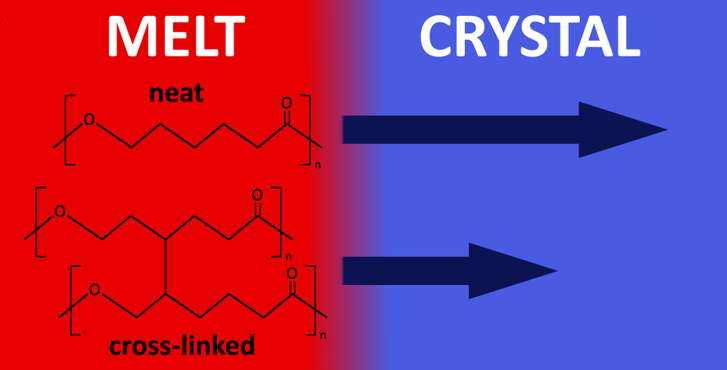
The crystal nucleation and overall crystallization kinetics of cross-linked poly(ε-caprolactone) was studied experimentally by fast scanning calorimetry in a wide temperature range. With an increasing degree of cross-linking, both the nucleation and crystallization half-times increase. Concurrently, the glass transition range shifts to higher temperatures. In contrast, the temperatures of the maximum nucleation and the overall crystallization rates remain the same independent of the degree of cross-linking. The cold crystallization peak temperature generally increases as a function of heating rate, reaching an asymptotic value near the temperature of the maximum growth rate. A theoretical interpretation of these results is given in terms of classical nucleation theory. In addition, it is shown that the average distance between the nearest cross-links is smaller than the estimated lamellae thickness, which indicates the inclusion of cross-links in the crystalline phase of the polymer.