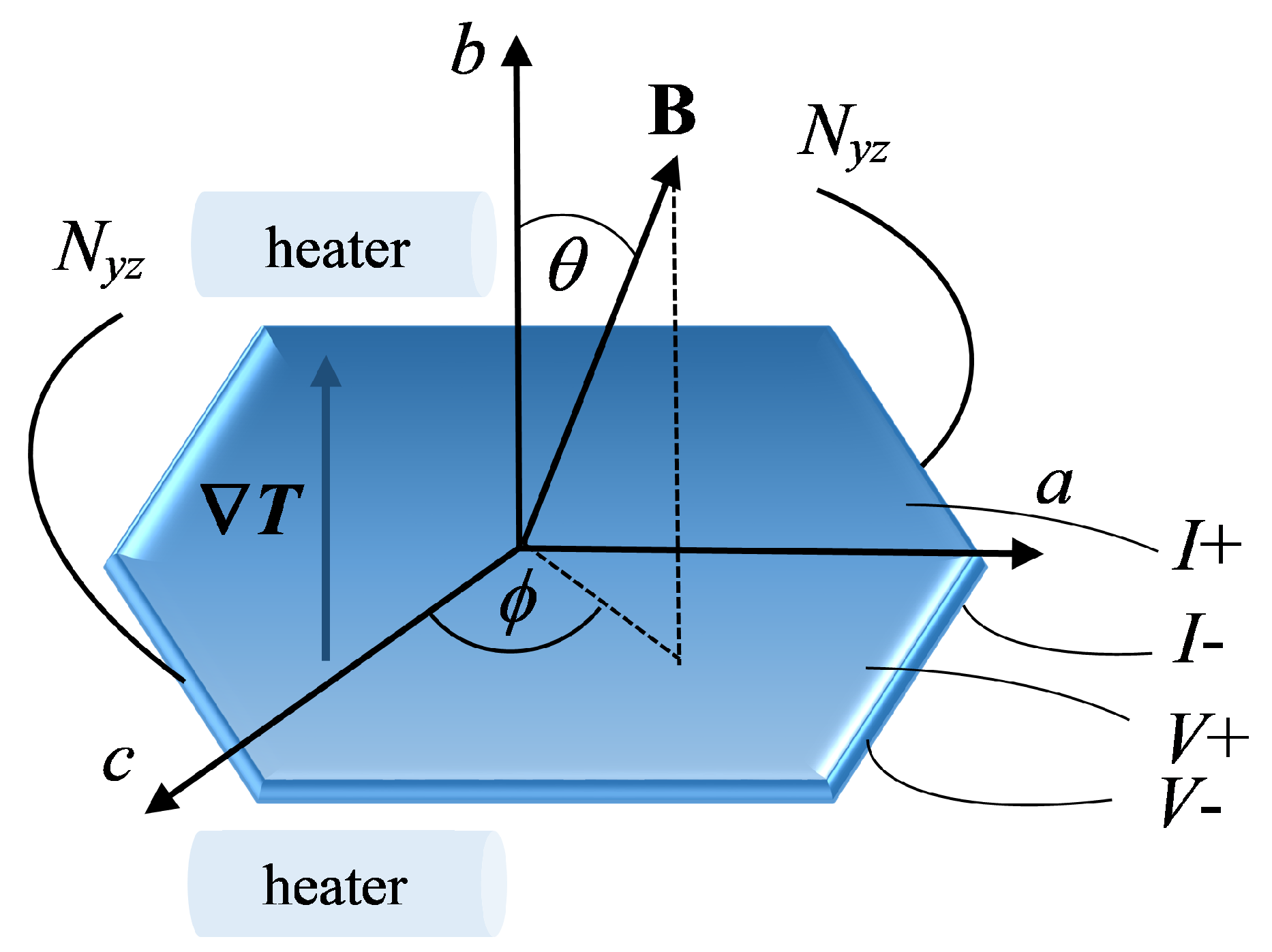
In the following we present a detail study of Nernst effect in the multiband organic conductor with the magnetic field magnitude, orientation and temperature. The magnetic field and angular dependencies are obtained in the low temperature regime in the CDW state of the conductor. The Nernst effect investigation allows to obtain more insights about the behavior of different CDW states that develop in this conductor as well as information on the driving mechanism for the CDW instabilities in . Additionally, it may give information about the role of quasiparticles in the transport processes in multiband systems.
3.1. Angular Hall and Nernst Effect Oscillations
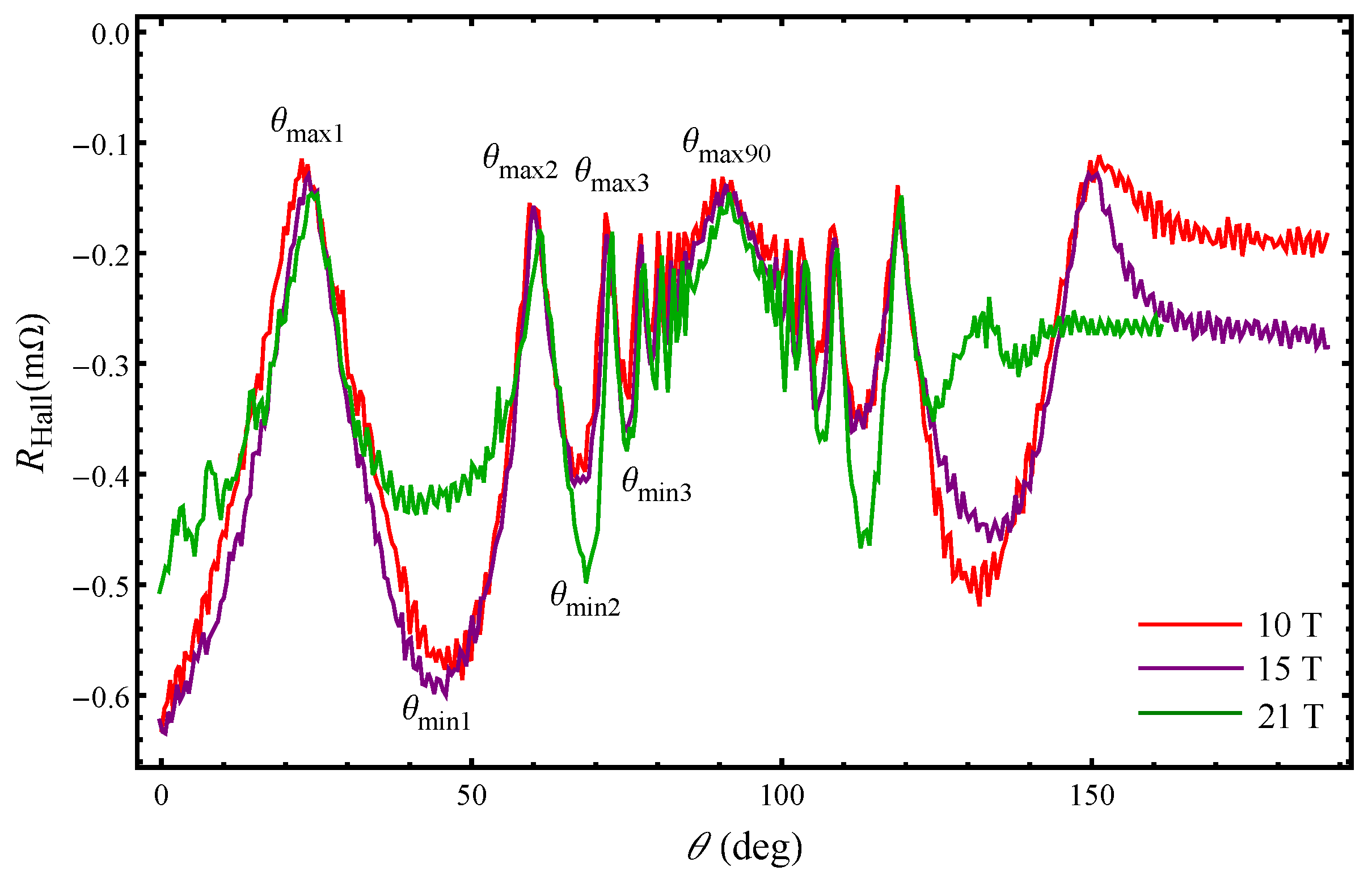
The angular Hall resistance oscillations (AHROs) in the
state of
are shown in
Figure 2 for several fields: 10 T, 15 T, 21 T at
K. The Hall resistance quantum oscillations, associated with Landau quantization of the closed FS orbit are observed superimposed on the angular oscillations for each magnetic field strength. Although in the CDW phase no q1D FS open sheets should survive, there appear clear angle-dependent Hall resistance oscillations similar to the Lebed resonances, which are characteristic for q1D organic conductors [
15]. The AHRO maxima and minima appear at angles
and
where
. Interestingly, the dips in the Hall resistance become sharp at angles above
whereas the first minimum occurring at
is rather broad especially with increasing magnetic field magnitude. This is in contrast to the angular magnetoresistance oscillations (AMROs) behaviour in
(see
Figure 2 in Ref. [
16]) where the maxima in the angular dependence are not as sharply pronounced as those in the AHROs. The Hall resistance is negative indicating that, in
, the in-plane transport is mainly electron-like independently on the field direction with respect to the layers. An important observation is that the AHRO maxima occur at angles at which AMRO minima appear known as Lebed magic angles. Consequently, AHRO minima are observed at angles at which AMRO maxima are detected. However, there is a slight shift between the AMRO (AHRO) maxima (minima) seen only at angles below
. This can be more clearly identified from the corresponding curves presented in
Figure 5 below. With rotation of the magnetic field towards the plane of the layers more charge carriers have been involved in the transport processes which can account for the absence of a shift between the AMRO (AHRO) maxima (minima) at angles above
