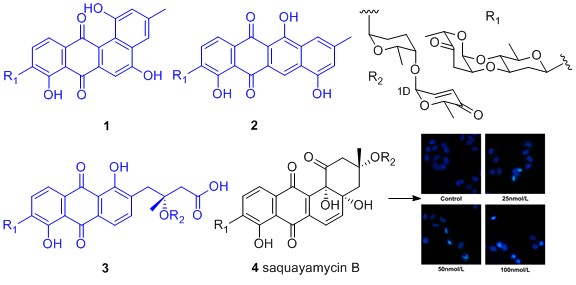
Four angucycline glycosides including three new compounds landomycin N (1), galtamycin C (2) and vineomycin D (3), and a known homologue saquayamycin B (4), along with two alkaloids 1-acetyl-β-carboline (5) and indole-3-acetic acid (6), were identified from the fermentation broth of an intertidal sediments derived Streptomyces sp. Their structures were mainly established by IR, HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR techniques. Among the isolated angucyclines, saquayamycin B displayed potent cytotoxic activity against hepatoma carcinoma cells HepG-2, SMMC-7721 and plc-prf-5, with IC50 values 0.135, 0.033 and 0.244 μM respectively, superior to positive drug doxorubicin. Saquayamycin B treatment to SMMC-7721 cells led to the typical morphological signs of apoptosis in 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining experiment.