Submitted:
13 January 2026
Posted:
14 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
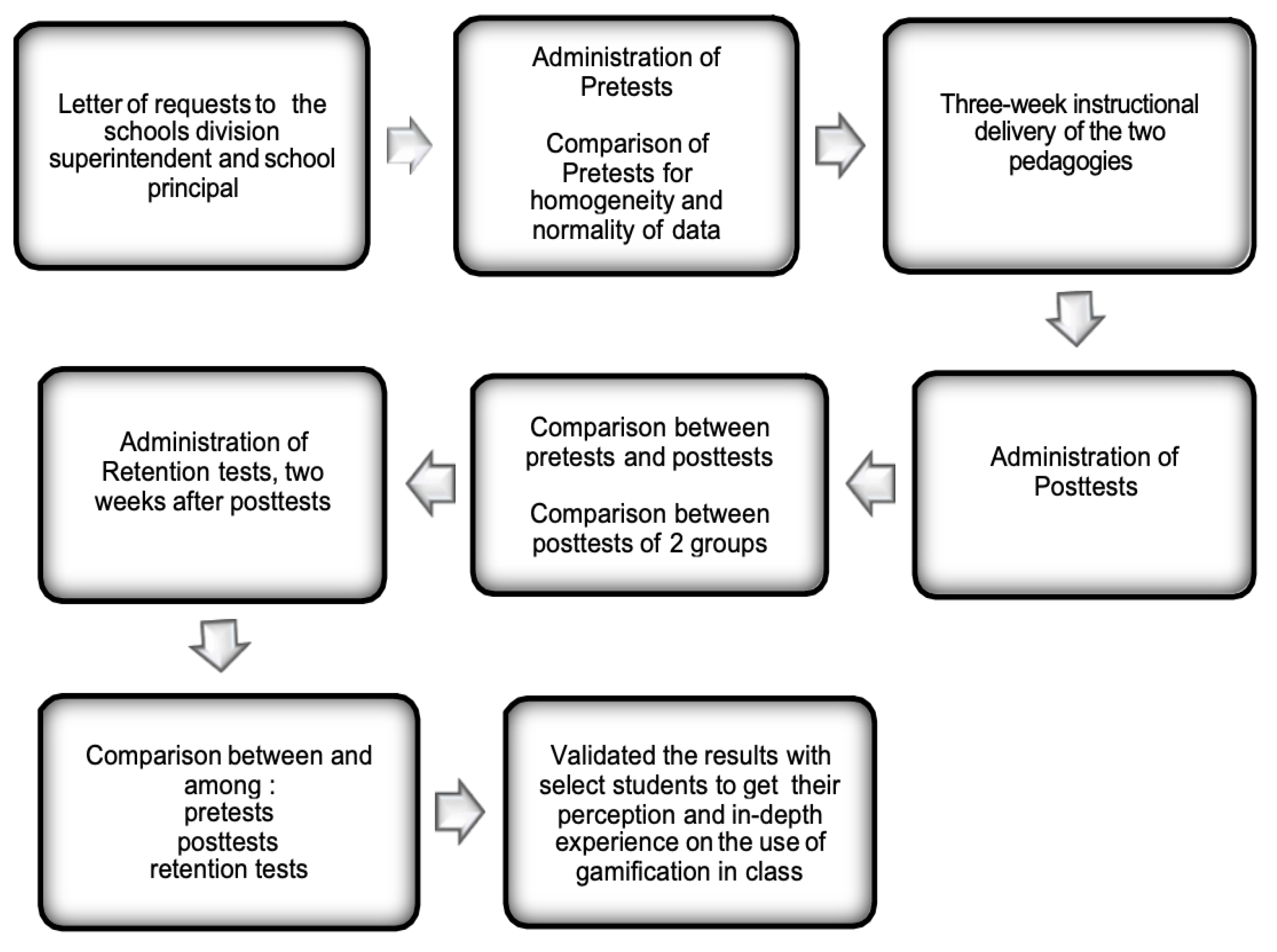
Methodology
Research Design
Respondents of the Study
Research Instrument
Gamification
Course Implementation
Data Gathering Procedure
Data Analysis Procedure
Results and Discussions
Level of Performance Between Conventional and Intervention Groups
Comparison of Test Performance of the Conventional Group
Comparison of Test Performance of the Intervention Group
Comparison of Concept Retention Between the Conventional and Intervention Groups
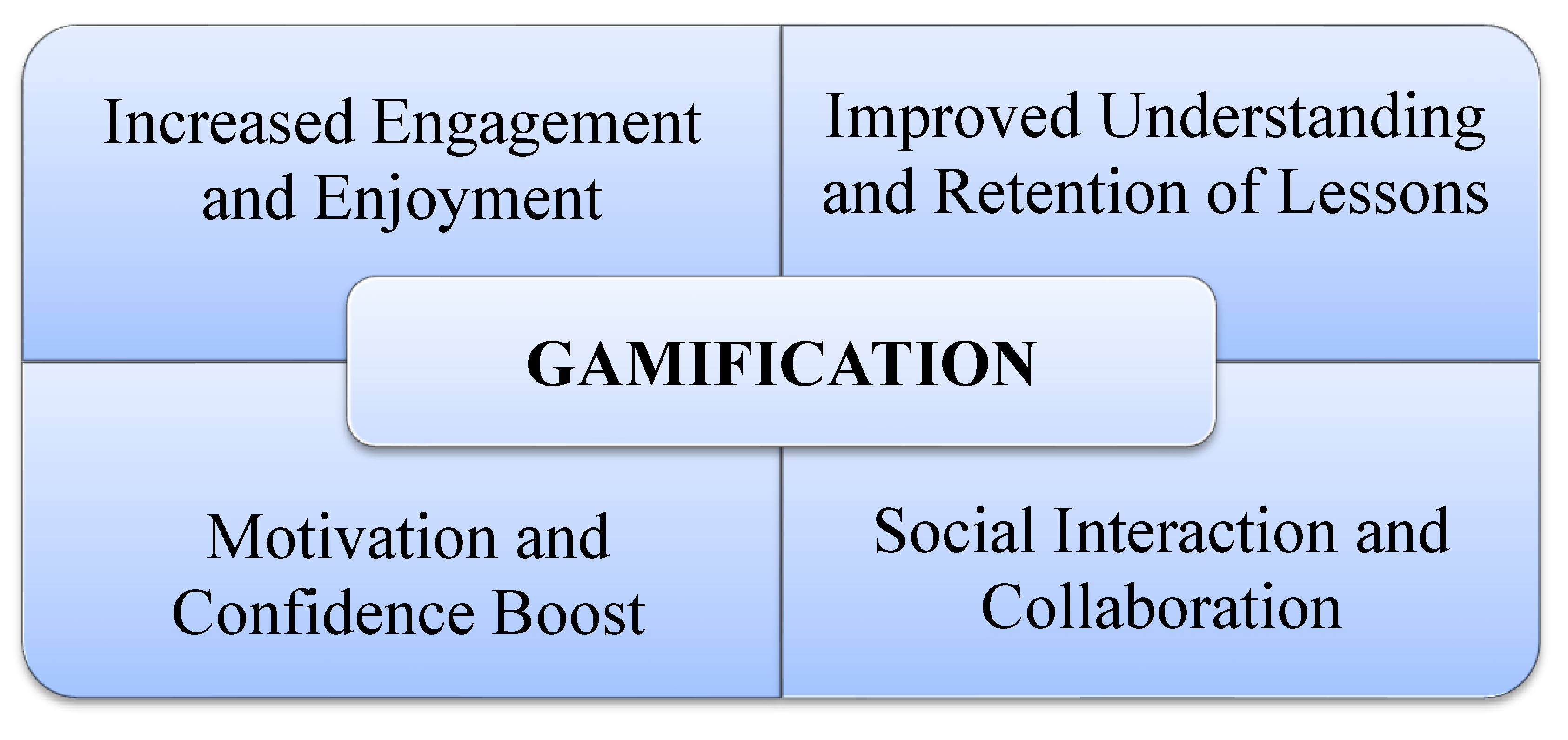
Perception of Students on the Use of Gamification
Increased Engagement and Enjoyment
Improved Understanding and Retention of Lessons
Motivation and Confidence Boost
Social Interaction and Collaboration
Conclusion
Recommendations
Implications
References
- Abdelrahman, G., & Wang, Q. (2019). Knowledge tracing with sequential key-value memory networks. In Proceedings of the 42nd international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (pp. 175-184). https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3331184.3331195. [CrossRef]
- Abed Khasawneh, Y. J., Khasawneh, N., & Saleem Khasawneh, M. A. (2024). Exploring the long-term effects: Retention and transfer of skills in gamified learning environment. International Journal of Data & Network Science, 8(1).
