Introduction
Biological aging is a complex molecular process that takes place over time in all organisms. However, organisms have evolved mechanisms to repair various forms of age-related damage. For example, DNA repair enzymes exist that can fix damage in nuclear DNA. Mitophagy enables the degradation of damaged mitochondria. The immune system, when one is young at least, eliminates at least some proportion of one’s senescent cells.
There are many theories about why we age, but one stands out as being the most plausible based on the evolutionary and mechanistic evidence. That is the “garbage catastrophe theory of aging.” Drs. Brunk and Terman postulated years ago that the problem of aging can essentially be summed up as a “garbage disposal issue [
1].” The main idea is that basically old molecules are sometimes damaged in ways that prevent the lysosomes from breaking them down properly, and over time these damaged, old molecules accumulate inside the lysosomes. Eventually, the lysosomes become full of this indigestible garbage, i.e., “lipofuscin”, and cannot perform their normal function - then there is a garbage back-up and the cell starts to decline health-wise.
Years ago, Dr. Aubrey de Grey posited that there are seven types of damage that accumulate with age in the human body. These include extracellular aggregates, senescent cells, extracellular matrix stiffening, intracellular aggregates, mitochondrial mutations, cancerous cells, and cell loss/tissue atrophy. He devised a strategy to eliminate each form of damage from the body, called Strategies for Engineered Negligible Senescence (SENS) [
2]. He is of the belief that all seven categories must be addressed before substantial life extension can be attained.
However, I believe that one of his categories, i.e., intracellular aggregate accumulation, actually underlies many of the other categories of damage - and that the removal of indigestible lysosomal garbage (lipofuscin) could, by itself, substantially extend the human lifespan. It could serve to substantially reverse aging and also prevent it (if the therapy were applied perhaps every decade or so to individuals starting at an age of ~30).
There are two arguments for lipofuscin removal being the most important goal of anti-aging science currently. One is evolutionary and one is mechanistic.
Evolutionary argument
In nature, there are only a handful of organisms that can be said to be essentially biological immortal.
Hydra vulgaris (i.e.,
magnipapillata) is one of such organisms, and the reason for this might be that its indigestible garbage is essentially released from its body over time. It has three cell lineages - ectodermal epithelial, interstitial, and endodermal epithelial. All the epithelial cells in its body column are stem cells that continuously divide - displacing cells toward its extremities. The cells at the extremities slough off eventually [
3,
4]. In terms of the interstitial lineage, the differentiated cells that its stem cells produce are closely associated with epithelial cells and so are continuously displaced as well. This is a convenient way to dispose of lipofuscin - i.e., through dilution and cell shedding. However, continuous replacement of neurons may not allow for the stable inter-neuronal interactions required for long-term memory [
5]. Lobsters continually grow throughout life; their fully differentiated cells express telomerase, allowing them to keep dividing as needed [
6]. This includes the cells of their central nervous system, which allows for adult neurogenesis [
7]. They also shed their shells periodically. Thus, the same logic appears to apply to them. However, their growth process does not appear to be fast enough to prevent lipofuscin from accumulating over time [
8]. Notably, lipofuscin accumulation in eyestalk ganglia [
9] is used as a gauge of biological age in lobsters (and myocardial lipofuscin accumulation can be used a marker of chronological age in humans [
10]). Lobsters can retain memories, but only for a short time span [
11]. Naked mole rats are also very long lived, and it has been shown that they have unusually active autophagic systems [
12,
13] (in addition to better anti-cancer defenses [
14]). Even with better autophagy, naked mole rats still do accumulate lipofuscin in their post-mitotic tissues [
15].
It appears as though all animals that age, e.g., flies [
16], worms [
17,
18], lobsters, naked mole rats, mice [
19], non-human primates [
20], and humans [
21] accumulate lipofuscin in their post-mitotic tissues. None of the aforementioned organisms seem to possess any evolutionarily “built-in” ways of exporting the lipofuscin that accumulates in their post-mitotic cells from their bodies, presumably because that would be an unnecessary expenditure of energy in light of procreation. Export from the post-mitotic cells themselves is possible through exocytosis [
22], exosome/microvesicle secretion, or secretory autophagy. That part is not too energetically costly. However, from
in vitro studies, it does not seem as though lipofuscin is exported from post-mitotic cells very often [
23]. It also has never been observed
in vivo [
24]. More importantly, if exported
en masse, there would be nowhere for the garbage to go except to be picked up by tissue-resident phagocytes, which themselves become bloated with lipofuscin - probably mostly from damaged molecules deriving from their own metabolic processes [
25,
26]. (Transfer of lipofuscin to tissue-resident phagocytes through tunneling nanotubes or partial cell fusion is also theoretically possible.) Finally, I have seen no evidence in the literature that tissue-resident phagocytes - full of lipofuscin or not - are able to efficiently leave the body through migration to the gastrointestinal tract, skin, or lungs.
Mechanistic argument
Lipofuscin can eventually occupy a large portion of the cytoplasm in certain cell types. If it reaches a critical level that negatively affects cellular metabolism in a large enough number of cells in a tissue, it could not only cause pathology, but also cause a downward spiral of functionality due to an exponential increase in the whole-body accumulation of the other six categories of age-related damage as defined by Dr. Aubrey de Grey. For example, damaged mitochondria will not be mitophagized as rapidly and may then start to accumulate. Beta-amyloid that is normally degraded may sit around for longer in the extracellular space and begin to form plaques. Senescent cells may start to accumulate if the tissue-resident immune cells are rendered inert either by phagocytosis of ejected lipofuscin or more likely, the general non-functionality of the parenchymal cells around them leading to dilapidation of the extracellular matrix. Cancer will be more likely to form if many microenvironments throughout the body are corrupted. Similarly, stem cell niche corruption may prevent them from replicating efficiently to replenish tissues. And, it is clear that with the extracellular matrix not being tended to properly by its resident cells, stiffening due to cross-links may occur more frequently than they can be cleaved.
It has been argued that lipofuscin is inert. Recently, more researchers are starting to look into whether it may in fact play a pathological role inside a given cell [
21,
27,
28]. Even if the damaged molecules are mostly sequestered within lysosomes and are not actively harmful to the cell, the fact that many lysosomes become full of garbage and therefore are almost surely unable to perform their normal functions nearly as well just logically seems as though it must be a major problem for the cell. Along these lines, lipofuscin-loaded human fibroblasts display reduced autophagy and decreased survival when exposed to amino acid starvation [
29]. If a critical threshold is reached in enough cells in a tissue, e.g., the brain, it clearly would be problematic.
Whether or not lipofuscin itself can exert negative effects on the cell that contains it, simply accumulating to a critical level would logically cause a garbage backup. The cells may try to produce more lysosomes - but will eventually reach capacity. It also makes sense that reaching a critical threshold of lipofuscin in non-dividing cells throughout the body could accelerate the accumulation of the other six categories of age-related damage as defined by Dr. Aubrey de Grey [
30]. (Intracellular aggregates, i.e., lipofuscin, is his fourth category of age-related damage.)
