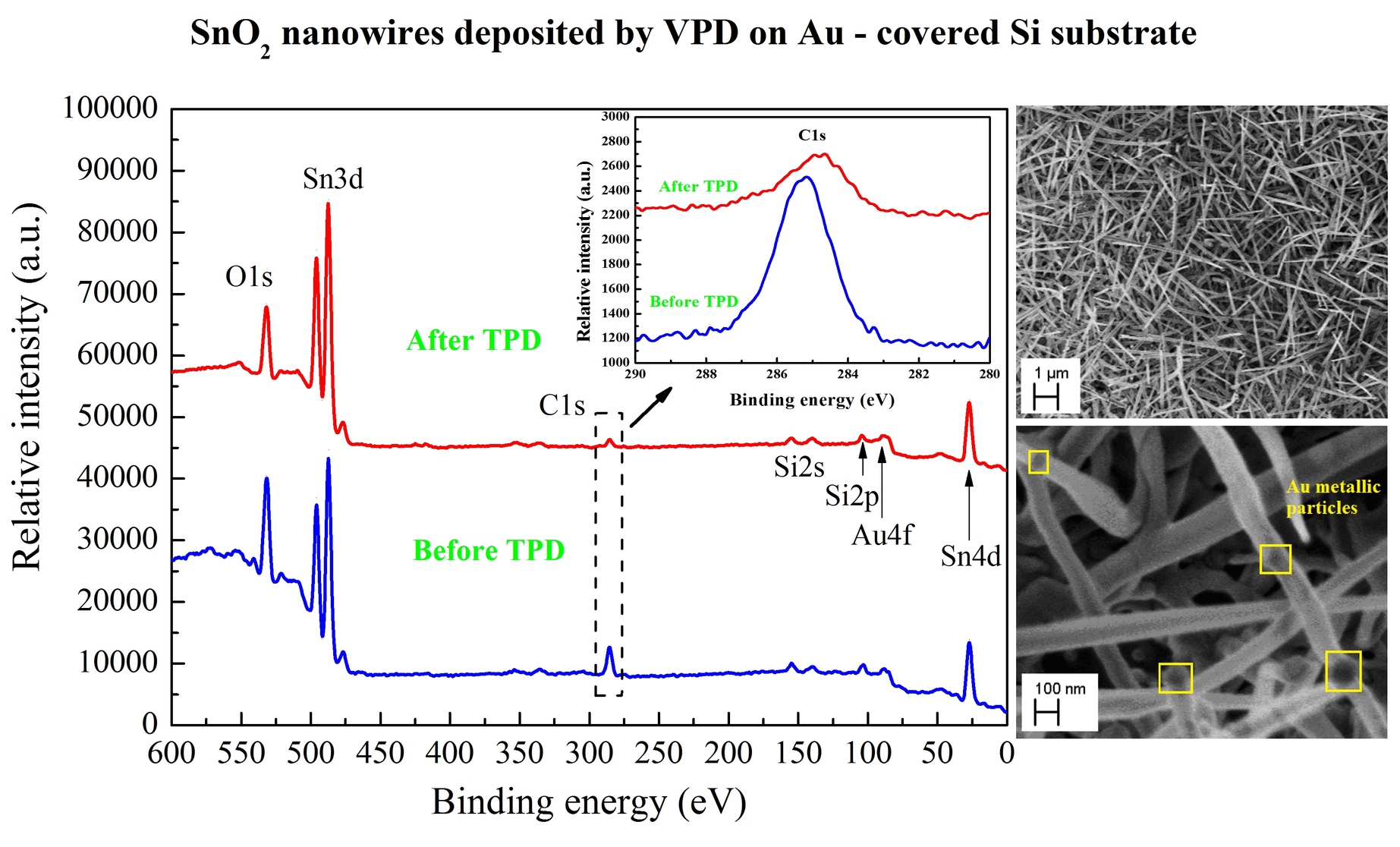
The surface chemistry and the morphology of SnO2 nanowires, deposited by Vapour Phase Deposition (VPD) method on Au-covered silicon substrate, were studied before and after subsequent air exposure. For this purpose, surface-sensitive methods including X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Thermal Desorption Spectroscopy (TDS) and the Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) were applied. The studies presented within this paper allowed to determine the surface non-stoichiometry combined with the presence of carbon contaminations, in a good correlation with the surface morphology. The relative concentrations of the main components [O]/[Sn]; [C]/[Sn]; [Au]/[Sn] together with the O – Sn; O – Si bondings were analyzed. The results of TDS remained in a good agreement with the observations from XPS. Moreover, conclusions obtained for SnO2 nanostructures deposited with the use of Au catalyst were compared to the previous obtained for Ag-assisted tin dioxide nanowires. The information obtained within this studies are of great importance for the potential application of SnO2 nanowires deposited on Au covered Si substrate in the field of novel chemical nanosensor devices, since the results can provide an interpretation of how aging effects influence gas sensor dynamic characteristics.