- Almusharraf, N. (2023). Incorporation of a game-based approach into the EFL online classrooms: students’ perceptions. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(7), 4440-4453. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2021.1969953. [CrossRef]
- Babicz, S. (2025). Comparing Learning Outcomes in Traditional and Gamified Lecture Formats. In Conference Proceedings. The Future of Education 2025. https://conference.pixel-online.net/library_scheda.php?id_abs=7492.
- Bouchrika, I., Harrati, N., Wanick, V., & Wills, G. (2021). Exploring the impact of gamification on student engagement and involvement with e-learning systems. Interactive Learning Environments, 29(8), 1244-1257. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2019.1623267. [CrossRef]
- Cameron, K. E., & Bizo, L. A. (2019). Use of the game-based learning platform KAHOOT! to facilitate learner engagement in Animal Science students. Research in Learning Technology, 27. https://journal.alt.ac.uk/index.php/rlt/article/view/2225. [CrossRef]
- Candel, E. C., de-la-Peña, C., & Yuste, B. C. (2024). Pre-service teachers’ perception of active learning methodologies in history: Flipped classroom and gamification in an e-learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 29(3), 3365-3387. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10639-023-11924-0. [CrossRef]
- Candel, E. C., de-la-Peña, C., & Yuste, B. C. (2024). Pre-service teachers’ perception of active learning methodologies in history: Flipped classroom and gamification in an e-learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 29(3), 3365-3387. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10639-023-11924-0. [CrossRef]
- Chans, G. M., & Portuguez Castro, M. (2021). Gamification as a strategy to increase motivation and engagement in higher education chemistry students. Computers, 10(10), 132. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-431X/10/10/132. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R. J. F. (2023). STEM STUDENTS’DIRECT AND DEFERRED CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING AND SELF-EFFICACY USING THE INVERTED LEARNING APPROACH IN BIOLOGY: AN EXPLANATORY SEQUENTIAL MIXED METHODS STUDY.
- Costello, R. (Ed.). (2020). Gamification Strategies for Retention, Motivation, and Engagement in Higher Education: Emerging Research and Opportunities: Emerging Research and Opportunities. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=NTDeDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR1&dq=Importance+of+researching+gamification+in+education+and+engagement+strategies&ots=r6L0NmQneT&sig=AhNYL_EiqgwYrZdunPqoW5h0bc8.
- Dewi, P. Y. A., & Primayana, K. H. (2019). Effect of learning module with setting contextual teaching and learning to increase the understanding of concepts. International Journal of Education and Learning, 1(1), 19-26. https://www.pubs2.ascee.org/index.php/ijele/article/view/26. [CrossRef]
- Dichev, C., Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education: what is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: a critical review. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 14, 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0042-5. [CrossRef]
- Duggal, K., Gupta, L. R., & Singh, P. (2021). Gamification and machine learning inspired approach for classroom engagement and learning. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021(1), 9922775. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1155/2021/9922775. [CrossRef]
- Ehsanpur, S., & Razavi, M. R. (2020). A Comparative analysis of learning, retention, learning and study strategies in the traditional and M-learning systems. European Review of Applied Psychology, 70(6), 100605. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1162908820301171. [CrossRef]
- Eze, T. I., Onwusuru, I. M., & Ginigeme, O. O. (2021). Gender-relative Effect of Project-Based Learning Method on Academic Achievement AND retention of Technical College Students in Basic Electricity. NAU Journal of Technology and Vocational Education, 6(1). https://journals.unizik.edu.ng/naujtved/article/download/4844/3976.
