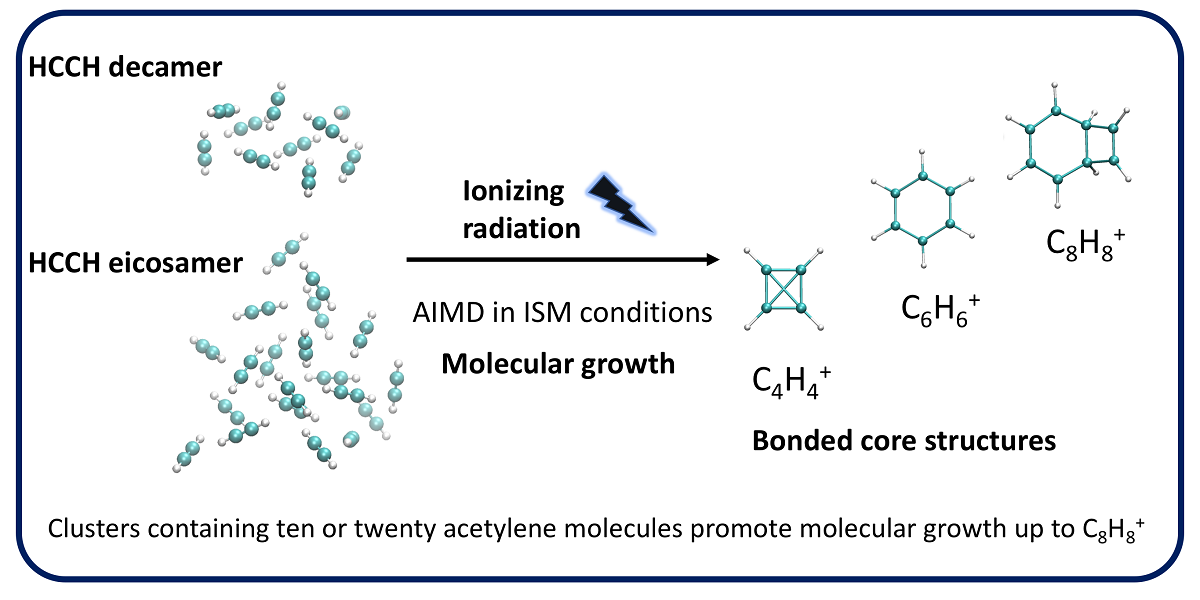
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are widespread in the interstellar medium (ISM). The abundance and relevance of PAHs call for a clear understanding of their formation mechanisms, which, to date, have not been completely deciphered. Of particular interest is the formation of benzene, the basic building block of PAHs. It has been shown that ionization of neutral clusters can lead to an intra-cluster ionic polymerization process that results in molecular growth. Ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) studies in clusters consisting of 3–6 units of acetylene modeling ionization events under ISM conditions have shown maximum aggregation of three acetylene molecules forming bonded C6H6+ species: the larger the number of acetylene molecules, the higher the production of C6H6+. These results lead to the question of whether clusters bigger than those studied thus far promote aggregation beyond three acetylene units, and whether larger clusters can result in higher C6H6+ production. In this study, we report results from AIMD simulations modeling the ionization of 10 and 20 acetylene clusters. The simulations show aggregation of up to four acetylene units producing bonded C8H8+. Interestingly, C8H8+ bicyclic species were identified, setting precedent for their astrochemical identification. Comparable reactivity rates were shown with 10 and 20 acetylene clusters.