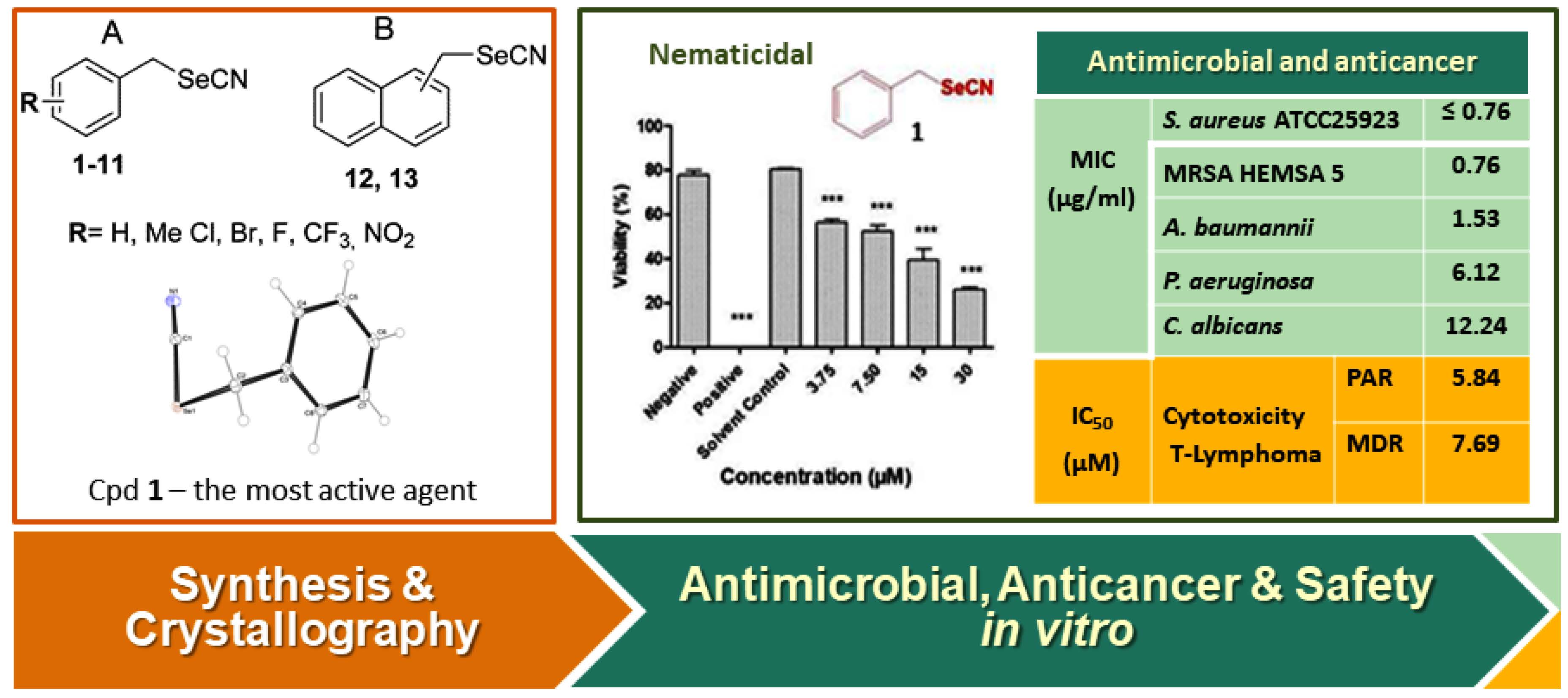
Selenocyanates form an interesting class of organic selenium compounds as they serve as multifunctional agents (being the precursors of seleninic acids and diselenides in synthetic chemistry and as antimicrobial and cytotoxic agent in biology) and, due to their similarity with better known thiocyanates promise high biological activity. Yet whilst selenocyanates are common in synthetic chemistry, they are rarely considered in pharmaceutical design. Arylmethyl selenocyanates (1-13) have been synthesized and an insight into their structural properties using X-ray crystallography has been obtained. The compounds subsequently have been evaluated for their potential antimicrobial, nematicidal and cytotoxic activity. ADMET properties in vitro, using mutagenicity (AMES) and permeability (PAMPA) tests, have been determined. The compounds exhibit pronounced activity against various strains of bacteria (both Gram-positive and Gram-negative) and yeasts. Among them, benzylselenocyanate (1) represents the most active anti-ESKAPE agent, with potent antibacterial activity, especially against multidrug resistant MRSA strains (HEMSA 5). Our results demonstrate that the arylmethyl selenocyantes are not only non-mutagenic but also possess moderate cytotoxic activity against cancer cells.