With regard to short-lived species, like mice and rats, lipofuscin may not have enough time to accumulate to pathological levels before they die of cancer. It is estimated that 50-90% of aged mice die of cancer [
31]. Even still, it was shown that in the cerebral cortex neurons of lamina Vb in 630-700-day old rats, lipofuscin occupied 23% of the soma volume [
32,
33]. This could still certainly have a negative physiological effect. Unsurprisingly, we do see a cognitive decline in mice with age [
34]. However, even the oldest mice do not develop age-related neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [
35]. Ostensibly, they simply do not live long enough for sufficient build-up of lipofuscin in their neurons. Other conditions like age-related macular degeneration and sarcopenia do occur in mice, but whether their most severe cases are as bad as the most severe human cases is unclear to me. It is also possible that some mouse tissues accumulate lipofuscin more rapidly than others due to cell type differences in metabolic rates, etc. Some types of human neurons, for example, have not accumulated much lipofuscin by the time others are nearly full [
36].
With regard to humans, it has been demonstrated that multiple neuronal cell subtypes become densely packed with lipofuscin granules with age [
37,
38,
39]. In large motor neurons of centenarians, lipofuscin constitutes up to 75% of total cytoplasmic volume [
40]. Other post-mitotic cell types also accumulate substantial amounts of lipofuscin [
10,
41,
42]. Lipofuscin-laden lysosomes are often much larger than typical lysosomes. The typical size of a lysosome in a fed, unaged cell is ~100 nm-500 nm in diameter [
43]. In contrast, lipofuscin granules are generally 1-5 microns in diameter [
40].
Also, it should be noted that many studies of lipofuscin have relied upon autofluorescence measurements [
44], but lipofuscin is also very heterogeneous with regard to its structure and composition between different species, tissues, perhaps even cells of the same type, and when found at different concentrations [
21]. Thus, it seems as though relying on a specific wavelength range to visualize a cell’s lipofuscin deposits may not be prudent.
If one could remove the lysosomes from laden macrophages stuck at plaques in artery walls, the plaques may eventually regress, given a healthy diet and sufficient exercise as well [
45]. Similarly, with regard to extracellular plaques like beta-amyloid plaque, Le Chatelier's principle may apply. If there are fewer of the soluble protein monomers in solution in that area, the solid mass may dissolve back into solution. Parenchymal cells devoid of lipofuscin could endocytose monomers; as they are degraded, the extracellular plaques could start to dissolve and be taken up as monomers as well - for subsequent degradation. Tau tangles would be autophagocytosed and degraded as well. For the elderly, multiple rounds of lysosomal clearance may be necessary to achieve full results - because, for example, defective mitochondria could have accumulated that will be mitophagized after the initial lipofuscin clearance, which may then become lipofuscin inside the lysosomes due to extensive damage of the mitochondrial membranes by free radicals.
Dysfunctional mitochondria are a hallmark of aging [
46]. With lipofuscin accumulation, damaged mitochondria - sometimes with mtDNA mutations, sometimes just with damage to their membranes, proteins, lipids, and DNA - will not be recycled as rapidly and may then start to accumulate. Mitochondrial DNA mutation accumulation is Dr. de Grey’s fifth category of age-related damage - and they can in fact accrue over time. However, I will address this on a fundamental level later.
Tau will begin to build up inside neurons due to the garbage back-up, eventually becoming hyper-phosphorylated and forming neurofibrillary tangles. Similarly, β-amyloid that is normally degraded may continue to persist, building to levels that lead to plaque formation. Hopefully, if lipofuscin is removed, plaques that have already formed could regress - in line with Le Chatelier’s Principle. In other words, if lipofuscin is cleared and β-amyloid in solution is taken up and autophagocytosed, insoluble plaques may start to dissipate back into solution as well - at which point the β-amyloid in solution would again be taken up and degraded. Transthyretin amyloid could also be another amyloid that forms in the extracellular spaces of our bodies as a result of lipofuscin accumulation in various tissues.
Furthermore, it is clear that with the extracellular matrix (ECM) not being properly cared for by its resident cells, other damage such as fragmentation, glycation, elastocalcinosis, and cross-linking could rapidly reach pathological levels. After extensive lipofuscin removal, hopefully much of this will damage prove to be reversible. If healthy proteostasis could be restored within our parenchymal cells, ECM turnover efficiency should be restored to youthful levels - although it may not be able to reverse all the damage that has accumulated in elderly individuals. Certain cross-links may be cleavable by endogenous, secreted enzymes; after treatment, said cross-link–degrading enzymes could be secreted at the appropriate levels.
Glucosepane is a cross-link that becomes prevalent with age in human tissues that is uncleavable - or at least not cleaved very efficiently/often. Exogenously administered cross-link–breaking enzymes could be helpful. However, there are almost certainly a multitude of indigestible cross-links that accumulate with age. Just like with lipofuscin, an unfeasible number of enzymes might be required to address the problem in this way. Fortunately, even if there are some cross-links that can’t be degraded by endogenous enzymes - if the ECM turnover efficiency is restored through extensive lipofuscin removal - molecules bound together by uncleavable cross-links could be excised and endocytosed by tissue-resident cells or phagocytosed by (bioengineered or regular) tissue-resident macrophages.
Importantly, ECM damage doesn’t seem to be an issue with the “immortal”
Hydra vulgaris [
47].
H. vulgaris has a body column with cells that continuously divide - driving cells out towards its extremities. The cells at its extremities slough off. Thus, it has a built-in mechanism for ridding itself of lipofuscin. Its layer of ECM, the mesoglea, is not shed along with the cells at its extremities; it is turned over. Without lipofuscin accumulation in its cells, and with constant ECM turnover, this organism appears not to age - or at least age very slowly. Of course, the human ECM is much more complex than that of
H. vulgaris. However, the longevity of its mesoglea may indicate that if lipofuscin removal is done periodically (e.g., every decade) in humans starting at a young age, ECM damage may not really be a problem for a long time at least. If started at an older age, a large portion of the damage may be reversed, and then subsequent ECM damage accumulation would hopefully be very slow.
Additionally, cancer is more likely to initiate or progress if many microenvironments throughout the body are corrupted by lipofuscin accumulation. Along those lines, stem cell niche corruption may prevent them from replicating efficiently to replenish tissues.
Senescent cells may start to accumulate if tissue-resident immune cells are rendered inert by lipofuscin accumulation and the non-functionality of the parenchymal cells around them also caused by lipofuscin accumulation, leading to dilapidation of the ECM. Here I refer to irreversibly senescent cells, which have suffered DNA damage and can no longer function properly. However, many cells that show signs of senescence like the senescence-associated secretory phenotype [
48] may be
reversibly senescent. They may have entered into that state due to epigenetic damage brought on by lipofuscin accumulation. I have much hope that this epigenetic state can revert back to a youthful state once lipofuscin is removed, however.
