Submitted:
29 December 2022
Posted:
04 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient
2.2. Immunological studies on tumor tissue from patients and controls
2.3. Cell lines and culture conditions
2.4. Immunocytochemistry – surface antigen labeling and quantification
2.5. Western blot
2.6. Quantitative reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase-chain-reaction
2.7. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)
2.8. Gene expression profiling
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. mGluR5 is expressed on Hodgkin lymphoma tissue at varying levels
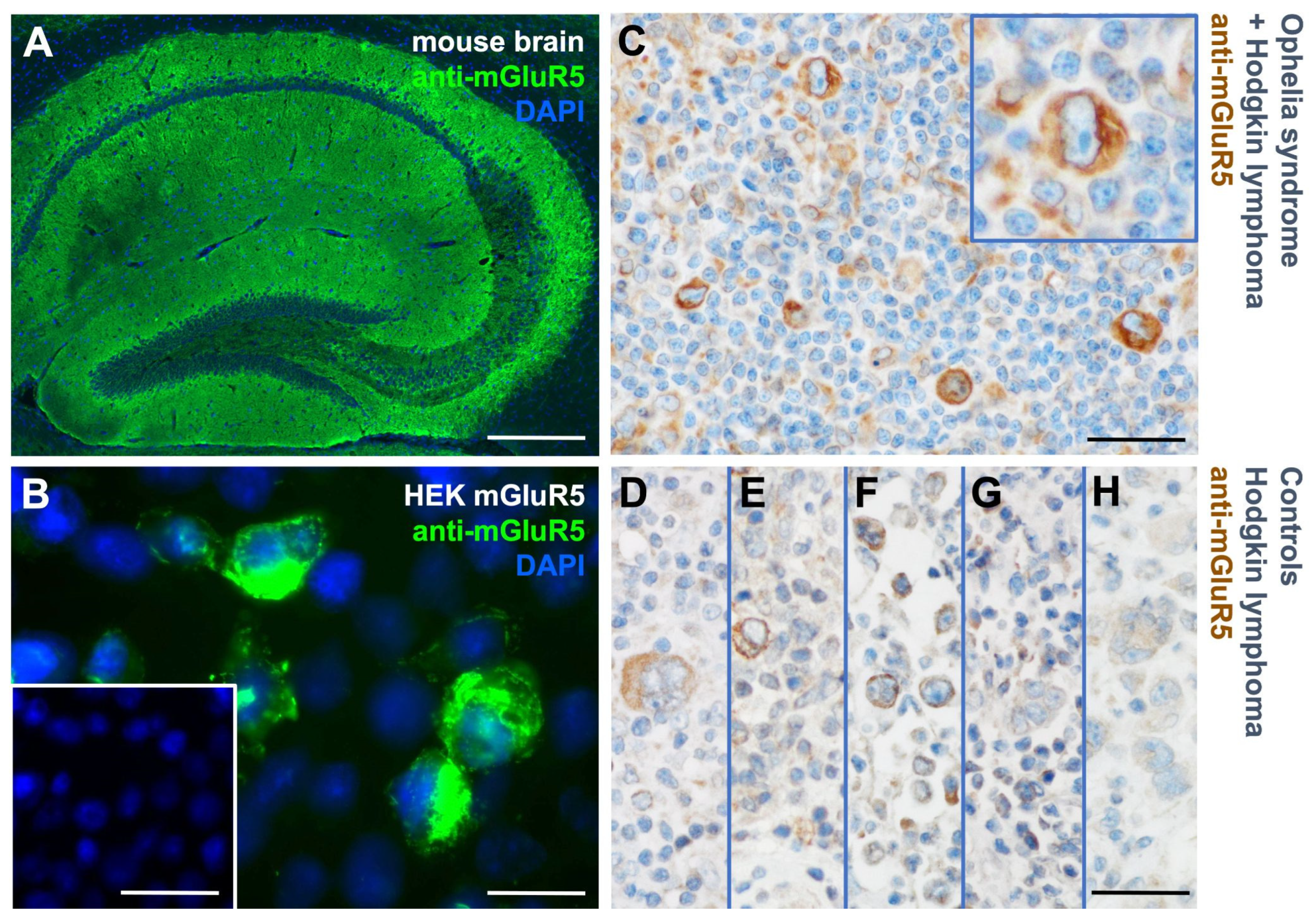
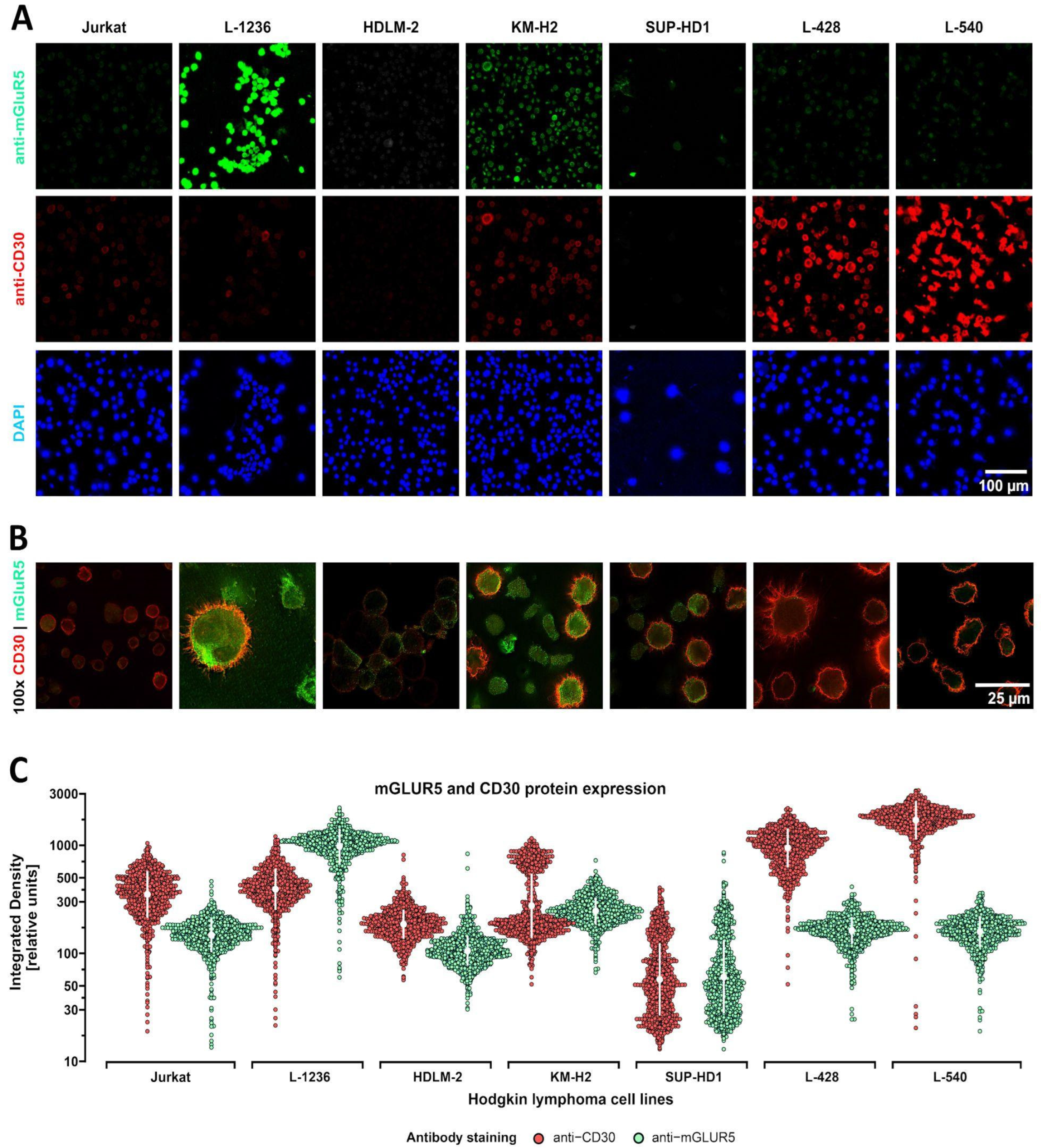
3.2. Heterogeneous mGluR5 expression patterns
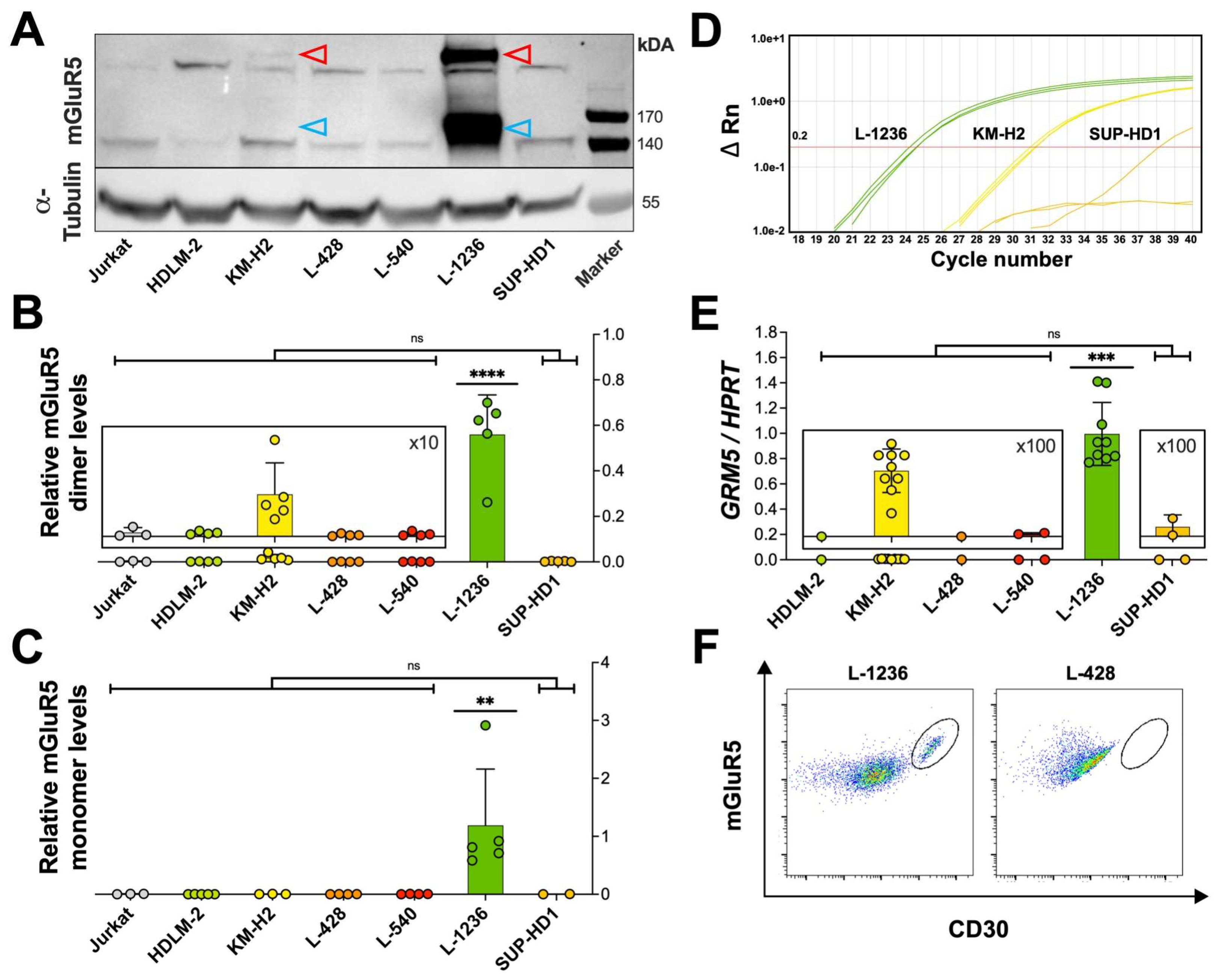
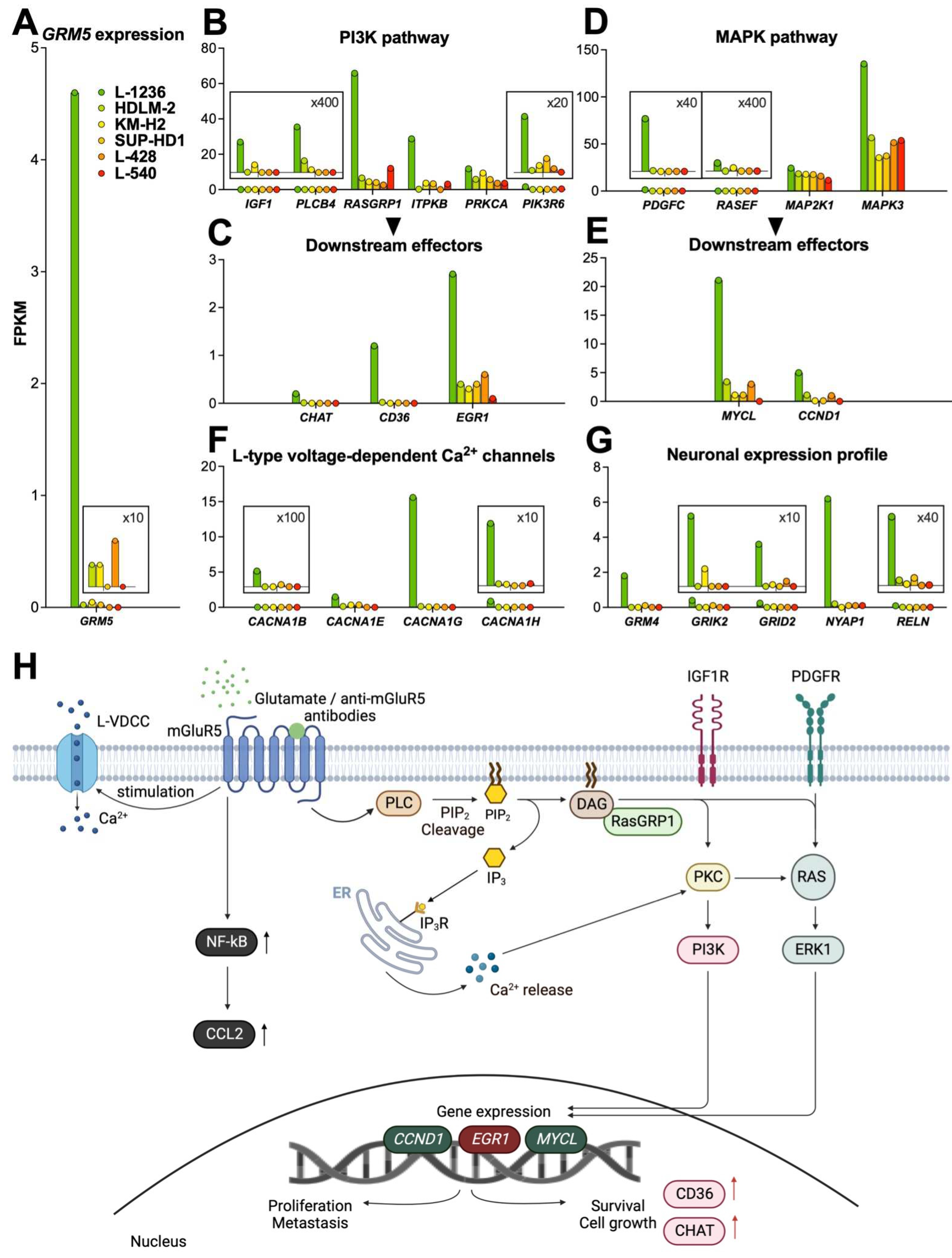
3.3.1. PI3K pathway
3.3.2. MAPK pathway
3.3.3. Calcium signaling
3.3.4. NF-kB pathway
- Neuronal expression profile
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weniger, M.A.; Küppers, R. Molecular Biology of Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 968–981. [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; Döring, C.; Brune, V.