Submitted:
18 July 2023
Posted:
19 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
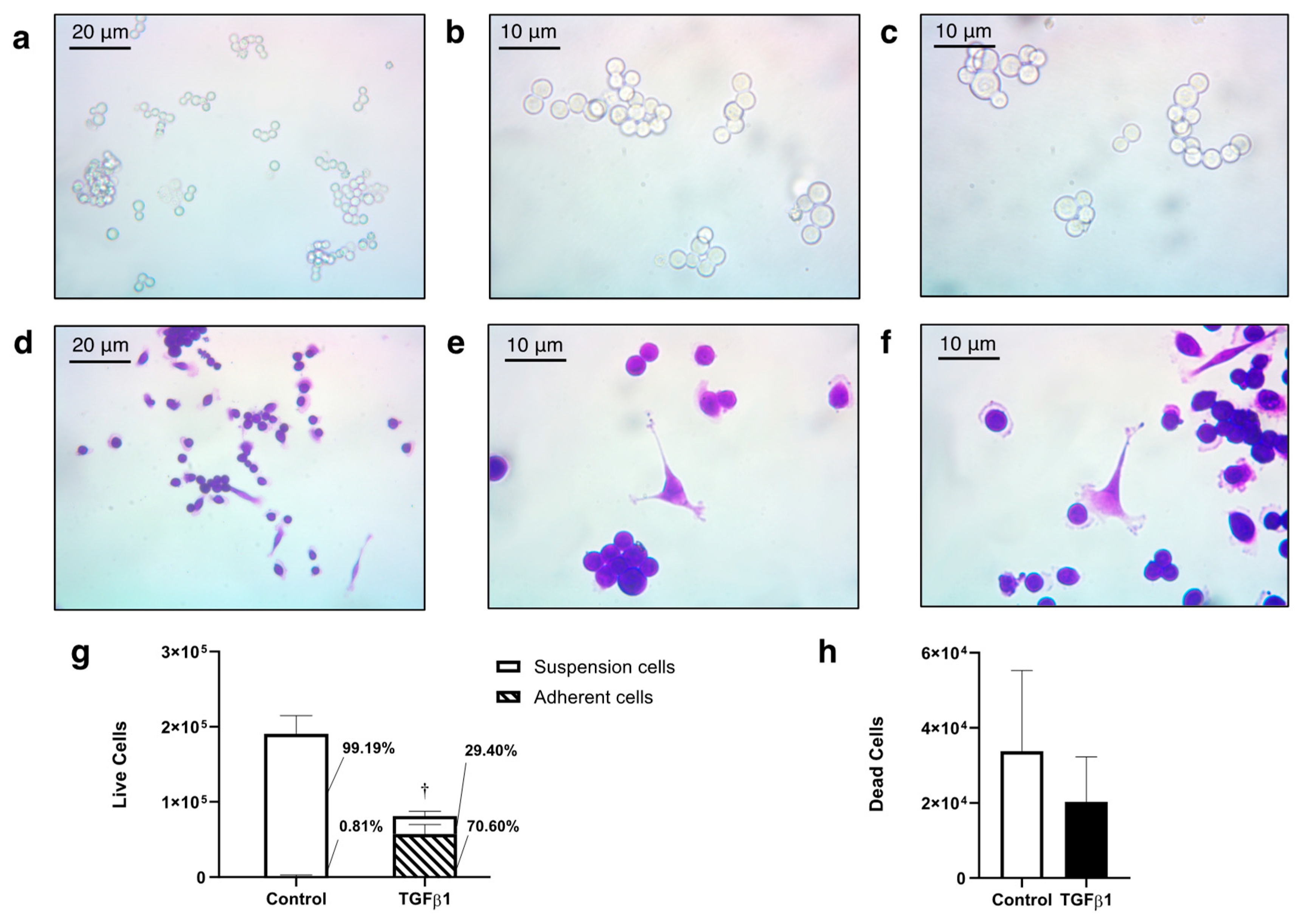
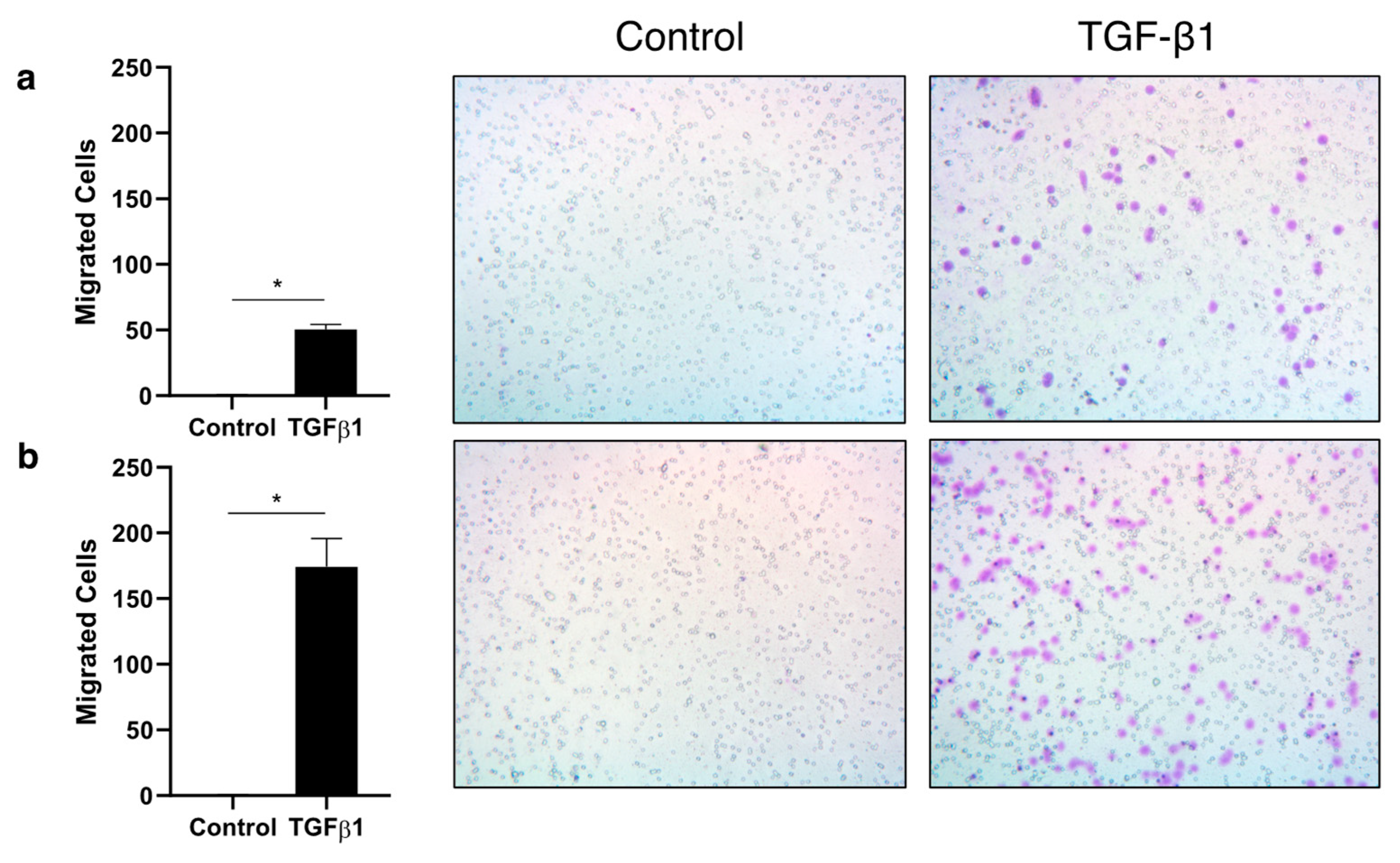
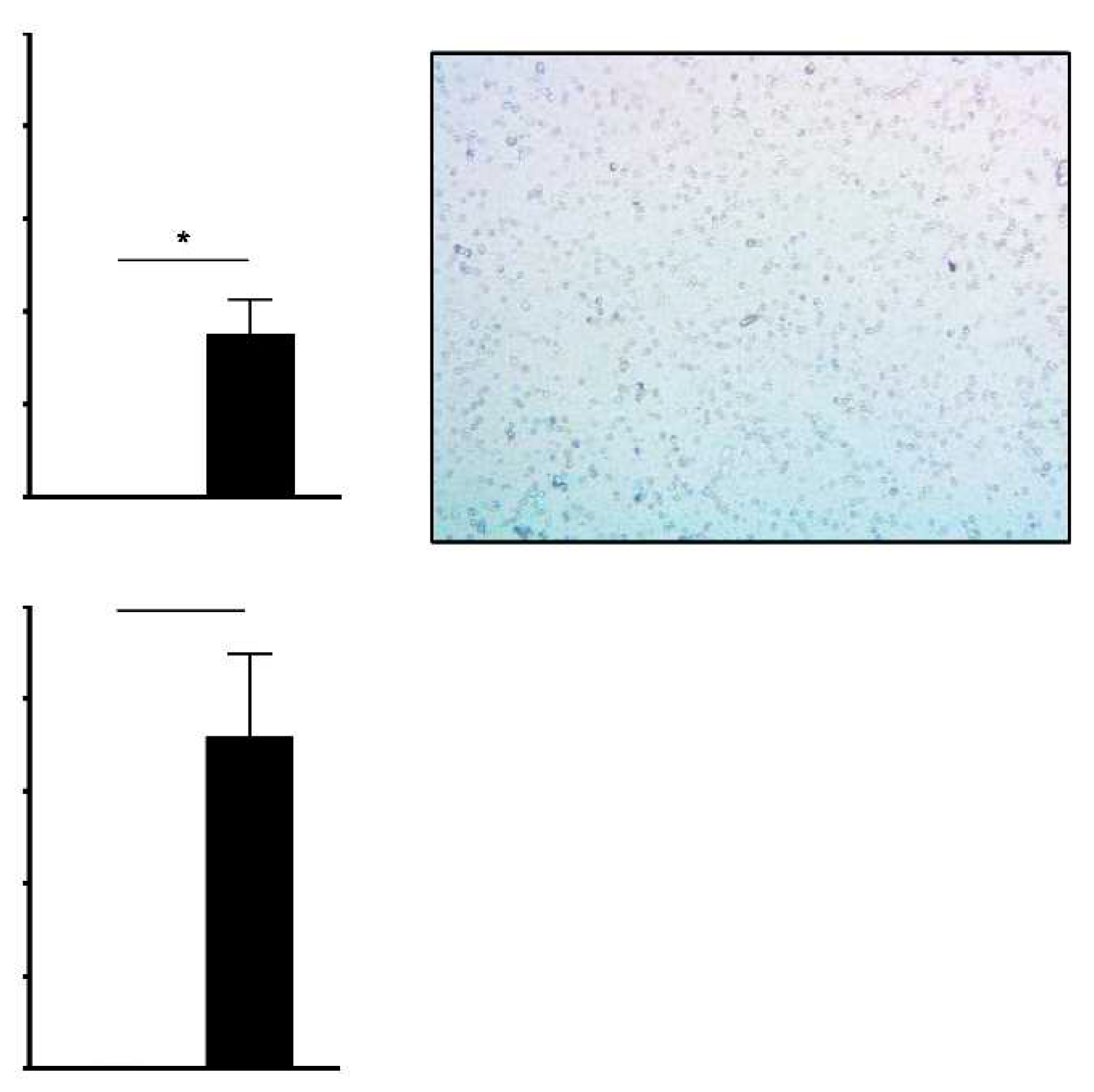
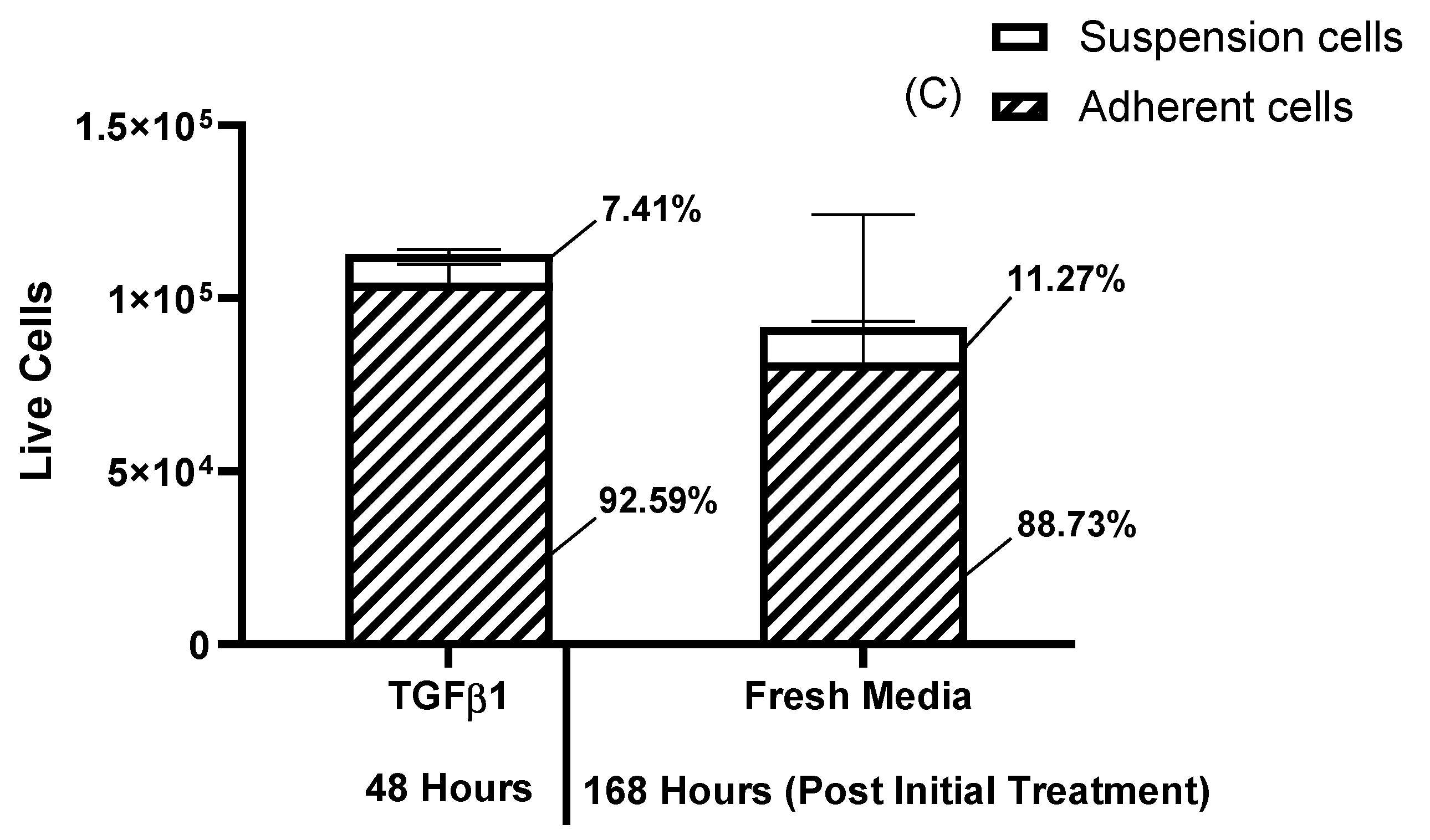
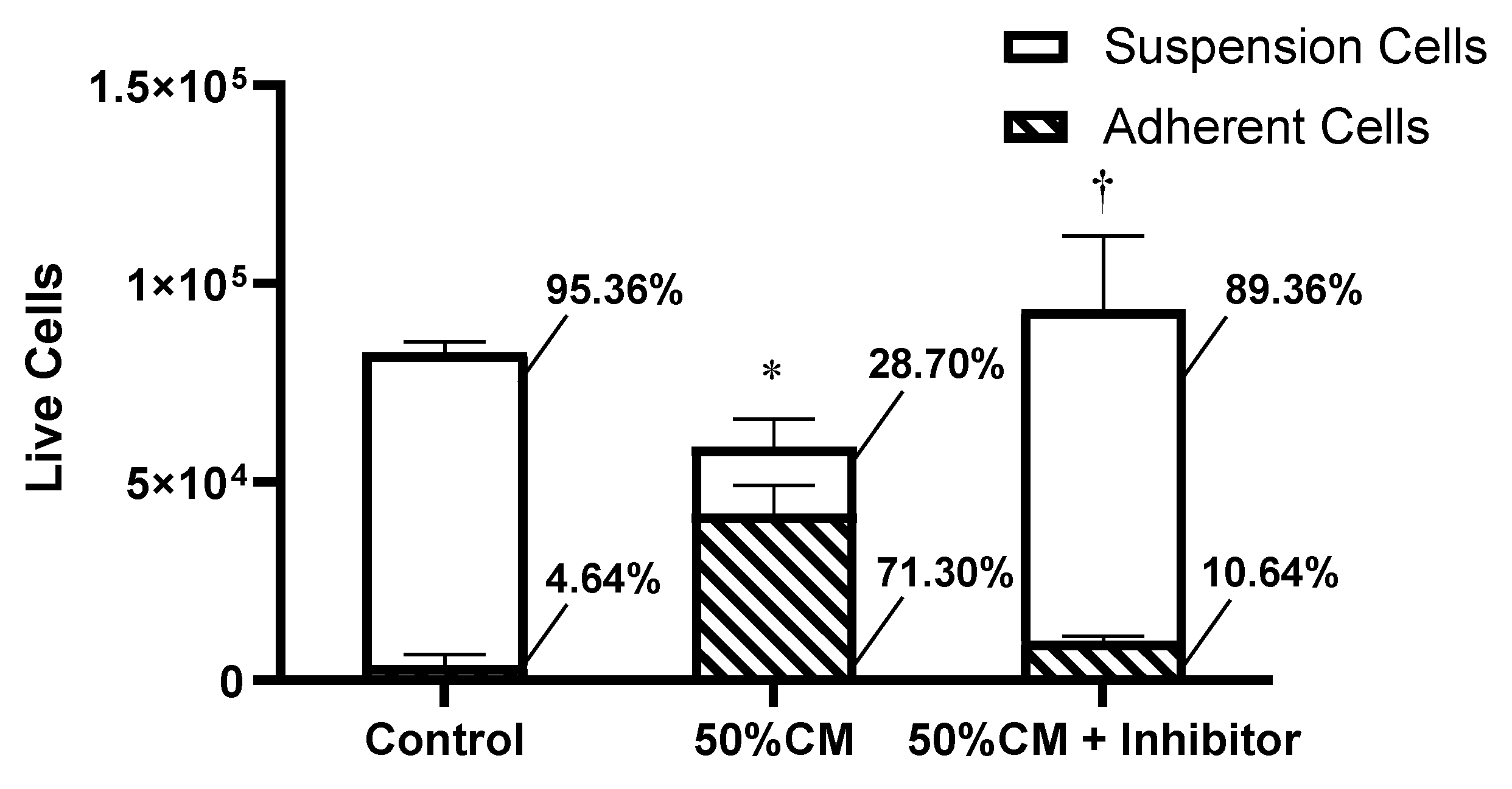
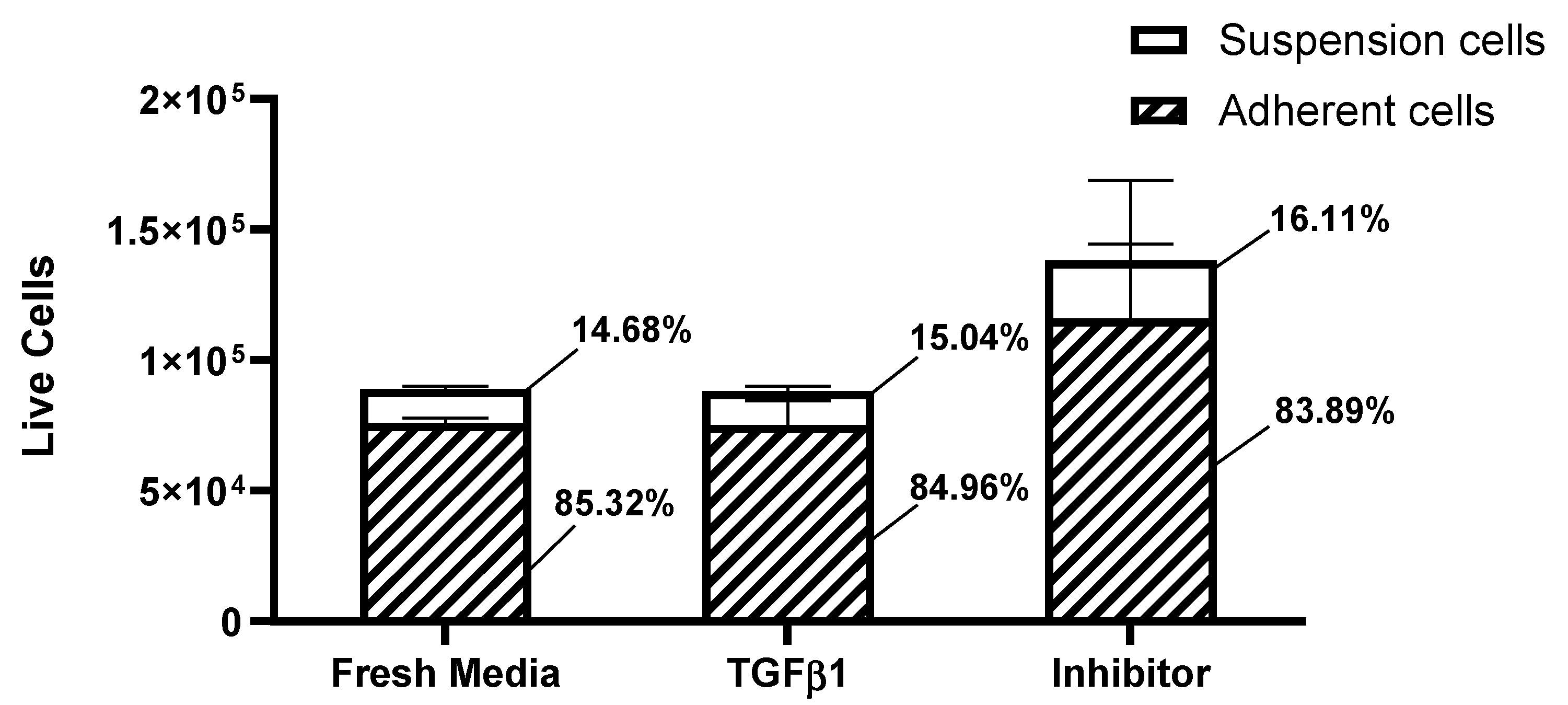
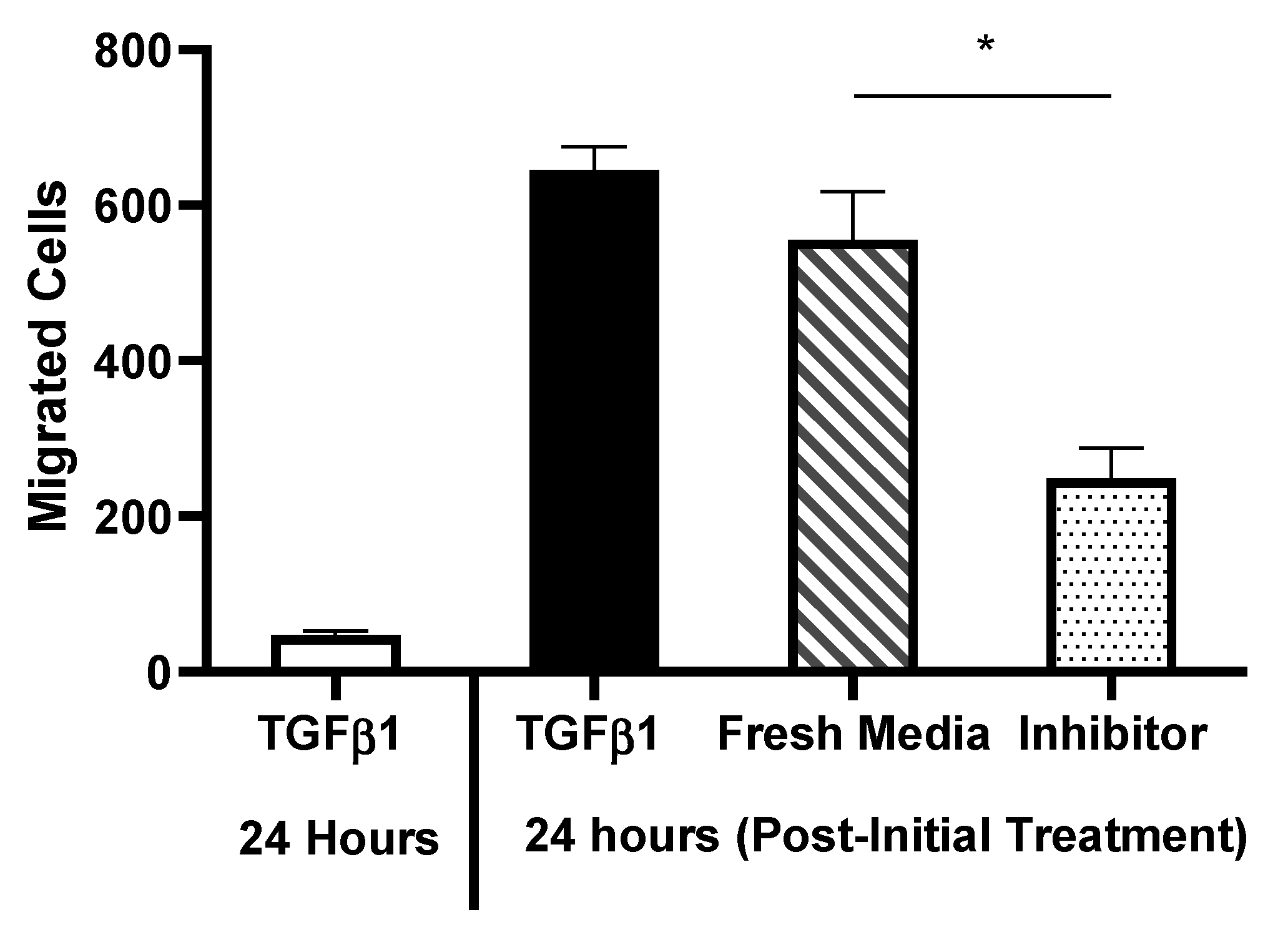
Results
Discussion
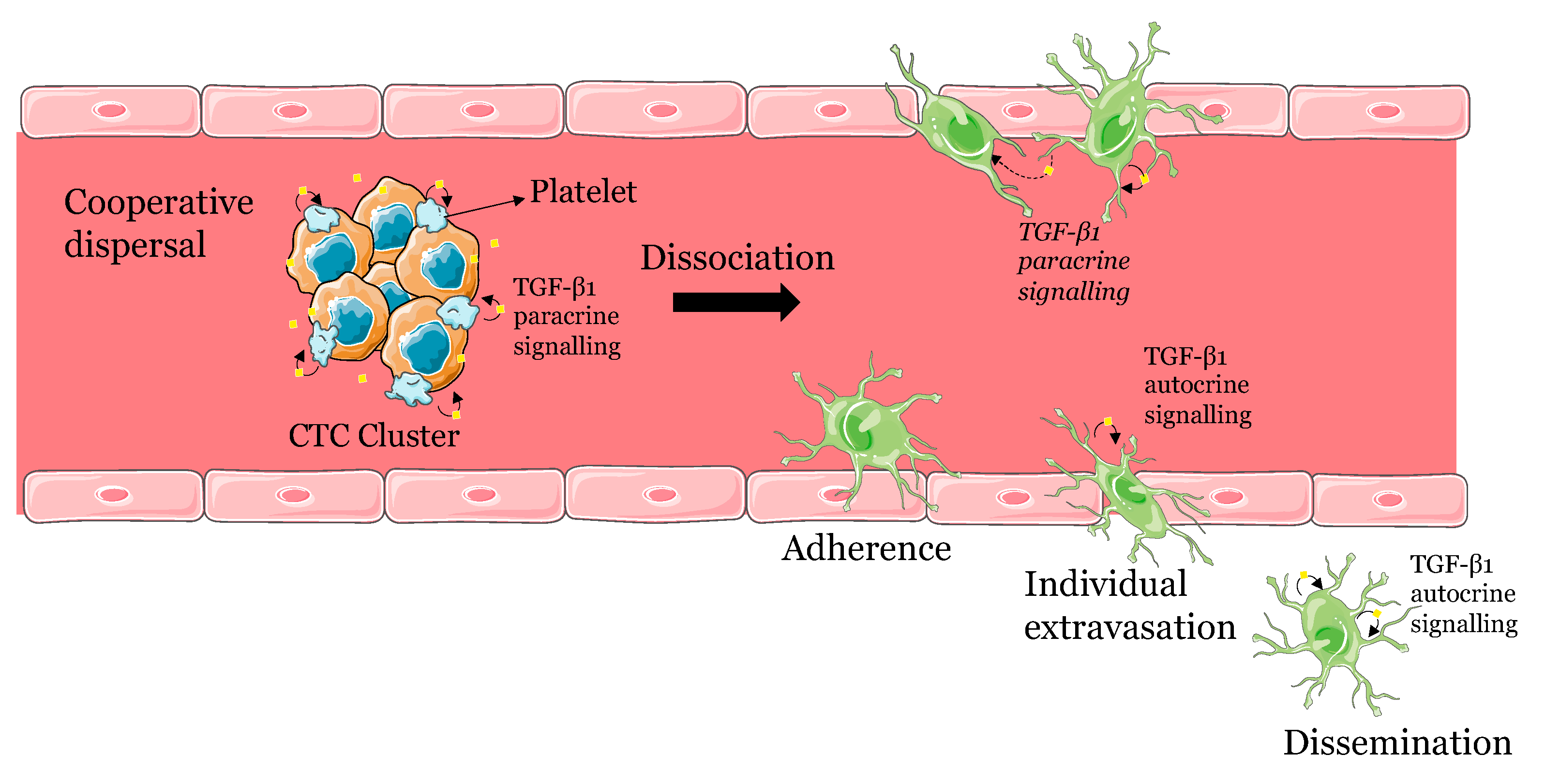
A model for the dissemination of CTC clusters involving platelet recruitment and TGF-β1 signalling
CTC dispersal and dissemination involves both cooperative and individual behaviours
Clinical implications and limitations
Conclusion
Materials and Methods
Cell line and culture conditions
General Experimental Set-up
Reagents
Cell Counting and Viability Assessment
Conditioned Media Collection
Transwell Assays
Staining Adherent Cells and Transwell Inserts
Microscopy and Image Processing
Statistical Analyses
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Availability of data and materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.W.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Emerging Biological Principles of Metastasis. Cell. 2017, 168, 670–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J.; Obenauf, A.C. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature 2016, 529, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, M.; Shaikh, A.; Lo, H.C.; Arpino, G.; de Placido, S.; Zhang, X.H.; et al. Perspective on circulating tumor cell clusters: Why it takes a village to metastasize. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Neelakantan, D.; Ford, H.L. Clonal cooperativity in heterogenous cancers. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 64, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceto, N. Bring along your friends: Homotypic and heterotypic circulating tumor cell clustering to accelerate metastasis. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.R.; Rao, A.; Hunter, M.V.; Sznurkowska, M.K.; Briker, L.; Zhang, M.; Baron, M.; Heilmann, S.; Deforet, M.; Kenny, C.; et al. Cooperation between melanoma cell states promotes metastasis through heterotypic cluster formation. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 2808–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.J.; Ewald, A.J. A collective route to metastasis: Seeding by tumor cell clusters. Science 2016, 352, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, D.; Drasin, D.J.; Ford, H.L. Intratumoral heterogeneity: Clonal cooperation in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 9, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, I.; Castro-Giner, F.; Maurer, M.; Gkountela, S.; Szczerba, B.M.; Scherrer, R.; Coleman, N.; Carreira, S.; Bachmann, F.; Anderson, S.; et al. Detection of circulating tumour cell clusters in human glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Park, S.; Jeong, H.