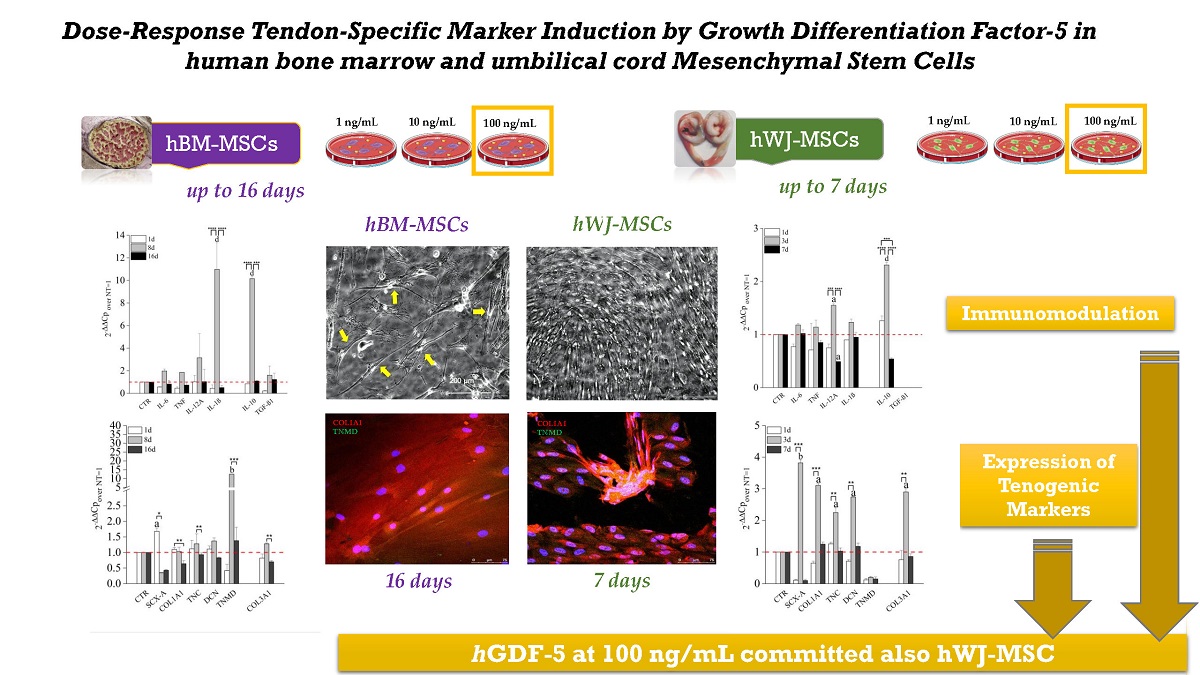
Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from bone marrow (hBM-MSCs) are utilized in tendon tissue‐engineering protocols while extra-embryonic cord-derived, including from Wharton’s Jelly (hWJ-MSC), are emerging as useful alternatives. To explore the tenogenic responsiveness of hBM-MSCs and hWJ-MSCs to hGDF-5 we supplemented each at doses of 1, 10, and 100 ng/mL and determined proliferation, morphology and time-dependent expression of tenogenic markers. We evaluated expression of Collagen types 1 (COL1A1) and 3 (COL3A1), Decorin (DCN), Scleraxis A (SCX-A), Tenascin-C (TNC) and Tenomodulin (TNMD) noting the earliest and largest increase with 100 ng/mL. With 100 ng/mL, hBM-MSCs showed upregulation of SCX-A (1.7-fold) at day 1, TNC (1.3-fold) and TNMD (12-fold) at Day 8. hWJ-MSCs, at the same dose, showed up-regulation of COL1A1 (3-fold), DCN (2.7-fold), SCX (3.8-fold) and TNC (2.3-fold) after 3 days of culture. hWJ-MSCs also showed larger proliferation rate and marked aggregation into a tubular shaped system at Day 7 (with 100 ng/mL of hGDF-5). Simultaneous to this we explored expression of pro-inflammatory (IL-6, TNF, IL-12A, IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10, TGF-β1) cytokines across for both cell types. hBM-MSCs exhibited a better balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines upregulating IL-1β (11-fold) and IL-10 (10-fold) at Day 8; hWJ-MSCs, had a slight expression of IL-12A (1.5-fold) but a greater up-regulation of IL-10 (2.5-fold). Collagen type I and tenomodulin proteins, detected by immunofluorescence, confirming the greater protein expression when 100 ng/mL were supplemented. In the same conditions, both cell types showed specific alignment and shape modification (fibroblast-like) with a Lenght/Width ratio increase at value higher than 1, suggesting their response in activating tenogenic commitment events, and they both potential use in 3D in vitro tissue engineering protocols.