1. Introduction
Myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) is the most common acquired cardiac condition in adult and geriatric dogs, particularly small to medium-sized dogs [
1]. MMVD is mostly a chronic, slowly progressive disorder characterized by myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve. The progression of the disease results in increased left atrioventricular volume overload, atrial dilation, ventricular eccentric hypertrophy and can lead to congestive heart failure (CHF). Echocardiography plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and staging of MMVD using reliable markers to identify atrioventricular enlargement such as left-atrial-to-aortic ratio (LA:Ao) and left internal diameter in diastole normalized to body weight (LVIDDn) [
1,
2,
3]. However, these parameters assess the chambers independently.
The close relationship between the left atrium (LA) and the left ventricle (LV) is critical for an efficient cardiac function. This interplay suggests that the assessment of both cardiac chambers could better reflect the atrioventricular dysfunction and can be used as a useful index for heart failure. The left atrioventricular coupling index (LACi), defined by the ratio between LA and LV end-diastolic volume, has emerged as a novel echocardiographic index in human medicine. This index has shown promising results in risk stratification, in predicting cardiovascular disease progression and as an early marker of cardiovascular dysfunction in conditions such as atrial fibrillation and heart failure [
4,
5,
6,
7].
No studies have assessed LACi in veterinary medicine. Therefore, the aim of this study was to provide reference intervals for LACi, and to investigate the association between LACi and the severity of MMVD compared with the current ACVIM grading system.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
This retrospective study included 233 adult dogs (> 1 year) selected from an ongoing database of the University Teaching Hospital of Perugia from January 2017 to February 2025: 105 healthy dogs and 128 affected by MMVD [B1 stage (n=38), B2 (n=52) and C (n=38)]. Dogs with persistent non-sinus rhythms or inadequate image quality for left apical four-chamber view were excluded. No dogs were excluded based on breed, age, sex and bodyweight. All healthy dogs had been recruited for prior echocardiographic studies and had no history of disease or abnormal findings at the physical examination. Dogs affected with MMVD were staged according with the ACVIM guidelines [
1].
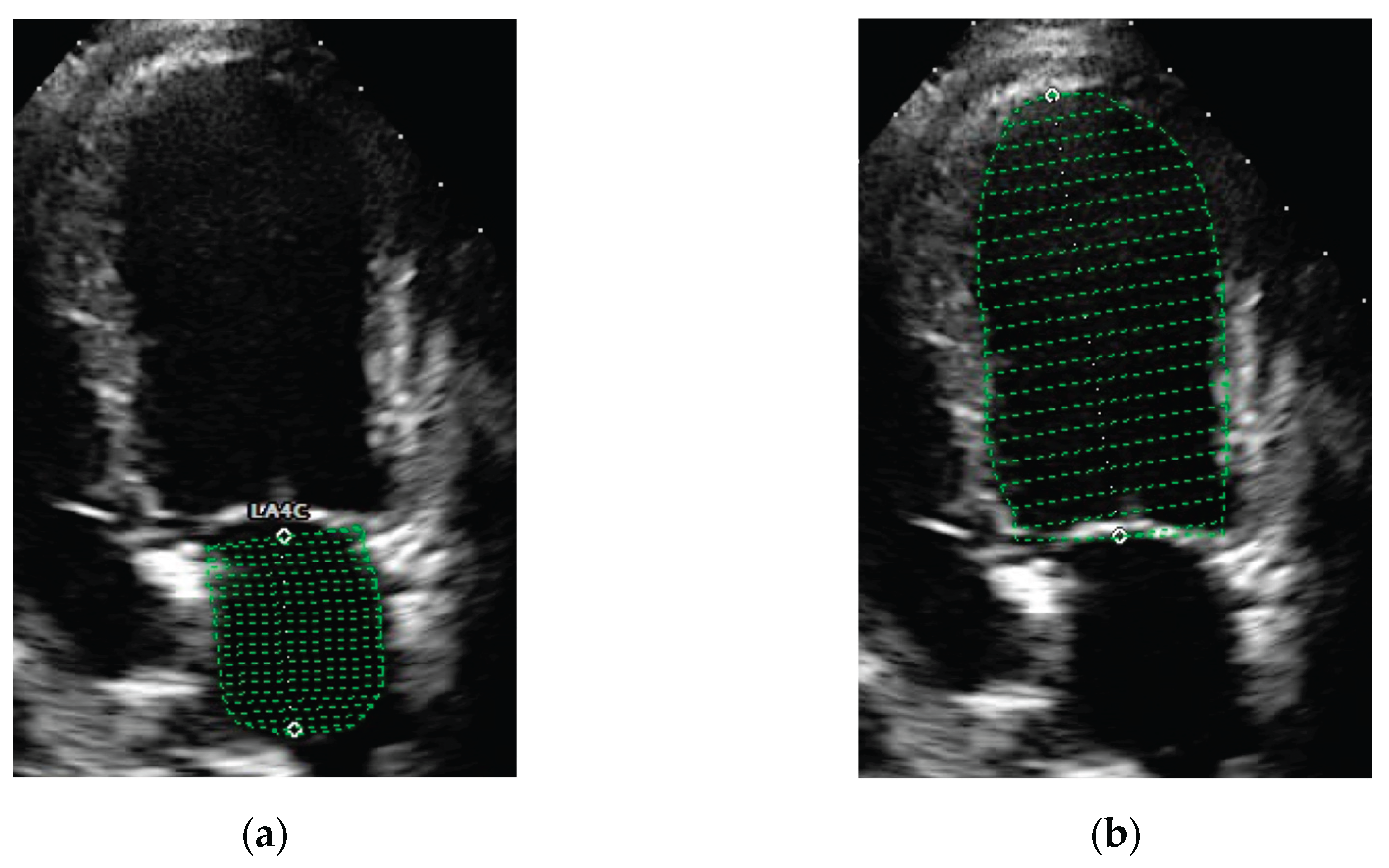
The same investigator (FV) selected appropriate frames from stored cineloops of each dog and performed the measurements from those frames. LA and LV volumes were measured at the same end-diastolic phase defined by the frame just after mitral valve closure (around the onset of the QRS complex) and at the same end systolic phase defined by the frame just before mitral valve opening (typical after end of the T wave). Echocardiographic volumes were measured using a single plane Simpson’s Method of Discs from the apical four-chamber view. The internal border of the LA was traced manually beginning at the septal mitral annulus (first hinge point), around the LA roof and ending at the lateral mitral annulus (second hinge point) using the blood-tissue interface (
Figure 1). The ostia of the pulmonary veins were excluded, and a straight line drawn from hinge point to hinge point across the mitral valve annulus defined the boundary of LA. The height of the stacked discs was selected to be perpendicular to the midpoint of the mitral valve annulus, bisecting LA. The internal border of the LV was traced manually beginning at the septal mitral annulus, around the apex and ending at the lateral mitral annulus, using the blood-tissue interface (
Figure 1). These two points were joined by a bisecting line by software on the ultrasound systems. The maximum length of the LV was defined by the distance between the mitral annulus and the apex.