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; Klapper, W.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Falini, B.; Küppers, R.; Hansmann, M.-L. Analyzing Primary Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells to Capture the Molecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2012, 120, 4609–4620. [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Cozen, W.; Steidl, C.; Carbone, A.; Hoppe, R.T.; Flechtner, H.-H.; Bartlett, N.L. Hodgkin Lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2020, 6, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Grimm, S.; Chamberlain, M. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: A Review of Neurologic Complications. Adv. Hematol. 2010, 2011, e624578. [CrossRef]
- Gopas, J.; Stern, E.; Zurgil, U.; Ozer, J.; Ben-Ari, A.; Shubinsky, G.; Braiman, A.; Sinay, R.; Ezratty, J.; Dronov, V.; et al. Reed-Sternberg Cells in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Present Features of Cellular Senescence. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2457. [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.B. Autoimmunity and Lymphoma: A Brief Review. J. Rheum. Dis. Treat. 2018, 4. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Brewster, D.H.; Black, R.J.; Macfarlane, G.J. Risk of Malignancy among Patients with Rheumatic Conditions. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 497–502. [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Ariño, H.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes in Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Blood 2014, 123, 3230–3238. [CrossRef]
- Maslovsky, I.; Volchek, L.; Blumental, R.; Ducach, A.; Lugassy, G. Persistent Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndrome after Successful Therapy of Hodgkin’s Disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2001, 66, 63–65. [CrossRef]
- Juneja, M.; Kaur, S.; Mishra, D.; Jain, S. Ophelia Syndrome: Hodgkin Lymphoma with Limbic Encephalitis. INDIAN Pediatr. 2015, 52, 2.
- Rosenfeld, M.R.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Clin. 2018, 36, 675–685. [CrossRef]
