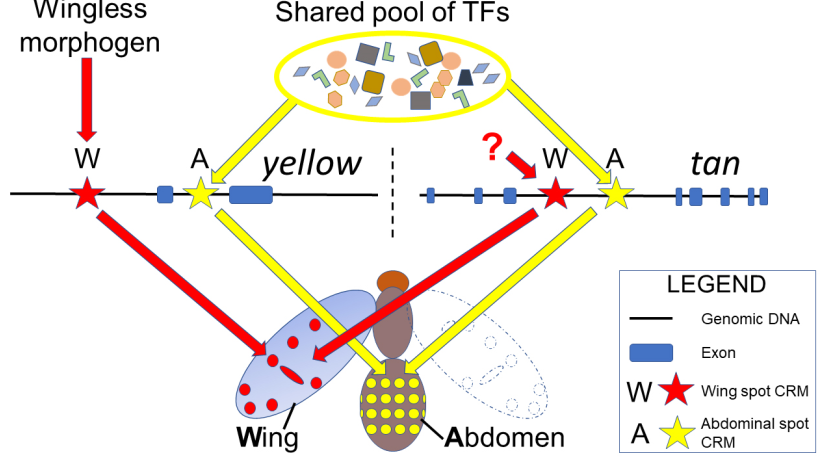
How complex morphological patterns form is an intriguing question in developmental biology. However, the mechanisms that generate complex patterns remain largely unknown. Here we sought to identify the genetic mechanisms that regulate the tan (t) gene in a multi-spotted pigmentation pattern on the abdomen and wings of Drosophila guttifera. Previously, we showed that yellow (y) gene expression completely prefigures the abdominal [1] and wing [2] pigment patterns of this species. In the current study, we demonstrate that the t gene is co-expressed with the y gene in nearly identical patterns, both transcripts foreshadowing the adult abdominal and wing melanin spot patterns. We identified cis-regulatory modules (CRMs) of t, one of which drives reporter expression in six longitudinal rows of spots on the developing pupal abdomen, while the second CRM activates the reporter gene in a spotted wing pattern. Comparing the abdominal spot CRMs of y and t, we found a similar composition of putative transcription factor binding sites that are thought to regulate the complex expression patterns of both terminal pigmentation genes y and t. In contrast, the y and t wing spots appear to be regulated by distinct upstream factors. Our results suggest that the D. guttifera abdominal and wing melanin spot patterns have been established through the co-regulation of y and t, shedding light on how complex morphological traits may be regulated through the parallel coordination of downstream target genes.