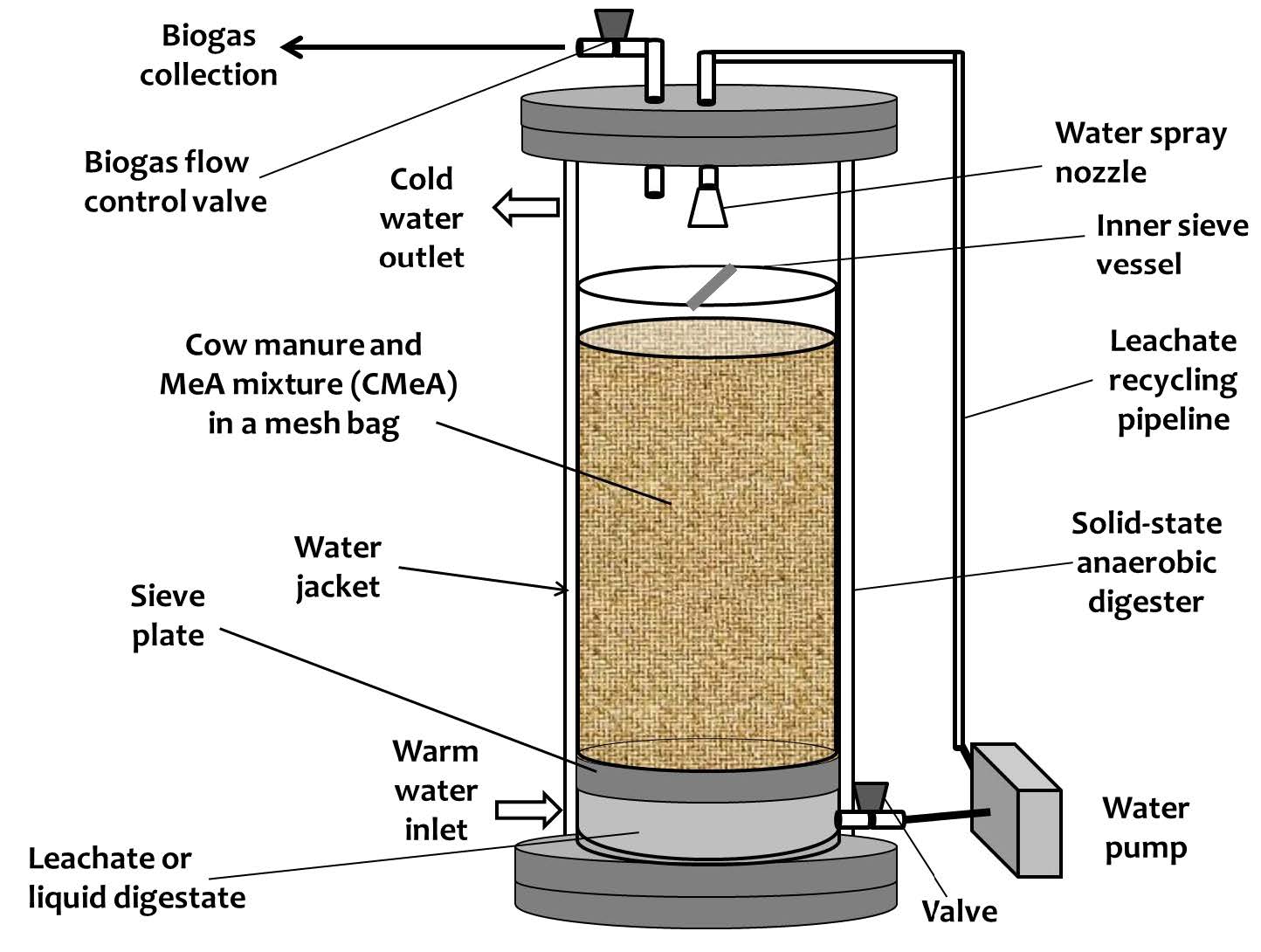
This study was conducted to evaluate the feasibility of applying a two-step biological treatment process, solid-state anaerobic digestion (SSAD) and black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) composting, for treating dairy cattle manure. Biogas from SSAD of dairy cattle manure, and the digestate of SSAD was fed to BSFL. In turn, BSFL can be fed to animals as a protein supplement. Adjustment of pH and 30% inoculation ratio (IR30) during SSAD produced the highest theoretical methane yield, 626.1±28.7 L CH4/kg VSdes, with an ultimate methane yield of 96.81±2.0 L CH4/kg VSload. For BSFL composting, the groups with a feeding rate of 75 and 100 mg/day/larvae had the highest body weight change, which was 969.6±28.4 and 984.1±177.6%, respectively. The combination process of SSAD and BSFL composting increases the incentive for dairy cattle manure treatment enabled higher waste removal efficiency, and produced more valuable products.