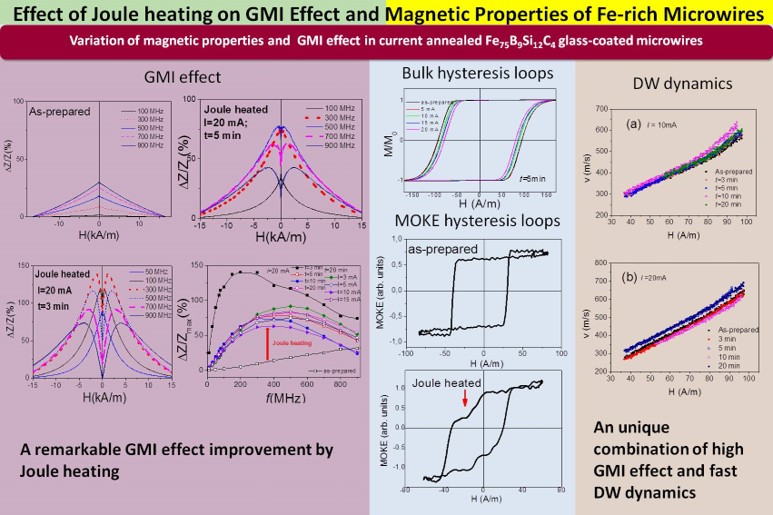
Influence of Joule heating on magnetic properties, giant magnetoimpedance (GMI) effect and domain wall (DW) dynamics of Fe75B9Si12C4 glass-coated microwires was studied. A remarkable increase in GMI ratio is observed in Joule heated samples. The hysteresis loops of Joule heated samples maintain a rectangular shape, while a slight decrease in coercivity after Joule heating is observed. On the other hand, a modification of MOKE hysteresis loops is observed upon Joule heating. Additionally, DW dynamics improvement after Joule heating is observed. The observed GMI ratio improvement along with the change in MOKE loops and DW dynamics improvement has been discussed considering magnetic anisotropy induced by Oersted magnetic field in the surface layer during Joule heating and the internal stress relaxation. A remarkable GMI ratio im-provement observed in Fe-rich Joule-heated microwires with a rectangular hysteresis loop and fast DW propagation, together with the fact that Fe is a more common and less expensive metal than Co, makes them suitable for use in magnetic sensors.