Submitted:
26 December 2022
Posted:
04 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
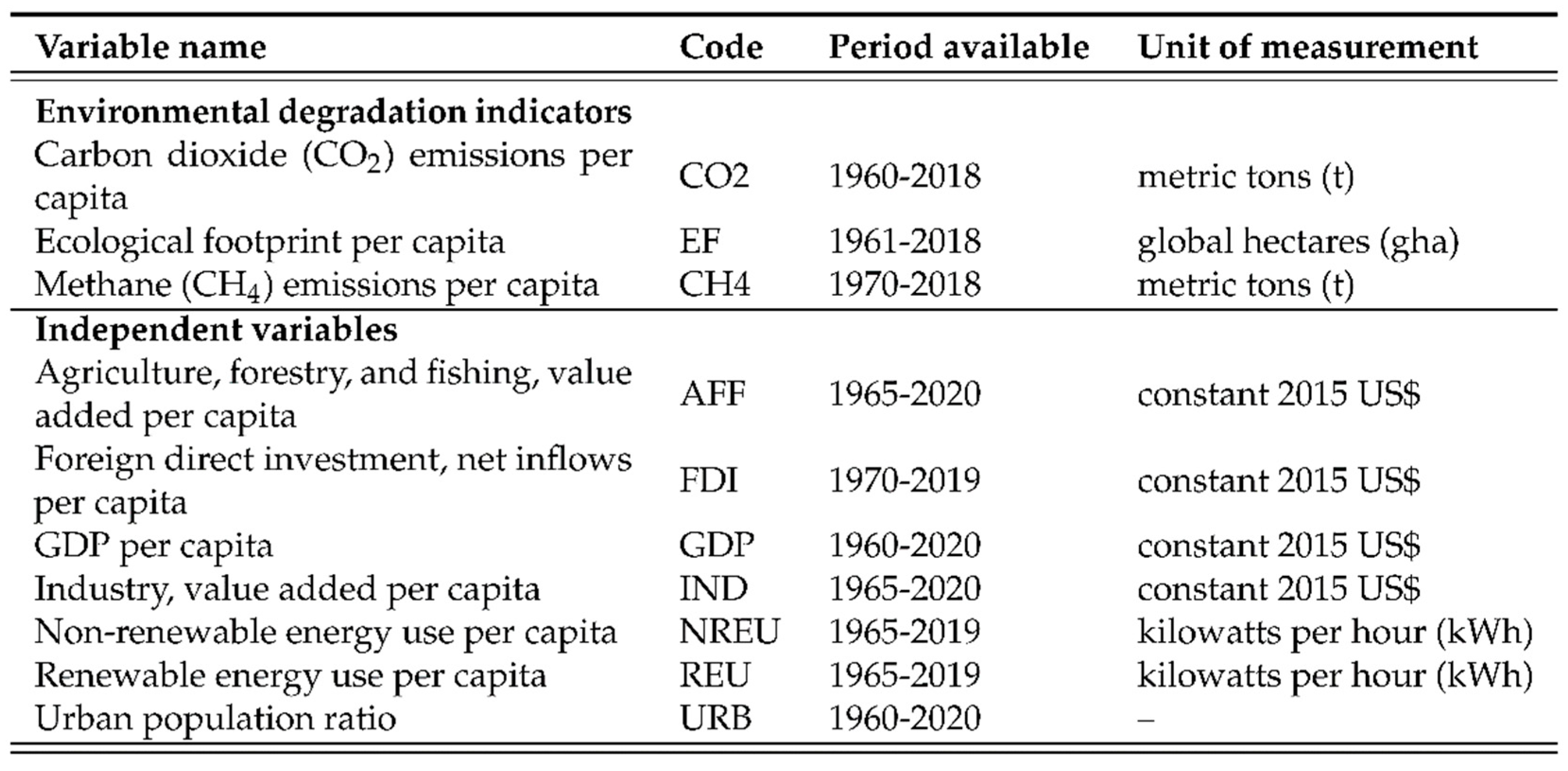
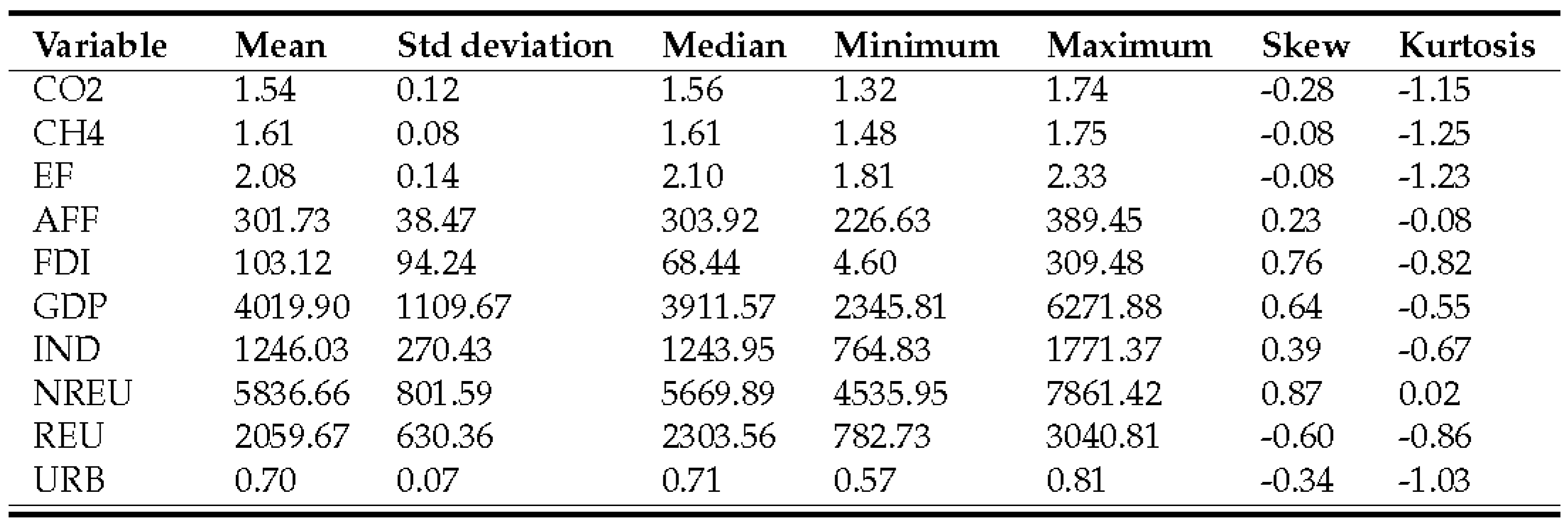
3.1. Environmental degradation indicators
3.2. Economic development indicator
3.3. Additional macroeconomic variables
3.4. ARDL estimation, validation and model selection
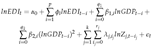
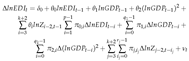
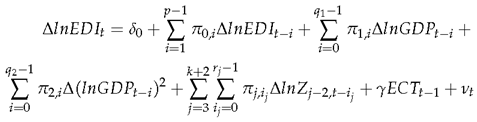
3.5. Dynamic simulations
3.6. EKC validation
4. Results and discussion
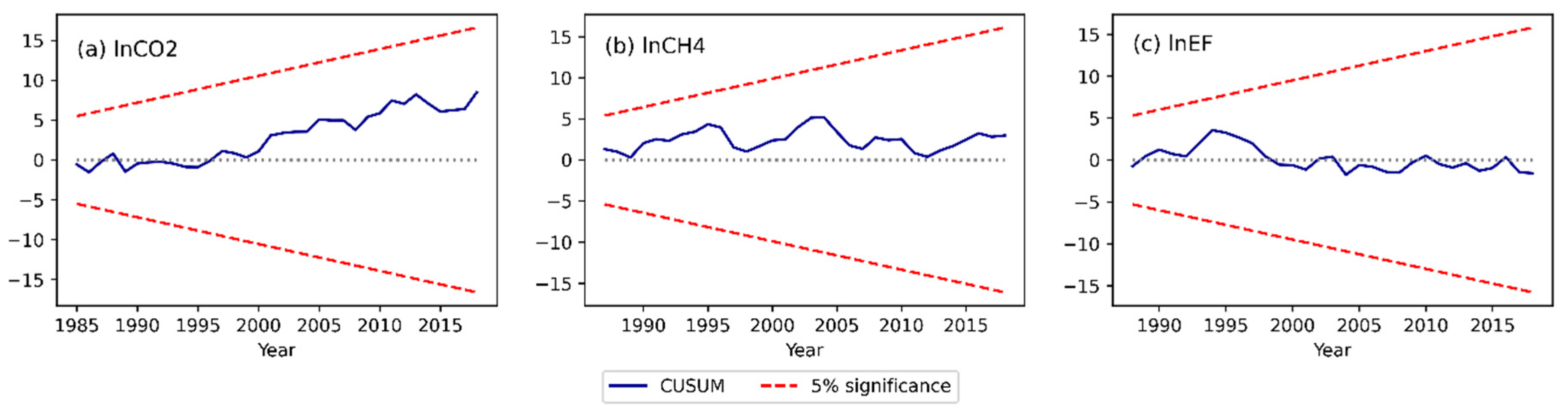
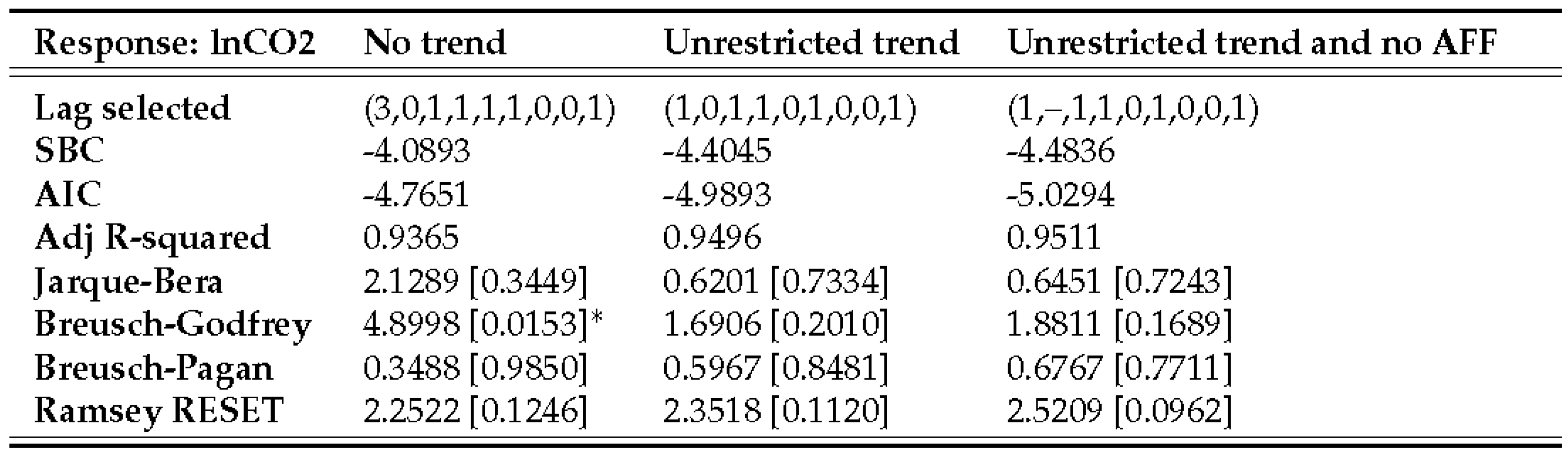
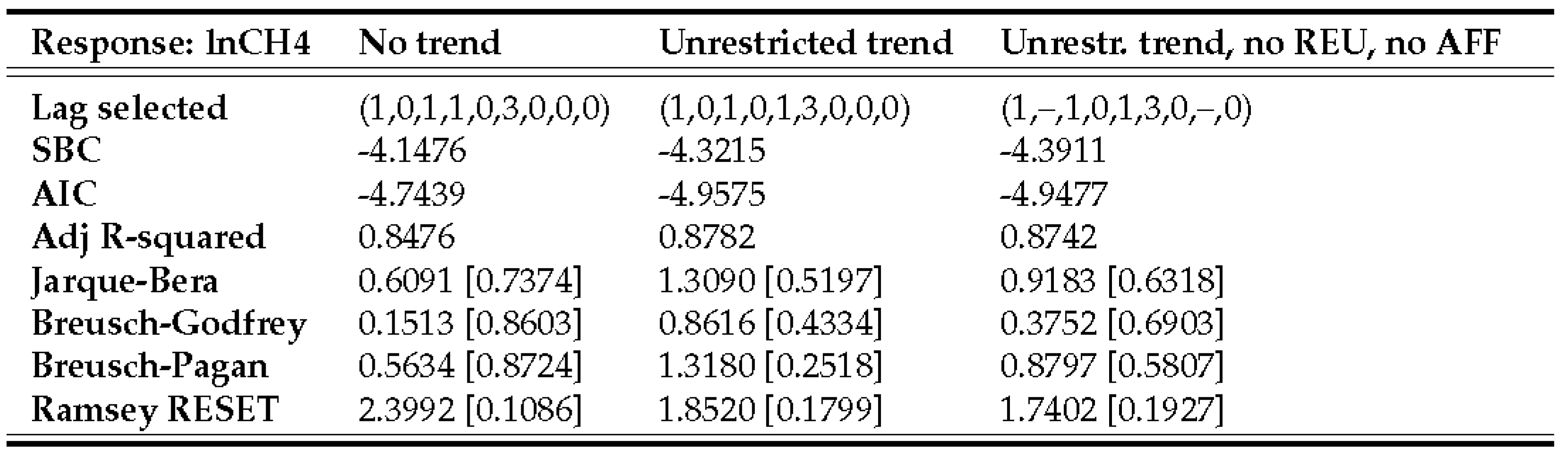
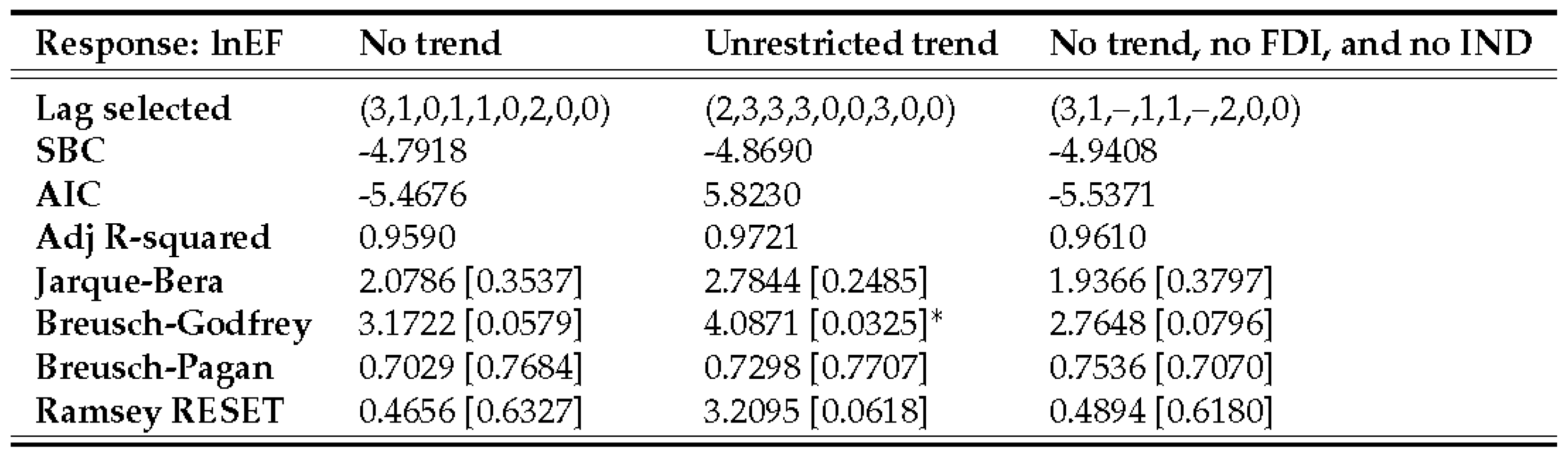
4.1. ARDL estimation, validation, and final model selection
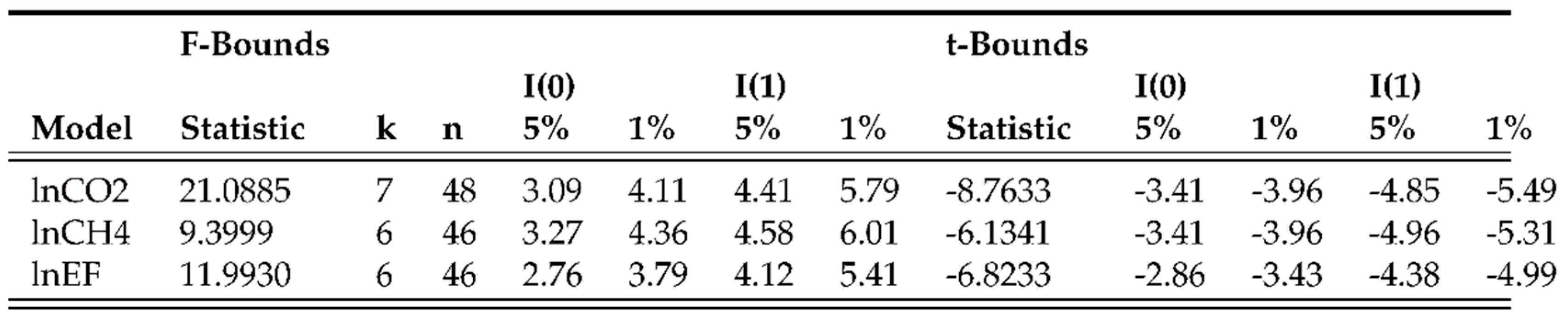
4.2. ARDL bounds tests
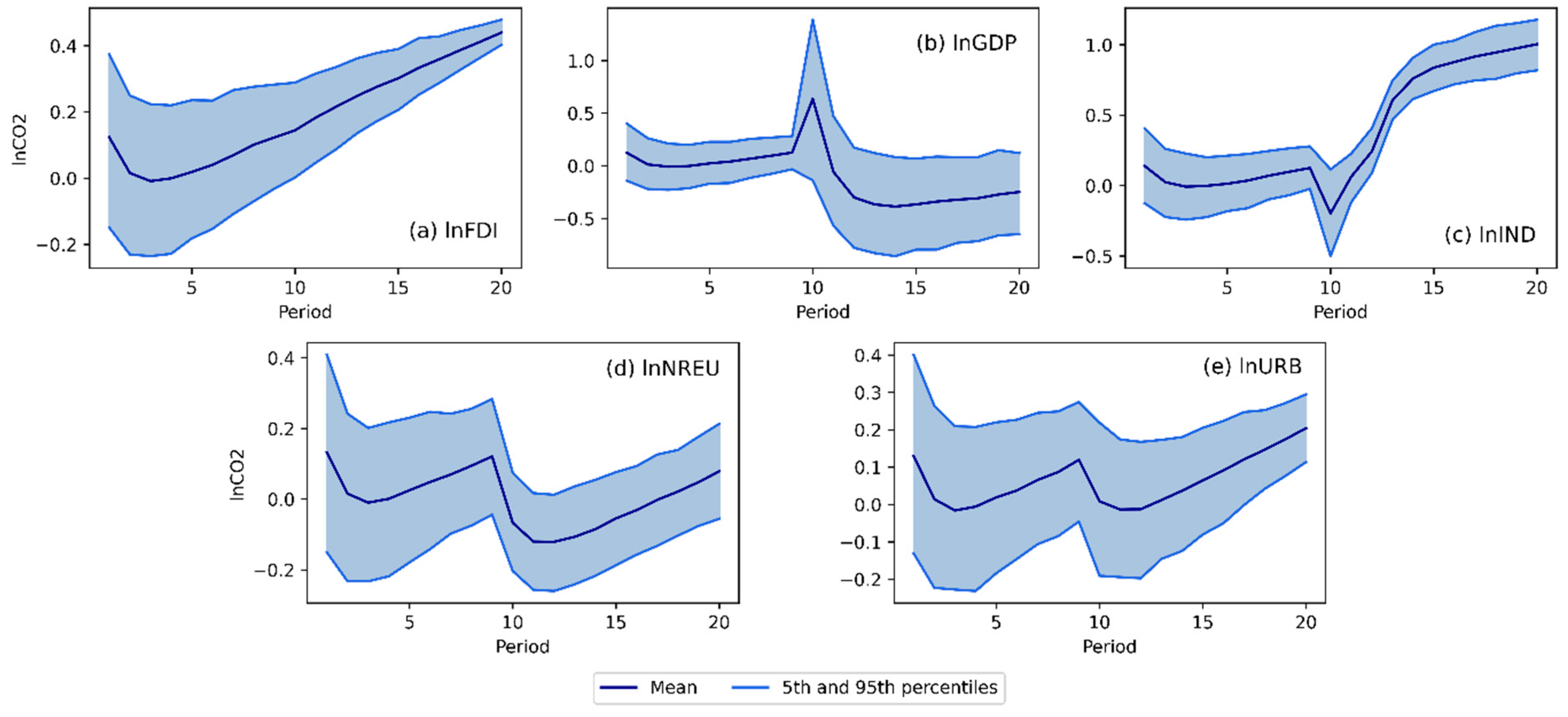
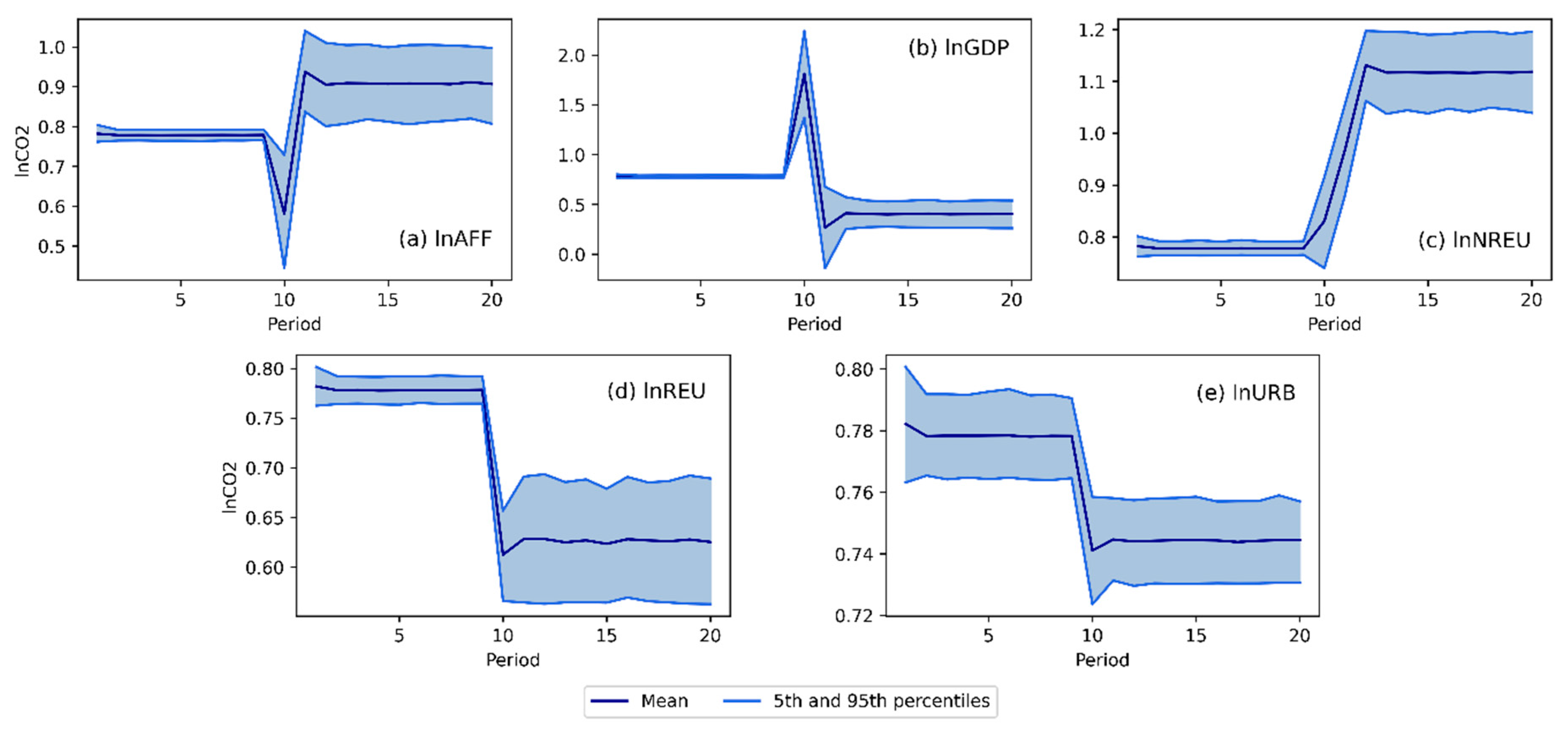
4.3. Models interpretation, dynamic simulations and EKC validation
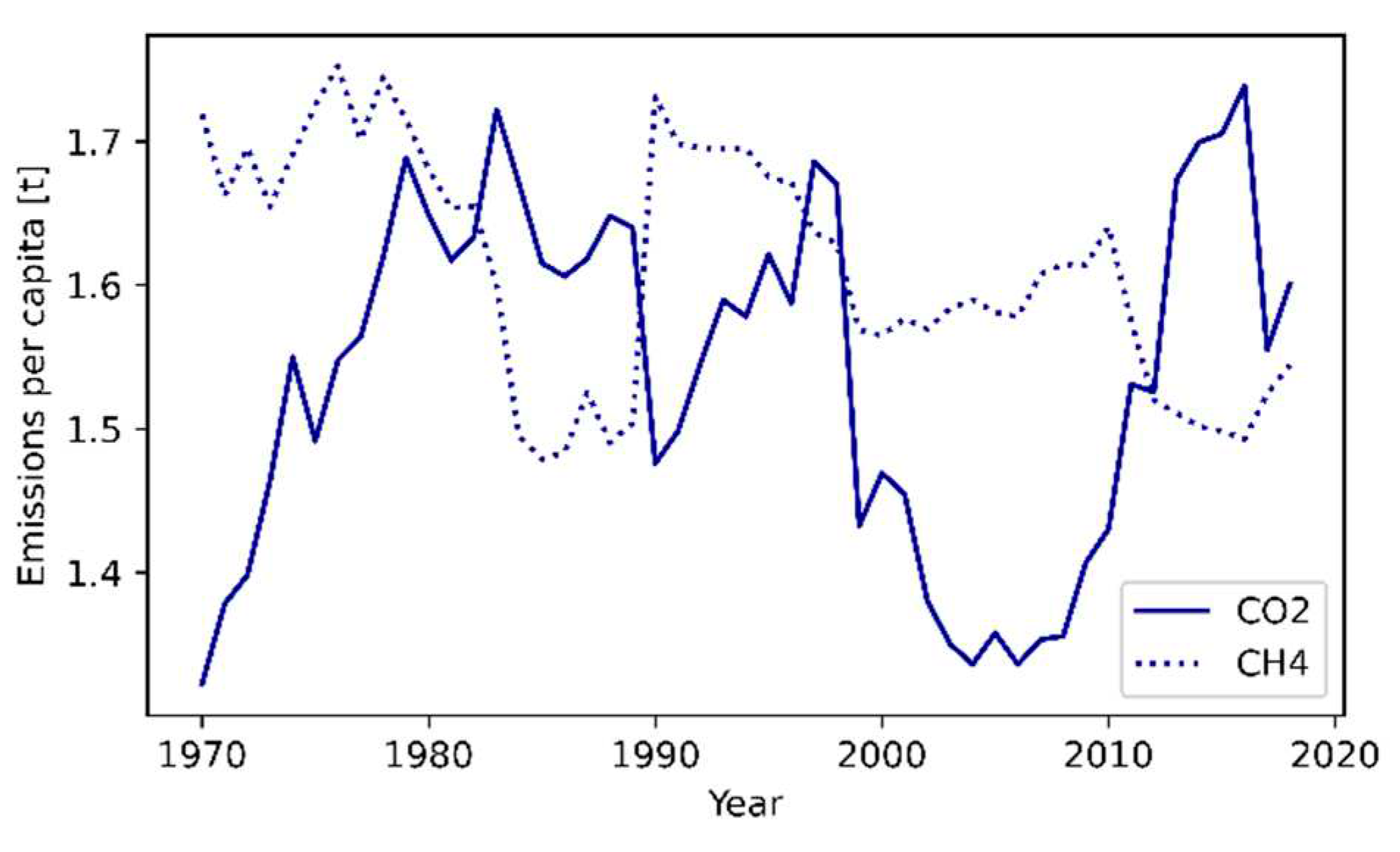
