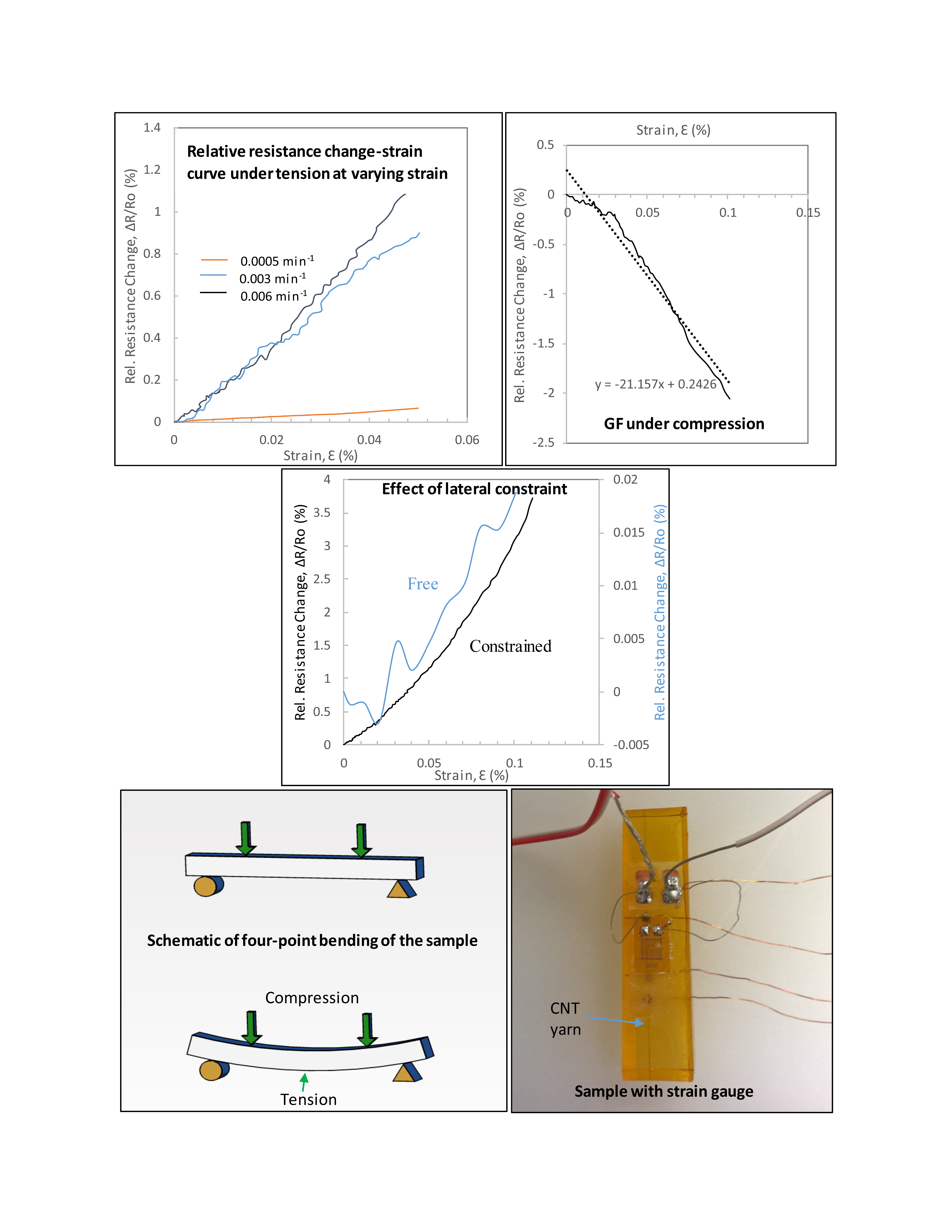
Carbon nanotube (CNT) yarns are fiber-like materials that exhibit excellent mechanical, electrical and thermal properties. More importantly, they exhibit a piezoresistive response that can be tapped for sensing purposes. The objective of this study is to determine experimentally the piezoresistive response of CNT yarns that are embedded in a polymeric medium while subjected to either compression or tension, and compare it with that of the free or unconstrained CNT yarns. The rationale for this study is the need to know the response of the CNT yarn while in a medium, which provides a lateral constraint to the CNT yarn thus mimicking the response of integrated CNT yarn sensors. The experimental program will include the fabrication of samples and their electromechanical characterization. The CNT yarns are integrated in polymeric beams and subjected to four-point bending, allowing the determination of their response under tension and compression. The electrical resistance data from an Inductance-Capacitance-Resistance (LCR) device is used with the data acquired from the mechanical testing system to determine the piezoresistive response of the CNT yarns. This data and information will be used for future modeling efforts and to study the phenomena that occur when CNT yarns are integrated in polymeric and composite materials and structures.