Left atrial and ventricular volume measurements were used to calculate LACi at the end-diastole (LACi-ED) and LACi at the end-systole (LACi-ES), as following reported:
The sum of LA:Ao and LVIDDn (LA:Ao + LVIDDn) was also calculated, as linear combined severity score [
8,
9]. All measurements were performed three times, and the average of the three values was used for analysis.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
We examined relationship of bodyweight, heart rate and age with LACi-ES and LACi-ED in healthy dogs by creating scatter plots and performing univariable linear regression where appropriate. We then generated reference intervals (and 90% confidence intervals around the reference limits) from healthy dogs using ReferenceValueAdvisor software [
10]. We used a non-parametric method because the software identified this approach as appropriate for the provided data.
We examined whether LACi-ED and LACi-ES were different across ACVIM stages (Healthy, B1, B2, and C) using a Kruskal Wallis test followed by pairwise comparisons using the Dunn Conover method. Further, we compared these indices across the ACVIM B2 stage after stratifying the dogs into “mild”, “moderate” and “severe” levels of subclinical disease using a previously proposed classification scheme [
11] with either Kruskal Wallis tests and post-hoc pairwise comparisons, or Mann Whitney U tests (when comparing just two levels of disease severity). The distributions of LACi-ED and LACi-ES values across disease stages were visually represented using box plots.
We examined the diagnostic utility of LACi variables, LA:Ao and LA:Ao + LVIDDn in identifying dogs with CHF using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. We compared select ROC curves to determine if any variables were substantially superior to others in diagnosis of CHF. For this analysis, we included only dogs in ACVIM Stage B2 or those with CHF (n = 90).
3. Results
The study sample consisted of 233 dogs, including of 105 healthy and 128 affected by MMVD. Healthy dogs ranged in bodyweight from 3.8 to 45 kg (median: 17 kg) and were aged between 1 to 14 years (median: 4 years). MMVD dogs were ranged in bodyweight from 2.5 to 32.2 kg (median: 9.6 kg) and were aged between 3 to 17 years (median: 11 years). Thirty-eight dogs were classified as ACVIM stage B1, fifty-two as ACVIM stage B2 and thirty-eight had CHF (ACVIM stage C).
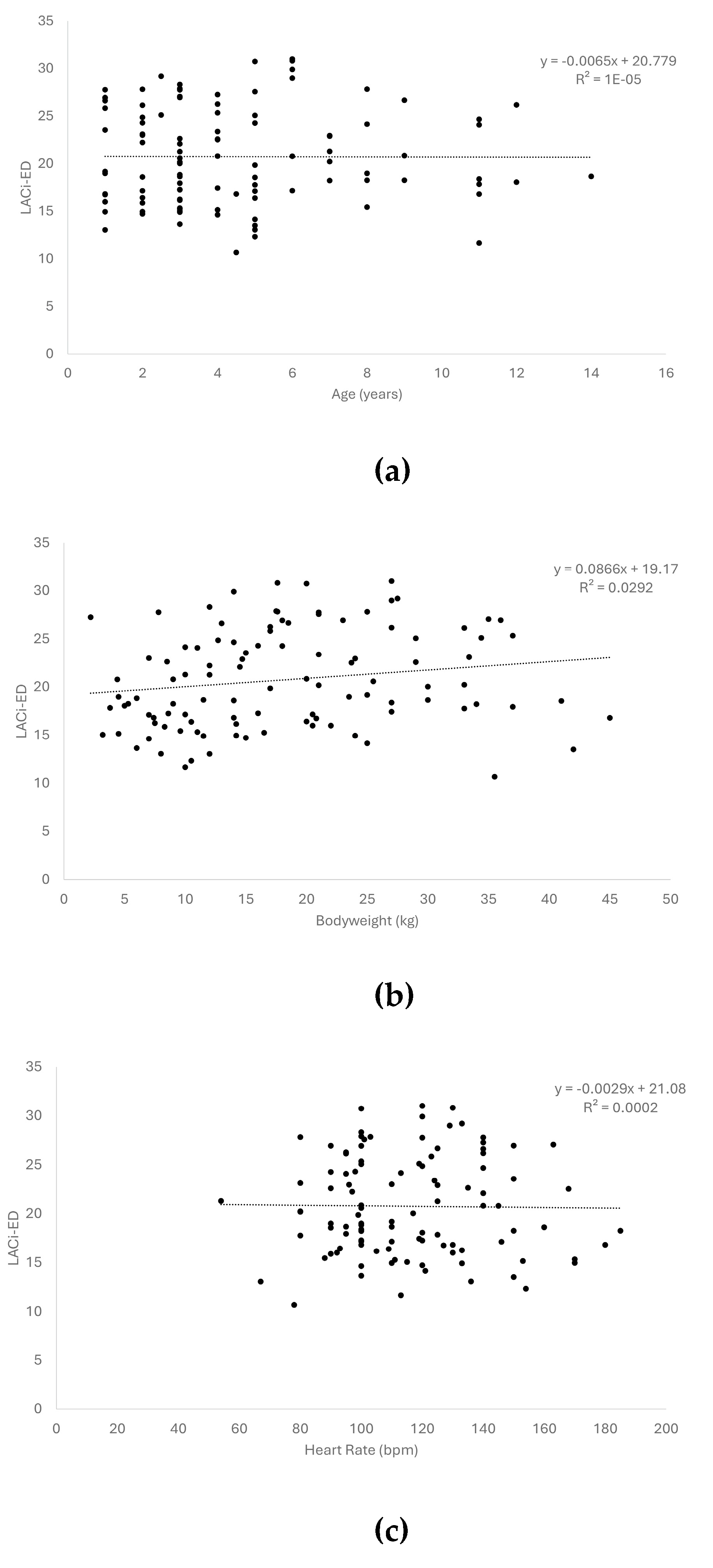
We failed to observe any linear relationship between LACi (both LACi-ED and LACi-ES) and age, bodyweight, or heart rate in healthy dogs (R² < 0.03 for all variables;
Figure 2).
