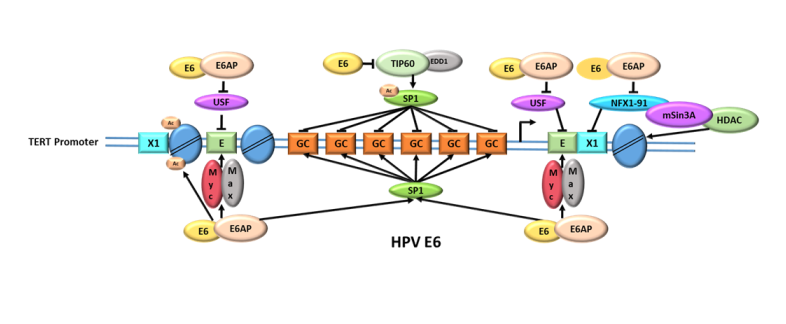
Human oncoviruses are able to subvert telomerase function in cancer cells through multiple strategies. The activity of the catalytic subunit of telomerase (TERT) is commonly enhanced in virus-related cancers. Viral oncoproteins, such as high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) E6, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP1, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (HHV-8) LANA, hepatitis B virus (HBV) HBVx, hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein and human T-cell leukemia virus-1 (HTLV-1) tax protein, interact with regulatory elements in the infected cells and contribute to the transcriptional activation of TERT gene. Specifically, viral oncoproteins have been shown to bind TERT promoter, to induce post-transcriptional alterations of TERT mRNA and to cause epigenetic modifications, which have important effects on the regulation of telomeric and extra-telomeric functions of the telomerase. Other viruses, such as herpesviruses, operate by integrating their genomes within the telomeres or by inducing alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) in non-ALT cells. In this review, we recapitulate recent findings on virus-telomerase/telomeres interplay and the importance of TERT-related oncogenic pathways activated by cancer causing viruses.