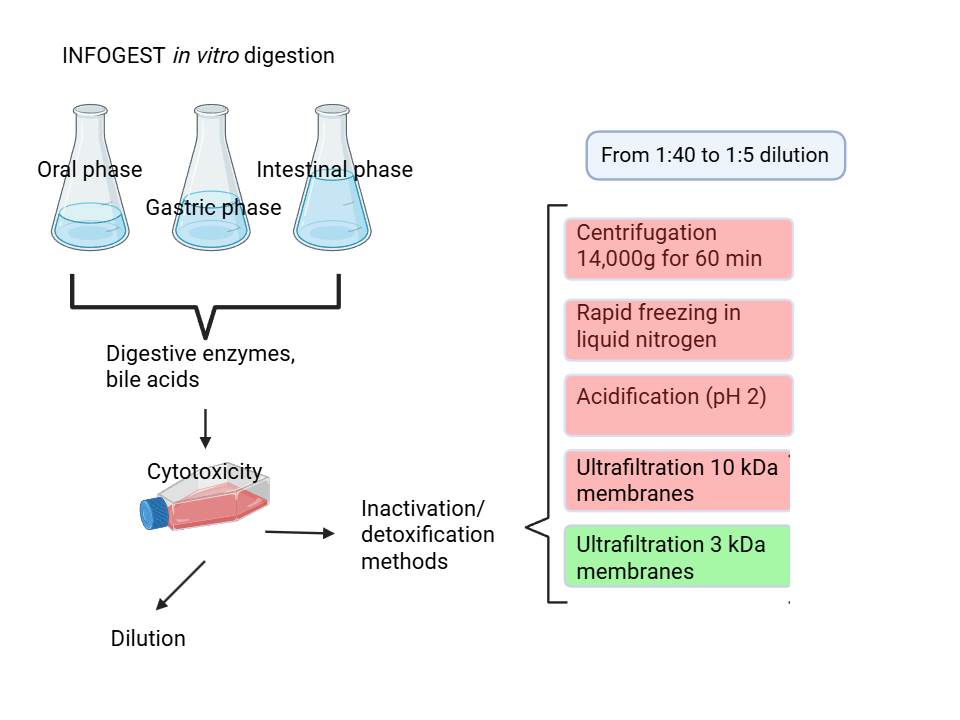
1. Introduction
In food and nutrition sciences, two concepts are gaining increasing importance: bioaccessibility and bioavailability. Bioaccessibility is the fraction of an ingested compound that is biochemically and/or physically released from the food matrix during digestion and becomes solubilized in gastrointestinal fluids in an absorbable form, thus becomes potentially available for absorption; bioavailability is the fraction of the ingested compound that is actually absorbed, reaches the systemic circulation (relative bioavailability), and then the target cells, tissues, or organs in the body [
1].
Understanding the bioavailability of nutrients and bioactive compounds is essential for accurately linking food composition to physiological effects. While the chemical composition of foods provides valuable information, only the fraction of a compound that becomes bioaccessible during digestion and is subsequently absorbed through the intestinal epithelium can exert biological activity. Consequently, the assessment of bioaccessibility and bioavailability has become a central aspect of contemporary nutrition research.
Although the mechanisms that make a food component bioaccessible and bioavailable vary depending on the nature of the component itself (macronutrients, micronutrients and bioactives), they nevertheless represent a critical bottleneck for biological activity. It is therefore evident that it is necessary to verify the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of nutrients and bioactives before evaluating the effects of a food.
In vitro approaches are increasingly employed to investigate these processes, and several models have been developed to measure bioaccessibility
in vitro. Among them, INFOGEST [
2] is a widely recognized standardized static model [
3] that shows good correlation with
in vivo animal feeding studies [
4] and is extensively used to estimate nutrient bioaccessibility across different food matrices.
In vitro assessment of relative bioavailability is much more difficult, and currently
in vivo methods, which rely on measuring a compound of interest in blood, represent the "gold standard." However, these studies present ethical issues and are time- and resource-intensive [
4]. To assess the absorption of bioaccessible compounds, cellular models are frequently used, including both cultured intestinal cells (
in vitro models) and intestinal fragments (
ex vivo models). Caco-2 cells, human cells that derive from a colorectal adenocarcinoma and spontaneously differentiate into enterocyte-like cells at confluence [
5] are among the most used models, sometimes in combination with mucus-secreting HT29-MTX cells. To evaluate absorption and metabolism through intestinal cells, Caco-2 are grown on cell culture inserts that allow for an apical chamber (intestinal lumen) and a basolateral chamber representing the blood compartment.