. Interestingly, changes in the angle-dependent Nernst effect also occur around this angle at each magnetic field magnitude. Our results show that, in the compound under consideration, the thermoelectric transport is more complex than previously anticipated as the large Nernst signal arises in total absence of superconducting fluctuations. This opens a new window for investigation of the driving mechanism for the CDW instabilities in
.
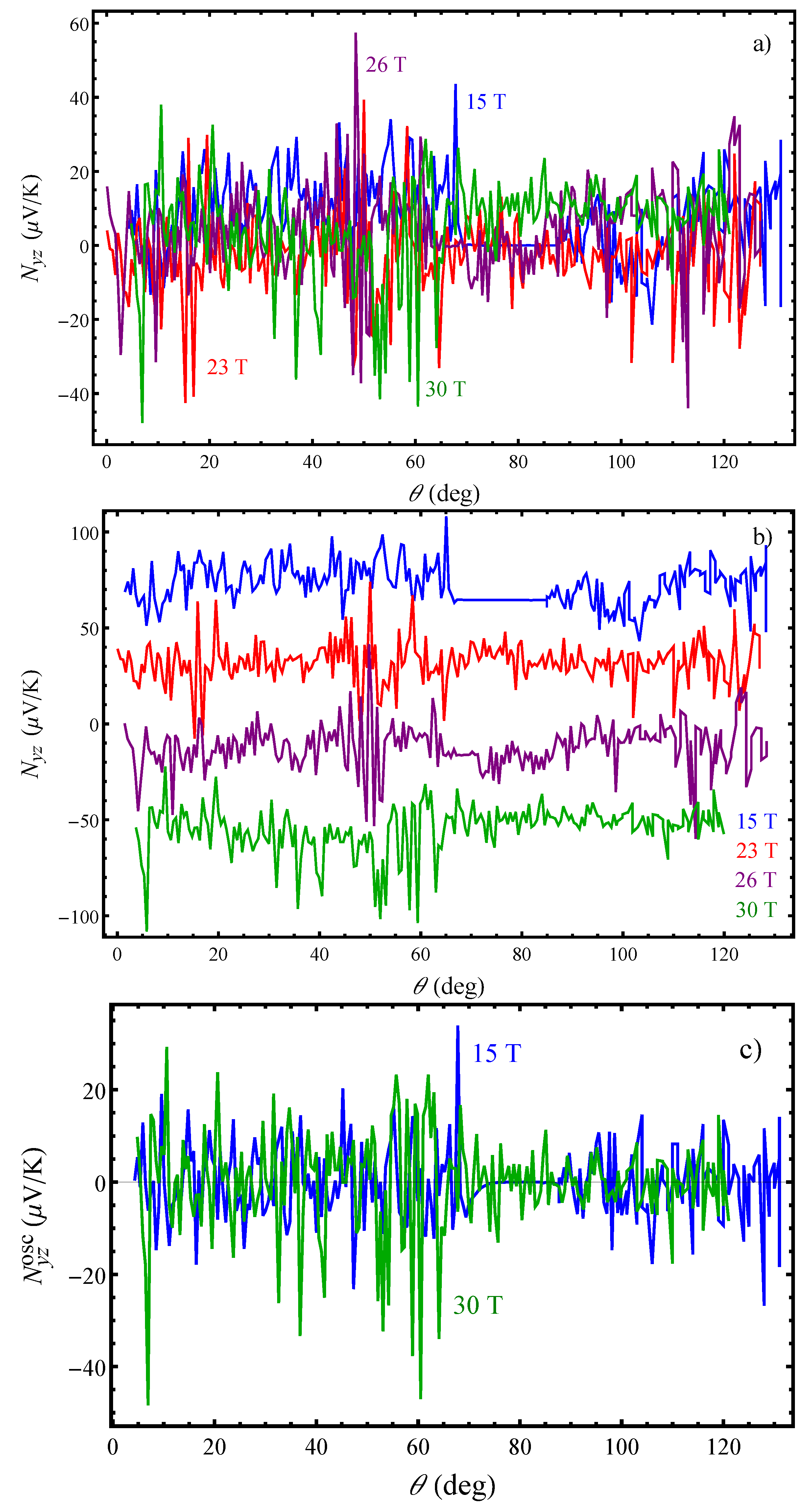
We present in
Figure 3 the angular dependence of the total Nernst effect in
for several fields:
T, 23 T, 26 T and 30 T at
K. We have detected an angular Nernst signal with a large amplitude for each magnetic field magnitude. Exceptions from this are certain angles as discussed below. We find that, in
, the angular Seebeck effect (thermopower) [
16] is much smaller than the Nernst effect although the thermoelectric measurements are performed for a longitudinal temperature gradient. Both effects show oscillations, but the transverse component is clearly dominant as it is about 10 times larger than the longitudinal one. This is also a case even for magnetic field orientations close to the less conducting axis (
b-axis) where the thermopower is expected to be the dominant thermoelectric response. The rather complex nature of the observed angular Nernst signal in
is correlated with its multiband character as two kinds of carriers are involved in the thermoelectric transport. The giant Nernst effect previously observed in some of the q1D organic compounds with undetectable Seebeck effect has been ascribed to the vortex flow [
4,
5]. On contrary, the superconducting state in
develops below
K and for a quasi-hydrostatic pressure of
kbar [
17]. This indicates that, in the compound under consideration, the quasi-particles are responsible for the observed large amplitude of the Nernst effect.
For obtaining a more detailed picture on the thermoelectric transport in
one should study the behaviour of the two components, the quantum oscillating component and the background term. The quantum oscillations are visible at each magnetic field magnitude in the whole range of angles. Exception are only the angles close to the layer’s plane at 15 T in the
state (
Figure 3c) where the total Nernst signal is vanishing although it should not be zero because the transverse voltage is the largest along the