Reference values for LACi-ED and LACi-ES were established using data from the 105 healthy dogs included in the study. For LACi-ED reference values ranged from 12.09% to 30.76%, and for LACi-ES from 34.88% to 115.34% (
Table 1).
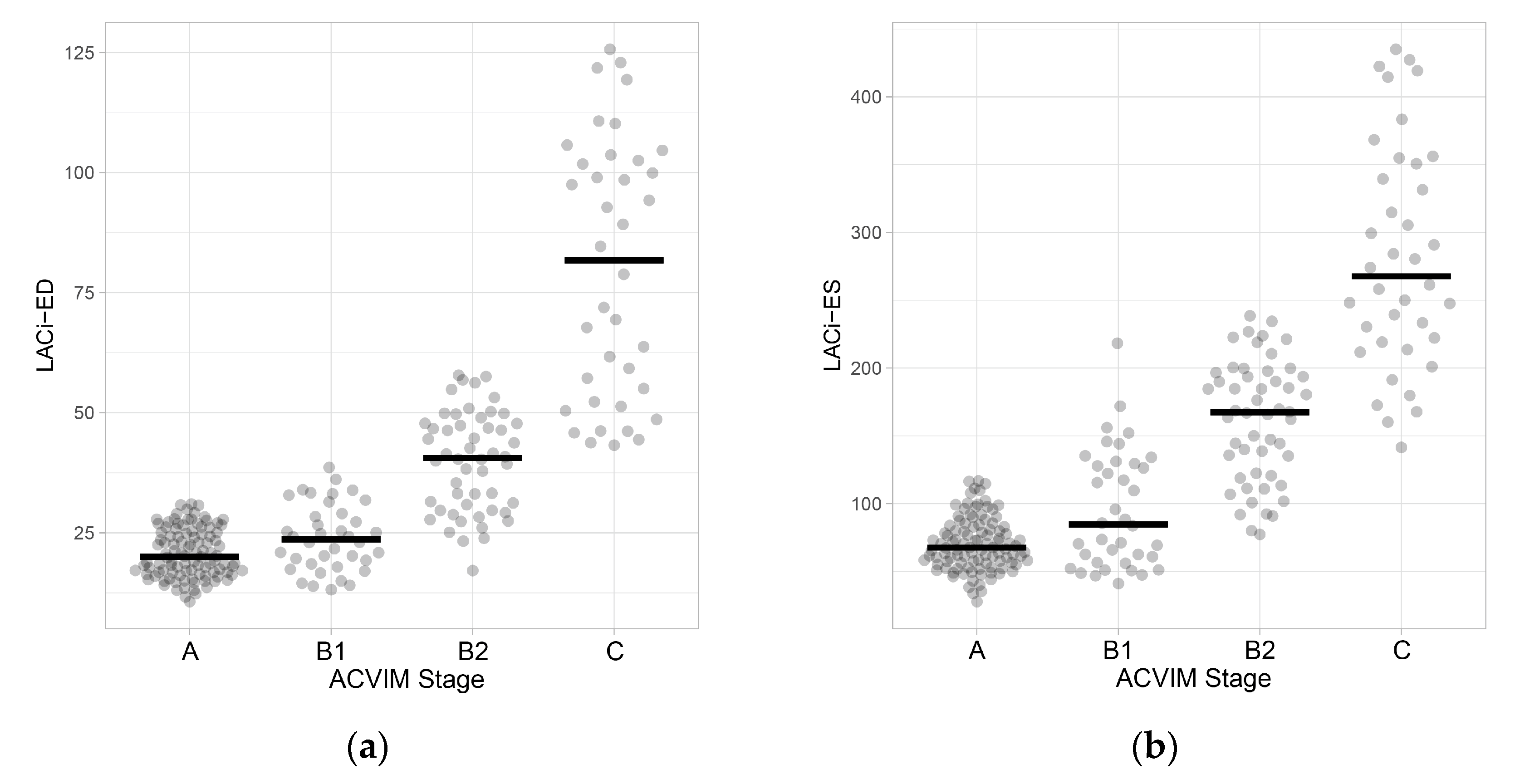
When comparing the LACi values across the different ACVIM stages, both LACi-ED and LACi-ES increased progressively with advancing disease stages (P < 0.001 and P < 0.02, respectively) (
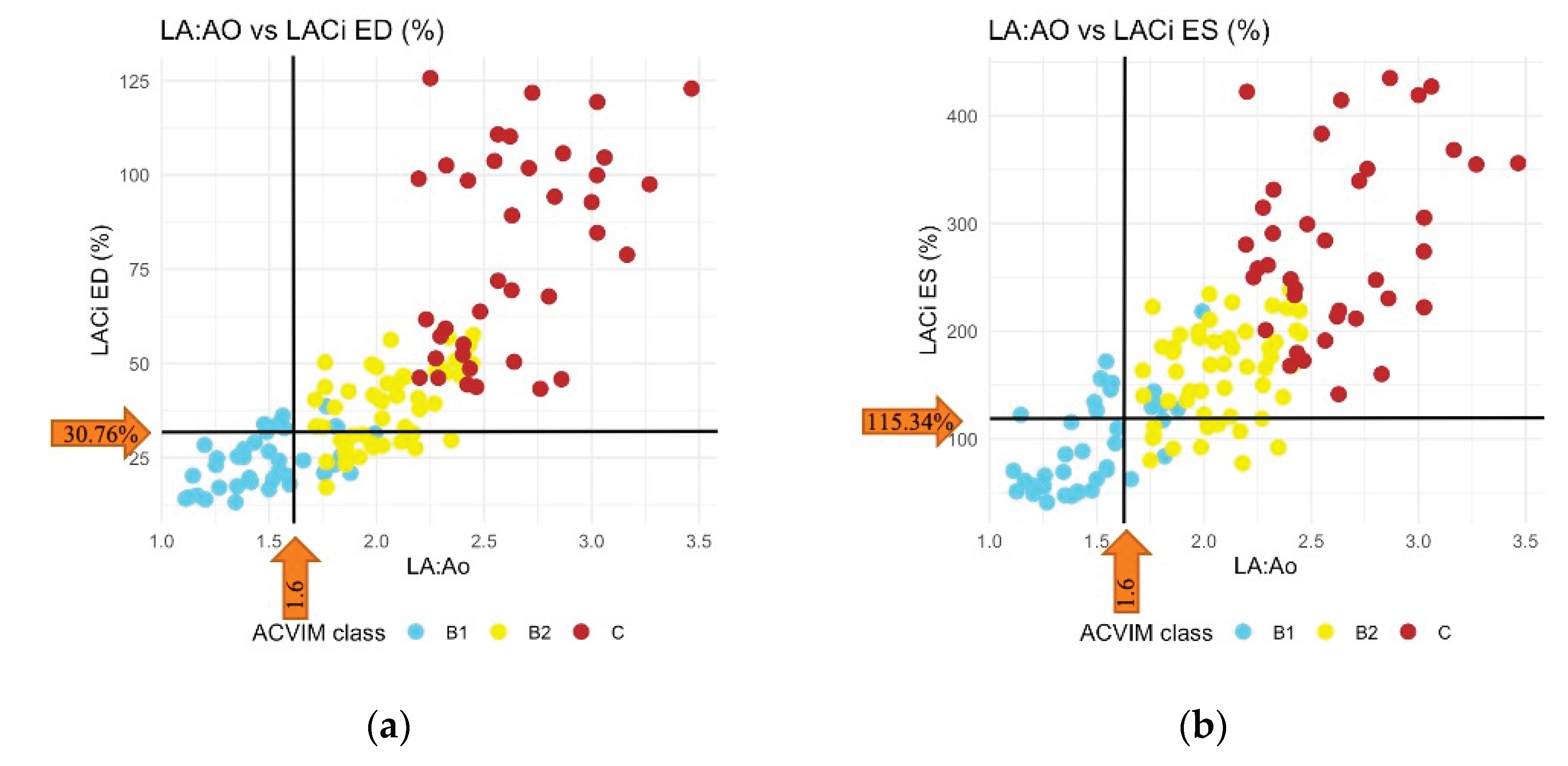
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). We found no differences between healthy dogs and those in ACVIM stage B1 for either LACi-ED or LACi-ES (P > 0.20). However, when cutoff values of 30.76% for LACi-ED and 115.34% for LACi-ES were applied as reasonable upper working limits for healthy dogs, LACi-ED and LACi-ES identified left atrioventricular impairment in 9 and 15 Stage B1 dogs, respectively (
Figure 4). Conversely, LACi-ED and LACi-ES did not identify left atrioventricular impairment in 13 and 12 Stage B2 dogs, respectively (
Figure 4).
