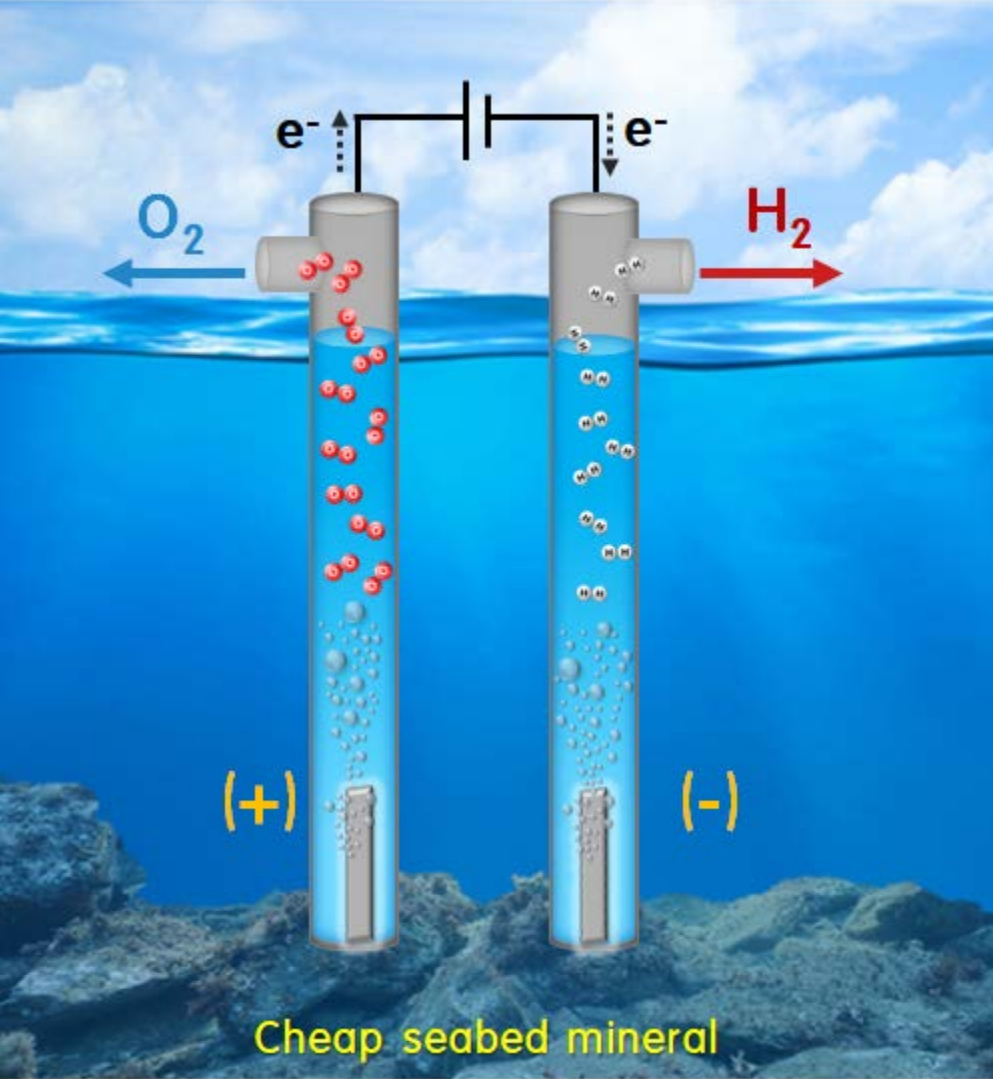
For efficient electrode development in an electrolysis system, Fe2O3, MnO, and heterojunction Fe2O3-MnO materials were synthesized via a simple sol-gel method. These particles were coated on a Ni-foam electrode, and the resulting material was used as an electrode to be used during an oxygen evolution reaction (OER). A 1000-cycle OER test in a KOH alkaline electrolyte indicated that the heterojunction Fe2O3-MnO/NF electrode exhibited the most stable and highest OER activity: it exhibited a low overvoltage (n) of 370 mV and a small Tafel slope of 66 mV/dec. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the excellent redox performance contributed to the synergy of Mn and Fe, which enhanced the OER performance of the Fe2O3-MnO/NF electrode. Furthermore, the effective redox reaction of Mn and Fe indicated that the structure maintained stability even under 1000 repeated OER cycles.