y direction. The quantum oscillations are mainly due to the fundamental frequency of the closed FS
orbit,
T, which is present above
T. The oscillatory part of the transport coefficients is determined by the oscillatory dependence of the relaxation time
that result from the summation over all the electron states in the incoming term of the collision integral. In the Born approximation, for
,
where
ℏ is the Planck constant divided by 2
,
is the cyclotron frequency,
is the cyclotron effective mass,
is the interlayer transfer integral,
and
are the non-oscillatory and oscillatory part of the relaxation time. The oscillatory part of relaxation time is a sum of the contributions from all extremal orbits,
, on the Fermi surface for a particular orientation in a magnetic field
, where
accounts for finite temperature effects,
for impurity scattering,
for spin-splitting effects, and
for the magnetic breakdown effects. As a result of the oscillatory dependence of
, the thermoelectric coefficient
acquires an oscillatory component
and so the oscillatory part of the Nernst effect is
. It is large when a Landau level meets the chemical potential
and is damped when
is between two successive Landau levels. The amplitude of the Nernst effect quantum oscillations is much larger than that of the Hall resistance quantum oscillations (about
times larger) as can be seen by comparing the
Figure 2 and
Figure 3. This is in correlation with the high fundamental frequency of the main oscillations,
, for
which strongly increases the amplitude of the effect when performing the derivative of the density of states over
.
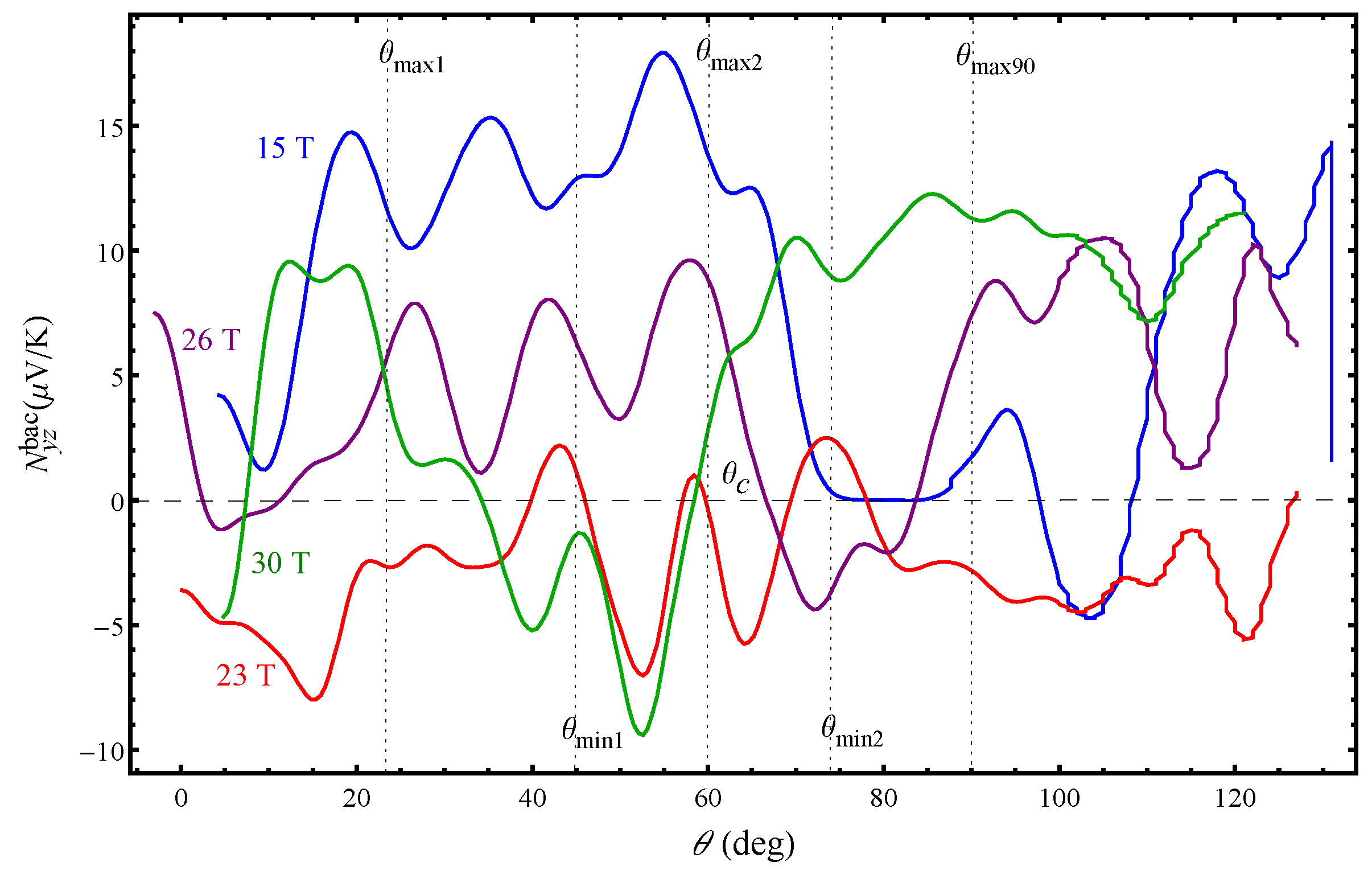
The background Nernst effect shown in
Figure 4 reveals oscillatory features emphasizing the resonant-like character of the effect. The resonance-like behaviour of the background Nernst effect is evident at each magnetic field magnitude similar to that previously observed in the angular dependence of the Seebeck effect [
16]. Apart from that, the angular dependence of the Nernst effect changes significantly with increasing magnetic field strength. This is a reflection of the complex electronic properties associated with existence of different CDW states in this organic metal. It should be specifically emphasized that all of the Nernst effect curves show different behaviour above a certain tilt angle,
, which corresponds to the second maximum in the Hall resistance angular dependence. At a lower field (
T), when the system is in the