To realistically simulate the
in vivo situation, the cell models are combined with
in vitro digestion models. This combination of the two
in vitro methodologies, however, poses a major problem because the digest obtained through
in vitro static digestion protocols such as INFOGEST contains digestive enzymes and bile salts at concentrations that can impair viability and barrier integrity in epithelial cell models such as Caco-2 [
6]. Osmolality can also be a problem, since increase in osmolality caused by food components in the digesta can enhance paracellular permeability of the Caco-2 monolayer [
7].
Various approaches have been developed to make the INFOGEST digest compatible with cell cultures, as reviewed by Kondrashina et al. [
6]. These include dilution, heat inactivation, enzyme inhibition, filtration, centrifugation, pH, and dialysis, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. Currently, no consensus protocol has been established. This lack of standardization hampers reproducibility and complicates comparisons between studies.
The present study addresses this methodological gap by systematically comparing five commonly used digest conditioning strategies with the aim of identifying an approach that preserves intestinal epithelial integrity while enabling exposure at physiologically relevant concentrations. To this end, by examining the most frequently used conditioning approaches, we selected the most physiological and least time-consuming ones [
6]. All experiments were performed in parallel with a blank digest (digestion without any food) conditioned with the same procedure, to allow distinguishing between potential toxic effects of the intrinsic digestive juices and the food component. We hypothesized that digest conditioning would differentially improve the biocompatibility of INFOGEST digests, enabling identification of a procedure that maintains Caco-2 viability and barrier function and supports discrimination between effects of digestive fluids and food-derived components.
By focusing on multiple food matrices, this work seeks to provide practical guidance for improving the reliability and comparability of in vitro nutrient bioavailability studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) high glucose, DMEM without phenol red, penicillin, streptomycin, non-essential amino acids, and Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, United States). Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) was bought from Euroclone (Milan, Italy). Trypan blue was provided by Bio-Rad Laboratories (Hercules, United States). Corning Transwell 12-well plates were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). All other chemicals and solvents were of the highest analytical grade from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Food Samples
Three different commercial foods were considered: whole yogurt, biscuits, and canned mackerel. All food samples were purchased at a local market. The chemical composition of the foods under examination, as reported in the nutritional label, is shown in supplementary Table 1.
2.3. In Vitro Digestion
Five grams of each food were
in vitro digested according to the INFOGEST protocol [
2]. Each time, a blank digestion was carried forward using the same procedure, replacing the food sample with water (5 mL). The digestion was carried out at 37 °C and included a 2-min oral phase at pH 7, a 120-min gastric phase at pH 3, and a 120-min intestinal phase at pH 7. During the different phases, simulated salivary fluid (containing 75U/mL of amylase), simulated gastric fluid (containing 2000U/mL of pepsin), and simulated pancreatic fluid (containing 160mM of bile and an amount of pancreatin such that the trypsin activity in the final mixture was 100U/mL) were added, respectively. At the end of the intestinal digestion, samples were centrifuged at 4500 × g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the supernatants were aliquoted into different tubes to be subsequently treated with the different conditioning protocols.
2.4. Digest Conditioning
To mitigate the reported toxic effects [
6], yogurt digests were conditioned with different protocols: (i) acidification to pH 2.0 using 1 M HCl (adapted from Cilla et al., [
8]); (ii) centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 60 min at 4 °C [
9]; (iii) ultrafiltration at 4,000 × g for 60 min at 4° C using 10 kDa and (iv) 3 kDa cut-off membranes (Vivaspin 20) [
10,
11]; (v) rapid freezing in liquid nitrogen for 35s [
12]. After treatment, digests were sterile-filtered (0.22 µm) and stored at −80 °C until use. Biscuits and canned mackerel digests were conditioned with ultrafiltration on 10kDa and 3kDa membranes, sterile-filtered (0.22 µm) and stored at −80 °C until use.