- Briani, C.; Vitaliani, R.; Grisold, W.; Honnorat, J.; Graus, F.; Antoine, J.C.; Bertolini, G.; Giometto, B.; Euronetwork, F. the P. Spectrum of Paraneoplastic Disease Associated with Lymphoma. Neurology 2011, 76, 705–710. [CrossRef]
- Dropcho, E.J. Neurologic Paraneoplastic Syndromes. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 6, 26–31. [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Geis, C.; Graus, F. Autoantibodies to Synaptic Receptors and Neuronal Cell Surface Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 839–887. [CrossRef]
- Goldin, L.R.; Landgren, O. Autoimmunity and Lymphomagenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1497–1502. [CrossRef]
- Váróczy, L.; Gergely, L.; Zeher, M.; Szegedi, G.; Illés, Á. Malignant Lymphoma-Associated Autoimmune Diseases – a Descriptive Epidemiological Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2002, 22, 233–237. [CrossRef]
- Ammannagari, N.; Chikoti, S.; Bravin, E. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Presenting as a Complex Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Reports 2013, 7, 96. [CrossRef]
- Spatola, M.; Sabater, L.; Planagumà, J.; Martínez-Hernandez, E.; Armangué, T.; Prüss, H.; Iizuka, T.; Oblitas, R.L.C.; Antoine, J.-C.; Li, R.; et al. Encephalitis with MGluR5 Antibodies: Symptoms and Antibody Effects. Neurology 2018, 90, e1964–e1972. [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Boulos, M.; Weaver, S.; Antoine, J.-C.; Liebers, E.; Kornblum, C.; Bien, C.G.; Honnorat, J.; et al. Antibodies to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Ophelia Syndrome. Neurology 2011, 77, 1698–1701. [CrossRef]
- Carr, I. THE OPHELIA SYNDROME: MEMORY LOSS IN HODGKIN’S DISEASE. The Lancet 1982, 319, 844–845. [CrossRef]
- Betcherman, L.; University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Punnett, A.; University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Division of Hematology/Oncology, Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Paraneoplastic Syndromes in Children with Hodgkin Lymphoma. Oncol. Hematol. Rev. US 2017, 13, 41. [CrossRef]
- Guevara, C.; Farias, G.; Silva-Rosas, C.; Alarcon, P.; Abudinen, G.; Espinoza, J.; Caro, A.; Angus-Leppan, H.; de Grazia, J. Encephalitis Associated to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (MGluR5) Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9.