state, the Nernst effect decreases above
without changing the sign. A decrease in the Nernst effect amplitude is also seen at
T above
accompanied with a sign change around
. At
T, the Nernst effect is zero at
above which is positive with a pronounced increase in the amplitude. For
T and
T the system is supposed to be in the
state, but the observed distinct behavior of the Nernst effect around
implies that this is not the case. The curve obtained for
T demonstrates the most unusual behaviour as the Nernst effect constantly changes sign in the angular range between the first and third AHRO maximum. Most strikingly, the curve is mirroring its angular behaviour exactly at
which is not characteristic for the other curves. The observed different Nernst effect behaviour, especially above
, with or without a sign change, indicates that significant changes occur in the density of states.
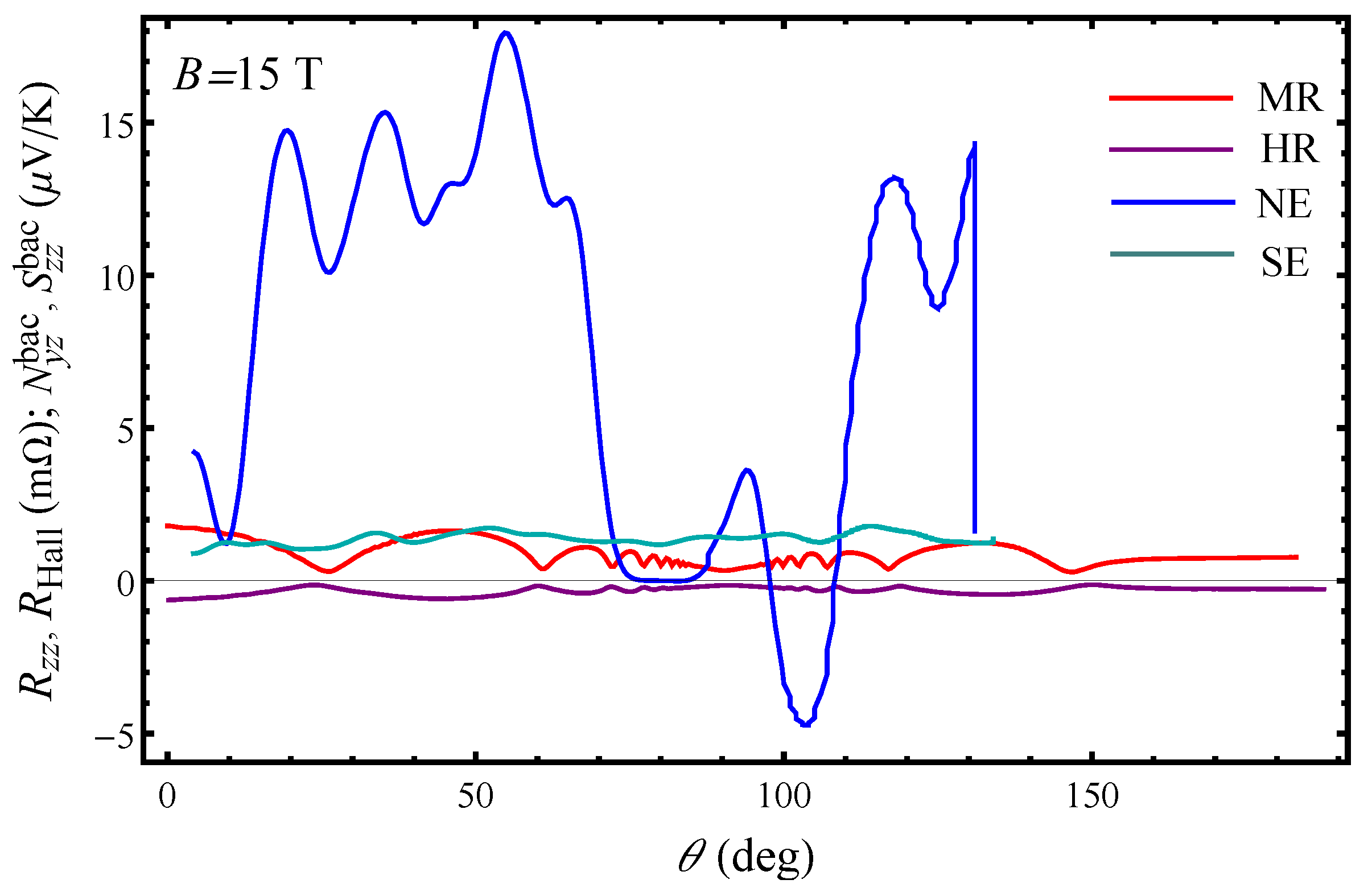
In order to capture the magnitude of the observed Nernst signal at low temperature, we present in
Figure 5 the AMROs, AHROs, Seebeck and Nernst effect angular oscillations at
T and
K. It is clearly seen that the amplitude of the Nernst effect is exceeding by far the amplitudes of the other effects with an exception of a small interval of field orientations near the layer’s plane where the Nernst signal is zero and the Seebeck effect is the main thermoelectric response, although this should not be observed when the temperature gradient is along the normal to layer’s plane. Beside the large amplitude, there are other features that should be addressed concerning the behaviour of the angular Nernst effect in the CDW state. The features observed in the angular Nernst effect for
K neither appear at the magic angles (where the peaks and dips in the AMRO and AHRO are observed) nor are located at the mid angle positions. However, the latter was observed in the Nernst effect angular oscillations for
K [
18]. Another interesting observation is that for
K, in the
state, the Nernst effect is also oscillatory up to angles
but with a 10 times smaller amplitude than that for
K. However, for
K, the Nernst effect is the largest in the
state up to angles
(
Figure 4). This implies that at low temperatures, deep down in the
, there are some processes that are dominant leading to an existence of a large transverse thermoelectric response in the current compound, and the Nernst effect is very sensitive to these low-temperature processes.
