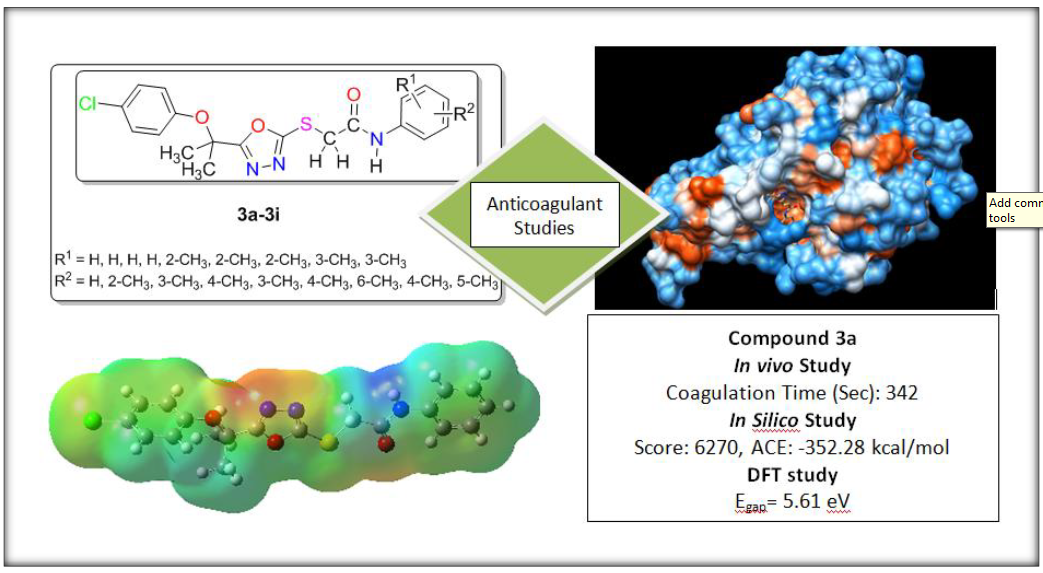
A new series of 1,3,4-oxadiazoles derivatives was synthesized, characterized and evaluated for their in vitro and in vivo anti-thrombotic activity. Compounds (3a-3i) exhibited significant clot lysis with respect to negative control and reference drug streptokinase (30,000 IU) while enhanced clotting time (CT) values were observed (130-342 sec) for these tested compounds than the standard drug heparin (110 sec.). High affinity towards 1NFY with greater docking score was observed for the compounds (3a, 3i, 3e, 3d and 3h) than the control ligand RPR200095. In addition, very good inhibitory potential against factor Xa (F-Xa) was observed with higher docking scores (5612-6270) with ACE values (–189.68 to –352.28 kcal/mol) than the control ligand RPR200095 (Docking score 5192; ACE –197.81 kcal/mol. In vitro, in vivo and in silico results proposed that these newly synthesized compounds can be used as anti-coagulant agents.