-O.; Park, S.H.; Kumar, S.; Jang, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.U.; Cho, Y.-K. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters Are Cloaked with Platelets and Correlate with Poor Prognosis in Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, I.; Schwab, F.D.; Carbone, R.; Ritter, M.; Picocci, S.; De Marni, M.L.; Stepien, G.; Franchi, G.M.; Zanardi, A.; Rissoglio, M.D.; et al. Detection of clustered circulating tumour cells in early breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2021, 125, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, P.; Ma, H.; Huang, F.; Jin, M.; Dai, X.; Zheng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, T. Circulating tumor microemboli (CTM) and vimentin+ circulating tumor cells (CTCs) detected by a size-based platform predict worse prognosis in advanced colorectal cancer patients during chemotherapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klezl, P.; Pospisilova, E.; Kolostova, K.; Sonsky, J.; Maly, O.; Grill, R.; Pawlak, I.; Bobek, V. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Disease Stage Correlation and Molecular Characterization. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-J.; Shu, C.; Yang, H.-Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.-N.; Tao, R.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.-P.; Xiao, W. The Presence of Circulating Tumor Cell Cluster Characterizes an Aggressive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Subtype. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 734564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-M.; Krebs, M.G.; Lancashire, L.; Sloane, R.; Backen, A.; Swain, R.K.; Priest, L.J.C.; Greystoke, A.; Zhou, C.; Morris, K.; et al. Clinical Significance and Molecular Characteristics of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor Microemboli in Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- uo, X.; Mitra, D.; Sullivan, R.J.; Wittner, B.S.; Kimura, A.M.; Pan, S.; Hoang, M.P.; Brannigan, B.W.; Lawrence, D.P.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Circulating Melanoma Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Donaldson, M.C.; Wittner, B.S.; Spencer, J.A.; et al. Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of breast cancer metastasis. Cell. 2014, 158, 1110–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, S.; Bendahl, P.-O.; Larsson, A.-M.; Aaltonen, K.E.; Rydén, L. Prognostic impact of circulating tumor cell apoptosis and clusters in serial blood samples from patients with metastatic breast cancer in a prospective observational cohort. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.J.; Padmanaban, V.; Silvestri, V.; Schipper, K.; Cohen, J.D.; Fairchild, A.N.; et al. Polyclonal breast cancer metastases arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor cell clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016, 113, E854–E863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amintas, S.; Bedel, A.; Moreau-Gaudry, F.; Boutin, J.; Buscail, L.; Merlio, J.-P.; Vendrely, V.; Dabernat, S.; Buscail, E. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters: United We Stand Divided We Fall. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshiro, M.; Shinriki, S.; Liu, R.; Nakachi, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ohtsubo, K.; Yoshida, R.; Iwamoto, K.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Colonization of distant organs by tumor cells generating circulating homotypic clusters adaptive to fluid shear stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Barclay, M.; Hilkens, J.; Guo, X.; Barrow, H.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.-G. Interaction between circulating galectin-3 and cancer-associated MUC1 enhances tumour cell homotypic aggregation and prevents anoikis. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.C.; Xu, Z.; Kim, I.S.; Muscarella, A.; Liu, J.; Hein, S.; et al. Circulating tumor cell clusters exhibit enhanced immune evasion from natural killer cells. The Journal of Immunology 2020, 204, 88.18. Available online: http://www.jimmunol.org/content/204/1_Supplement/88.18.abstract. [CrossRef]
- Bithi, S.S.; Vanapalli, S.A. Microfluidic cell isolation technology for drug testing of single tumor cells and their clusters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell. 2019, 176, 98–112e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuschagne, C.F.; Cheung, E.C.; Blagih, J.; Domart, M.C.; Vousden, K.H. Cell Clustering Promotes a Metabolic Switch that Supports Metastatic Colonization. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 720–734e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, N.; D’Agua, B.B.; Ridley, A.J. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Taftaf, R.; Kawaguchi, M.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, W.; Entenberg, D.; et al. Homophilic CD44 interactions mediate tumor cell aggregation and polyclonal metastasis in patient-derived breast cancer models. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, C.; Kunz, L.; Castro-Giner, F.; Paasinen-Sohns, A.; Strittmatter, K.; Szczerba, B.M.; Scherrer, R.; Di Maggio, N.; Heusermann, W.; Biehlmaier, O.; et al. Hypoxia Triggers the Intravasation of Clustered Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilic, B.; Offermanns, S. Intravascular Survival and Extravasation of Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, N.; Im, J.H.; Garg, R.; Vega, F.M.; D’agua, B.B.; Riou, P.; Cox, S.; Valderrama, F.; Muschel, R.J.; Ridley, A.J. Cdc42 promotes transendothelial migration of cancer cells through β1 integrin. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strilic, B.; Yang, L.; Albarrán-Juárez, J.; Wachsmuth, L.; Han, K.; Müller, U.C.; et al. Tumour-cell-induced endothelial cell necroptosis via death receptor 6 promotes metastasis. Nature 2016, 536, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.A.; Gracieux, D.; Talib, M.; Tokarz, D.A.; Hensley, M.T.; Cores, J.; Vandergriff, A.; Tang, J.; de Andrade, J.B.; Dinh, P.-U.; et al. Angiopellosis as an Alternative Mechanism of Cell Extravasation. STEM CELLS 2016, 35, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.H.; Storey, B.D.; Moore, J.C.; Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.-L.; Javaid, S.; Sarioglu, A.F.; Sullivan, R.; Madden, M.W.; O’Keefe, R.; et al. Clusters of circulating tumor cells traverse capillary-sized vessels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4947–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.A.; Cullen, M.M.; Hawkey, N.; Mochizuki, H.; Nguyen, L.; Schechter, E.; Borst, L.; Yoder, J.A.; Freedman, J.A.; Patierno, S.R.; et al. A Zebrafish Model of Metastatic Colonization Pinpoints Cellular Mechanisms of Circulating Tumor Cell Extravasation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 641187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.A.; Asad, D.; Amu, E.; Hensley, M.T.; Cores, J.; Vandergriff, A.; Tang, J.; Dinh, P.-U.; Shen, D.; Qiao, L.; et al. Circulating tumor cells exit circulation while maintaining multicellularity augmenting metastatic potential. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs231563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.H.; Edd, J.; Stoddard, A.E.; Wong, K.H.K.; Fachin, F.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Stott, S.L.; Kapur, R.; Toner, M. Microfluidic Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters by Size and Asymmetry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-M.; Krebs, M.; Ward, T.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G.; Ranson, M.; Blackhall, F.; Dive, C. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Window on Metastasis Biology in Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Shiddiky, M.J. Circulating tumor microemboli: Progress in molecular understanding and enrichment technologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1367–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, L.; Colciago, A.; Castiglioni, S.; Maier, J.A. Platelets in Wound Healing: What Happens in Space? Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 716184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, V. TGF-β Signaling in Cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2016, 117, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.N.; Crawford, B.D.; Nedelcu, A.M. In Vitro Model-Systems to Understand the Biology and Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, E.D.; Chan, I.C.W.; Nedelcu, A.M. A model-system to address the impact of phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity on the development of cancer therapies. Front Oncol. 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Stott, S.L.; Smas, M.E.; Ting, D.T.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Wells, M.N.; Shah, A.M.; et al. Circulating Breast Tumor Cells Exhibit Dynamic Changes in Epithelial and Mesenchymal Composition. Science 2013, 339, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainger, D.J.; Mosedale, D.E.; Metcalfe, J.C. TGF-b in blood: a complex problem. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000, 11, 133–145 Available from: wwwelseviercom/locate/cytogfr. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, L.M.; Letterlo, J.J.; Chen, T.; Danielpour, D.; Allison, R.S.H.; Pai, L.H.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-B1 Circulates in Normal Human Plasma and Is Unchanged in Advanced Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Assoian, R.K.; Sporn, M.B. Type B Transforming Growth Factor in Human Platelets: Release during Platelet Degranulation and Action on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J Cell Biol. 1986, 102, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovicá, V.; Todorovic, N.; Demajo, M.; Nesˇkovic, Z.; Subota, V.; Ivanisěvic, O.; et al. Elevated plasma levels of transforming growth factor-B1 (TGF-B1) in patients with advanced breast cancer: association with disease progression. European Journal of Cancer 2003, 39, 454–461 Available from: wwwejconlinecom. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Kim, B.; Ahn, D.H.; Kang, N.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Yim, H.W.; et al. TGF-β induced EMT and stemness characteristics are associated with epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinskii, O.V.; Huxley, V.H.; Glinsky, G.V.; Pienta, K.J.; Raz, A.; Glinsky, V.V. Mechanical Entrapment Is Insufficient and Intercellular Adhesion Is Essential for Metastatic Cell Arrest in Distant Organs. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Radjendirane, V.; Wary, K.K.; Chakrabarty, S. Transforming growth factor β regulates cell–cell adhesion through extracellular matrix remodeling and activation of focal adhesion kinase in human colon carcinoma Moser cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5558–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong Shen, M.; Zhu, D.M.; Ying Wang, L.; Liang Zha, X. TGF-β1-promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation and cell ad-hesion contribute to TGF-β1-enhanced cell migration in SMMC-7721 cells. Cell Res. 2003, 13, 343–350 Available from: http://wwwcell. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.P.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.A.; Jong, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Weon, L.E.E.J.; et al. TGF-β1 (transforming growth factor-β1)-mediated adhesion of gastric carcinoma cells involves a decrease in Ras/ERKs (extracellular-signal-regulated kinases) cascade activity dependent on c-Src activity. Biochem J. 2004, 379, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjaastad, M.D.; Angres, B.; Lewis, R.S.; Nelson, W.J. Feedback regulation of cell-substratum adhesion by integrin-mediated intracellular Ca2+ signaling (epithelial cells/signal transduction/substrate adhesion). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91, 8214–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressner, O.A.; Lahme, B.; Siluschek, M.; Rehbein, K.; Herrmann, J.; Weiskirchen, R.; Gressner, A.M. Activation of TGF-β within cultured hepatocytes and in liver injury leads to intracrine signaling with expression of connective tissue growth factor. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungefroren, H. Autocrine TGF-β in Cancer: Review of the Literature and Caveats in Experimental Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, C.; von der Ohe, J.; Hass, R.; Ungefroren, H. TGF-β-Dependent Growth Arrest and Cell Migration in Benign and Malignant Breast Epithelial Cells Are Antagonistically Controlled by Rac1 and Rac1b. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, Z.; Yu, D.; Lin, J.; Cai, W. RUNX1 regulates TGF-β induced migration and EMT in colorectal cancer. Pathol. - Res. Pr. 2020, 216, 153142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, S.; Manning, C.; Hooper, S.; Jones, L.; Hill, C.S.; Sahai, E. Localized and reversible TGFβ signalling switches breast cancer cells from cohesive to single cell motility. Nature 2009, 11, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegerfeldt, Y.; Tusch, M.; Bröcker, E.-B.; Friedl, P. Collective cell movement in primary melanoma explants: plasticity of cell-cell interaction, beta1-integrin function, and migration strategies. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.; del Ama, L.F.; Ferguson, J.; Kamarashev, J.; Wellbrock, C.; Hurlstone, A. Heterogeneous Tumor Subpopulations Cooperate to Drive Invasion. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Khan, S.; Joyce, J.; Tsuda, T. Quantification of active and total transforming growth factor-β levels in serum and solid organ tissues by bioassay. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, T.; Pagnotti, G.M.; Guise, T.A.; Mohammad, K.S. The Role of TGF-β in Bone Metastases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Acar, A.; Eaton, E.N.; Mellody, K.T.; Scheel, C.; Ben-Porath, I.; Onder, T.T.; Wang, Z.C.; Richardson, A.L.; Weinberg, R.A.; et al. Autocrine TGF-β and stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) signaling drives the evolution of tumor-promoting mammary stromal myofibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 20009–20014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daroqui, M.C.; Vazquez, P.; Joffé, E.B.D.K.; Bakin, A.V.; Puricelli, L.I. TGF-β autocrine pathway and MAPK signaling promote cell invasiveness and in vivo mammary adenocarcinoma tumor progression. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Nichols, R. W. Blockade of Autocrine TGF-β Signaling Inhibits Stem Cell Phenotype, Survival, and Metastasis of Murine Breast Cancer Cells. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, D.A.; Gupta, S.; Mombach, J.C.M. Systems biology approach suggests new miRNAs as phenotypic stability factors in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Systems biology approach suggest new miRNAs as phenotypic stability factors in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J R Soc Interface. 2020, 17, 20200693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling, E.; Roche, N.S.; Flanders, K.C.; Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. PEDIATRICS 1988, 263, 7741–7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fraser, D.; Phillips, A. ERK, p38, and Smad Signaling Pathways Differentially Regulate Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Autoinduction in Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ballim, D.; Rodriguez, M.; Cui, R.; Goding, C.R.; Teng, H.; Prince, S. The Anti-proliferative Function of the TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway Involves the Repression of the Oncogenic TBX2 by Its Homologue TBX3. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35633–35643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallaher, J.A.; Brown, J.S.; Anderson, A.R.A. The impact of proliferation-migration tradeoffs on phenotypic evolution in cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Xiong, X.; Chen, Y.-G. Feedback regulation of TGF-β signaling. Acta Biochim. et Biophys. Sin. 2017, 50, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, R.; Axelrod, D.E.; Pienta, K.J. Evolution of cooperation among tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 13474–13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhan, Y.; Fan, S. An emerging tumor invasion mechanism about the collective cell migration. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, A.S.; Leonard, T.L.; Gestl, S.A.; Gunther, E.J. Tumour cell heterogeneity maintained by cooperating subclones in Wnt-driven mammary cancers. Nature 2014, 508, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.C.; Xu, Z.; Kim, I.S.; Muscarella, A.; Liu, J.; Hein, S.; Wang, H.; Krupnick, A.; Neilson, J.; Paust, S.; et al. Circulating tumor cell clusters exhibit enhanced immune evasion from natural killer cells. Perspect. Surg. 2020, 204, 88–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, W.F. Cell signaling during development of Dictyostelium. Dev. Biol. 2014, 391, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, P.; Locker, J.; Sahai, E.; Segall, J.E. Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nature 2012, 14, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, D.; Zhou, H.; Oliphant, M.U.J.; Zhang, X.; Simon, L.M.; Henke, D.M.; et al. EMT cells increase breast cancer metastasis via paracrine GLI activation in neighbouring tumour cells. Nat Commun. 2017, 9, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.; del Ama, L.F.; Ferguson, J.; Kamarashev, J.; Wellbrock, C.; Hurlstone, A. Heterogeneous Tumor Subpopulations Cooperate to Drive Invasion. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Pardillos, A.; Valls Chiva, Á.; Bande Vargas, G.; Hurtado Blanco, P.; Piñeiro Cid, R.; Guijarro, P.J.; et al. The role of clonal communication and heterogeneity in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Shen, J.; Wu, J.; Lu, Z.; et al. Metformin is a novel suppressor for transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Qian, W.; Zhou, C.; Cao, J.; Qin, T.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Metformin suppresses the invasive ability of pancreatic cancer cells by blocking autocrine TGF-ß1 signaling. Oncol Rep. 2018, 40, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, S.; Luo, L.; Yan, X.; Huang, D.; et al. AMPK inhibits Smad3-mediated autoinduction of TGF-β1 in gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2021, 25, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2014, 88, 51046. [Google Scholar]
- Boyden, S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 115, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of Image Analysis HHS Public Access. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-M.; Ho, M.-H.; Liao, M.-H.; Lin, Y.-L.; Lai, C.-H.; Lin, P.-I. Improving effects of chitosan nanofiber scaffolds on osteoblast proliferation and maturation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.L.S.; Carrossini, N.; Teixeira, L.K.; Ribeiro-Pinto, L.F.; Bozza, P.T.; Viola, J.P.B. Cell Cycle Progression Regulates Biogenesis and Cellular Localization of Lipid Droplets. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e0037418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




