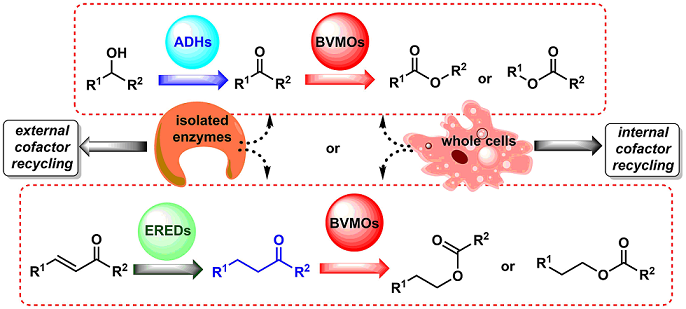
Baeyer-Villiger monoxygenases (BVMOs) are flavin-dependant oxidative enzymes capable to catalyse the insertion of an oxygen atom between a carbonylic Csp2 and the Csp3 at the alpha position, therefore transforming linear and cyclic ketones into esters and lactones. These enzymes are dependent on nicotinamides (NAD(P)H) for the flavin reduction and subsequent reaction with molecular oxygen to furnish peroxyflavin, the ultimate responsible for the substrate oxidation. BVMOs can be included in cascade reactions, coupled to other redox enzymes such as alcohol dehydrogenases (ADHs) or ene-reductases (EREDs), so that the direct conversion of alcohols or α,β-unsaturated carbonylic compounds to the corresponding esters can be achieved. This way, it is possible to develop smart synthetic strategies with a convenient cofactor recycling, both using whole cells (native or genetically engineered) as well as isolated enzymes, via multi-steps reaction through sequential or parallel methodologies. Some examples will be commented dealing with these biotransformations, highlighting the advantages of the coupling of enzymatic steps.