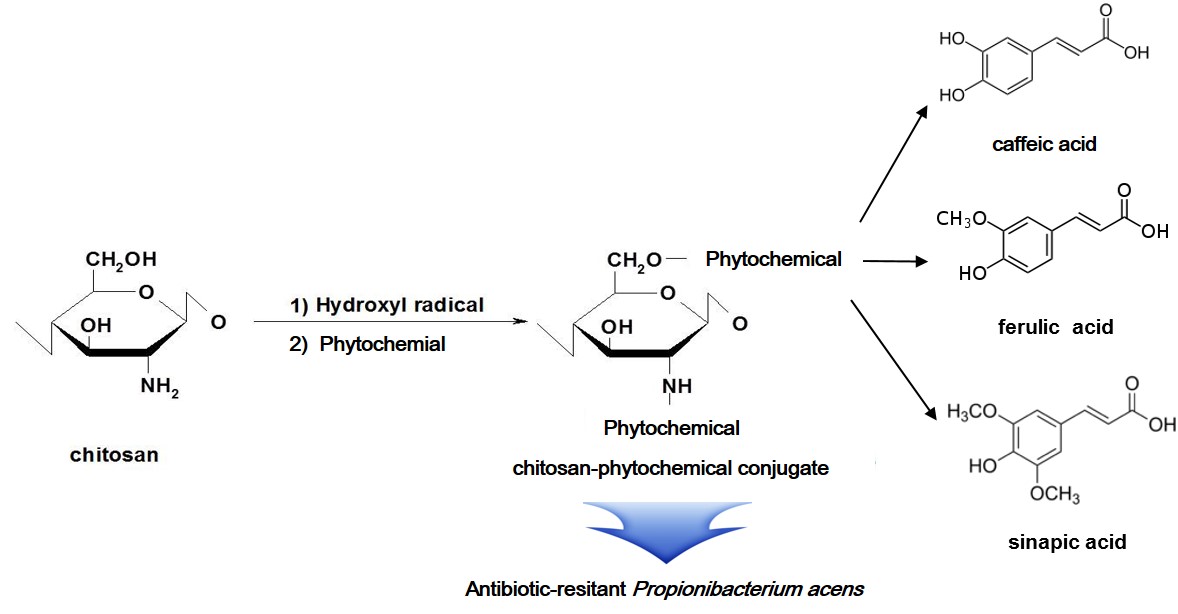
The object of this study was to discover an alternative therapeutic agent with fewer side effects against acne vulgaris, which is one of the most common skin diseases. Acne vulgaris often associates with acne-related bacteria such as <i>Propionibacterium acnes</i>, <i>Staphylococcus epidermidis</i>, <i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> and <i>Pseudomonas aeruginosa</i>, some of which exhibit a resistant against commercial antibiotics used in the treatment of acne vulgaris (tetracycline, erythromycin, and lincomycin). In the current study, we evaluated <i>in vitro</i> antibacterial activity of chitosan-phytochemical conjugates against acne-related bacteria. Three of chitosan-phytochemical conjugates used in this study showed stronger antibacterial activity than that of chitosan (unmodified control). Chitosan-caffeic acid conjugate (CCA) exhibited the highest antibacterial activity against acne-related bacteria with minimum inhibitory concentration values of 8 μg/mL to 256 μg/mL. In addition, the MICs of antibiotics against antibiotic resistant <i>P. acnes</i> and <i>P. aeruginosa</i> strains were dramatically reduced in the combination with CCA, suggesting that CCA would restore the antibacterial activity of the antibiotics. The analysis of fractional inhibitory concentration indices clearly revealed a synergistic antibacterial effect between CCA and the antibiotics. Thus, the median ∑FIC values against the antibiotic resistant bacterial strains were ranged from 0.375 to 0.533 in the combination mode of CCA and antibiotics.