- Felszeghy, S., Pasonen-Seppänen, S., Koskela, A., Nieminen, P., Härkönen, K., Paldanius, K. M., ... & Mahonen, A. (2019). Using online game-based platforms to improve student performance and engagement in histology teaching. BMC medical education, 19(1), 273. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12909-019-1701-0. [CrossRef]
- Fitrianto, I., & Saif, A. (2024). The role of virtual reality in enhancing Experiential Learning: a comparative study of traditional and immersive learning environments. International Journal of Post Axial: Futuristic Teaching and Learning, 97-110. https://journal.amorfati.id/index.php/postaxial/article/view/300.
- Fowler, S., Roush, R., & Wise, J. (2024). Concepts of biology. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=H34gEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT8&dq=Strategies+to+simplify+complex+Biology+concepts+for+better+student+engagement+and+understanding&ots=vpbp4CCp2Y&sig=_Yo6_k7jS9YQKz7TO2avPtOcQjo.
- Gambari, A. I., Sobowale, F. M., Owotomi, A. D., & Mohammed, A. N. (2024). Effects of Gimkit Gamification Software on the Achievement and Retention of Senior Secondary School Biology Students in Minna Metropolis. http://irepo.futminna.edu.ng:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/29691.
- Gaurina, M., Alajbeg, A., & Weber, I. (2025). The power of play: Investigating the effects of gamification on motivation and engagement in physics classroom. Education sciences, 15(1), 104. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/15/1/104. [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, A. Y., & Akkoyunlu, B. (2020). Effectiveness of gamification in flipped learning. Sage Open, 10(4), 2158244020979837. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/2158244020979837. [CrossRef]
- Guskey, T. R. (2022). Implementing mastery learning. Corwin Press. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=SICKEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Benefits+of+instructional+games+in+education+for+skills+and+concept+mastery&ots=08HWZKbC3x&sig=ERcEv-k3wsGjFFE7O1SWCYtFalQ.
- Gute, B. D., & Wainman, J. W. (2019). Factors influencing student engagement, motivation, and learning: Strategies to enhance student success and retention. In From general to organic chemistry: Courses and curricula to enhance student retention (pp. 159-172). American Chemical Society. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bk-2019-1341.ch012. [CrossRef]
- Hodges, L. C. (2020). Student engagement in active learning classes. In Active learning in college science: The case for evidence-based practice (pp. 27-41). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-33600-4_3. [CrossRef]
- Huang, R., Ritzhaupt, A. D., Sommer, M., Zhu, J., Stephen, A., Valle, N., ... & Li, J. (2020). The impact of gamification in educational settings on student learning outcomes: A meta-analysis. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68(4), 1875-1901. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11423-020-09807-z. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. T., & Wang, T. H. (2025). Effect of integrating gamified teaching activities on learning emotions of design students with different learning styles. Interactive Learning Environments, 33(5), 3614-3634. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2024.2446538. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. T., & Wang, T. H. (2025). Effect of integrating gamified teaching activities on learning emotions of design students with different learning styles. Interactive Learning Environments, 33(5), 3614-3634. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2024.2446538. [CrossRef]
- James, C. R. (2024). Students’ Direct and Deferred Concept Understanding and Self-Efficacy Using the Inverted Learning Approach in Biology. SEAQIS Journal of Science Education, 4(02), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Jo, J., Jun, H., & Lim, H. (2018). A comparative study on gamification of the flipped classroom in engineering education to enhance the effects of learning. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 26(5), 1626-1640. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cae.21992. [CrossRef]
- Jones, S. M., Katyal, P., Xie, X., Nicolas, M. P., Leung, E. M., Noland, D. M., & Montclare, J. K. (2019). A ‘KAHOOT!’approach: The effectiveness of game-based learning for an advanced placement biology class. Simulation & Gaming, 50(6), 832-847. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1046878119882048. [CrossRef]