2.5. Caco-2 Cell Culture and Supplementation
Experiments were carried out using Caco-2 cells (European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures (ECACC) cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 4.5 g/L glucose, supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% L-glutamine, 1% non-essential amino acids (NEAAs), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin, at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. The medium was refreshed every 2 days, and cells were passaged when reaching 80% confluence. Caco-2 cells were used between passages 24 and 38 for all experiments. For experiments, cells were seeded on Transwell 12-well plates (Corning Incorporated, New York, NY, USA) at 1 × 105 cells/mL and differentiated for 21 days. Differentiation was confirmed by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement using a Millicell ERS apparatus (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). TEER values between 1000 and 2000 Ω*cm2 were considered acceptable for the assay. Indeed, in Caco-2 intestinal monolayers TEER values have been observed from ~600 up to ~2800 Ω·cm² under various conditions, with values above ~1000 Ω·cm² consistent with established barrier formation and used as an integrity benchmark in the literature. Additionally, modern TEER measurement systems are validated across ranges up to ~2000 Ω·cm², further supporting the use of this range as acceptable for assessing intact epithelial resistance [
13,
14].
After complete differentiation, apical and basal compartments were washed twice with 1 mL phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and supplemented with the conditioned digests at decreasing dilutions (from 1:40 to 1:5) in serum-free, phenol red-free DMEM for 2–4 h. Controls received only DMEM. All results are the mean ± SD of at least two independent experiments.
2.6. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
Cytotoxicity was assessed by evaluating cell viability and monolayer integrity. Cell viability was measured with the methylthiazolyldi-phenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) colorimetric assay [
15] using a Tecan Infinite F200 microplate reader (Tecan), and it was expressed as a percentage of control cells (assigned as 100%). Monolayer integrity was evaluated by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement using a Millicell ERS apparatus (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). TEER was measured immediately before and immediately after the end of the treatment, and percent TEER was calculated as
TEER variation in the treated sample was then normalized on control TEER variation.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test, considering p<0.05 as significant.
3. Results
In this study, each experiment was planned based on the results of the previous experiment. Starting with the 1:40 dilution, cells were supplemented with yogurt and corresponding blank digests treated with the different conditioning methods. Supplementation was considered cytotoxic if cell viability and/or normalized TEER were less than 80% of control cells, a conservative threshold commonly applied in
in vitro studies to exclude cytotoxic effects and avoid confounding functional readouts [
10,
15,
16,
17]. In this case, the corresponding supplemented digest was excluded and subsequent experiments were repeated under the same experimental conditions using the remaining conditioning treatments at lower dilutions and/or in combination.
Supplementing cells with the 1:40 dilution of the conditioned digests, no cytotoxic effects were evidenced (data not shown), and experiments were repeated using a lower dilution (1:30). As shown in
Figure 1, the MTT assay did not evidence any cytotoxicity, but centrifugation and rapid freezing in liquid nitrogen did not exceed the TEER cut-off, either for the food or the blank digests after 2 and 4 h supplementation.
Therefore, in the following experiment centrifugation and rapid freezing in liquid nitrogen were excluded, and yogurt and blank digests detoxified with the other treatments were supplemented at 1:20 dilution. In this experiment, since acidification showed borderline results when supplemented at 1:30 dilution, it was also combined with ultrafiltration.
As shown in
Figure 2, cell viability was less than 80% of the control value after 2 hours of supplementation with the acidified digest, which also caused a TEER variation that did not exceed the cut-off. Although TEER measurements revealed high variability within the same treatment, acidification was clearly unable to detoxify the digests. The combination of acidification and ultrafiltration did not prove to be a successful strategy as it did not provide synergistic protection compared to ultrafiltration alone. Therefore, considering that acidification can substantially alter the chemical composition of the food digest, further experiments were conducted using only ultrafiltered digests.
By supplementing cells with digests at a 1:10 dilution, ultrafiltration through 10 kDa membranes proved to be an effective method to make the digest compatible with Caco-2 when cytotoxicity was assessed by MTT, but the TEER decreased strongly after either 2 or 4 h of supplementation. Ultrafiltration on 3 kDa membranes effectively protected cells from toxicity. Indeed, both MTT and TEER results exceed the chosen cut-off (
Figure 3).
Experiments were repeated using the 1:5 dilution, and we observed similar results (
Figure 3). Therefore, ultrafiltration with 3kDa membranes was found to be the most suitable method to condition the yogurt digest, which did not appear cytotoxic even at very low dilution (1:5), at least in the experimental conditions reported.