4.3.1. Carbon dioxide emissions
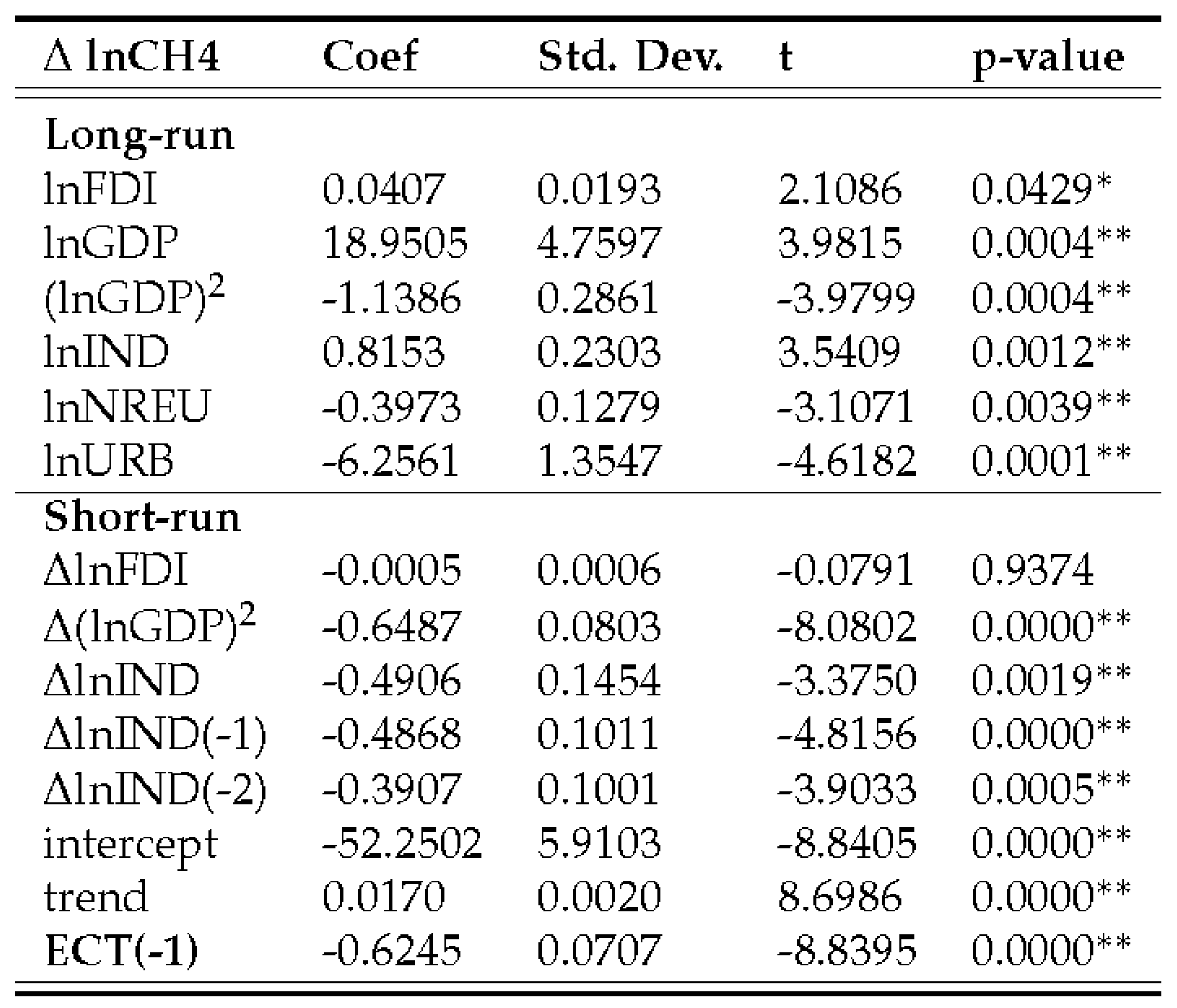
4.3.2. Methane emissions
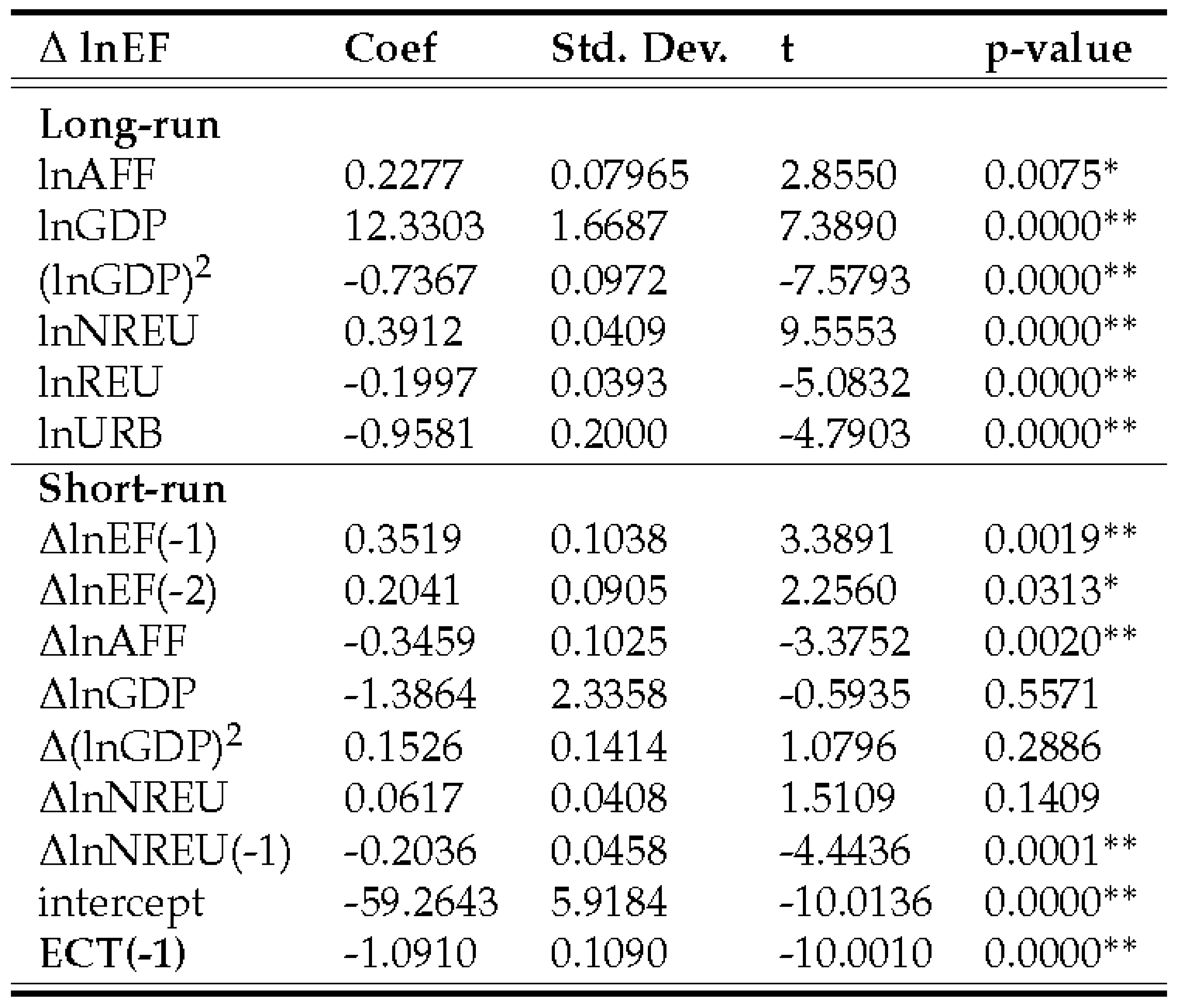
4.3.3. Ecological footprint
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations

References
- UNFCC. Glasgow Climate Pact | COP26, 2021.
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Silva-Zambrano, C.A.; Davalos-Penafiel, J.L.; Zambrano-Monserrate, A.; Ruano, M.A. Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Peru: The role of renewable electricity, petroleum and dry natural gas. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 82, 4170–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Development Indicators. https://databank.worldbank.org/reports.aspx?source=world-development-indicators, 2021. Accessed: 2021-11-30.
- United States National Intelligence Council. Climate Change and International Responses Increasing Challenges to US National Security Through 2040, 2021.
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. Working Paper 3914, National Bureau of Economic Research, 1991. [CrossRef]
