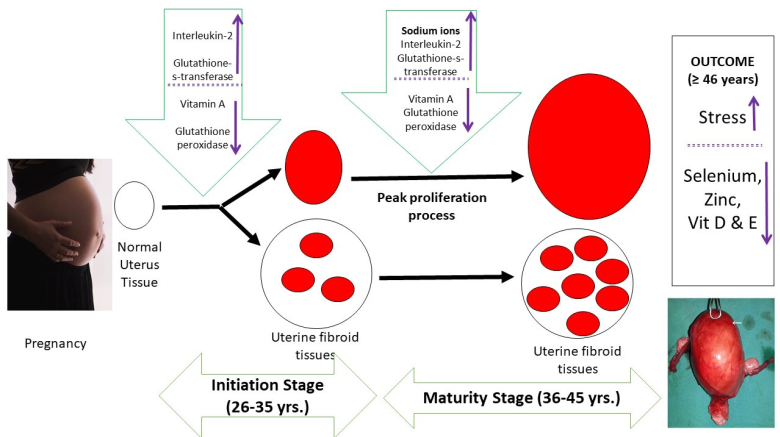
Uterine fibroid (UF) is a tumour in some parts of the uterus, which introduces health challenges or death due to failed surgery among women globally. This study was designed to ascertain the involvement of micro-nutrients, inflammation, and antioxidant enzymes in the UF development to gain further insights and provide a strategy for managing the disease. One hundred ninety reproductive-aged women were recruited and classified equally into case and control subjects. The supernatant obtained from excised tissues from the fibroid and the normal samples from the adjacent myometrium were assessed for the selected biochemical parameters with standard methods. The levels of vitamin A and sodium between 26-35 years; vitamins D, E, zinc, and selenium between 46-55 years; and vitamin E at 56 years and above significantly decreased (p<0.05). Interleukin-2 (IL-2) level significantly increased (P < 0.05) among the case between 36-45 years. An increase in the activity of glutathione-s-transferase and the reduction in glutathione peroxidase activity and vitamin A level in the uterus between 26-45 years were the most pronounced significant findings (p<0.05) recorded. Prolonged vitamin A deficiency coupled with excess sodium salts facilitating inflammation induced by IL-2 are critical factors for UF development.