other healthcare centre in Southern Europe and being responsible for over half of the implants performed in Spain, the sample is limited and from a single centre. Of note, a common follow-up protocol with the HF nurse and doctor was applied to all patients during the whole study period, limiting possible bias introduced by different management strategies.
Second, the relative reduction in HF hospitalisations in post-CardioMEMS period was greater than that observed in the CHAMPION trial, but similar to other more recent reports.[
19] Finally, a potential limitation lies in the fact that the sensor's effectiveness depends on the quality of the existing HF unit. If a HF Unit is already very efficient at preventing HF admissions using other remote non-invasive strategies, the CardioMEMS system may not be as effective.
CONCLUSIONS
The findings from this analysis strongly support the utilisation of remote monitoring of PAP with the CardioMEMS HF system as a cost-effective, long-term strategy within healthcare centres in Southern Europe. Given the considerable benefits observed in terms of prevention of HF admissions, the CardioMEMS system emerges as a superior alternative to usual management for selected patients at high risk of HF hospitalisation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the nurses in the heart failure unit for data collection and for their invaluable work in the unit.
Declaration of interest
A.B.G and P.C received speaker fees from Abbott.
References
- Sicras-Mainar, A.; Sicras-Navarro, A.; Palacios, B.; Varela, L.; Delgado, J.F. Epidemiology and treatment of heart failure in Spain: the HF-PATHWAYS study. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2022, 75, 31–38 English, Spanish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, C.; Varela, L.; Palacios, B.; Capel, M.; Sicras, A.; Sicras, A.; Hormigo, A.; Alcázar, R.; Manito, N.; Botana, M. Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with heart failure in Spain. BMC Heal. Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioni, A.P.; Dahlström, U.; Filippatos, G.; Chioncel, O.; Leiro, M.C.; Drozdz, J.; Fruhwald, F.; Gullestad, L.; Logeart, D.; Fabbri, G.; et al. EURObservationalResearch Programme: regional differences and 1-year follow-up results of the Heart Failure Pilot Survey (ESC-HF Pilot). Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2013, 15, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Codina, P.; Altisent, O.A.-J.; Santiago, E.; Domingo, M.; Cediel, G.; Spitaleri, G.; Lupón, J. Advanced remote care for heart failure in times of COVID-19 using an implantable pulmonary artery pressure sensor: the new normal. Eur. Hear. J. Suppl. 2020, 22, P29–P32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Adamson, P.B.; Bourge, R.C.; Aaron, M.F.; Costanzo, M.R.; Stevenson, L.W.; Strickland, W.; Neelagaru, S.; Raval, N.; Krueger, S.; et al. Wireless pulmonary artery haemodynamic monitoring in chronic heart failure: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugts, J.J.; Radhoe, S.P.; Clephas, P.R.D.; Aydin, D.; van Gent, M.W.F.; Szymanski, M.K.; Rienstra, M.; Heuvel, M.H.v.D.; A da Fonseca, C.; Linssen, G.C.M.; et al. Remote haemodynamic monitoring of pulmonary artery pressures in patients with chronic heart failure (MONITOR-HF): a randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowie, M.R.; Simon, M.; Klein, L.; Thokala, P. The cost-effectiveness of real-time pulmonary artery pressure monitoring in heart failure patients: a European perspective. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2017, 19, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpiñán, J.M.A.; Martínez, F.I.S.; Pérez, J.E.M. La medición de la calidad de los estudios de evaluación económica: Una propuesta de "checklist" para la toma de decisiones. [Quality assessment of economic evaluations in health care: a checklist and user guide]. Rev Esp Salud Publica 2009, 83, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, A.T.; Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D.; Owens, D.K.; Turakhia, M.P.; Kaiser, D.W.; Heidenreich, P.A. Cost-Effectiveness of Implantable Pulmonary Artery Pressure Monitoring in Chronic Heart Failure. JACC: Hear. Fail. 2016, 4, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinson, M.; Bharmi, R.; Dalal, N.; Abraham, W.T.; Adamson, P.B. Pulmonary artery pressure-guided heart failure management: US cost-effectiveness analyses using the results of the CHAMPION clinical trial. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2016, 19, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmier, J.K.; Ong, K.L.; Fonarow, G.C. Cost-Effectiveness of Remote Cardiac Monitoring With the CardioMEMS Heart Failure System. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, A.; Rojas-Roque, C.; Prina, D.; González, J.M.; Pichon-Riviere, A.; Augustovski, F.; Palacios, A. Improving the monitoring of chronic heart failure in Argentina: is the implantable pulmonary artery pressure with CardioMEMS Heart Failure System cost-effective? Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Generalitat de Catalunya. Ordre SLT/71/2020, de 2 de juny, per la qual es regulen els supòsits i conceptes facturables i s'aproven els preus públics corresponents als serveis que presta l'Institut Català de la Salut. 2020. Available online: https://cido.diba.cat/legislacio/10263520/ordre-slt712020-de-2-de-juny-per-la-qual-es-regulen-els-suposits-i-conceptes-facturables-i-saproven-els-preus-publics-corresponents-als-serveis-que-presta-linstitut-catala-de-la-salut-departament-de-salut (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Institut Català de Salut. LLIBRE DE RETRIBUCIONS 2022, PERSONAL ESTATUTARI DE L’ICS. 2022. Available online: https://administraciopublica.gencat.cat/web/.content/funcio-publica/empleats-publics/retribucions/2022/Llibre-de-retribucions-2022.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Vallejo-Torres, L.; García-Lorenzo, B.; Serrano-Aguilar, P. Estimating a cost-effectiveness threshold for the Spanish NHS. Heal. Econ. 2017, 27, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Torres, L.; García-Lorenzo, B.; Rivero-Arias, O.; Pinto-Prades, J.L. The societal monetary value of a QALY associated with EQ-5D-3L health gains. Eur. J. Heal. Econ. 2019, 21, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husereau, D.; Drummond, M.; Augustovski, F.; de Bekker-Grob, E.; Briggs, A.H.; Carswell, C.; Caulley, L.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Greenberg, D.; Loder, E.; et al. Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards 2022 (CHEERS 2022) statement: updated reporting guidance for health economic evaluations. Eur. J. Heal. Econ. 2022, 23, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavelle, D.M.; Desai, A.S.; Abraham, W.T.; et al. CardioMEMS Post-Approval Study Investigators. Lower Rates of Heart Failure and All-Cause Hospitalizations During Pulmonary Artery Pressure-Guided Therapy for Ambulatory Heart Failure: One-Year Outcomes from the CardioMEMS Post-Approval Study. Circ Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e006863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).