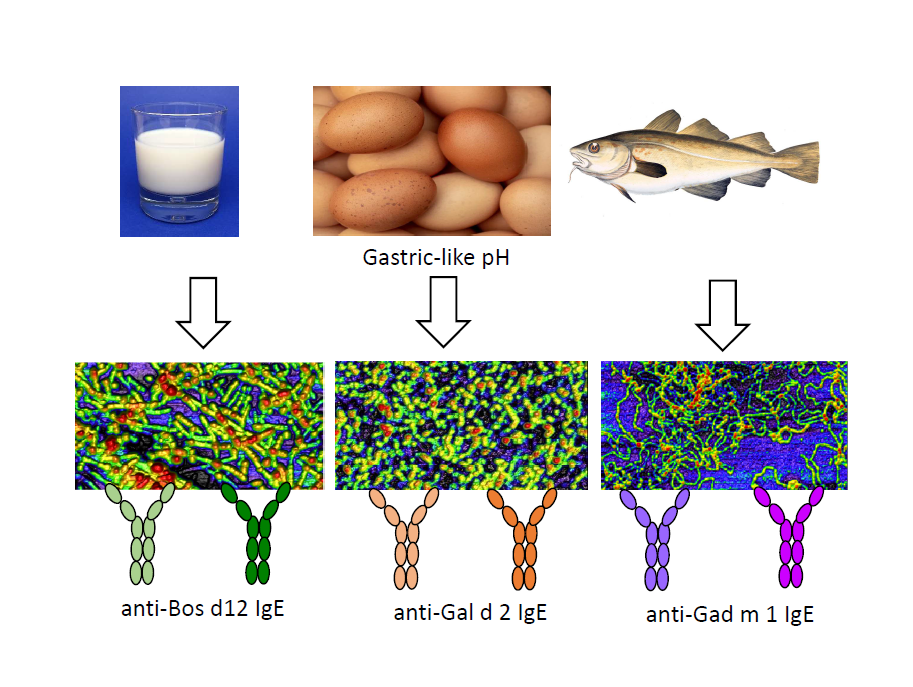
Several animal food allergens assembly into amyloids under gastric-like environments. These aggregated structures provide Gad m 1 with an enhanced IgE interaction due to the amyloid assembly of the epitope regions. However, whether these properties are unique of Gad m 1 or common to other food allergens has not yet been addressed. Using Bos d 5, Bos d 12 and Gal d 2 as food allergen models and Gad m 1 as control, aggregation reactions and the sera of milk, egg and fish allergic patients we have analyzed the IgE interaction of the distinct amyloids. We found that amyloids formed by Bos d 12 and Gal d 2 full-length and truncated chains are recognized by the IgEs of milk and egg allergic patient sera. As with Gad m 1, in most cases amyloid recognition is higher than that of the precursor structure. Bos d 5 was not recognized under any fold by the IgE of the sera studied. These results support that formation of IgE-binding amyloids might be a common feature to animal food allergen.