- Shafik, N.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Economic growth and environmental quality : time series and cross-country evidence. Policy Research Working Paper Series 904, The World Bank, 1992.
- Panayotou, T. Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. Ilo working papers, International Labour Organization, 1993.
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznets, S. Economic Growth and Income Inequality. The American Economic Review 1955, 45, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, D.I. The Environmental Kuznets Curve. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Beckerman, W. Economic growth and the environment: Whose growth? whose environment? World Development 1992, 20, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alstine, J.; Neumayer, E. The Environmental Kuznets Curve. In Handbook on Trade and the Environment; Gallagher, K.P., Ed.; Chapters, Edward Elgar Publishing, 2008; chapter 3.
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Strezov, V. A review on Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis using bibliometric and meta-analysis. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 649, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfeddine, L.; Mrabet, Z. The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: A panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 76, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Ozturk, I. Investigating the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis in Kenya: A multivariate analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 117, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soytas, U.; Sari, R.; Ewing, B.T. Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecological Economics 2007, 62, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, F.M.; Kanwal, A. Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Pakistan: Dynamic causality analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 72, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekun, F.V.; Emir, F.; Sarkodie, S.A. Another look at the relationship between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in South Africa. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 655, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, L.; Dong, S.; Xue, L.; Liang, Q.; Yang, W. Energy consumption-economic growth relationship and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivyiro, P.; Arminen, H. Carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and foreign direct investment: Causality analysis for Sub-Saharan Africa. Energy 2014, 74, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Strezov, V. Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 646, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaunky, V.C. The CO2 emissions-income nexus: Evidence from rich countries. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekun, F.V.; Alola, A.A.; Sarkodie, S.A. Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 657, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodha, M.; Zaghdoud, O. Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: An empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; York, R. Agricultural Exports and the Environment: A Cross-National Study of Fertilizer and Pesticide Consumption*. Rural Sociology 2008, 73, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.B. Deforestation and the Environmental Kuznets Curve in Developing Countries: A Panel Smooth Transition Regression Approach. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue canadienne d’agroeconomie 2012, 60, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Chiu, Y.B.; Sun, C.H. The environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for water pollution: Do regions matter? Energy Policy 2010, 38, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.L.A.; Lewis, L. The disappearing Environmental Kuznets Curve: A study of water quality in the Lower Mekong Basin (LMB). Journal of Environmental Management 2013, 131, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz–Agudelo, C.; Sánchez, G.; Sáenz, J.; Higuera, L. Biodiversity and growth in Colombia, 1995–2015: an approach from the environmental kuznets hypothesis. Journal of Environmental Economics and Policy 2019, 8, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mulali, U.; Tang, C.F.; Ozturk, I. Estimating the Environment Kuznets Curve hypothesis: Evidence from Latin America and the Caribbean countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 50, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Romero, M.; De Jesús, J. Economic growth and energy consumption: The Energy-Environmental Kuznets Curve for Latin America and the Caribbean. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 60, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, E.; García, J. Calidad ambiental y su relación con el crecimiento económico en el Área Metropolitana del Valle de Aburrá. Ecos De Economía: A Latin American Journal of Applied Economics 2003.