To evaluate whether the results obtained were related to yogurt digest only or could be generalized to other types of food, digests of biscuits and canned mackerel were supplemented to Caco-2 cells after ultrafiltration through 10 and 3 kDa membranes.
Similar to what observed for the yogurt digest, at 1:10 dilution ultrafiltration through 10 kDa membranes did not preserve the integrity of the monolayer – assessed by TEER measurement - in any of the digests although no cytotoxicity was detected by MTT assay except in mackerel after 4 h of supplementation (
Figure 4). Ultrafiltration through 3 kDa membranes efficiently counteracted toxicity of biscuits digest, while monolayer integrity was disrupted after 2 h – but not 4 h - supplementation with mackerel digest.
At the 1:5 dilution, although cell viability was significantly affected only by the ultrafiltered mackerel digest (< 10 kDa) after 4 hours of supplementation, the TEER variation showed an alteration of the monolayer integrity after supplementation of all digests except the ultrafiltered biscuit < 3 kDa after 2 hours (
Figure 5). Supplementary Table 2 and Table 3 summarize and compare the effectiveness of digest ultrafiltration across the various food matrices studied.
Lower digest dilutions (< 1:5) were not considered for further experiments, since the most effective treatment (ultrafiltration < 3 kDa) did not meet the TEER acceptance criterion for all samples, suggesting a food-specific effect.
The results of the study are summarized in
Figure 6.
4. Discussion
Growing awareness of the importance of assessing food bioavailability increases the need for standardized protocols that enable meaningful comparison between
in vitro studies. Currently, several inactivation/detoxification methods have been tested, as reviewed by Kondrashina et al. [
6], and since each involves modifications to the digest, defining the best method is difficult without a direct comparison. In this study, we detoxified the same yogurt digest obtained with the INFOGEST protocol using five different methods, then supplemented the resulting detoxified samples to Caco-2 cells at decreasing dilutions, with the aim of identifying the method that allowed supplementation at the highest concentration. Procedures such as enzyme inhibition, temperature and dialysis, considered non-physiological or time-consuming [
6] were not tested in the study. A condition involving dilution without digest conditioning was not included, as unconditioned INFOGEST digests are known to impair epithelial viability and barrier integrity even at high dilutions, and therefore do not represent a suitable or interpretable control for intestinal bioavailability studies [
6,
18,
19].
Regardless of the conditioning method, no signs of toxicity were observed when supplementing digests diluted 1:40. The 1:30 dilution, however, discriminated between the different methodologies; in fact, neither centrifugation nor rapid freezing in liquid nitrogen met the viability criteria. At a 1:20 dilution, we also tested the potential synergistic effect of treatments by combining acidification and ultrafiltration on 10 or 3 kDa membranes. Combining the two methodologies did not provide additional benefits, and acidification (pH 2.0) caused extensive protein precipitation, significantly altering the chemical properties of the digest. Therefore, although acidification has been successfully applied in studies targeting specific classes of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols allowing supplementation even at lower dilutions (1:13) [
8], it was excluded, as it does not preserve the native characteristics of the digest.
Ultrafiltration is a less invasive method than acidification and better preserves the nature and composition of the digests, considering that further studies for which they may be intended usually focus on the presence of small molecules that are not retained by ultrafiltration membranes. We ultrafiltered the digests through 10 and 3 kDa membranes, since the enzymes used in
in vitro digestion have molecular weights greater than 10 kDa (porcine pepsin, 41 kDa; pancreatic lipase, 51 kDa; porcine trypsin, 24 kDa; chymotrypsin, 29 kDa; porcine α-amylase, 57 kDa) [
20].
Using a 1:10 dilution, it became evident that ultrafiltration on 10kDa membranes was not sufficient to preserve the integrity of the monolayer, even though cell viability was comparable to that of control cells. This observation highlights the need to go beyond the simple measurement of cell viability before defining the concentration of digest to be supplemented to intestinal cells. Indeed, although cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay, which has been reported to be one of the most sensitive tests for detecting cytotoxicity [
15], the results obtained by considering this assessment alone would have been misleading. The integrity of the Caco-2 monolayer should be assessed by evaluating the TEER, a noninvasive technique that measures the impedance between the lumen and the basolateral tissue. Toxic effects can affect the stability of the tight junctions altering cellular permeability, and monitoring epithelial barrier function by measuring TEER values before and after the supplementation test is essential to consistently assess the bioavailability of a food component [
16].