There was a paper published recently in
Nature Aging that suggests that epigenetic damage is mostly reversible at least [
49]. The hallmarks of aging that it related to were mitochondrial dysfunction, nutrient sensing, and stem cell composition. If lipofuscin is removed, damaged mitochondria will be recycled and nutrient sensing processes should go back to normal. Stem cells in this study likely show a younger epigenetic age because they divide frequently and thus dilute out their lipofuscin. That relates to my hypothesis about why Yamanaka factors rejuvenate tissues [
50]; I believe it may be because they transiently induce a pluripotent stem cell state. Thus, cells that normally wouldn’t divide start to divide transiently, and thereby dilute out their lipofuscin. Sox2, one of the four Yamanaka factors, also initially stimulates autophagy [
51] - which decreases “false” lipofuscin. I’m defining false lipofuscin as intracellular garbage that a cell could potentially recycle if it were encouraged in some way. “Real” lipofuscin is intracellular garbage that cannot be digested no matter how we manipulate a cell’s metabolism - namely the junk that must be removed. Perhaps, however, some age-related epigenetic changes will not revert after lipofuscin removal. If so, the aforementioned rejuvenation technique, known as partial reprogramming, could help to reverse them. However, partial reprogramming may be dangerous; it poses a serious risk of causing cancer through teratoma formation.
Of course, the other types of age-related damage aside from lipofuscin can occur simply through random metabolic errors, but perhaps not very often. And damage of those sorts can often be dealt with by endogenous processes. It seems likely that eventually, the steady accumulation of lipofuscin throughout life reaches a point where it increases the rate of accumulation of other age-related damage due to decreasing autophagy/proteasomal efficiency. That may in turn increase the rate of lipofuscin accumulation as well by elevating cellular stress. Eventually, lipofuscin and other age-related damage accumulation must reach a critical threshold level in or around cells throughout our body, leading to a downward spiral, pathologically-speaking [
52]. However, even then, removing the lipofuscin may halt/at least somewhat reverse this downward spiral.
The elderly will likely need a more extensive first lipofuscin removal session. When we do the first round of lysosome removal, we must wait for a period of time for any cytosolic garbage to be sent to the new lysosomes and dysfunctional mitochondria to be mitophagized, etc. Some of that material may prove to be indigestible as well. Thus, we must do multiple rounds of removal potentially during an elderly patient’s first treatment. Furthermore, we may wish to export their autophagosomes as well as their lysosomes. Old autophagosomes may accumulate that were unable to fuse with lipofuscin-laden lysosomes and were therefore sitting in the cytoplasm for quite some time. If so, these old autophagosomes may have compromised outer membranes, and as a result be unable to fuse even with new lysosomes when they are generated. Also, if ECM turnover efficiency is restored to youthful levels, damaged extracellular molecules could potentially be excised from the surrounding ECM and taken up; at least some of them may be indigestible by lysosomal enzymes [
53].
Two remaining issues in the near future
There are two remaining age-related issues that we may wish to consider with regard to the immediate future. One is telomere shortening. Telomeres are simply non-sense, repetitive sequences of DNA on both ends of every one of our chromosomes. Telomeres exist because otherwise, important chromosomal DNA would be lost every time the cell divides. To replenish our telomere lengths, stem cells - the cells that divide - use an enzyme called “telomerase”. If our telomeres shorten too much through not expressing enough telomerase, too much division, damage, or some combination of these factors, it triggers a program where the cell either undergoes apoptosis or enters a senescent state. It has been proposed that not enough telomerase is made in our stem cells, and that over time their telomeres shorten so much they become senescent and we age. (Shorter telomeres are also associated with an increased risk of cancer.) However, even though stem cell telomeres do shorten with age in some individuals, for some individuals, their telomeres stay the same length or even lengthen with age.
Blood stem cells from aged individuals can still function normally if they are “rejuvenated”
ex vivo - and then transplanted into a young niche [
54]. It appears as though every compound that I’ve seen used to “rejuvenate” aged stem cells (e.g., CASIN and rapamycin) actually decreases false lipofuscin in the cells through the stimulation of autophagy [
55,
56]. From the theoretical perspective, one could imagine that if a stem cell is slowly-dividing, it could build up lipofuscin over time even with some replication. Alternatively, a rapidly-dividing stem cell could be restrained by a niche full of lipofuscin, and then start to accumulate lipofuscin itself. Lipofuscin removal from the stem cells/their niches may make them better able to degrade damaged telomerase components and generate new ones, but it is still possible that a gene vector encoding telomerase could be needed to lengthen the telomeres of our stem cells - preventing them from becoming cancerous or senescent. To negate this potential issue, we could deliver a gene vector encoding inducible telomerase to our stem cells using essentially the same delivery system I am proposing for lipofuscin clearance - and overexpress it periodically.
The second issue is whether we should worry about memory B and T cells. Specifically, should we worry that they will eventually build up in our bodies over time through exposure to different pathogens to the point where there is no more space for naïve B and T cells? Dr. de Grey mentioned this as being an issue, especially for CMV. If the thymus and other lymphoid tissues are free of lipofuscin and still functioning properly, perhaps this will not be a problem - as the clonal expansion of memory B and T cells may be a compensatory action to counter the marked drop in the output of naïve B and T cells due to bone marrow/spleen aging and age-related regression of the thymus, respectively [
57].
However, perhaps for the elderly who already suffer from a clonal expansion of memory B and T cells, removing lipofuscin from lymphoid tissues may not be enough. We may also need to eliminate the memory B and T cells that have clonally expanded and massively skewed their pathogen resistance profiles. It would be relatively simple to do that with immunotoxins against B and T cells in general or CAR T-cells against them. Perhaps we could specifically target clones that are most prevalent using a gene vector-type approach wherein sensors look for particular DNA or RNA sequences and kill the cell if they are detected. We could pre-emptively lengthen the telomeres of our hematopoietic stem cells to ready them for massive expansion after that. Notably, if memory B and T cells sit around for long periods of time without replicating - i.e., when the body is not exposed to their corresponding pathogen, they could fill with lipofuscin over time and be unable to function properly (e.g., re-enter a replicative state when necessary) after that.
Lipofuscin removal strategies in vivo (on a cellular basis)
The simplest way to prevent lipofuscin accumulation is to prevent the excessive uptake of biomolecules from external sources via caloric restriction [
58]. Caloric restriction triggers upregulated autophagy [
59], meaning that reversal and prevention are possible to some degree through this method. Exercise also increases the degradative capacity of our cells [
60]. But, of course, these two methods alone are not enough to reverse/prevent aging in a truly substantial manner.
Dr. Aubrey de Grey, an anti-aging pioneer, first introduced me to the concept of lipofuscin through his 2005 TED talk and book that he co-authored with Michael Rae, “Ending Aging: The Rejuvenation Breakthroughs That Could Reverse Human Aging in Our Lifetime [
61].” He proposed a way of eliminating it from the body involving “xenocatabolism”. It is based on his realization that lipofuscin, which is typically fluorescent, must be eliminated from human corpses by microbial enzymes, or else graveyards would glow in the dark. He postulated that we can co-opt enzymes from soil bacteria and fungi and install them in our cells to degrade our lipofuscin [
62]. However, I do not believe this will be feasible in our lifetimes at least, as lipofuscin is quite heterogeneous - it varies widely in composition between cell types and even cells of the same type, potentially [
63]. It also varies in composition between different individuals, probably in part due to differences in diet.
Thus, it would likely require an inordinate number of microbial enzymes to degrade the majority of our lipofuscin, almost all of which would still have to be discovered, evolved, or rationally-designed - and many of them may be toxic to our cells. There are some molecular species that seem to be major contributors to lipofuscin or lipofuscin’s toxic effects at least in some cell types, like the fluorophore A2E (retina) [
64] and the oxysterol 7-ketocholesterol (throughout the body - especially atherosclerotic plaques and the retina) [
65], but we cannot neglect other organs or tissues, or they will fail and we will die anyway. It is worth looking into to see if there are major lipofuscin constituents present across a wide variety of cell types that would be very good targets. But it is unlikely, at least in my mind, that a small number of enzymes will be sufficient to degrade the majority of our lipofuscin deposits.
TFEB is the master regulator of autophagy, and its overexpression can increase lysosomal acidity and boost lysosomal hydrolase levels in lysosomes, which could help to shrink existing lipofuscin deposits in lysosomes. Here, it is important to draw a distinction between “false” and “true” lipofuscin. False lipofuscin would be any intracellular garbage that can be digested by cellular machinery if said machinery is maximally expressed. True lipofuscin is that which is indigestible by cells no matter how they are transcriptionally manipulated. But TFEB (i.e., HLH-30) overexpression only grants a 15-20% increase in lifespan for
C. elegans [
66]. Presumably this is because lipofuscin still accumulates in the intestinal cells over time, even with HLH-30 overexpression. For this truly indigestible garbage, TFEB could still be of use. It also induces the exocytosis of lysosomal contents through fusion of the lysosomal and plasma membranes.
One problem with boosting endogenous exocytosis processes is that they may lose potency with age; oxidatively warped lipids from lipofuscin may insert themselves into the membranes of the lysosomes that contain them and prevent efficient fusion with the plasma membrane. The main problem, however, is that the two most well-known inducers of lysosomal exocytosis, Ca
2+ and TFEB, do not induce a substantial amount of exocytosis - even in youthful cells [
67,
68]. Perhaps over time, TFEB could work well enough to exocytose all a post-mitotic cell’s lipofuscin, but other cellular mechanisms may need to be combined with TFEB for truly effective exocytosis - and there may be cell type differences in what machinery is required. A small molecule was shown to induce some lipofuscin exocytosis in monkey retinal pigment epithelial cells, which are important in macular degeneration [
24]. A final issue is that with lysosomal exocytosis, lipofuscin granules may break apart and/or get caught in various parts of the extracellular matrix - causing a problem by being there. The lipofuscin could also at least eventually be taken up by the same cells that ejected it, neighboring cells that need to be cleared of garbage themselves, or tissue-resident macrophages. It’s probably better for the lipofuscin to be inside an intact vesicle that can prevent re-uptake - only to be picked up by bioengineered macrophages.
Lipofuscin could also theoretically be exported from post-mitotic cells through microvesicular secretion of lysosomes or by transferring lysosomes through tunneling nanotubes (TNTs) to bioengineered macrophages delivered to their locale. (However, the diameter of some lipofuscin-laden lysosomes may be too great for them to be transferred through TNTs.) Secretory autophagy may also be relevant here [
69,
70]. Secretory autophagy utilizes autophagosomes, which are double-membrane vesicles. Perhaps a pathway involving the exocytosis of lysosomes engulfed in single-membrane vesicles could also be possible [
71].
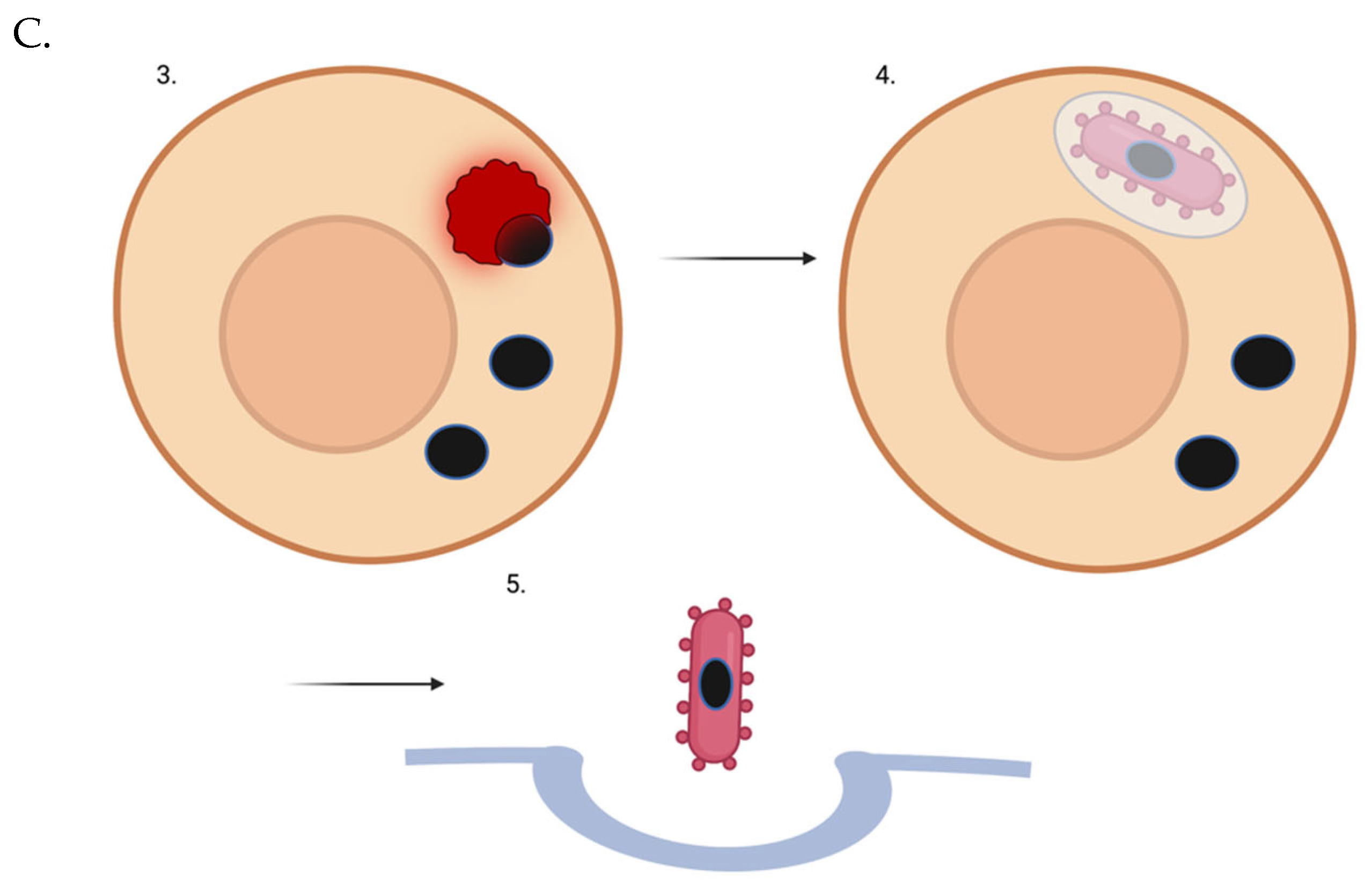
Figure 1.