- Lai, A. K. H., Noor Azhar, A. M. B., Bustam, A. B., Tiong, X. T., Chan, H. C., Ahmad, R. B., & Chew, K. S. (2020). A comparison between the effectiveness of a gamified approach with the conventional approach in point-of-care ultrasonographic training. BMC Medical Education, 20(1), 263. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12909-020-02173-7. [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G., & Sidiropoulos, A. (2024). Impact of gamification on students’ learning outcomes and academic performance: A longitudinal study comparing online, traditional, and gamified learning. Education Sciences, 14(4), 367. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/14/4/367. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. F., Chen, P. Y., & Cheng, S. C. (2024). Improve learning retention, self-efficacy, learning attitude and problem-solving skills through e-books based on sequential multi-level prompting strategies. Education and Information Technologies, 29(3), 3663-3680. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10639-023-11994-0. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Hew, K. F., & Du, J. (2024). Gamification enhances student intrinsic motivation, perceptions of autonomy and relatedness, but minimal impact on competency: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Educational technology research and development, 72(2), 765-796. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11423-023-10337-7. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Hew, K. F., & Du, J. (2024). Gamification enhances student intrinsic motivation, perceptions of autonomy and relatedness, but minimal impact on competency: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Educational technology research and development, 72(2), 765-796. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11423-023-10337-7. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., & Elms, P. (2019). Animating student engagement: The impacts of cartoon instructional videos on learning experience. Research in Learning Technology, 27. https://journal.alt.ac.uk/index.php/rlt/article/view/2124.
- Liu, Z. Y., Shaikh, Z., & Gazizova, F. (2020). Retracted article: using the concept of game-based learning in education. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(14), 53-64. https://www.learntechlib.org/d/217589/.
- Mangintay, H., Sofianidis, A., & Cheng, R. J. (2025). Students’ Performance and Self-Efficacy Using the Design Thinking Model in Grade 7 Science.
- Mula-Falcón, J., Moya-Roselo, I., & Ruiz-Ariza, A. (2022). The active methodology of gamification to improve motivation and academic performance in educational context: A meta-analysis. Rev. Eur. Stud., 14, 32. https://heinonline.org/hol-cgi-bin/get_pdf.cgi?handle=hein.journals/rveurost14§ion=17.
- Nguyen-Viet, B., Nguyen-Duy, C., & Nguyen-Viet, B. (2025). How does gamification affect learning effectiveness? The mediating roles of engagement, satisfaction, and intrinsic motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 33(3), 2635-2653. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2024.2414356. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Viet, B., Nguyen-Duy, C., & Nguyen-Viet, B. (2025). How does gamification affect learning effectiveness? The mediating roles of engagement, satisfaction, and intrinsic motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 33(3), 2635-2653. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2024.2414356. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C. Q., Carmo, B. P. R., & Andrade, L. C. C. (2025). Randomized study: lecture versus gamification in knowledge retention in Medical students. Revista Brasileira de Educação Médica, 49, e025. https://www.scielo.br/j/rbem/a/QyXyLDwdZcXZXJgZsnw4vgf/?lang=en. [CrossRef]
- Omeh, C. B., & Olelewe, C. J. (2021). Assessing the effectiveness of innovative pedagogy and lecture method on students academic achievement and retention in computer programming. Education Research International, 2021(1), 5611033. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rojas, M., Chiluiza, K., & Valcke, M. (2019). Gamification through leaderboards: An empirical study in engineering education. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 27(4), 777-788. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cae.12116. [CrossRef]
- Owoc, M. L., Sawicka, A., & Weichbroth, P. (2019). Artificial intelligence technologies in education: benefits, challenges and strategies of implementation. In IFIP international workshop on artificial intelligence for knowledge management (pp. 37-58). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-85001-2_4. [CrossRef]
- Putz, L. M., Hofbauer, F., & Treiblmaier, H. (2020). Can gamification help to improve education? Findings from a longitudinal study. Computers in Human Behavior, 110, 106392. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S074756322030145X. [CrossRef]