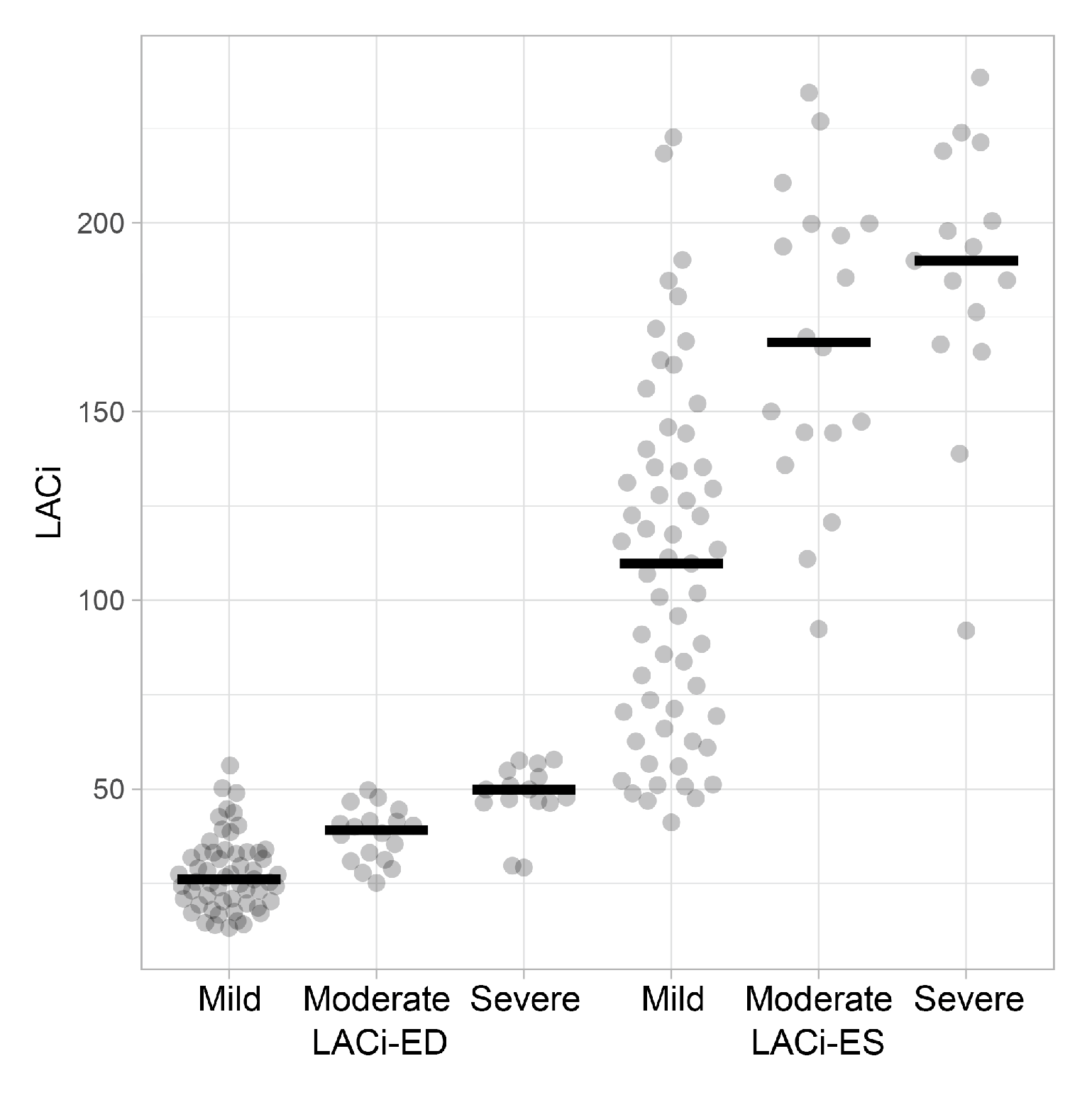
When comparing the LACi-ED values across the different levels of severity of subclinical MMVD, LACi-ED increased progressively with advancing subclinical disease severity (mild
vs moderate: P < 0.001, moderate
vs severe: P = 0.041) (
Figure 5). Furthermore, healthy dogs differed from dogs with mild subclinical MMVD (P < 0.001). Finally, LACi-ED differed between dogs with severe subclinical disease and dogs with CHF (P < 0.001).
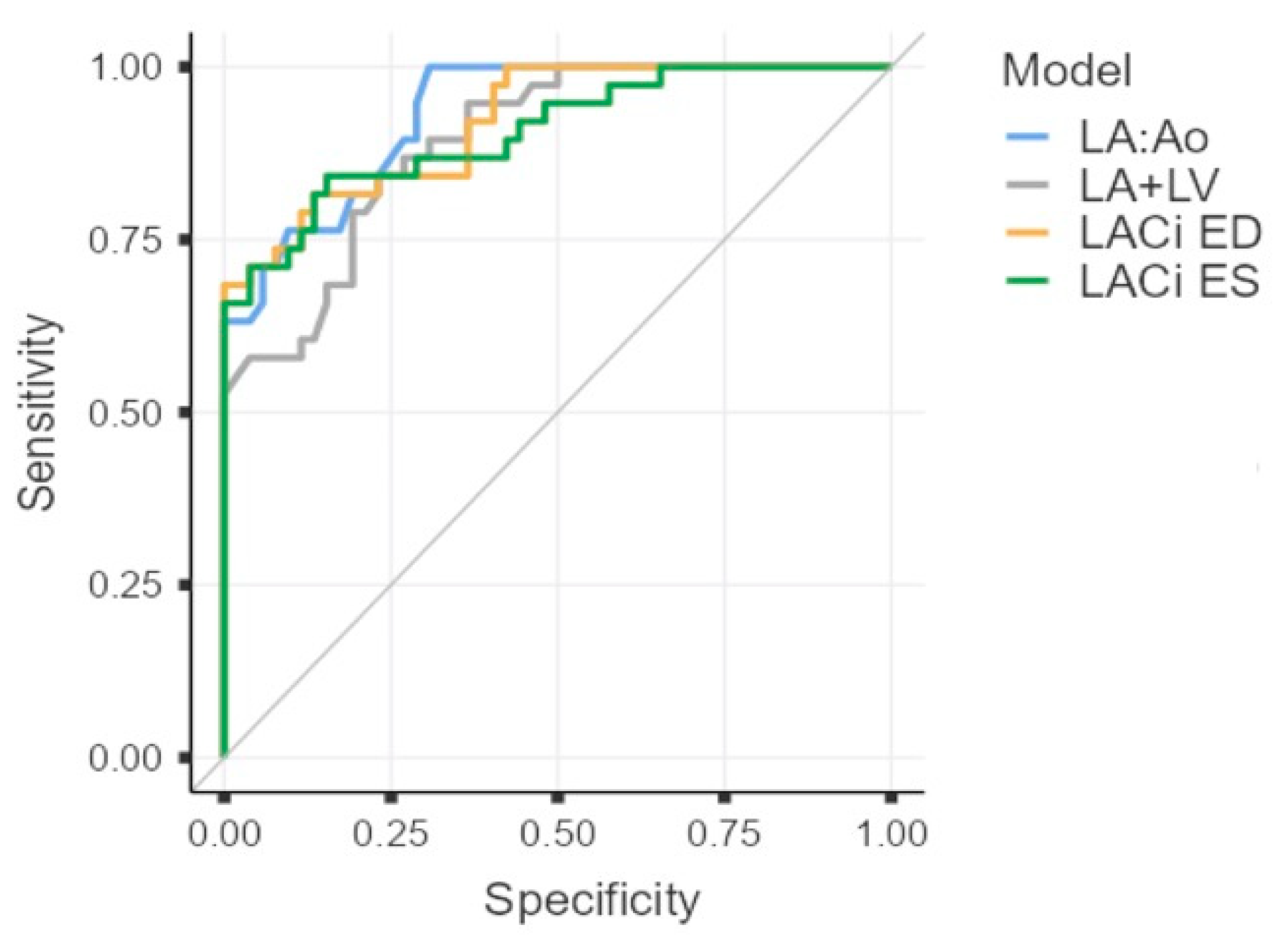
All four indices (LACi-ED, LACi-ES, LA:Ao, and the composite index LA:Ao+LVIDDn) demonstrated similar, good, diagnostic accuracy for identifying CHF, with the areas under the curve (AUC) of 0.920, 0.906, 0.931, and 0.893, respectively. (
Table 2 and
Figure 6). However, sensitivity and specificity of each method differed (
Table 2).
4. Discussion
Our study demonstrates that left atrioventricular coupling indices show a progressive impairment of left atrioventricular function in dogs affected by MMVD with advancing ACVIM stages and, within subclinical disease, by advancing disease severity. We describe for the first time the use of LACi-ED and LACi-ES as indices of left atrioventricular disfunction in dogs, providing reference values for these echocardiographic indices in healthy adult dogs. Whether these indices can provide useful prognostic information for dogs with subclinical disease remains to be determined.
In humans, LA and LV volumes used to calculate LACi are measured at end-diastole, when the atrium and ventricle are directly connected through the mitral valve, thereby reflecting the interaction between atrial and ventricular function [
6]. LACi has emerged as a promising echocardiographic index for patient prognostication in several clinical scenarios and is expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating a relatively larger atrial volume compared with ventricular volume, representing a more abnormal atrioventricular coupling state [
4,
5,
6,
7]. In our study, we obtained LACi measurements at end-diastole (LACi-ED) and end-systole (LACi-ES), as these phases represent moments in the cardiac cycle when LA and LV are directly connected through the mitral valve. Both LACi variables showed a significant, progressive increase with advancing disease severity, and their diagnostic accuracy in identifying dogs with CHF was comparable. Therefore, we speculate that left atrioventricular coupling is similarly impaired at end-diastole and end-systole in dogs affected by MMVD.
Both LACi variables were found to be independent of body weight, age, and heart rate in healthy dogs. Our results differ from those of previous human studies regarding the association with age [
6,