Lipofuscin-laden lysosome removal from a non-dividing or slowly-dividing cell using a “trash-collecting” microbe. (A) The intracellular microbe enters the target post-mitotic cell. (B) The intracellular microbe escapes the vacuole. C3. The intracellular microbe phagocytoses a lipofuscin-laden lysosome. Of course, not all of a target cell’s lysosomes may be full of lipofuscin. But over time, through random chance, even with new lysosomes being generated naturally or via TFEB induction - many if not most of the garbage-filled lysosomes will be removed. C4. Microbes that have picked up indigestible lysosomal cargo re-enter a vesicle. C5. Full microbes are ejected from the cell via exocytosis.
Figure 1.
Lipofuscin-laden lysosome removal from a non-dividing or slowly-dividing cell using a “trash-collecting” microbe. (A) The intracellular microbe enters the target post-mitotic cell. (B) The intracellular microbe escapes the vacuole. C3. The intracellular microbe phagocytoses a lipofuscin-laden lysosome. Of course, not all of a target cell’s lysosomes may be full of lipofuscin. But over time, through random chance, even with new lysosomes being generated naturally or via TFEB induction - many if not most of the garbage-filled lysosomes will be removed. C4. Microbes that have picked up indigestible lysosomal cargo re-enter a vesicle. C5. Full microbes are ejected from the cell via exocytosis.
Instead of trying to determine which combination of proteins would promote each post-mitotic cell type to efficiently rid itself of its lipofuscin, an intracellular microbe could be harnessed to enter post-mitotic cells and engulf lipofuscin-laden lysosomes directly, then escape the cell. The smallest white blood cell with phagocytic properties has a diameter of 12-15 microns (neutrophils). Some post-mitotic cells have a diameter of around 10 microns. Thus, instead of trying to bioengineer a leukocyte to be intracellular, it might be best to use a micro-organism with a diameter of ~3 microns so that they can enter the cell and engulf lysosomes that have grown to a relatively large size due to lipofuscin accumulation. If the micro-organism could expand (i.e., if it had a ruffled membrane) to accommodate even larger cargo, that would be ideal. Perhaps phagocytic bacteria (~4-5 microns in diameter) [
72] would be easier to work with than amoebae in terms of having them survive inside host cells and not damage said cells. However, one micro-organism of the appropriate size and with phagocytotic properties is an amoeba known as
Massisteria voersi [
73].
It might be necessary to prevent the attempted digestion of the phagocytosed material - in order to prevent metabolic failure of/cytotoxicity to the microbe. Also, a mechanism may need to be in place that could prevent phagocytosis of more than one target. Finally, perhaps a mechanism should be put in place to induce growth [
74], detachment, or lysis (to avoid microbial stress-mediated detrimental effects like chromosomal instability or, potentially, toxin secretion) upon phagocytosis frustration - possibly via a timer-based mechanism involving a temporal promoter cascade as in early, intermediate, and late viral gene expression.
An even smaller microbe may be required to treat certain cells; the somas of cerebellar granules cells, for example, are only around 5 microns in diameter. Perhaps a single microbe could treat all target cells if it can identify smaller human cell types based on surface proteins - inducing shrinking of the microbe if it recognizes a smaller human cell type [
74]. (Being smaller initially might help with cell entry; the microbe could potentially grow a bit after entering a target cell and escaping the endosome. Encountering a smaller cell, plausibly with smaller lysosomes in general - even with lipofuscin accumulation - could trigger a counting mechanism wherein it picks up more than one lysosome in the target cell [
75]. This may increase the “cleaning” efficiency of this approach.)
Non-replicating intracellular bacteria can be rapidly generated by introducing into them a plasmid encoding the
dnaA gene that has a temperature sensitive origin of replication and then deleting the
dnaA gene from the bacterial genome [
76]. When the temperature is increased, the bacteria will lose the plasmid and become non-replicating; ampicillin can then be added to the culture to lyse the dividing cells while sparing the non-dividing cells. However, those bacteria elongate substantially and may have other metabolic abnormalities. (Moreover, it is plausible that bacteria that are so elongated could potentially have trouble entering certain target cells.) Alternatively, RelA overexpression induces the large scale production of pppGpp and ppGpp. These two molecules are known together as (p)ppGpp, and they are known to drastically slow bacterial growth [
77,
78]. Thus, (perhaps truncated) RelA overexpression could be the baseline state in the trash-collecting intracellular bacteria [
79]. However, some amount of RelA may be necessary for the vector to survive in host cells [
80].
Only two genes are required to change a normally extracellular bacterium to an intracellular bacterium, an invasin gene and the listeriolysin O gene from
Listeria monocytogenes [
81]. Perhaps those two could be utilized here as well for an amoeba. Moreover, ActA could potentially be utilized to promote intracellular movement of the amoebae [
82]. The phagocytic receptors on the microbes would be redirected to LAMP-1, a lysosomal transmembrane protein. The microbes could also secrete Bcl-2 to prevent stress-induced apoptosis of host cells - in case its presence inside the cell is excessively detrimental to the metabolism of that cell [
83]. However, further bioengineering may certainly be necessary to prevent host cell cytotoxicity.
The intracellular microbe could be bioengineered to phagocytose lysosomes only, perhaps via selective recognition of targets heavily decorated with LAMP-1 [
84]. (If LAMP-1 is too non-specific in terms of its localization on other autophagic/endocytic vesicles, an AND-gated receptor system could certainly be developed - similar to SynNotch [
85].) After a microbe binds its target, there could then be a pause using a synthetic gene circuit like a temporal promoter cascade, allowing for the engulfment process to proceed and be completed. Then, the microbe would escape via extrusion, budding, actin-mediated protrusion [
86], ejection, expulsion, or exocytosis [
87]. Notably,
F. tularensis, an intracellular bacterium, is known to re-enter the endocytotic compartment after cytoplasmic replication - perhaps at least in part due to its ability to then be exocytosed, spreading to neighboring cells [
88]. A microbe with a T3SS might be able to translocate proteins across the vesicle into the cytoplasm to force its exocytosis. There is a
Mycobacterium tuberculosis surface protein that promotes engulfment of the bacteria into LC3-associated autophagosomes [
89].
(Of course, prior to a microbe engulfing a lysosome, autophagosomal engulfment of the microbe must be prevented. ActA would help - through motility-dependent and motility-independent mechanisms [
90,
91]. Also, expression of USP30 [
92,
93] on the surface of the microbe could help. Production of at least the former protein should be halted when the microbe has engulfed its target and needs to be autophagocytosed.)
TFEB expression [
94] by the microbes prior to engulfment - using a time delay synthetic gene circuit, could help to consolidate garbage by promoting autophagosome-lysosome fusion and get most of the lipofuscin in vesicles rather than some of it being free in the cytoplasm. It would also be important to induce TFEB expression after engulfment, but prior to leaving - in order to force the generation of new lysosomes, so the cell is not left at a serious deficit. A small molecule that increases TFEB activity could perhaps alternatively be used instead prior to and periodically throughout treatment - such as the one currently being developed by Generian. Incorporating TFEB activity would likely increase the overall treatment time, as it would generate new lysosomes that may be targeted by the intracellular microbes, but over time, eventually all the lipofuscin-laden lysosomes would be removed as well - and it seems much safer/like it would lead to a much more thorough “deep clean".