- Putz, L. M., Hofbauer, F., & Treiblmaier, H. (2020). Can gamification help to improve education? Findings from a longitudinal study. Computers in Human Behavior, 110, 106392. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S074756322030145X. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M. A., Khaskheli, A., Qureshi, J. A., Raza, S. A., & Yousufi, S. Q. (2023). Factors affecting students’ learning performance through collaborative learning and engagement. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(4), 2371-2391. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10494820.2021.1884886. [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, Y., Ridwan, A., Cahyana, U., & Wuryaningsih, T. (2020). The integration of ethnopedagogy in science learning to improve student engagement and cultural awareness. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(2), 662-671. https://www.academia.edu/download/73529843/UJER39-19514569.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Rai, B., Tan, H. S., & Leo, C. H. (2019). Bringing play back into the biology classroom with the use of gamified virtual lab simulations. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 2(2), 48-55. https://jalt.journals.publicknowledgeproject.org/index.php/jalt/article/view/139. [CrossRef]
- Raju, R., Bhat, S., Bhat, S., & Singh, A. B. (2021). Effective usage of gamification techniques to boost student engagement. Journal of Engineering Education Transformations, 713-717. https://journaleet.in/index.php/jeet/article/view/1522. [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E. S., & Garden, C. L. P. (2021). Gamification for student engagement: a framework. Journal of further and higher education, 45(7), 999-1012. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0309877X.2021.1875201. [CrossRef]
- Salama, W., & Daraghmi, Y. (2025). ENHANCING STUDENT ENGAGEMENT AND LEARNING OUTCOMES THROUGH GAMIFIED FLIPPED CLASSROOMS: A STUDY ON MOTIVATION, PERFORMANCE, AND RETENTION IN HIGHER EDUCATION. In EDULEARN25 Proceedings (pp. 8496-8500). IATED. https://library.iated.org/view/SALAMA2025ENH.
- Sionillo, J. (2024). Gamified Learning Approaches and Academic Performance in Cell and Molecular Biology of Second-Year BSED Science Students at Abuyog. Available at SSRN 5305205. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm?abstractid=5305205.
- Skinner, E. A., Rickert, N. P., Vollet, J. W., & Kindermann, T. A. (2022). The complex social ecology of academic development: A bioecological framework and illustration examining the collective effects of parents, teachers, and peers on student engagement. Educational Psychologist, 57(2), 87-113. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00461520.2022.2038603. [CrossRef]
- Suchyadi, Y., & Suharyati, H. (2021). The Use Of Multimedia As An Effort To Improve The Understanding Ability Of Basic School Teachers ‘Creative Thinking In The Era ‘Freedom Of Learning,’. Yogyakarta: Zahir Publishing, 42-53. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=dPwxEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA42&dq=Benefits+of+instructional+games+in+education+for+skills+and+concept+mastery&ots=_9Q09SlJqr&sig=mG9MFovLqK_N2Nxne1GkXMFMZWE.
- Taghipour, E., Vizeshfar, F., & Zarifsanaiey, N. (2023). The effect of gamification-based training on the knowledge, attitudes, and academic achievement of male adolescents in preventing substance and internet addiction. BMC Medical Education, 23(1), 860. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12909-023-04858-1. [CrossRef]
- Thongmak, M. (2019). The student experience of student-centered learning methods: Comparing gamification and flipped classroom. Education for Information, 35(2), 99-127. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.3233/EFI-180189. [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, E. O., Olulowo, T. G., & Adedayo, I. O. (2020). Using guided discovery to improve students’ retention and academic attitudes to financial accounting concepts. Education Research International, 2020(1), 6690082. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1155/2020/6690082. [CrossRef]
- Varol Selçuk, Z., & Özer Keskin, M. E. L. İ. K. E. (2024). Gamification in biology education: A systematic review analysis. Uluslararası Avrasya Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 15(55). https://avesis.gazi.edu.tr/yayin/6884fe4a-5a2f-410e-9b24-3ffd53df78e8/gamification-in-biology-education-a-systematic-review-analysis. [CrossRef]
- Winget, M., & Persky, A. M. (2022). A practical review of mastery learning. American journal of pharmaceutical education, 86(10), ajpe8906. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002945923007386. [CrossRef]
- Yuliansyah, A., & Ayu, M. (2021). The implementation of project-based assignment in online learning during covid-19. J. English Lang. Teach. Learn, 2(1), 32-38. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f395/a3af94eeafe2007cf5ac4dbd26eb8a84efcc.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, Z. (2018). Students’ learning performance and perceived motivation in gamified flipped-class instruction. Computers & education, 126, 75-88. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360131518301787.