By comparing the
Figure 2 and
Figure 4, one can see that the transverse thermoelectric transport represents more remarkable signatures of the CDW transitions as the Nernst effect is very different from the Hall resistance. This is because, in
, Nernst effect is especially sensitive to both the Landau-level spectrum and energy gap in the electronic structure. We find that both quantum oscillating and background component of the Nernst effect, behave differently with increasing angle and field. At
T the amplitude of the quantum oscillations is of the same order as the background up to angles
while above this angle there is a sudden decrease in both components which vanish for field orientations close to the plane of the layers. This behaviour however, is not expected as the Nernst signal is supposed to be the largest when the generated transverse electric field is the largest. With increasing field, at
T and
T, the quantum oscillating component is dominant over the background one in the whole range of angles. For
T the the quantum oscillating component is larger only below
.
Figure 4 shows that, above
, the Nernst effect amplitude is large only at high magnetic fields. In the absence of systematic studies of the Nernst effect in other layered q2D organic systems, one may speculate in several directions concerning the origin of the giant Nernst signal. We first note that, due to change of the quantum Nernst effect component below and above
, there might be a significant change in the quasiparticle density of states at the Fermi energy which may lead to an enhanced Nernst signal. On the other hand, the background Nernst effect is intimately related to the off-diagonal component of the thermoelectric coefficient tensor
which is the energy derivative of the off-diagonal conductivity component
, at the Fermi energy, according to the Mott formula
. Thus, if,
changes due to to a small change in the Fermi surface volume, this could also lead to an enhanced
and hence to a sizable Nernst signal. Since Nernst effect is very sensitive to changes in the Fermi surface this implies that, in
, large changes occur in the out-of-plane electronic structure.
With investigation of the magnetic and temperature dependence of the Nernst effect, in addition to the angular dependence, one can obtain information about the possible sources for detection of the large angular Nernst effect in this multiband system. In regards to that, the obtained magnetic and temperature dependencies of the Nernst effect (discussed below) suggest that not the asymmetry of the quasi-particle density of states but the change in the carriers relaxation times ( and thus, in the carriers scattering rates) are the primary source of producing a large Nernst signal. Although the charge relaxation dynamics has not been much considered in studying the thermoelectric effects, in many cases it can be dominant in producing a sizeable thermoelectric response, especially a transverse one. However, we have detected a large angular Nernst signal in contrast to the observed much smaller magnetic Nernst signal (
Figure 7 below). This implies that the observed giant angular Nernst effect is not only due to changes in the density of states and scattering rates, but also due to changes in the charge carriers velocity, as they move along different parts of the FS. Indeed, with changing the field orientation, the electron trajectories along the corrugated FS also change. For specific field orientations the velocity is more effectively averaged to zero and therefore, transport is reduced. For the Fermi cylinder, the velocity vector along the cylinder axis goes to zero when all closed orbits have a same area. For the open Fermi sheets, the velocity vector is reduced when the electrons are not moving along the corrugation axis. This can explain the zero angular Nernst signal observed at certain angles in
Figure 4. Also, the Nernst effect is most clearly manifested when the temperature gradient and the velocity vector of the q1D charge carriers are not perpendicular to each other [
19]. This might be the reason for observing the largest angular Nernst effect in the
state for angles below
and a zero Nernst effect for angles close to the plane of the layers (blue curve in
Figure 4). On the other hand, a large Nernst effect is observed above
at a high field (green curve for
T in
Figure 4). The Nernst signal is positive and large as a result of the formation of a significant number of new closed hole-like orbits obtained as a result of the magnetic breakdown effect. Considering that a field of 30 T is larger than the magnetic breakdown field (
T) many new closed orbits with different area are formed and therefore, the q2D charge carriers velocity vector along the cylinder axis significantly differs from zero. For
T (purple curve in
Figure 4), the Nernst effect is resembling that for 15 T for angles below
but is not zero for field orientations close to the plane of the layers. It seems that, at high fields, the
state is still present for angles below
, although the magnetic field for this measurement is larger than the kink field
and the
state is expected to be observed instead of the
. However, above
the system is in the
state due to appearance of new electron-like closed orbits resulting from the magnetic breakdown. The peculiar behavior of the Nernst effect for
T (red curve in
Figure 4) is correlated to the proximity of the field (for which this angular dependence is obtained) to the kink field,
T, at which the
transition occurs. Therefore, for
T, the Nenst effect curve is most probably a result of the mixing of contributions from several bands and hence it reflects the properties of both the
and
state.
With rotation of the magnetic field from the direction of the temperature gradient towards the plane of the layers the average velocity of charge carriers along the
axis,
, decreases but the average velocities along the
and
axis,
and
, are rather large. This can lead to generation of a substantial in-plane Nernst signal
. In other words, the in-plane Nernst effect component can be significant and its contribution can not be neglected as it can affect the overall behavior of the out-of-plane Nernst signals due to mixing of the components of the thermoelectric tensor
. In support to this scenario, Choi
et al. [
20] have shown that, at low temperatures, the in-plane Nernst effect
is large enough even when the magnetic field is applied along the
axis, i.e., along the direction of the temperature gradient.
3.2. Resonant magnetic field Nernst effect
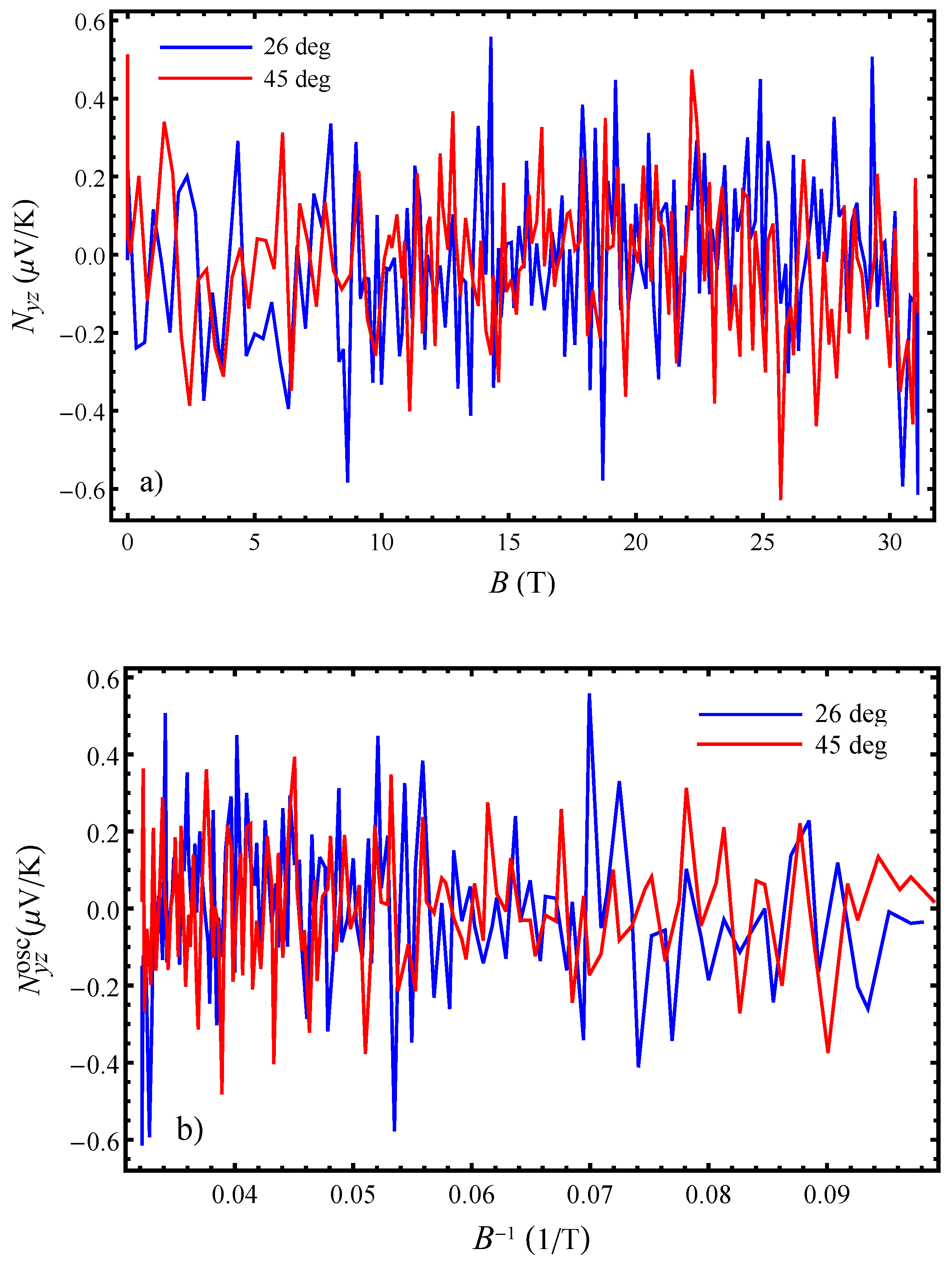
Figure 6a shows the magnetic field dependence of the total Nernst effect in
obtained at
K and:
. The angles correspond to the orientations of the magnetic field where the AHROs have a maximum and a minimum (first maximum and minimum in
Figure 2) since the Nernst effect behaves differently at these orientations. At low temperatures, the magnetic Nernst effect is small compared to the Seebeck effect [
16]. The magnetic Nernst effect has a similar amplitude for orientations corresponding to both the AHRO maximum and minimum. From
Figure 6b, which presents the magnetic quantum oscillations of the Nernst effect with the inverse magnetic field, one can see that the total magnetic Nernst effect is dominated by the quantum oscillating component in fields above 8 T. The quantum oscillations are mainly determined by the fundamental
frequency with a small contribution from its second harmonic only for
. There is no significant change in the amplitude of the magnetic quantum oscillations on crossing the kink field
T, i.e., with the transition from
to
state. This is opposite from what was observed for the angular quantum oscillations where the amplitude of the oscillations changes significantly depending if the field, for which a given angular dependence is obtained, is below or above the kink field
. This implies that, if indeed there are changes happening in the out-of-plane electronic structure in this organic metal, as suggested by the angular Nernst effect behaviour, than these changes are greatly triggered by the magnetic field rotation and are manifested mostly in the Nernst effect and not in the Seebeck effect (as evident from the large angular Nernst effect in this work and the small angular Seebeck effect in the Ref. [
16]).
