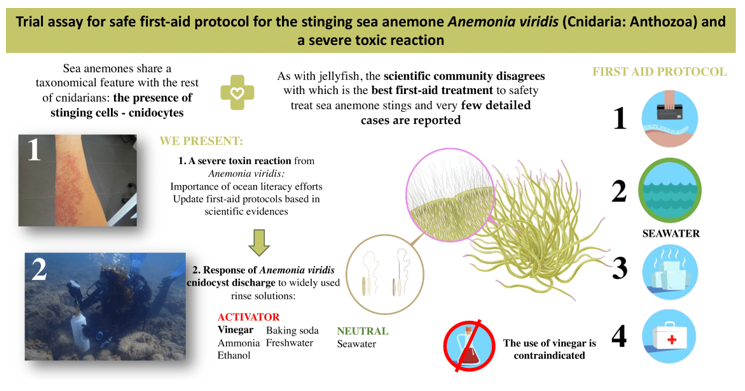
Anemonia viridis is an abundant and widely-distributed temperate sea anemone that can form dense congregations of individuals. Despite the potential severity of its sting, few detailed cases have been reported. We report a case of a severe toxic reaction following an A. viridis sting in a 35-year-old oceanographer. She developed severe pain, itching, redness and burning sensation, which worsened one week after treatment with anti-inflammatories, antihistamines and corticosteroids. Prompted by this event, and due to the insufficient risk prevention, lack of training for marine-environment users and lack of research into sting-specific first-aid protocols, we evaluated the cnidocyst response to five different compounds commonly recommended as rinse solutions in first-aid protocols (seawater, vinegar, ammonia, baking soda and freshwater) by means of the Tentacle Solution Assay. Vinegar and ammonia triggered an immediate and massive cnidocyst discharge after their application and were classified as activator solutions. Baking soda and freshwater were also classified as activator solutions, although with a lower intensity of discharge. Only seawater was classified as a neutral solution and therefore recommended as a rinse solution after A. viridis sting, at least until an inhibitory solution is discovered.