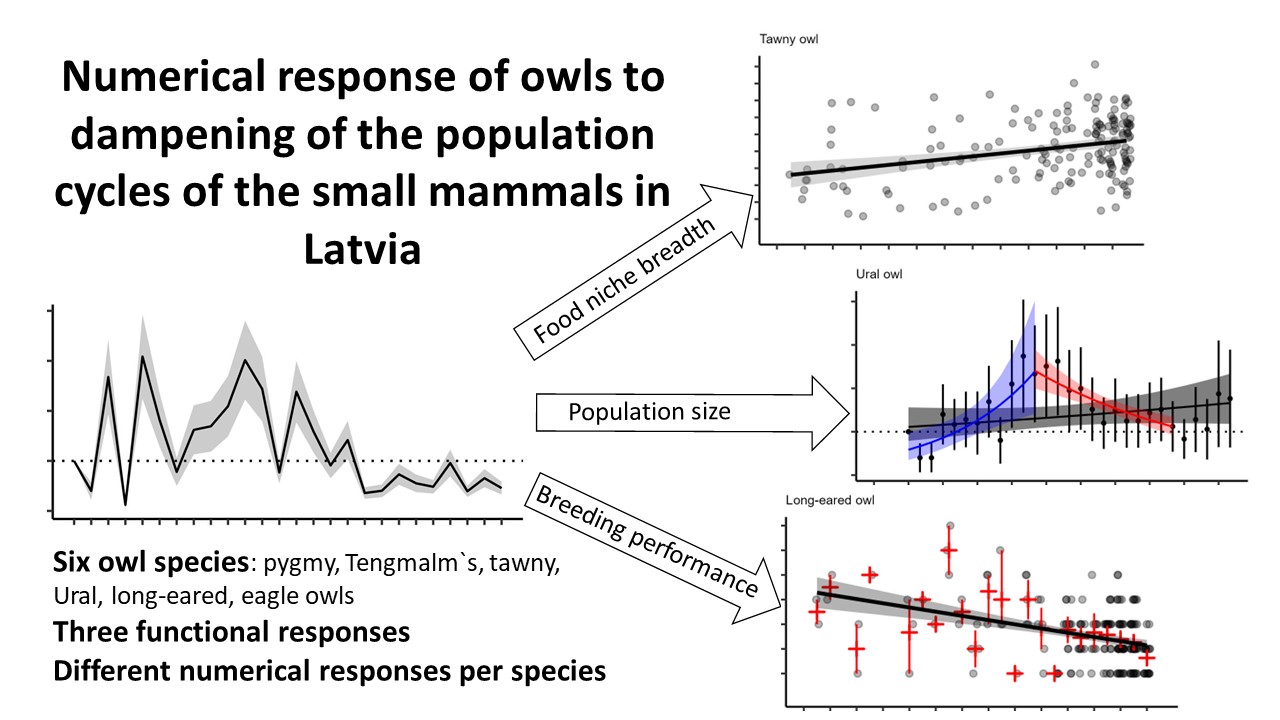
Strong numerical and functional response of owls to voles in cyclic environments is well known, but there is insufficient knowledge from boreonemoral region, in particular, with depleted populations of the small mammals. In this study we describe the dynamics of the small mammal population in Latvia from 1991 to 2016 and link them to owl population characteristics. We used food niche breadth, number of fledglings and population trends to describe the numerical response of six owl species to dampened small mammal population cycles. We found temporarily in-creasing food niche breadth in tawny and Ural owls. There were no other responses in tawny owl, whereas the breeding performance of three forest specialist species – pygmy, Tengmalm`s and Ural owls – were similar to vole crash years in Fennoscandia. Moreover, the populations of forest specialist owls are decreasing and the change in Ural owl can be attributed to the depletion of small mammal populations. We found evidence of carry-over effect in eagle owl arising from strong correlation of declining breeding performance with the small mammal abundance indices in previous autumn. We conclude that dampening of the small mammal population cycles is an important covariate to overwhelming impacts of habitat destruction with stronger response in more specialized (to prey or habitat) species.