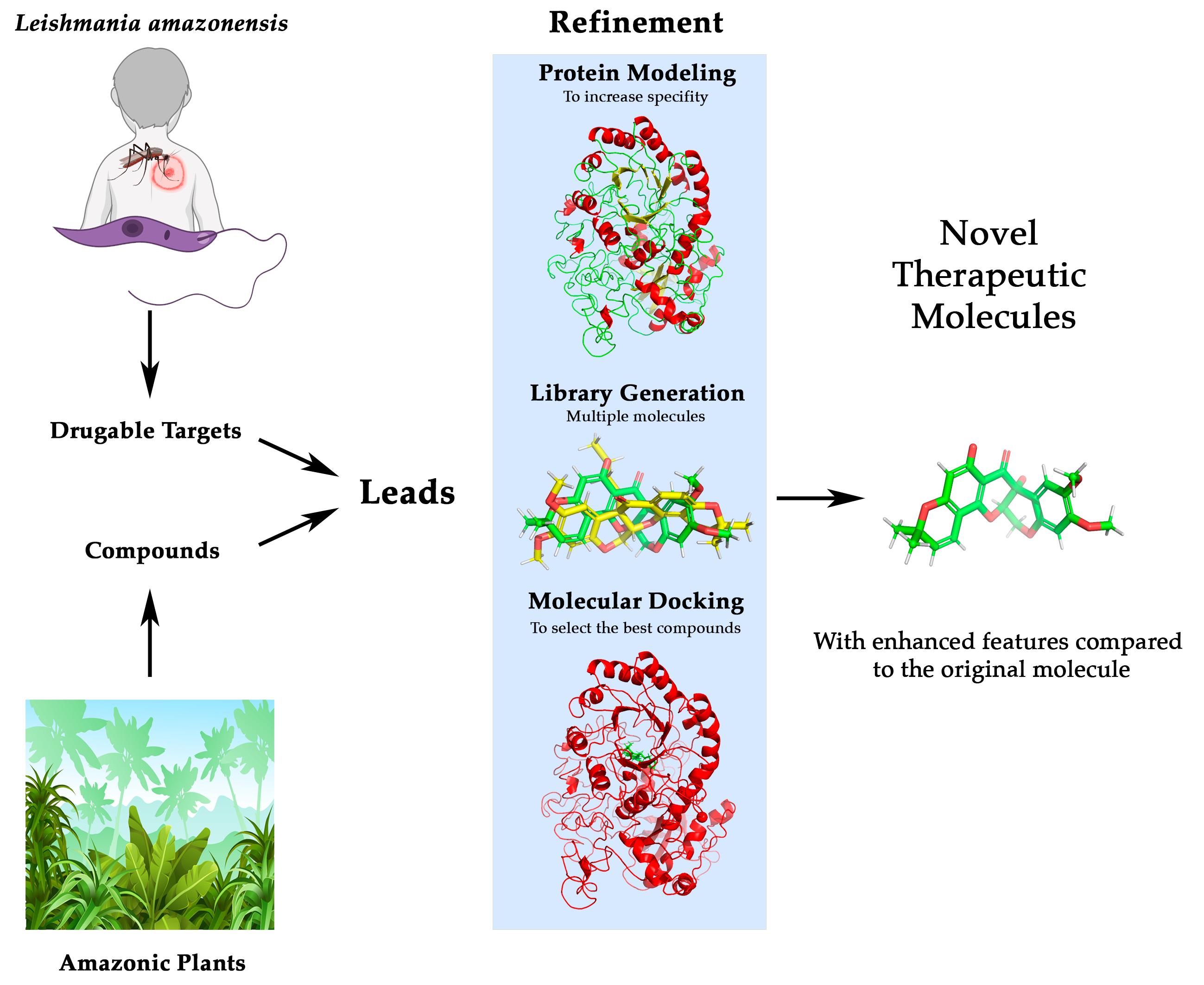
Yearly, 1,500,000 cases of leishmaniasis are diagnosed, causing thousands of deaths. To advance in its therapy, we present an interdisciplinary protocol that unifies ethnobotanical knowledge of natural compounds and the latest bioinformatics advances to respond to an orphan disease such as leishmaniasis and specifically the one caused by Leishmania amazonensis. The use of ethnobotanical information serves as a basis for the development of new drugs, a field in which computer-aided drug design (CADD) has been a revolution. Taking this information from Amazonian communities, located in the area with the highest prevalence of this disease, a protocol has been designed to verify new leads. Moreover, a method has been developed that allows the evaluation of lead molecules, and the improvement of their affinity and specificity against therapeutic targets. Through this approach, deguelin has been identified as a good lead to treat the infection due to its potential as an ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) inhibitor, a key enzyme in Leishmania development. Using an in silico-generated combinatorial library followed by docking approaches, we have found deguelin derivatives with better affinity and specificity against ODC than the original compound, suggesting that this approach could be adapted for developing new drugs against leishmaniasis.