- Lo, A.C.; Dieckmann, K.; Pelz, T.; Gallop-Evans, E.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; Vordermark, D.; Kelly, K.M.; Schwartz, C.L.; Constine, L.S.; Roberts, K.; et al. Pediatric Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28562. [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H.G.; Gignac, S.M.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Leber, B.F.; Norton, J.; Lok, M.S.; Minowada, J. Characterization of Hodgkin’s Disease Derived Cell Line HDLM-2. In Proceedings of the New Aspects in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hodgkin’s Disease; Diehl, V., Pfreundschuh, M., Loeffler, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1989; pp. 75–82.
- Naumovski, L.; Utz, P.; Bergstrom, S.; Morgan, R.; Molina, A.; Toole, J.; Glader, B.; McFall, P.; Weiss, L.; Warnke, R. SUP-HD1: A New Hodgkin’s Disease-Derived Cell Line with Lymphoid Features Produces Interferon-Gamma [See Comments]. Blood 1989, 74, 2733–2742. [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H.G.; Gaedicke, G.; Lok, M.S.; Diehl, V.; Minowada, J. Hodgkin’s Disease Derived Cell Lines HDLM-2 and L-428: Comparison of Morphology, Immunological and Isoenzyme Profiles. Leuk. Res. 1986, 10, 487–500. [CrossRef]
- Schaadt, M.; Fonatsch, C.; Kirchner, H.; Diehl, V. Establishment of a Malignant, Epstein-Barr-Virus (EBV)-Negative Cell-Line from the Pleura Effusion of a Patient with Hodgkin’s Disease. Blut 1979, 38, 185–190. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Kapp, U.; Bohlen, H.; Kornacker, M.; Schoch, C.; Stahl, B.; Mucke, S.; von Kalle, C.; Fonatsch, C.; Schaefer, H.; et al. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of a Patient with Advanced Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Give Rise to Permanently Growing Hodgkin-Reed Sternberg Cells. Blood 1996, 87, 3418–3428. [CrossRef]
- Diehl, V.; Kirchner, H.H.; Schaadt, M.; Fonatsch, Chr.; Stein, H.; Gerdes, J.; Bote, Chr. Hodgkin’s Disease: Establishment and Characterization of Four in Vitro Cell Lines. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1981, 101, 111–124. [CrossRef]
- Nikolaus, M.; Meisel, C.; Kreye, J.; Prüss, H.; Reindl, M.; Kaindl, A.M.; Schuelke, M.; Knierim, E. Presence of Anti-Neuronal Antibodies in Children with Neurological Disorders beyond Encephalitis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 28, 159–166. [CrossRef]
- Kreye, J.; Wenke, N.K.; Chayka, M.; Leubner, J.; Murugan, R.; Maier, N.; Jurek, B.; Ly, L.-T.; Brandl, D.; Rost, B.R.; et al. Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Monoclonal N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Autoantibodies Are Sufficient for Encephalitis Pathogenesis. Brain 2016, 139, 2641–2652. [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45–e45. [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie Enables Improved Reconstruction of a Transcriptome from RNA-Seq Reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-Level Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [CrossRef]
- Reiner, A.; Yekutieli, D.; Benjamini, Y. Identifying Differentially Expressed Genes Using False Discovery Rate Controlling Procedures. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 368–375. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Kir, J.; Liu, D.; Bryant, D.; Guo, Y.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded Annotation Database and Novel Algorithms to Better Extract Biology from Large Gene Lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W169–W175. [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, C.; Pileri, S. PATHOBIOLOGY OF HODGKIN LYMPHOMA. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, e2014040–e2014040. [CrossRef]
- Seitz, V.; Thomas, P.E.; Zimmermann, K.; Paul, U.; Ehlers, A.; Joosten, M.; Dimitrova, L.; Lenze, D.; Sommerfeld, A.; Oker, E.; et al. Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Shows Epigenetic Features of Abortive Plasma Cell Differentiation. Haematologica 2011, 96, 863–870. [CrossRef]
- Kirschstein, T.; Bauer, M.; Müller, L.; Rüschenschmidt, C.; Reitze, M.; Becker, A.J.; Schoch, S.; Beck, H. Loss of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Depression via Downregulation of MGluR5 after Status Epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 7696–7704. [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Yang, W.-L.; O’Malley, K.L. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Is a Disulfide-Linked Dimer*. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28612–28616. [CrossRef]
