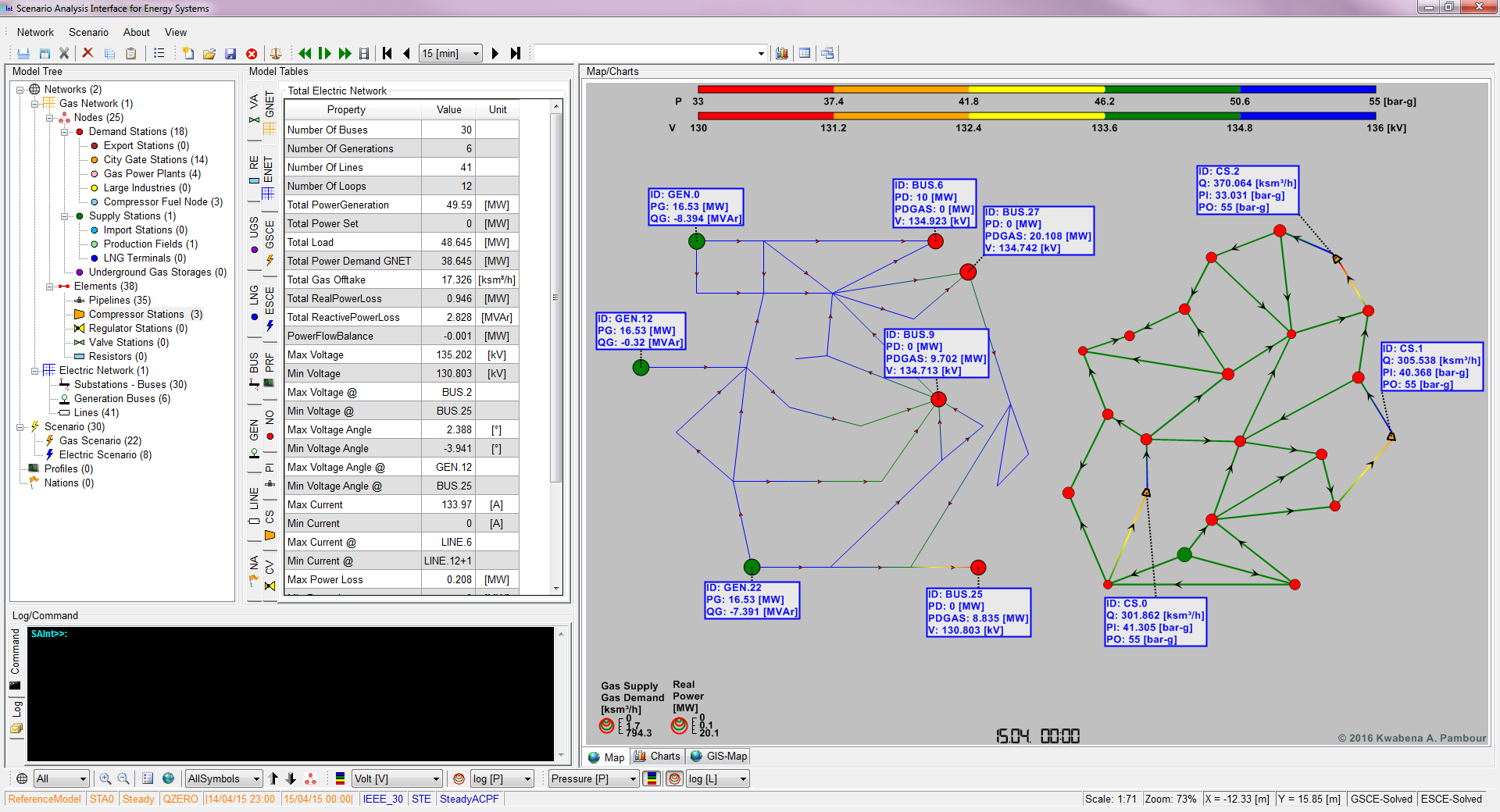
Gas and power networks are tightly coupled and interact with each other due to physically interconnected facilities. In an integrated gas and power network, a contingency observed in one system may cause iterative cascading failures, resulting in network wide disruptions. Therefore, understanding the impacts of the interactions in both systems is crucial for governments, system operators, regulators and operational planners, particularly, to ensure security of supply for the overall energy system. Although simulation has been widely used in the assessment of gas systems as well as power systems, there is a significant gap in simulation models that are able to address the coupling of both systems. In this paper, a simulation framework that models and simulates the gas and power network in an integrated manner is proposed. The framework consist of a transient model for the gas system and a steady state model for the power system based on AC-Optimal Power Flow. The gas and power system model are coupled through an interface which uses the coupling equations to establish the data exchange and coordination between the individual models. The bidirectional interlink between both systems considered in this studies are the fuel gas offtake of gas fired power plants for power generation and the power supply to LNG terminals and electric drivers installed in gas compressor stations and underground gas storage facilities. The simulation framework is implemented into an innovative simulation tool named SAInt (Scenario Analysis Interface for Energy Systems) and the capabilities of the tool are demonstrated by performing a contingency analysis for a real world example. Results indicate how a disruption triggered in one system propagates to the other system and affects the operation of critical facilities. In addition, the studies show the importance of using transient gas models for security of supply studies instead of successions of steady state models, where the time evolution of the line pack is not captured correctly.