12]. However, the healthy dogs included in our study had a limited age distribution (median age of four years); therefore, we cannot exclude age-associated cardiac changes in healthy geriatric dogs.
The LACi values did not differ between healthy dogs and dogs with stage B1 MMVD, suggesting that atrioventricular uncoupling is not yet evident during the early, asymptomatic phase of the disease. Furthermore, a small number of Stage B1 dogs showed mildly increased LACi values, which might indicate early impairment of atrioventricular coupling. We hypothesize that these dogs can already exhibit subtle left atrial dimensional alterations while still fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for ACVIM Stage B1, namely the absence of left ventricular remodeling. This is supported by our observations that LACi-ED values differed between healthy dogs and dogs with mild MMVD (which includes both Stage B1 and some Stage B2 dogs).
Dogs in Stage B2 MMVD showed substantial heterogeneity in LACi values: some exhibited measurements within the normal reference range, whereas others exceeded the established thresholds for healthy dogs. This underscores the lack of clinical utility with the current ACVIM staging scheme. Consequently, we used a newly proposed classification scheme to classify dogs with subclinical disease into three levels of severity: “mild”, “moderate”, and “severe” [
11]. When examined using this scheme, LACi-ED differed between all levels of subclinical disease severity, as well as between healthy dogs and dogs with mild disease, and dogs with severe subclinical disease and those with CHF. We did not apply the scheme to LACi-ES, because the scheme relies on end-diastolic measurements. Increased LACi values in B2 dogs might reflect early atrioventricular uncoupling, suggesting that the dynamic coordination between atrial and ventricular function is beginning to deteriorate even before the onset of clinical signs of CHF. Conversely, normal LACi values can indicate preserved atrioventricular coupling. This heterogeneity suggests that stage B2 encompasses a broad spectrum of structural and functional cardiac changes that are not fully captured by conventional ACVIM-defined staging criteria. From a pathophysiological perspective, an increase in LACi implies disproportionate left atrial enlargement relative to ventricular size, pointing to impaired left atrial reservoir function and increased atrial pressures. Whether this pattern can serve as an early marker of diastolic dysfunction or left atrial afterload mismatch, and whether this subpopulation is at higher risk of progression to CHF, remains undetermined and warrants further investigation. Overall, these findings highlight the potential prognostic value of LACi for improved clinical stratification of dogs with stage B2 MMVD.