Testing the importance of lipofuscin accumulation in aging in vitro now:
In order to test the theory that lipofuscin is the main issue with regard to age-related disease perhaps for the next few hundred years at least, it appears that we must either figure out how to induce a particular post-mitotic cell type (e.g., a neuron derived from an iPSC) to export its garbage using a gene vector or remove its lipofuscin-laden lysosomes with host cell-autonomous means. Then we could see how long it lives in culture as opposed to normal cells of the same type. However, while primary cell cultures often die after a few days-weeks [
95], the cause of death may not be related to normal aging. It may instead be related to infection or hyperosmolality due to evaporation of the media [
96]. It was shown, however, that at ~day 25, neurons
in vitro have an aged phenotype, including dysfunctional mitochondria, higher reactive oxygen species production, and at least one feature of senescence [
97]. It was also shown that defective autophagy was linked to this senescence-like phenotype - and that aged neurons in culture accumulate lipofuscin [
98]. Thus, if the lipofuscin were removed from the cells and new, functional lysosomes were introduced exogenously or generated through TFEB, their aged phenotype may reverse.
Another approach would be to study aged skeletal muscle cells that contain large quantities of lipofuscin taken from biopsies of elderly humans [
99]. Their lipofuscin-laden skeletal muscle cells may also eventually die from other causes than normal aging due to culture conditions. But by removing the lipofuscin from those cells, one could at least see if markers of health are restored in the cells; i.e., defective mitochondria could be mitophagized, any cytoplasmic lipofuscin granules could eventually be autophagocytosed and delivered to lysosomes, and a senescence-like phenotype could eventually be reversed.
To get a cell to export its garbage, perhaps one could force lysosomes out to the periphery via JIP4 inhibition [
100] while overexpressing the VAMP7, Stx4, and SNAP23 [
101] - and then administer Ca
2+ and the calcium ionophore A23187 to the cell to induce fusion of peripheral lysosomes with the plasma membrane [
53]. TFEB would subsequently be overexpressed to induce lysosomal biogenesis [
102]. This approach could be applicable to many cells in culture. (Other inhibitors like TMEM55B could also be inhibited via siRNA; the concept of inhibiting inhibitors is also clearly applicable to secretory autophagy.)
Another approach that may work and would be applicable to many cells in culture would be to target galectin-8 (or TRIM16 directly) to LAMP-1 while overexpressing Sec22b, Stx3/4, and SNAP23/29 to force the selective encapsulation of lysosomes into an autophagosome destined for secretory autophagy [
103,
104,
105]. Also, autophagosome-lysosome fusion could be cyclically inhibited via small molecule or the SARS-CoV-2 viral protein ORF3a to bias at least nascent autophagosomes toward secretory autophagy [
106,
107]. Targeting a plus-end directed motor protein to the cells’ autophagosomes would also be of use to move them to the periphery. Furthermore, TRIM16 could potentially be engineered so as not to bind to mIL-1β or any other native cargo - if necessary. However, TRIM16-mediated secretory autophagy has only been observed in the context of protein cargo, to my knowledge. Thus, I am not sure if this approach will work exactly as described. However, whole organelle secretion is possible via cellular mechanisms [
108,
109].
In reality, any protein targeted to LAMP-1 with an LC3-interaction region (LIR) [
110] and the ability to bind to Sec22b, in the context of Stx3/4 and SNAP23/29 overexpression, might be able to mediate secretory autophagy of lysosomes.
The efficiency of secretory autophagy for these vesicles specifically could potentially be enhanced by engineering/evolving all the proteins in the pathway to have more affinity for their respective binding partner(s). VEGAS [
111] may be of use here to enhance the binding affinity of these proteins - or perhaps coiled coils [
112] could simply be added, at least in some cases. One could also overexpress all of the altered proteins. (TFEB overexpression would again be helpful to replenish the cells’ lysosomes after each round of export.) This approach of increasing the interaction affinity of all the proteins in the pathway and overexpressing the altered proteins also applies to lysosomal exocytosis.
Two host cell-autonomous means occur to me. Both involve a FluidFM-based approach [
113]. Every few days or so, a single cell could be injected with large iron particles conjugated with antibodies against LAMP-1. Then, a magnetic field could be applied to cluster the lysosomes to one small area at the plasma membrane. They would then be removed by the needle. TFEB would subsequently be induced from an AAV vector genome in the nucleus via small molecule to replenish the intracellular supply of functional lysosomes. The second means would involve the bioengineered microbe described before. Microbes containing large quantities of magnetic nanoparticles could infect or be injected into host cells. They could then engulf the target lysosomes. After giving them some time to do so, a magnetic field could be applied near the cell to cluster them in one small area at the plasma membrane. Then, they could be withdrawn via needle. TFEB again would be utilized here.
Eventual in vivo strategy for delivery and pick-up of the “trash-collecting” microbes:
To treat whole organisms in a high-throughput manner, however, we will need to have a way of delivering trash-collecting (i.e., phagocytic) intracellular microbes to all the target cells throughout the body. As this probably includes most cells in the body, that really necessitates that we use the bloodstream as a systemic delivery system.
The trouble with trying to intravenously administer large liposomes or viral vectors, which can contain much more complex payloads, is that they cannot reach many intraparenchymal target cells throughout the body because the vascular endothelium serves as a stringent barrier. Some intracellular microbes can transcytose across the intestinal epithelium - but this is not necessarily helpful for the vascular endothelium [
114]. There are some pathogens that can cross the blood-brain barrier, but this is typically under conditions of systemic inflammation or bacterial-mediated cytolysis of vascular endothelial cells to cause gaps in the endothelium [
115]. Basically, we do not know nearly as much about effecting safe microbial transcytosis/paracellular passage across the vascular endothelium as we do about white blood cell extravasation [
116] - although we do not know all the mechanisms of leukocyte diapedesis either. Thus, in the more immediate future, to get the trash-collecting microbes across the vascular endothelium, we may have to employ a somewhat complex, two-step delivery system that involves carrier white blood cells.
The two-step system could involve first delivering a gene vector to vascular endothelial cells - this would then inducibly allow for the transmigration of bioengineered white blood cells containing the trash-collecting microbes. Basically, clinicians would seek to infect all or the majority of a patient’s vascular endothelial cells with a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) vector. (Different pseudotypes of HSV-1 or bi-specific antibodies may be necessary to ensure that all vascular endothelial cells throughout the body are transduced; one marker may not be enough - as vascular endothelial cells in different anatomical locales do not have the exact same gene expression patterns [
117].) They would then inducibly express from the viral genomes (upon small molecule administration) synthetic, luminal adherence proteins and chemokines [
118]. These would allow for the attachment and transmigration of bioengineered macrophages. After transmigration, perhaps chemorepellents could be secreted abluminally to direct them away from the vascular endothelial cells, across the rest of the vascular wall, and toward target tissue. The macrophages could then randomly migrate around until binding to a cell type of interest, at which point they could (directionally) donate trash-collecting microbes to the target cell.
In fact, the trash-collecting microbes could replicate within the carrier white blood cells up to a moderate copy number [
119] - restrained by AI-2-based quorum sensing, perhaps [
120]. The carrier white blood cells could then continuously donate the trash-collecting microbes to target cells via microvesicular secretion, secretory autophagy, transient TNTs, or even partial cell-cell fusion; they could enter target cells, engulf their lysosomes, and escape.
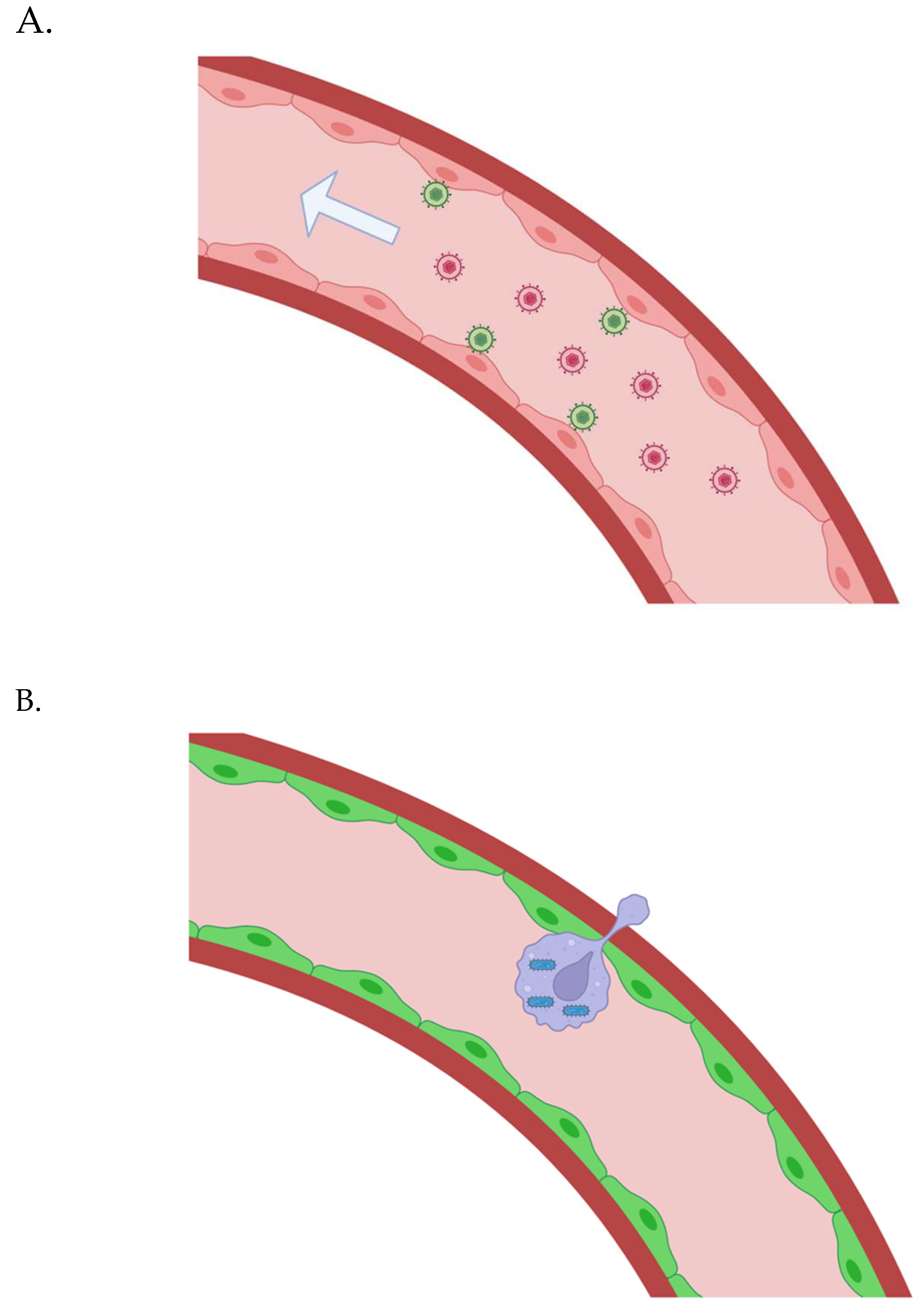
Figure 2.
(A) Gene vectors are administrated intravenously; they bind to vascular endothelial cells, are internalized, and transduce them to allow control over synthetic adherence proteins and chemokines that facilitate the extravasation of bioengineered white blood carrier cells. (B) The bioengineered white blood cells carrying intracellular microbes are “smuggled” across the vascular endothelium in many regions throughout the body.
Figure 2.
(A) Gene vectors are administrated intravenously; they bind to vascular endothelial cells, are internalized, and transduce them to allow control over synthetic adherence proteins and chemokines that facilitate the extravasation of bioengineered white blood carrier cells. (B) The bioengineered white blood cells carrying intracellular microbes are “smuggled” across the vascular endothelium in many regions throughout the body.
The vascular endothelial glycocalyx may make the delivery of large gene vectors difficult. AAV vectors are able to reach the vascular endothelial cells beneath the glycocalyx, at least in many regions (in mice) [
121,
122]. I suggested HSV, however, because I thought multiple proteins may be required to ensure extravasation of the bioengineered white blood cells carrying intracellular, trash-collecting microbes - perhaps multiple proteins that vary based on anatomical locale. But perhaps a single, synthetic chemokine will be enough. Multiple AAVs can be employed if necessary. (An adenoviral vector is also a possibility, perhaps [
123].) If a larger gene vector is required and can only transduce a small number of vascular endothelial cells throughout the body - that could still be enough, or at least very helpful. Imaging via HSV1-TK could let us know when the bioengineered white blood cells have reached the tissue parenchyma in various regions - and a small molecule could be intravenously administered to promote the replication of the bioengineered white blood cells in those regions. The intracellular microbes in the bioengineered white blood cells would keep pace with that division - restrained by quorum sensing. The two-step delivery process could, in this sense, still potentially save a given patient a lot of intraparenchymal infusions in different anatomical locales.
It may not require a gene vector, however, to see the effects we want. If the patient first undergoes leukapheresis, we could then deliver liposomally-encapsulated siRNA to endothelial cells that knocks down endomucin [
124], an inhibitor of endothelial cell-leukocyte adhesion and an important protein in enhancing the glycocalyx, and finally administer the bioengineered macrophages that will cross the vascular wall. Magnetic nanoparticle (MNP)-based permeabilization could also be applied for various areas that have a thicker glycocalyx, for example [
125]. Endothelial cells in those areas could be bound by peptides that recognize that vascular “zip code” - conjugated with MNPs. Importantly, though, endomucin is specifically expressed by venous and capillary endothelial cells [
126]. We may also need to remove lipofuscin from various cell types like smooth muscle cells in the arterial walls.
The only other option that I think makes any sense on a large scale is to manually inject parenchymal regions throughout the body with bioengineered white blood cells carrying the trash-collecting microbes. The bioengineered white blood cells could be induced to replicate up to a sufficient number once there via small molecule. That solution isn’t pretty, but if lipofuscin is truly the main culprit in age-related disease, we simply have to do whatever is required. More likely, we could combine the aforementioned two-step delivery system and intraparenchymal injections for full coverage. Please keep in mind that the small molecule-induced replication option works for the two-step system as well of course, and that in both scenarios there would be continuous donation of trash-collecting microbes from each carrier white blood cell while they randomly migrate around a given tissue.