The toxicity of digests after ultrafiltration through 10 kDa membranes leads us to hypothesize that digestive enzymes, although hydrolyzed during digestion, may form smaller (10 to 3 kDa in size) but still active residues. Furthermore, in the INFOGEST
in vitro digestion protocol, bile acids are used in the intestinal phase to emulsify the lipid content of the food. While single bile acids are relatively small, in an aqueous environment they form micelles that can reach dimension in the range of 3 – 6 (simple micelles) to 20 nm (mixed micelles including phospholipids, fatty acids, etc.) [
21]. Although bile salt micelles do not have a “kDa mass” because they are not single molecules, but dynamic aggregates of many amphipathic molecules, based on the average molecular mass of a conjugated bile acid and the estimated number of molecules per micelle, it can be hypothesized that most bile acid micelles do not cross the 3 kDa membrane, but that smaller micelles might be present in the <10 kDa ultrafiltered digest, explaining the difference in cytotoxicity parameters between the two.
Ultrafiltration <3 kDa allowed supplementation without detectable impairment of cell viability or barrier integrity for up to 4 hours at a 1:10 dilution, regardless of the type of food digested. The greater effects on TEER after 2 h of supplementation observed in mackerel may be due to mechanical stress from washing or medium changes that supplementation entails. Importantly, a further reduction in dilution (1:5) showed significant differences between the tested foods. Indeed, at this dilution the ultrafiltered (<3kDa) blank and yogurt digests were not toxic, this suggesting that ultrafiltration eliminated toxic components bound to digestive fluids required for
in vitro digestion, but that small, potentially cytotoxic molecules may be released during the digestion of some foods. We acknowledge that ultrafiltration at 3 kDa may reduce the recovery of larger digestion-derived bioactive peptides; however, gastrointestinal digestion generally produces peptide mixtures enriched in low-molecular-weight sequences, many of which fall below this cut-off and are most relevant for epithelial exposure and absorption [
22]. Larger peptides (>3 kDa), although potentially bioactive, are less likely to be absorbed intact and typically undergo further hydrolysis at the brush border prior to uptake. Thus, while some larger peptides may be excluded, 3 kDa ultrafiltration is expected to preferentially retain peptides with higher physiological relevance for
in vitro bioavailability studies. As an example, simulated gastrointestinal digestion of yogurt proteins, particularly caseins and whey proteins, generates a complex peptide mixture that is strongly enriched in low-molecular-weight peptides, with many well-characterized yogurt-derived bioactive sequences—such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory peptides— consistent with molecular weights below 3 kDa and often corresponding to oligopeptides of fewer than 20 amino acids [
23,
24].
Some limitations of the present study should be acknowledged. pH, osmolality and residual bile salt concentrations were not directly measured in the conditioned digests, although all these factors are known to influence epithelial barrier integrity in Caco-2 models [
25,
26,
27]. However, the study was designed as a functional, side-by-side comparison of conditioning strategies using complementary endpoints—cell viability and TEER—that are highly sensitive to these stressors and directly relevant for subsequent bioavailability assessments. In addition, a limited number of biological replicates was used for selected experimental conditions, reflecting the complexity, duration, and high resource demands of the coupled
in vitro digestion–epithelial barrier assays. Nevertheless, all key trends were reproducible across independent experiments and consistent across food matrices. Statistical analyses were therefore adapted to the experimental design, and conclusions are primarily based on consistent comparative trends observed across conditioning methods rather than on absolute effect sizes.
This study advances existing work on the biocompatibility of in vitro digests with intestinal epithelial models by providing a systematic, side-by-side comparison of commonly used INFOGEST digest-conditioning strategies applied to identical digestion outputs. Unlike many previous studies in which conditioning approaches are evaluated individually or selected empirically, the present work directly contrasts multiple methods across decreasing digest dilutions using both cell viability and epithelial barrier integrity as quantitative endpoints. The inclusion of identically conditioned blank digests further allows discrimination between cytotoxic effects arising from digestive fluids and those derived from food components. Importantly, the combined evaluation of MTT and TEER measurements demonstrates that preserved cell viability does not necessarily imply maintained epithelial barrier function, underscoring the need to incorporate barrier integrity as a critical criterion when coupling digestion models with intestinal cell systems.
Although the present study included food matrices differing in composition, extension of this approach to additional food categories, such as highly lipid-rich or polyphenol-rich matrices, will be required to further explore matrix-specific effects and refine general methodological recommendations.