- Steidl, C.; Lee, T.; Shah, S.P.; Farinha, P.; Han, G.; Nayar, T.; Delaney, A.; Jones, S.J.; Iqbal, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Survival in Classic Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 875–885. [CrossRef]
- Eddy, K.; Chen, S. Glutamatergic Signaling a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Melanoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3874. [CrossRef]
- Prickett, T.D.; Samuels, Y. Molecular Pathways: Dysregulated Glutamatergic Signaling Pathways in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4240–4246. [CrossRef]
- Ebinu, J.O.; Bottorff, D.A.; Chan, E.Y.; Stang, S.L.; Dunn, R.J.; Stone, J.C. RasGRP, a Ras Guanyl Nucleotide- Releasing Protein with Calcium- and Diacylglycerol-Binding Motifs. Science 1998, 280, 1082–1086. [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP Kinase Signalling Pathways in Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.K.; Kassai, H.; Watabe, A.M.; Aiba, A.; Manabe, T. Functional Coupling of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, InsP3 Receptor and L-Type Ca2+ Channel in Mouse CA1 Pyramidal Cells. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 3019–3034. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, X.; Wang, Y.; Förster, E.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S. Nyap1 Regulates Multipolar–Bipolar Transition and Morphology of Migrating Neurons by Fyn Phosphorylation during Corticogenesis. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 929–941. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhao, L.F.; Korwek, K.M.; Weeber, E.J. Differential Reelin-Induced Enhancement of NMDA and AMPA Receptor Activity in the Adult Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12943–12955. [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Klann, E. Activation of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Akt-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway Is Required for Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Depression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6352–6361. [CrossRef]
- Reiner, A.; Levitz, J. Glutamatergic Signaling in the Central Nervous System: Ionotropic and Metabotropic Receptors in Concert. Neuron 2018, 98, 1080–1098. [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Wall, B.A.; Wangari-Talbot, J.; Chen, S. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Cancer. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 193–202. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Geng, M.; Huang, M. Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK Pathway, in Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 552–562. [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-F.; Yu, Q.-Q.; Young, K.H. Critically Dysregulated Signaling Pathways and Clinical Utility of the Pathway Biomarkers in Lymphoid Malignancies. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 29–44. [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.L.F.; Chen, S. Glutamatergic Signaling in Cellular Transformation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 331–342. [CrossRef]
- Nakatsumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakayama, K.I. Noncanonical Pathway for Regulation of CCL2 Expression by an MTORC1-FOXK1 Axis Promotes Recruitment of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2471–2486. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y. CD36 Tango in Cancer: Signaling Pathways and Functions. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4893–4908. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, G. The Role of the Transcription Factor EGR1 in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11.
- González-Ruiz, L.; González-Moles, M.Á.; González-Ruiz, I.; Ruiz-Ávila, I.; Ayén, Á.; Ramos-García, P. An Update on the Implications of Cyclin D1 in Melanomas. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020, 33, 788–805. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Medeiros, L.J.; Xu, X.; Young, K.H. MYC-Driven Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas: Biology, Entity, Differential Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38591–38616.