There are two important considerations for the two-step delivery system. One is that clinicians should perhaps slowly infuse the patient with bioengineered macrophages after inducing the synthetic luminal adherence proteins and chemokines, so as not to create too much stress on the vasculature. The other is that one may need to employ superinfection exclusion (SIE) [
127] in terms of the HSV-1 vector to make sure that all or the majority of vascular endothelial cells are transduced - but without ending up with too high of a vector copy number per given cell. SIE would ideally be on the level of intracellular capsid trafficking. For example, the degradation system cited here [
128] could ensure the degradation of incoming capsids before they transfer their DNA to the nucleus [
129]. A synthetic gene circuit imbuing network-dosage compensation could also be of use in this situation potentially [
130]. Given that the average EC lifespan is >1 year [
131], there is a clear therapeutic window here if the vasculature can be thoroughly transduced first. The extent of vascular endothelial transduction could be visualized via the HSV-1 thymidine kinase. And a kill switch could be included to destroy the vector genomes (based on CRISPR, for example) after lipofuscin removal treatment.
This covers the delivery aspect perhaps, but there is still the issue of pick-up. If a large quantity of bare trash-collecting microbes were to migrate through various tissues to an extraction point, it might severely damage those tissues - as microbes have not adapted to migrate safely through human tissue. It is unclear to me what percentage of the damage we see is due to an inflammatory immune response, however. Recently developed “stealth” microbes [
132], however, may be able to migrate on their own without incurring damage.
Once the bacteria have entered target cells and engulfed target cell lysosomes - they must escape the cell non-lytically. Perhaps they could do so the same way that whole organelles are expelled from cells. Once they have escaped, and the PrfA promoter is no longer functional due to the absence of host cell glutathione [
133], they can lyse the vesicle around them if there is one through LLO secretion [
134] (on a timer-mechanism that stops after a period of time sufficient for vesicle lysis). Alternatively, they can simply swim inside the vesicle [
135]. In any of the above scenarios, the bacteria could also greatly increase the thickness of their capsules [
132]. (They could have the capsule from the beginning - but it may interfere with intracellular movement and phagocytosis.)
The thick capsule could shield them from re-entering the same cell or entering neighboring cells, and potentially allow them to migrate safely on their own to the peritoneal cavity via magnetosome-based magnetotaxis [
136,
137]. There, they could be withdrawn via suction-based laparoscopic removal. I am uncertain if a thick capsule is compatible with migration - it seems likely that an encapsulated bacteria could also be motile. If not, the capsule would still potentially protect them from (re-)uptake by parenchymal cells until the bioengineered macrophages get there and pinpoint their locations via a bacteria-produced small molecule. The bioengineered white blood cells could recognize the membrane surrounding the full microbe or the microbe themselves (depending on whether a double-membraned or single-membraned vesicle is used for export) via a T-cell receptor [
138]-type strategy, and that could trigger migration to an extraction point. Perhaps engulfment of the first microbe would trigger a counting mechanism [
75], and when perhaps ~10 microbe have been engulfed - the bioengineered white blood cells could be induced to migrate to an extraction point.
Withdrawal of trash-laden, carrier macrophages could be effected by implanting small biodegradable beads that slowly release a chemoattractant molecule [
139] inside small devices that serve as a trap for the bioengineered macrophages, perhaps via conjugation of antibodies to the interior of the trap that target a certain surface protein of the bioengineered macrophages. The extraction point could be laparoscopically-inserted “traps” for the bioengineered white blood cells as I just mentioned, the bloodstream (where they can be filtered out through dialysis), or the intestinal lumen. Magnetism could also be used to draw bioengineered macrophages loaded with magnetic nanoparticles to a singular, intraperitoneal extraction point, where they can be removed laparoscopically [
140,
141].
This strategy for
in vivo treatment will likely require immunosuppression throughout the duration of the treatment. With regard to the intracellular microbe, perhaps a fully immunologically “stealthed” vector [
132,
142] can eventually be developed through bioengineering. However, it is also important to note that the microbe could potentially be shielded from the extracellular environment at every step throughout the treatment, leaving only cell-autonomous innate immunity as an issue.
Testing this type of delivery system in mice may be more facile than actually implementing the real formulation because new mice strains can be engineered that express various foreign genes in their vascular endothelial cells. They could have a synthetic chemokine that brings across bioengineered macrophages [
143], endomucin siRNA, a chemorepellent from the abluminal side of the vascular endothelium, etc. Ferritin could even potentially be overexpressed in the mouse vascular endothelial cells [
144] to enable magnetic-based disruption of endothelial junctions in large regions of the body - as in the previously-cited article [
125].
If we test these therapies on mice, perhaps they should also be engineered to be cancer-resistant [
145,
146,
147,
148], although periodic lipofuscin removal would likely help decrease the likelihood of malignant growths occurring. However, by using cancer-resistant mice, we could see significantly improved motor and cognitive functionality with extensive lipofuscin removal - in the absence of possible premature death due to cancer.
Conclusions
Finally, the reason why I believe a phagocytic intracellular microbe may be the best approach to clear lipofuscin is that they already carry many gene networks capable of allowing entry into a wide variety of mammalian cell types, phagocytosis of micron-sized objects, and non-lytic escape from a wide variety of mammalian cell types. Screens can be performed to identify mutants that are even more adept at these three processes. Identifying or rationally-engineering/evolving proteins that can initiate lysosomal exocytosis, secretory autophagy with regard to lysosomes, or microvesicular secretion of lysosomes in all the necessary target cell types - may not be particularly facile. Also, all of the protein-based approaches would initiate mass export of lysosomes, which may be detrimental to the patient’s health even when done slowly - and especially if done throughout the whole body simultaneously.
Target cell-based mechanisms of lysosomal export would also potentially be taxing for them in terms of membrane lipid dynamics. In contrast, the microbes can enter one at a time and pick up cargo, keeping it encapsulated and theoretically preventing re-uptake by the same cell, neighboring cells, or tissue-resident phagocytes. If the microbe buds from the carrier leukocyte or is secreted through secretory autophagy, it would be delivering lipid contents to a given target cell. It would also engulf the target lysosome using its own membrane lipids. Most importantly, as opposed to requiring random bioengineered macrophage migration in a tissue to collect exported garbage, the bacteria could plausibly migrate on their own to an extraction point - or secrete a small molecule signal that allows bioengineered macrophages to hone in on their locations.
I call this in vivo lipofuscin removal approach, “Clearance of Undigested Rubbish by Encapsulation” (CURE). That is because regardless of how the lipofuscin is ejected from post-mitotic cells, it ends up in a bioengineered leukocyte that will at some point migrate to an extraction point.
Through synthetic biology, I believe we can clear lipofuscin from our tissues. There is a research article showing that TFEB overexpression can shrink lipofuscin deposits - but this work was done in the context of a transgenic mouse model with overproduction of an aggregating protein, which I would define as “false” lipofuscin [
149]. Namely, if the protein ceased to be produced and the cells weren’t already completely overwhelmed, it could be degraded over a reasonable amount of time by endogenous lysosomal hydrolases.
As we have never really had a way to clear true heterogeneous, age-related lipofuscin from our cells - it would be extremely interesting to put the “garbage catastrophe theory of aging” to the test with new techniques.