Left atrioventricular coupling index (LACi) values were markedly elevated in dogs at ACVIM stage C, consistent with the progressive nature of MMVD, which results in chronic volume overload and enlargement of the LA and LV. These findings suggest advanced atrial and ventricular remodeling, as well as marked impairment of atrioventricular coupling. Compared with traditional echocardiographic indices such as LA:Ao, LVIDDn, and the combined LA:Ao + LVIDDn, LACi demonstrated comparable diagnostic accuracy for identifying CHF. Specifically, LACi showed lower sensitivity but higher specificity than LA:Ao. Although LACi can represent an additional tool in the echocardiographic assessment of MMVD, particularly for evaluating atrioventricular function and refining risk stratification, further prospective studies are needed to confirm its clinical utility.
Our study has several limitations. As with all retrospective studies, we were unable to control data collection when cases were examined. Moreover, this limited our ability to assess the prognostic value of LACi over time. In addition, dogs in the MMVD group, particularly those in ACVIM Stages B2 and C, were receiving cardiac medications (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, pimobendan). These treatments can influence cardiac loading conditions and myocardial function, potentially affecting atrioventricular function and, consequently, LACi values. Furthermore, volumetric measurements were not validated using independent modalities such as three-dimensional echocardiography or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, but have been previously compared to other methods, and validated as a reasonable means of calculating volumes. Finally, intra- and inter-observer variability for LA and LV volume measurements were not assessed in this study, as these parameters have been extensively evaluated in previous studies [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
5. Conclusions
This study is the first to evaluate the left atrioventricular coupling in healthy dogs and in dogs affected by MMVD. LACi is a novel, non-invasive, and easily obtainable echocardiographic index that reflects the functional relationship between LA and LV. Our findings indicate a progressive impairment of left atrioventricular function in dogs with MMVD as ACVIM stage advances, and suggest that LACi might be a useful additional echocardiographic parameter for assessing disease severity and refining risk stratification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.V., M.C. and D.C.; formal analysis, M.R.; investigation, F.V., F.P., S.C. and D.C; data curation, F.V. and A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, F.V., M.R. and D.C; writing—review and editing, F.V., M.R., F.P., S.C., M.C., A.C. and D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because of the retrospective nature of the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all owners of dogs involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Keene, B.W.; Atkins, C.E.; Bonagura, J.D.; Fox, P.R.; Häggström, J.; Fuentes, V.L.; Oyama, M.A.; Rush, J.E.; Stepien, R.; Uechi, M. ACVIM consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of myxomatous mitral valve disease in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, C.C.; Kittleson, M.D.; Della Torre, P; Häggström, J.; Lombard, C.W.; Pedersen, H.D.; Vollmar, A.; Wey, A. Allometric scaling of M-mode cardiac measurements in normal adult dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 311–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishniw, M.; Caivano, D.; Dickson, D.; Vatne, L.; Harris, J.; Matos, JN. Two-dimensional echocardiographic left- atrial-to-aortic ratio in healthy adult dogs: a reexamination of reference intervals. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuni, F.; Biagioli, P.; Myagmardorj, R.; Mengoni, A.; Chua, A.P.; Zuchi, C.; Sforna, S.; Bax, J.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; Ambrosio, G.; Carluccio, E. Left Atrioventricular Coupling Index: A Novel Diastolic Parameter to Refine Prognosis in Heart Failure. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2024, 37, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfari, G.; Essayagh, B.; Nistri, S.; Maalouf, J.; Rossi, A.; Thapa, P.; Michelena, H.I.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. Left Atrial Volumetric/Mechanical Coupling Index: A Novel Predictor of Outcome in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, e011608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezel, T.; Venkatesh, B.A.; De Vasconcellos, H.D.; Kato, Y.; Shabani, M.; Xie, E.; Heckbert, S.R.; Post, W.S.; Shea, S.J.; Allen, N.B.; Watson, K.E.; Wu, C.O.; Bluemke, D.A.; Lima, J.A.C. Left Atrioventricular Coupling Index as a Prognostic Marker of Cardiovascular Events: The MESA Study. Hypertension 2021, 78, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meucci, M.C.; Fortuni, F.; Galloo, X.; Bootsma, M.; Crea, F.; Bax, J.J.; Marsan, N.A.; Delgado, V. Left atrioventricular coupling index in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 363, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, P.; Crosara, S.; Poggi, M.; Oricco, S.; Chiavassa, V.; Degiovanni, A.; Tarducci, A. Left atrial volume and function in Cavalier King Charles spaniels at different ACVIM stages. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 180, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patata, V.; Porciello, F.; Rishniw, M.; Caivano, D.; Corda, A.; Domenech, O.; Vezzosi, T.; Guglielmini, C.; Poser, H.; Spina, F.; Birettoni, F. Diagnostic accuracy of right pulmonary vein to right pulmonary artery ratio to identify congestive heart failure in dogs affected by myxomatous mitral valve disease submitted. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Geffré, A.; Concordet, D.; Braun, J.P.; Trumel, C. Reference Value Advisor: a new freeware set of macroinstructions to calculate reference intervals with Microsoft Excel. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 40, 107–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishniw, M. A modified mitral insufficiency echocardiographic score differentiates severities of subclinical mitral valve disease. In Proceedings of the ECVIM-CA Congress, Maastricht, Nederland, 18-20 September 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.X.; Li, S.W.; Pan, X.F.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Guan, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zuo, P.F.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.Q.; Ding, M.Y.; Lu, G.L.; Tan, J.; Yang, X.J.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Ren, W.D.; Ma, C.Y. Study Investigators. Normal Values of Echocardiographic Left Atrioventricular Coupling Index and Left Atrial Stiffness Index Reflecting Left Ventricular Diastolic Function: A Multicenter Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2025, 38, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höllmer, M.; Willesen, J.L.; Tolver, A.; Koch, J. Left atrial volume and phasic function in clinically healthy dogs of 12 different breeds. Vet. J. 2013, 197, 639–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, N.; Scollan, K.; Sisson, D. Quantitative evaluation of left atrial volume and function by one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional echocardiography in a population of normal dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2016, 18, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvard, J.; Thierry, F.; Culshaw, G.J.; Schwarz, T.; Handel, I.; Martinez Pereira, Y. Assessment of left atrial volume in dogs: comparisons of two-dimensional and real-time three-dimensional echocardiography with ECG-gated multidetector computed tomography angiography. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2019, 24, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.C.; Ciccozzi, M.M.; Sintov, D.J.; Sharpe, A.N. Echocardiographic quantitation of left heart size and function in 122 healthy dogs: A prospective study proposing reference intervals and assessing repeatability. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wess, G.; Bauer, A.; Kopp, A. Echocardiographic reference intervals for volumetric measurements of the left ventricle using the Simpson's method of discs in 1331 dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguignon, C.; Caivano, D.; Dickson, D.; Vatne, L.; Harris, J.; Rishniw, M.; Pariaut, R. Two-dimensional echocardiographic estimates of left ventricular volumes obtained in different views in dogs provide similar measurements but are not interchangeable. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2021, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Representative echocardiographic images of view and method of obtaining left atrial and left ventricle volumes estimates using Simpson’s Method of Discs (green lines). Left atrial (a) and left ventricle (b) volumes estimates obtained from left apical four-chamber view at end-diastole.