- Klapproth, K.; Wirth, T. Advances in the Understanding of MYC-Induced Lymphomagenesis. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 484–497. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Samimi, R.; Xie, G.; Shant, J.; Drachenberg, C.; Wade, M.; Davis, R.J.; Nomikos, G.; Raufman, J.-P. Acetylcholine Release by Human Colon Cancer Cells Mediates Autocrine Stimulation of Cell Proliferation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G591–G597. [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Sekhon, H.S.; Jia, Y.; Keller, J.A.; Blusztajn, J.K.; Mark, G.P.; Spindel, E.R. Acetylcholine Is Synthesized by and Acts as an Autocrine Growth Factor for Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 214–221.
- Hao, Q.; Vadgama, J.V.; Wang, P. CCL2/CCR2 Signaling in Cancer Pathogenesis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 82. [CrossRef]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the Cancer Microenvironment and Their Relevance in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Arcella, A.; Iacovelli, L.; Battaglia, G.; Giangaspero, F.; Melchiorri, D. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: New Targets for the Control of Tumor Growth? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 206–213. [CrossRef]
- Brocke, K.S.; Staufner, C.; Luksch, H.; Geiger, K.D.; Stepulak, A.; Marzahn, J.; Schackert, G.; Temme, A.; Ikonomidou, C. Glutamate Receptors in Pediatric Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 455–468. [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.; Chen, S. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Cancerous Growth. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2012, 1, 211–220. [CrossRef]
- Rzeski, W.; Turski, L.; Ikonomidou, C. Glutamate Antagonists Limit Tumor Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 6372–6377. [CrossRef]
- Marín, Y.E.; Namkoong, J.; Shin, S.-S.; Raines, J.; Degenhardt, K.; White, E.; Chen, S. Grm5 Expression Is Not Required for the Oncogenic Role of Grm1 in Melanocytes. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 70–79. [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; Chang, K.; Pickel, J.M.; Badger, J.D.; Roche, K.W. Expression of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (MGluR5) Induces Melanoma in Transgenic Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 15219–15224. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-A.; Han, I.-H.; Yoo, B.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Cha, I.-H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.-W. Clinical Significance of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 81–87. [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, F.; Corti, C.; Valerio, E.; Mion, S.; Xuereb, J. Activated Astrocytes in Areas of Kainate-Induced Neuronal Injury Upregulate the Expression of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 2/3 and 5. Exp. Brain Res. 2001, 137, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, R.; Gallart, T.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R. Role of Glutamate on T-Cell Mediated Immunity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 185, 9–19. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. Tumorigenesis as a Process of Gradual Loss of Original Cell Identity and Gain of Properties of Neural Precursor/Progenitor Cells. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 61. [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Alfonso, J.; Monyer, H.; Wick, W.; Winkler, F. Neuronal Signatures in Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 3281–3291. [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H.G.; Pommerenke, C.; Eberth, S.; Nagel, S. Hodgkin Lymphoma Cell Lines: To Separate the Wheat from the Chaff. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 511–523. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, R.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; Joubert, B.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Pajarón-Boix, E.; Fernández, V.; Salais, L.; Pozo, M. del; Armangué, T.; Sabater, L.; et al. Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Ataxia and Antibodies to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2. Neurol. - Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Deodhare, S.; O’Connor, P.; Ghazarian, D.; Bilbao, J.M. Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis in Hodgkin’s Disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 23, 138–140. [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, T.; Gärtner, J.; Körholz, D.; Janßen, G.; Schneider, D.; Engelbrecht, V.; Göbel, U.; Lenard, H.-G. Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis in Two Teenage Girls. Neuropediatrics 1998, 29, 159–162. [CrossRef]
- Ypma, P.F.; Wijermans, P.W.; Koppen, H.; Sillevis Smitt, P. a. E. Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration Preceding the Diagnosis of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Neth. J. Med. 2006, 64, 243–247.
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for Functional Genomics Data Sets—Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




