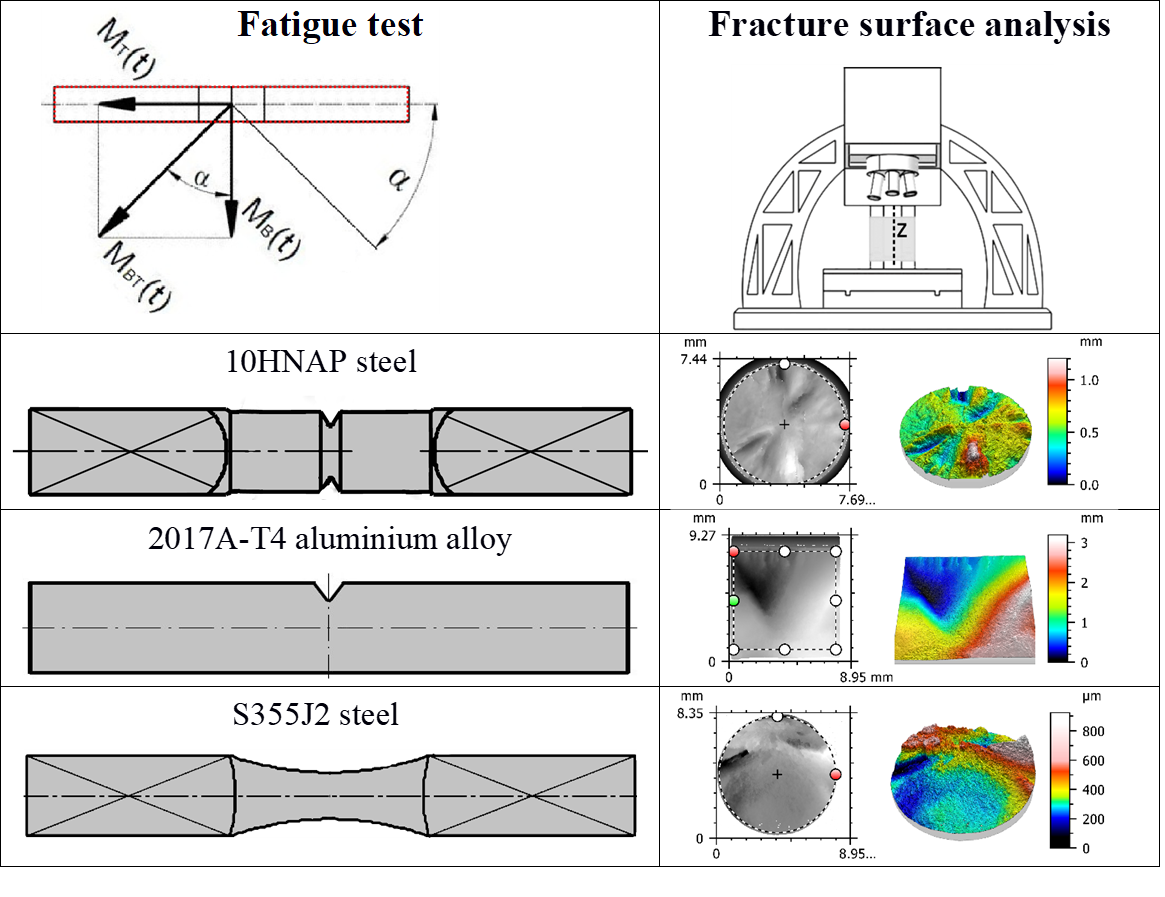
Post-mortem characterisation is a pivotal tool to trace back to the origin of structural failures in modern engineering analyses. This work presents a comparison of both the crack propagation profiles and the rupture roughness profiles based on areal parameters for total fracture area. Notched and smooth samples made of weather-resistant structural steel (10HNAP), popular S355J2 structural steel and aluminium alloy AA2017A under bending, torsion, and combined bending-torsion are investigated. After the fatigue tests, fatigue fractures are measured with an optical profilometer, and the relevant surface parameters are critically compared. The results show a great impact of the loading scenario on both the local profiles and the total fracture areas. In this work, the results of both approaches (local and total fracture zones) for specimens with different geometries are investigated. For all specimens, measured texture parameters decreased in the following order: total area, rupture area, and propagation area.