Figure 1.
Representative echocardiographic images of view and method of obtaining left atrial and left ventricle volumes estimates using Simpson’s Method of Discs (green lines). Left atrial (a) and left ventricle (b) volumes estimates obtained from left apical four-chamber view at end-diastole.
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED) values in healthy dogs showed no relationship with age (a), bodyweight (b), and heart rate (c).
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED) values in healthy dogs showed no relationship with age (a), bodyweight (b), and heart rate (c).
Figure 3.
Dot plots of left atrioventricular coupling index values at end-diastole (LACi-ED) (a) and at end-systole (LACi-ES) (b) in healthy dogs and dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease at different ACVIM stages. Horizontal lines represent the median values for each group.
Figure 3.
Dot plots of left atrioventricular coupling index values at end-diastole (LACi-ED) (a) and at end-systole (LACi-ES) (b) in healthy dogs and dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease at different ACVIM stages. Horizontal lines represent the median values for each group.
Figure 4.
Scatterplot showing classification agreement between left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED) (a) or at end-systole (LACi-ES) (b) and left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao). The threshold for identification of left atrial enlargement was 1.6 for LA:Ao, 30.76% for LACi-ED and 115.34% for LACi-ES.
Figure 4.
Scatterplot showing classification agreement between left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED) (a) or at end-systole (LACi-ES) (b) and left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao). The threshold for identification of left atrial enlargement was 1.6 for LA:Ao, 30.76% for LACi-ED and 115.34% for LACi-ES.
Figure 5.
Dot plots of left atrioventricular coupling index values at end-diastole (LACi-ED) and at end-systole (LACi-ES) in subclinical dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease (mild, moderate and severe). Horizontal lines represent the median values for each group.
Figure 5.
Dot plots of left atrioventricular coupling index values at end-diastole (LACi-ED) and at end-systole (LACi-ES) in subclinical dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease (mild, moderate and severe). Horizontal lines represent the median values for each group.
Figure 6.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED), left atrioventricular coupling index at end-systole (LACi-ES), left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao) and composite index LA:Ao+LVIDDn (LA+LV) to differentiate dogs with congestive heart failure. The area under the curve (AUC) is 0.920, 0.906, 0.931, and 0.893 for LACi-ED, LACi-ES, LA:Ao, and LA+LV, respectively.
Figure 6.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED), left atrioventricular coupling index at end-systole (LACi-ES), left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao) and composite index LA:Ao+LVIDDn (LA+LV) to differentiate dogs with congestive heart failure. The area under the curve (AUC) is 0.920, 0.906, 0.931, and 0.893 for LACi-ED, LACi-ES, LA:Ao, and LA+LV, respectively.
Table 1.
Reference intervals for LACi variables in 105 clinically healthy dogs.
Table 1.
Reference intervals for LACi variables in 105 clinically healthy dogs.
| Variable |
Lower limit (90% CI1)
|
Upper limit (90% CI) |
| LACi-ED |
12.09 % (CI 10.68-13.44) |
30.76 % (CI 28.99-31.01) |
| LACi-ES |
34.88 % (CI 27.81-42.07) |
115.34 % (CI 106.62-116.83) |
Table 2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED), left atrioventricular coupling index at end-systole (LACi-ES), left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao) and composite index LA:Ao+LVIDDn (LA+LV) for identifying congestive heart failure in dogs affected by myxomatous mitral valve disease.
Table 2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of left atrioventricular coupling index at end-diastole (LACi-ED), left atrioventricular coupling index at end-systole (LACi-ES), left atrial-to-aortic-root ratio (LA:Ao) and composite index LA:Ao+LVIDDn (LA+LV) for identifying congestive heart failure in dogs affected by myxomatous mitral valve disease.
| Variable |
Threshold
value
|
Sensitivity
(95% CI1)
|
Specificity
(95% CI)
|
Area under the curve |
| LACi-ED |
58.5 |
68 (51-82) |
100 (93-100) |
0.920 |
| LACi-ES |
200.8 |
84 (69-94) |
84 (72-93) |
0.906 |
| LA:Ao |
2.2 |
100 (91-100) |
69 (55-81) |
0.931 |
| LA+LV |
4.2 |
84 (69-94) |
77 (63-87) |
0.893 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).