- Correa, F.; Vasco, A.; Pérez, C. La curva medioambiental de Kuznets: Evidencia empírica para Colombia Grupo de Economía Ambiental (GEA). Semestre Económico 2005.
- Blanco, D.; Henriquez, S.; Fajardo, E.; Romero, H. Consumption of Energy, Economic Growth, and Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Colombia. Revista Fuentes: El Reventón Energético 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, P.V.; Navarro, D.M. Crecimiento, Complejidad Económica y Emisiones de CO2: Un Análisis para Colombia. Revista CIFE: Lecturas de Economía Social 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverde-Rojas, H.; Guevara-Fletcher, D.A.; Camacho-Murillo, A. Economic growth, economic complexity, and carbon dioxide emissions: The case of Colombia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Analysis Indicators Tool (CAIT) Data Explorer. Historical emissions. https://www.climatewatchdata.org/data-explorer/historical-emissions, 2021. Accessed: 2021-11-30.
- Van Dingenen, R.; Crippa, M.; Anssens-Maenhout, G.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F. Global trends of methane emissions and their impacts on ozone concentrations. JRC Science for Policy Report 2018.
- Martínez-Rocamora, A.; Solís-Guzmán, J.; Marrero, M. Toward the Ecological Footprint of the use and maintenance phase of buildings: Utility consumption and cleaning tasks. Ecological Indicators 2016, 69, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mulali, U.; Weng-Wai, C.; Sheau-Ting, L.; Mohammed, A.H. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecological Indicators 2015, 48, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, L.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Y. Estimating the environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint at the global level: A spatial econometric approach. Ecological Indicators 2013, 34, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Footprint Network. Ecological Footprint per person. https://data.footprintnetwork.org. Accessed: 2021-11-30.
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M.; Rosado, P. CO2 and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Our World in Data 2020. https://ourworldindata.org/co2- and-other-greenhouse-gas-emissions.
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M.; Rosado, P. Energy. Our World in Data 2020. https://ourworldindata.org/energy.
- Poumanyvong, P.; Kaneko, S. Does urbanization lead to less energy use and lower CO2 emissions? A cross-country analysis. Ecological Economics 2010, 70, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, H.; Shin, Y. An Autoregressive Distributed-Lag Modelling Approach to Cointegration Analysis. Econometrics and Economic Theory in the 20th Century: The Ragnar Frisch Centennial Symposium. [CrossRef]
- Philips, A.Q. Have Your Cake and Eat It Too? Cointegration and Dynamic Inference from Autoregressive Distributed Lag Models. American Journal of Political Science 2018, 62, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, B. Analysis of integrated and cointegrated time series with R; Springer, 2006.
- Pesaran, M.; Pesaran, B. Working with Microfit 4.0: Interactive Econometric Analysis; Oxford University Press, 1997.
- Jordan, S.; Philips, A.Q. Dynamic Simulation and Testing for Single-Equation Cointegrating and Stationary Autoregressive Distributed Lag Models. The R Journal 2018, 10, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, P.K. The saving and investment nexus for China: evidence from cointegration tests. Applied Economics 2005, 37, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; Whitten, G. Dynamic Simulations of Autoregressive Relationships. Stata Journal 2011, 11, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, J.T.; Mehlum, H. With or Without U? The Appropriate Test for a U-Shaped Relationship. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 2010, 72, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieller, E.C. Some Problems in Interval Estimation. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) 1954, 16, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwert, G.W. Tests for Unit Roots: A Monte Carlo Investigation. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics 1989, 7, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Saunois, M.; Stavert, A.R.; Poulter, B.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Raymond, P.A.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Houweling, S.; Patra, P.K.e.a. The Global Methane Budget 2000–2017. Earth System Science Data 2020, 12, 1561–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global Methane Assessment: Benefits and Costs of Mitigating Methane Emissions; 2021.
- Narayan, P.K.; Smyth, R. What determines migration flows from low-income to high-income countries? An empirical investigation of Fiji-U.S. migration 1972-2001. Contemporary Economic Policy 2006, 24, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, S.; Alvarez, A.C.; Loboguerrero, A.M.; Arango, S.; Calvin, K.; Kober, T.; Daenzer, K.; Fisher-Vanden, K. Achieving CO2 reductions in Colombia: Effects of carbon taxes and abatement targets. Energy Economics 2016, 56, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugge, M.M.; Hansen, T.; Klitkou, A. What Is the Bioeconomy? A Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, A.; McAlpine, C.; Possingham, H. Historical Patterns and Drivers of Landscape Change in Colombia Since 1500: A Regionalized Spatial Approach. Annals of the Association of American Geographers 2008, 98, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteras, D.; Cabrera, E.; Rodríguez, N.; Retana, J. National and regional determinants of tropical deforestation in Colombia. Regional Environmental Change 2013, 13, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadid, M.A.; Dávalos, L.M.; Molina, J.; Armenteras, D. A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot. Forests 2015, 6, 3828–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liévano-Latorre, L.F.; Brum, F.T.; Loyola, R. How effective have been guerrilla occupation and protected areas in avoiding deforestation in Colombia? Biological Conservation 2021, 253, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, N.; Armenteras, D.; Kareiva, P.; Botero, R.; Ramírez-Delgado, J.; Forero-Medina, G.; Ochoa, J.; Pedraza, C.; Schneider, L.; Lora, C.; et al. Deforestation in Colombian protected areas increased during post-conflict periods 2020. [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