- Zainuddin, Z.; Chu, S.K.W.; Shujahat, M.; Perera, C.J. (2020) The Impact of Gamification on Learning and Instruction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Evidence. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z., He, L., Tong, Y., Liang, X., Guo, S., & Lan, X. (2022). The effectiveness of gamification in programming education: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 3, 100096. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666920X22000510. [CrossRef]
| Gagne’s 9 Events of Instruction | Conventional Group (Standard Lecture) | Time Allotment | Intervention Group (Gamification) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gain Attention | Teacher starts with a brief question (prompt), or visual aid to stimulate curiosity. | 3 minutes | Leaners are introduced through a gem teaser or short challenge (Game Ka Na Ba? buzzer round) that reveals the objectives of the day. |
| Inform Learners of the Objectives | Teacher states learning objectives verbally | 2 minutes | Objectives presented as game goals or mission objectives |
| Stimulate Recall of Prior Learning | Teacher asks review questions about previous topic using Q and A or a short recitation. | 5 minutes | Interactive scenarios or problem-solving tasks are explored to to recall prior knowledge |
| Present the Content (Stimulus Material) | Teacher discusses new lesson with slides explaining Biology concepts and direct explanations. | 15 minutes | Students further explore examples through digital or board-based games that unlock content as they answer correctly. |
| Provide Learning Guidance | Teacher explains key points, uses diagrams, and more examples | 8 minutes | Students perform team-based tasks and earn nadges or tokens as they take hints, tips, and feedback embedded in the game environment |
| Elicit Performance (Practice) | Students answer questions or take notes, label diagrams or answer seat works. | 7 minutes | Students complete game tasks or engage in level-up or cooperative missions (e.g. Hormone Hero Role-Play). |
| Provide Feedback | Teacher reviews answers, clarifies misconceptions, and summarizes the lesson. | 5 minutes | Students generalize concepts through peer discussion supported by leaderbaord feedback from game system; they interpret their game performance and derive key ideas. |
| Assess Performance | Students answer written exercises, short quizzes, or textbook-based problems. | 8 minutes | Game level completion or score-based assessment; students complete timed quizzes. |
| Enhance Retention and Transfer | Teacher facilitates a short dicussion on real-life applications; or homework assignment | 7 minutes | Unlocking bonus levels or real-world scenario challenges; Students reflect on the lesson through scenario-based games (What Would You Do? cards) connecting biological concepts to real-life behavior and health. |
| Test Type | Group | Mean Score | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-test | Conventional | 20.96 | Low |
| Intervention | 22.38 | Low | |
| Post-test | Conventional | 43.84 | Moderate |
| Intervention | 44.96 | Moderate | |
| Retention-test | Conventional | 37.62 | Moderate |
| Intervention | 57.29 | High |
| Test Comparison | Mean difference | SD | t- value | p- value | Cohen’s d |
Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-test vs. Post-test | 22.88 | 7.68 | 13.04 | 0.00* | 0.78 | Moderate effect |
| Pre-test vs. Retention-test | 16.66 | 5.86 | 10.76 | 0.00* | 0.52 | Moderate effect |
| Post-test vs. Retention-test | 6.22 | 11.83 | 3.98 | 0.00* | 0.18 | Weak effect |
| Test Comparison | Mean difference | SD | t- value | p- value | Cohen’s d |
Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-test vs. Post-test | 22.58 | 7.80 | 13.45 | 0.00* | 0.80 | Moderate effect |
| Pre-test vs. Retention-test | 34.91 | 6.66 | 23.30 | 0.00* | 0.69 | Moderate effect |
| Post-test vs. Retention-test | 12.33 | 10.36 | 5.81 | 0.00* | 0.24 | Modest effect |
| Group | Mean | SD | t-value | p-value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 37.62 | 6.06 | 11.95 | 0.00* | significant |
| Intervention | 57.29 | 9.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.