5. Conclusions
In vitro approaches are increasingly employed to assess the bioavailability of nutrients and bioactive compounds, offering clear advantages in terms of ethical considerations, experimental control, and mechanistic insight. However, meaningful bioavailability assessment requires intestinal epithelial models that preserve barrier integrity, as impairment of epithelial viability or tight-junction function may lead to overestimation of absorption. When simulated digestion is coupled with epithelial models, components of the digestive fluids—rather than the food itself—can compromise cell viability and barrier function, and this issue is often addressed through extensive dilution, limiting physiological relevance and comparability among studies. The present study demonstrates that ultrafiltration using a 3 kDa molecular weight cut-off represents an effective and minimally invasive strategy to condition INFOGEST digests for application to intestinal epithelial models. This approach enabled exposure at a 1:10 dilution without detectable impairment of cell viability or epithelial barrier integrity across multiple food matrices, while lower dilutions revealed food-dependent effects, underscoring the need for preliminary compatibility testing. Despite variability related to digestion protocols, food matrices, and cell models, the systematic comparison presented here provides practical guidance to improve the reproducibility and physiological relevance of in vitro nutrient bioavailability studies. Some limitations should be acknowledged, including peptide partitioning after ultrafiltration. Future studies should integrate digest conditioning with quantitative physicochemical characterization and peptidomics-based bioactivity analyses of permeate and retentate fractions to clarify the contribution of larger digestion-derived bioactive peptides. Furthermore, translational research should aim to validate these findings using more complex models, such as co-cultures of intestinal epithelial cells and microbiota bacteria (colon models), to understand the impact of conditioning on microbial fermentation and metabolism. Integrating these standardized methodologies with absorption assays in in vivo animal models will be essential to confirm the physiological relevance of these results and further support methodological harmonization in nutrition research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C., C.C. and A.B.; methodology, A.B.; validation, G.C., C.C. and A.B.; formal analysis, G.C. and C.C.; investigation, G.C. and C.C.; resources, A.B.; data curation, G.C., C.C. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C. and A.B.; writing—review and editing, G.C., C.C. and A.B.; supervision, A.B.; funding acquisition, A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), CUP D93C22000890001, project “ON Foods - Research and innovation network on food and nutrition Sustainability, Safety and Security - Working ON Foods” (Project code PE00000003), and Mission 04 Component 2 Investment 1.5 – NextGenerationEU, Call for tender n. 3277 dated 30/12/2021, Award number 0001052 dated 23/06/2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Grundy, M.M.L.; Deglaire, A.; Le Feunteun, S.; Reboul, E.; Moughan, P.J.; Wilde, P.J.; McClements, D.J.; Marze, S. Bioaccessibility and Associated Concepts: Terminology in the Context of in Vitro Food Digestion Studies. Food Chem 2025, 485, 144424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static in Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat Protoc 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.B.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Mariutti, L.R.B.; Mercadante, A.Z.; Failla, M.L. Comparison of Two Static in Vitro Digestion Methods for Screening the Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids in Fruits, Vegetables, and Animal Products. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65, 11220–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.; de Carvalho, N.M.; de Oliveira, D.L.; Madureira, A.R. A Critical Review on In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models of the Intestinal Epithelium of Humans and Monogastric Animals. Gastrointest Disord 2024, Vol 6 6, Pages 337-358 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Faria, M.A.; Petit, V.; Alves, B.; Alvito, P.; Arranz, E.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; Corredig, M.; Dijk, W.; et al. A Shared Perspective on in Vitro and in Vivo Models to Assay Intestinal Transepithelial Transport of Food Compounds. J Agric Food Chem 2023, 71, 19265–19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashina, A.; Arranz, E.; Cilla, A.; Faria, M.A.; Santos-Hernández, M.; Miralles, B.; Hashemi, N.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Young, J.F.; Barberá, R.; et al. Coupling in Vitro Food Digestion with in Vitro Epithelial Absorption; Recommendations for Biocompatibility. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2024, 64, 9618–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuchi, H.; Takei, T.; Aikawa, K.; Shimizu, M. The Effect of Hyperosmosis on Paracellular Permeability in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2009, 73, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, A.; González-Sarrías, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C.; Barberá, R. Availability of Polyphenols in Fruit Beverages Subjected to in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion and Their Effects on Proliferation, Cell-Cycle and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Caco-2 Cells. Food Chem 2009, 114, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, T.C.; Pinheiro, P.N.; Fernandes, A.S.; Murador, D.C.; Neves, B. V.; de Menezes, C.R.; de Rosso, V. V.; Jacob-Lopes, E.; Zepka, L.Q. Bioaccessibility and Intestinal Uptake of Carotenoids from Microalgae Scenedesmus Obliquus. LWT 2021, 140, 110780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsawad, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Choowongkomon, K.; Kitts, D.D.; Chen, X.M.; Meng, G.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Transepithelial Transport across Caco-2 Cell Monolayers of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Simulated in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Cooked Chicken Muscles. Food Chem 2018, 251, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yuan, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Meng, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Peptides Derived from In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Germinated and Heat-Treated Foxtail Millet (Setaria Italica) Proteins. J Agric Food Chem 2020, 68, 9415–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.M.; Chang, P.S. Effects of Freezing Rate on Structural Changes in L-Lactate Dehydrogenase during the Freezing Process. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J.; Peterson, B.W. Two-Stage Interpretation of Changes in TEER of Intestinal Epithelial Layers Protected by Adhering Bifidobacteria During E. Coli Challenges. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 599555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimetz, J.; Shah, P.; Keese, C.; Dehnert, C.; Detweiler, M.; Michael, S.; Toniatti-Yanulavich, C.; Xu, X.; Padilha, E.C. Automated Measurement of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) in 96-Well Transwells Using ECIS TEER96: Single and Multiple Time Point Assessments. SLAS Technol 2024, 29, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunzio, M.; Valli, V.; Tomás-Cobos, L.; Tomás-Chisbert, T.; Murgui-Bosch, L.; Danesi, F.; Bordoni, A. Is Cytotoxicity a Determinant of the Different in Vitro and in Vivo Effects of Bioactives? BMC Complement Altern Med 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanzaga, M.; Bollati, C.; Ranaldi, G.; Sucato, S.; Fustinoni, S.; Roda, G.; Lammi, C. Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Foods 2023, 12 12, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzza, S.; Rossi, C.; Scarino, M.L.; Sambuy, Y. A Protocol for Differentiation of Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells in Asymmetric Serum-Containing Medium. Toxicol Vitr 2012, 26, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, N.; Gramacho, A.C.; Silva, M.; Cardoso, M.; Alvito, P.; Kranendonk, M.; Silva, M.J.; Louro, H. Challenges of the Application of In Vitro Digestion for Nanomaterials Safety Assessment. Foods 2024, 13, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.S.; Batchelor, H.; Butler, J.M.; Khadra, I.; Minstry, N.; Stamatopoulos, K. Compatibility of Caco-2 Cells with Simulated Intestinal Fluid-Predicting Permeability. Br J Pharm 2023, 8, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Adesina, A.; Ahmad, S.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Carpentier, D.; Denny, P.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res 2025, 53, D609–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, Y.S.R. Multifaceted Applications of Bile Salts in Pharmacy: An Emphasis on Nanomedicine. Int J Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Eun, J.B.; Shim, J.H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Bioactivities, Applications, Safety, and Health Benefits of Bioactive Peptides From Food and By-Products: A Review. Front Nutr 2022, 8, 815640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, F.; Yan, J.; Zou, H. Peptide Profiling and the Bioactivity Character of Yogurt in the Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. J Proteomics 2016, 141, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.H.; Gathercole, J.L.; Day, L.; Dalziel, J.E. Differences in Peptide Generation Following in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Yogurt and Milk from Cow, Sheep and Goat. Food Chem 2020, 317, 126419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzinga, J.; Grouls, M.; Hooiveld, G.J.E.J.; van der Zande, M.; Smidt, H.; Bouwmeester, H. Systematic Comparison of Transcriptomes of Caco-2 Cells Cultured under Different Cellular and Physiological Conditions. Arch Toxicol 2023 973 2023, 97, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inokuchi, H.; Takei, T.; Aikawa, K.; Shimizu, M. The Effect of Hyperosmosis on Paracellular Permeability in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2009, 73, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Katoh, T.; Ogawa, A.; Bamba, S.; Andoh, A.; Koyama, S.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. Bile Acid Modulates Transepithelial Permeability via the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Caco-2 Cell Line. Free Radic Biol Med 2005, 39, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |