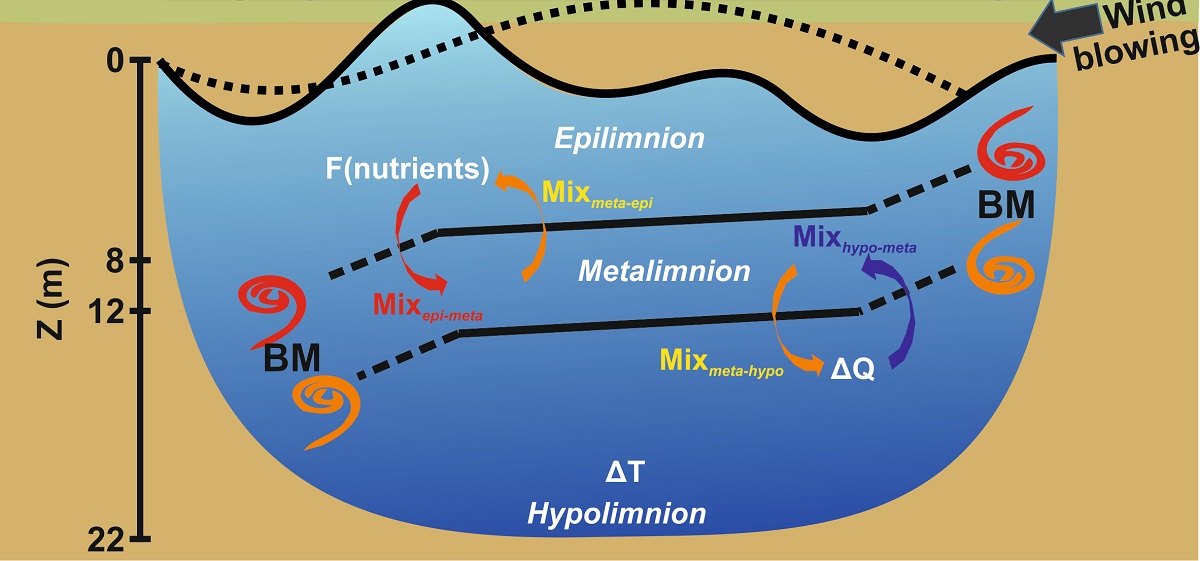
Physical processes play important roles in controlling eutrophication and oligotrophication. In stratified lakes, internal waves can cause vertical transport of heat and nutrients without breaking the stratification, through boundary mixing events. Such is the case in tropical Valle de Bravo (VB) lake, where strong diurnal winds drive internal waves, boundary mixing and hypolimnetic warming during stratification periods. We monitored VB during 18 years (2001-2018) when important water-level fluctuations (WLF) occurred, affecting mixing and nutrient flux. Mean hypolimnetic temperature increase (0.06–1.04°C month-1) occurred in all the stratifications monitored. We analyzed temperature distributions and modeled the hypolimnion heat budget to assess vertical mixing between layers (26,618–140,526 m-3h-1), vertical diffusivity coefficient KZ (6.2x10-7–3.3x10-6 m2s-1) and vertical nutrient entrainment to epilimnion on monthly scale. Stability also varied as a function of WLF. Nutrient flux to the epilimnion ranged 0.36–5.99 mg m-2d-1 for soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) and 5.8–97.1 mg m-2d-1 for dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN). During low water-level years, vertical nutrient fluxes increase and can account for up to >40% of the total external nutrients load to the lake. Vertical mixing changes related to WLF affect nutrient recycling, their flux to sediments, ecosystemic metabolic balance and planktonic composition of VB.