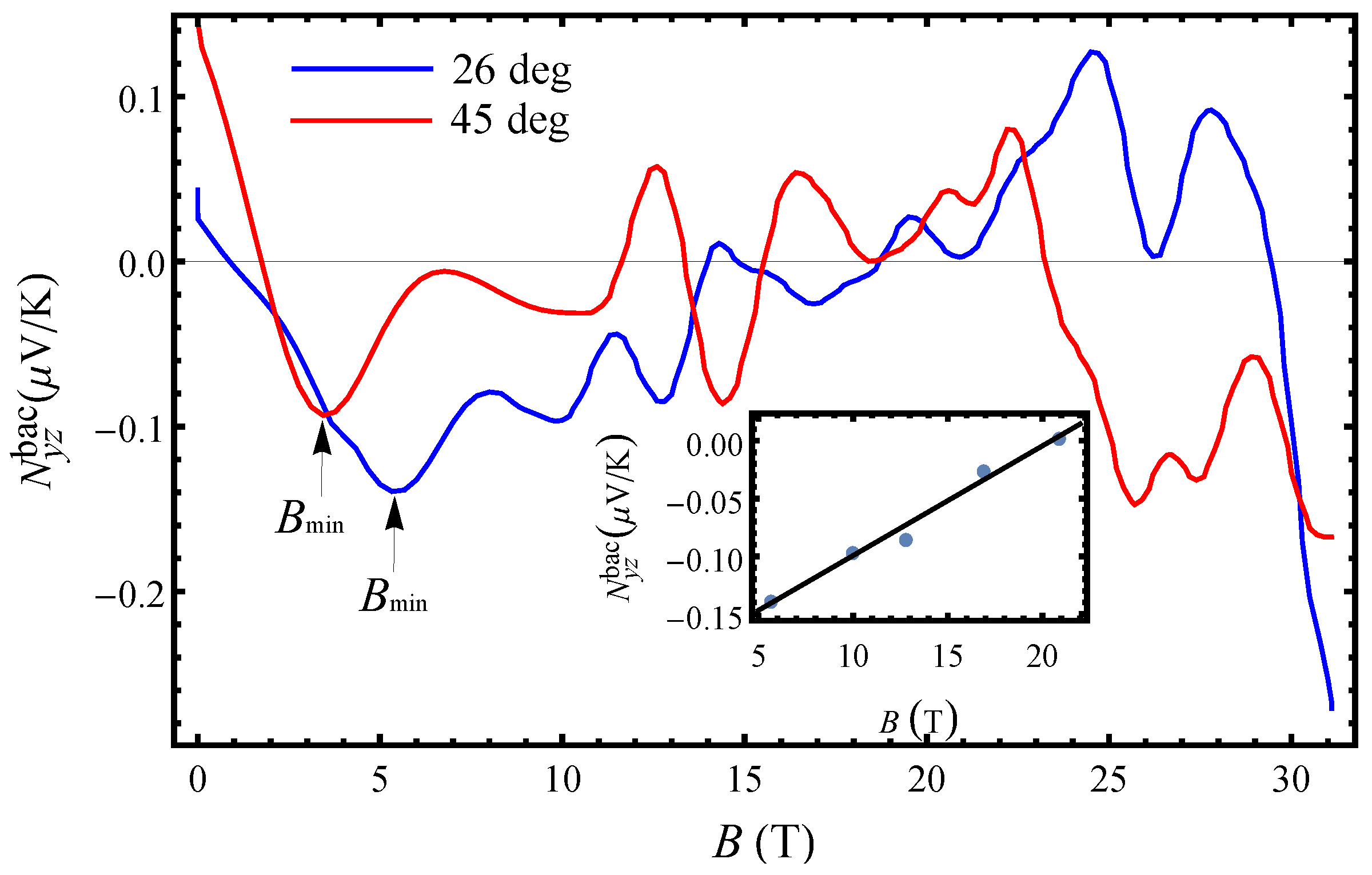
The background Nernst effect shown in
Figure 7 also manifests minimum and maximum features in the magnetic field dependence similarly to those previously observed in the background Seebeck effect in Ref. [
16]. However, the features seen in the Nernst effect are slightly more pronounced (especially with increasing angle) although the Seebeck effect is exceeding the Nernst effect. For angles close to the
axis (
, corresponding to the first AHRO maximum) Nernst effect shows weak oscillatory features and changes sign at
T and also around
T. The electron-hole asymmetry in the
state is evident as the transport changes from electron-like to completely hole-like. In the
state, the Nernst signal changes significantly at
T from a relatively linear (below
) to an approximately linear (increase in slope) with field. For
, the dip-to-dip Nernst effect amplitude changes linearly with field as shown in the inset in
Figure 7. The negative Nernst effect below 18 T, in the
state, indicates that the transport is essentially electron-like due to the electrons on the open Fermi sheets. This, on the other hand, confirms that the small closed orbits do not form in the
state after the Fermi surface reconstruction, i.e., there are only open electron orbits in this state. However, since magnetic breakdown effects take place around
T, the probability for formation of closed hole orbits is increasing with increasing field.
With tilting the field at the first AHRO minimum (), the oscillatory features become more prominent but the Nernst effect is in general small. An important observation is that, when the field is located at the AHRO minimum, the Nernst effect changes sign first at a low field, then in between 10-18 T and again just before entering the high-field state where it becomes negative. Above the kink field for this angle, T, the Nernst signal is weakly field dependent resembling the behaviour of the Seebeck effect but with a smaller amplitude. Here the field dependence from linear changes to a non-linear at T. The sign change in the field range T is due to formation of new electron and hole closed orbits as a result of the magnetic breakdown. In that way, with increasing angle and field both types of charge carriers become involved in the thermoelectric transport while their dominance changes with increasing field. For this field orientation, the closed electron/hole orbits are formed much below the magnetic breakdown field. The different Nernst effect behaviour with the magnetic field from that observed for shows that the q1D charge carriers are not the dominant carriers with increasing angle but the role of the q2D carriers becomes essential in the transport processes at moderate fields of 10 T.
The charge carrier concentration changes depending on the magnetic field direction (maximum or minimum location). Although the carrier density
n is difficult to estimate for the present metal with both open and closed bands, we could obtain
and
for
T by using the simple relation
. Since
decreases with rotation of the field at the location of the first minimum, the amplitude of magnetic Nernst effect quantum oscillations slightly grows and their frequency becomes smaller (
Figure 6b). For these carrier concentrations, giant angular Nernst quantum oscillations with a single frequency are observed. Taking into account that these are not very high carrier concentrations and given that the in-plane conductivity is large it follows that the carrier mobility,
, will be high. Also, as
changes with the field rotation from the AHRO maximum to the AHRO minimum the charge mobility changes rapidly with the rotation of the field from the AHRO maxima to the AHRO minima. We further investigate, with the temperature dependent measurements of the Nernst effect, what processes contribute to the rapidly changing carrier mobility, which can significantly contribute to the Nernst effect enhancement in the given compound.
3.3. Temperature dependence of the Nernst effect
The temperature dependence of the out-of-plane Nernst effect presented in
Figure 8 shows that the effect is strongly nonlinear in the given temperature range and the temperature profile changes significantly with increasing field and angle. One striking feature of
Figure 8a is the presence of a large negative Nernst signal in the
state and even larger Nernst effect in the mixed state. The Nernst effect has a magnitude drastically exceeding what is expected for a multiband system. A large Nernst effect has been also discovered in some Bechgaard salts for fields oriented along the magic angles [
5] and in some heavy-fermion compounds [
21]. More interestingly, our results show that the Nernst effect in the organic metal
has a very similar behavior and size compared to that in heavy-fermion superconductor
[
22]. This indicates that quasiparticels can lead to a large Nernst signal in total absence of superconducting fluctuations.
For a magnetic field of 20 T oriented along the first AHRO maximum (
) the temperature dependence of the Nernst effect shown in
Figure 8a reveals there is a
state below 8 K with a
dependence (
and
D are constants). Above 8 K, instead of the expected metallic behaviour, a mixed state with a
dependence (
and
H are constants) is realized. The Nernst signal changes sign from positive to negative around 6 K indicating a change in the dominant charge carriers in the thermoelectric transport. The observed broad positive and negative maximum in
Figure 8a might be an indicator that there is a thermally induced counterflow of electrons and holes when the field is oriented at the first AHRO maximum. Our results reveal that the temperature profile is complex as several terms arising from different processes appear in the temperature dependence. The thermal activation over an energy band gap gives a
dependence as expected since the system is driven into the
state. The presence of this term indicates that the electron-phonon coupling has an essential role in the transport processes at low temperatures and high fields. However, only the phonon drag term does not provide a reasonable fit to the data. There are two additional terms in the temperature dependence proportional to
and
, respectively. This was not observed in the Seebeck effect temperature profile for the same field magnitude and orientation [
16]. The presence of these terms in the given temperature dependence is a clear indicator that the relaxation times (on which the components of the kinetic and thermoelectric coefficients depend) have different temperature dependence. The absence of the above terms in the Seebeck effect temperature dependence indicate that Nernst effect is much more sensitive to the change in the relaxation dynamics in this organic metal. The energy relaxation processes governing the electron-phonon interactions and the momentum relaxation processes governing the charge carriers mobility are described by the temperature-dependent scattering times,
and
. The components of the electrical conductivity tensor
depend on
and the components of the thermoelectric coefficient tensor
depend on
. At temperatures much less than the Debye temperature
, as it is in the case under consideration, the temperature dependence of
is different than that of
. With the obtained
and
terms in the Nernst effect temperature profile, our results show that the energy and momentum relaxation processes might have an important role in observing the large Nernst signal, especially in the
state. For
, electron-phonon scattering processes make a significant contribution to the energy relaxation. In that case,
is proportional to
and the momentum relaxation time
is proportional to
[
19]. The presence of the latter term indicates presence of significant momentum relaxation dynamics in the
state. A significant gradient of charge relaxation processes can generate a sizeable contribution to the transverse thermoelectric signal. The observed temperature dependence of the Nernst effect arises predominantly from the presence of the q1D group of charge carriers in accordance with the picture of a reconstructed Fermi surface with strongly corrugated open Fermi sheets in the
state. Thus, except for the phonon drag, the change of the electron scattering rates can lead to an unusually large Nernst effect signal. As already known, peak structures in the temperature dependence of Nernst effect appear as a result of the phonon drag effect (since Nernst effect is more sensitive to the phonon drag effect than thermopower) but in this case the change in the electron scattering rates additionally contributes to the observed large Nernst effect. It is known that the momentum relaxation time is proportional to the charge carrier mobility,
. In that way, any change in
will lead to a change in the charge carrier mobility. If
is large enough than there is a counter-flow of high mobility charge carriers (thermally induced quasi-particles) that contributes in generating a large transverse voltage. This is in agreement with previously obtained from the angular and magnetic field dependence of the Nernst effect. In that way, in a material with a changing carrier mobility, resulting from changes in the relaxation dynamics, the Lorenz force acting on the slow and fast carriers of the cold and hot ends of the sample will not be fully compensated which can lead to a sizeable Nernst effect. Above 8 K, instead of observing only a metallic state, there is a mixed state with a non-metallic behaviour in which the
state still exists indicating that the FS is still reconstructed. The phonon drag effect is not affecting the Nernst effect behaviour but the relaxation processes are not reduced up to
K. In the mixed state, the momentum relaxation is adding more to the Nernst signal than the energy relaxation leading to a peak around 11.8 K.
For a magnetic field of 25 T oriented along the first AHRO minimum
, (
Figure 8b) the Nernst effect has significantly smaller amplitude and a
dependence (
and
L are constants) below 4.5 K. At this angle and field the
state (high field CDW state) is realized in
below 4.5 K. This shows that, in the high field state, Nernst effect is a result of the phonon drag effect and electron-phonon interactions. The absence of the
term for the
state excludes the contribution from the momentum relaxation processes in this state. This refers to the decrease in the carriers mobility with increasing angle and field. Above 4.5 K, a non-metallic behaviour is observed characterized with the following temperature dependence
(
and
R are constants). This implies that, a mixed state showing properties of a weakened
state and metallic state, is realized. Interestingly, mixed states have been also observed in the thermopower temperature dependence when the magnetic field is located exactly at the AMRO maximum or minimum. No mixed state is found when the field is along the normal to the conducting
plane [
16]. Obviously, the rotation of the magnetic field away from the temperature gradient direction, at the the AMRO (AHRO) maxima and minima locations, brings the system into some kind of mix states which is an indication of a significant change in the electronic structure. The transitions from a pure CDW state into a mixed state occur at different temperature. The apparent trend is that with increasing angle the transition is reached at a lower temperature. This shows that, most probably, the FS is not completely restored in the given temperature range indicating that this organic metal has a very complex electron structure that changes depending on the underlying conditions. It seems that the presence of a temperature gradient contributes greatly to these changes by affecting the dynamics and flow of the quasiparticles. The obtained temperature dependencies clearly show that the relaxation processes change when system transitions from one into another ordered state. Obviously, they are most pronounced in the
state (
Figure 8a) while are strongly reduced in
state which is evident from the much smaller Nernst effect amplitude with increasing field and angle (
Figure 8b). The predicted Nernst effect behaviour for temperatures outside of the temperature range used in these measurements is seen from the insets in
Figure 8. The presented results greatly contribute not only for revision of the previous findings about the thermoelectric transport but also for obtaining information for the possible mechanisms responsible for existence of different phases in the given organic metal.