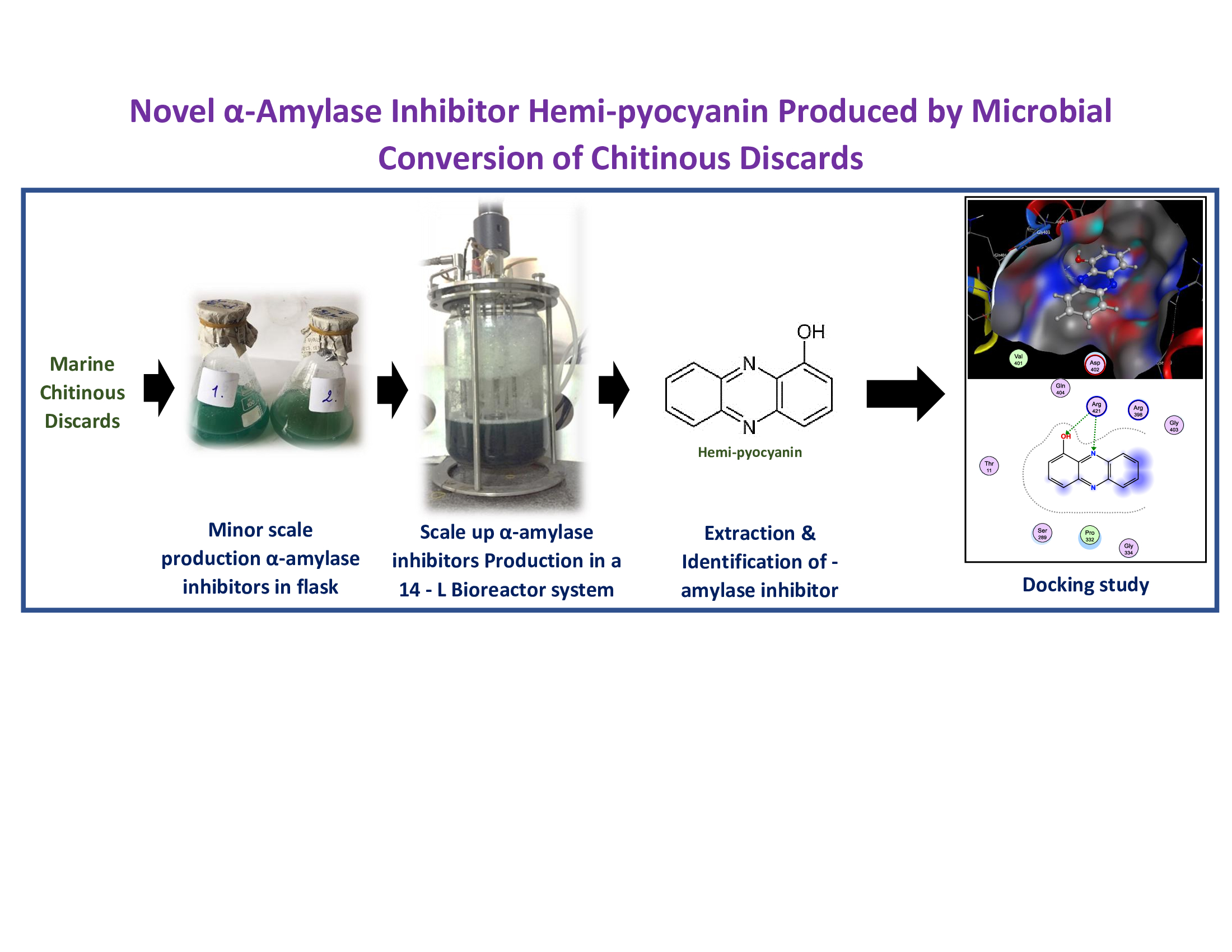
α-amylase inhibitors (aAIs) have been proved efficient for the management of type 2 diabetes. This study aimed to search the potential aAIs produced by microbial fermentation. Among various bacterial strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa TUN03 was found as a potential aAI - producing strain, and shrimp heads powder (SHP) was screened as the most suitable C/N source for fermentation. P. aeruginosa TUN03 exhibited the highest aAIs productivity (3100 U/mL) in the medium containing 1.5% SHP with the initial pH of 7-7.5, and fermentation was performed at 27.5 °C in 2 days. Further, aAIs compounds were investigated for scale-up production in a 14 L – bioreactor system, and the results highlighted high yield (4200 U/mL) in much shorter fermentation time (12 h) compared to fermentation in flasks. The bioactivity-guided purification resulted in the isolation of one major target compound. This active compound was confirmed as hemi-pyocyanin (HPC), with good purity, via using high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Notably, HPC demonstrated potent activity comparable to acarbose, a commercial antidiabetic drug; this is the first-ever report of aAI activity of HPC. The docking study indicated that HPC inhibits α-amylase via binding to amino acid Arg421 at the biding site on enzyme α-amylase with good binding energy (-9.3 kcal/mol) and creating two linkages of H-acceptor.