Submitted:
04 January 2026
Posted:
06 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Agents
2.2. Preparation of MXene (Ti3C2Tx) Nanosheets
2.3. Preparation of MXene-Hydrogel Copolymer Inks for 3D Printing
| Sample name | Sample composition | PVA | AA | PEGDA | MXene | LAP | H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA-PAA-0.28MX | 10PVA25PAA-0.28MXene | 3 g | 7.5 g | 75 mg | 30 mg | 60 mg | 30 g |
| PVA-PAA-0.14MX | 10PVA25PAA-0.14MXene | 3 g | 7.5 g | 75 mg | 15 mg | 60 mg | 30 g |
| PVA-PAA-0.07MX | 10PVA25PAA-0.07MXene | 3 g | 7.5 g | 75 mg | 7.5 mg | 60 mg | 30 g |
| PVA-PAA | 10PVA25PAA | 3 g | 7.5 g | 75 mg | 3.75 mg | 60 mg | 30 g |
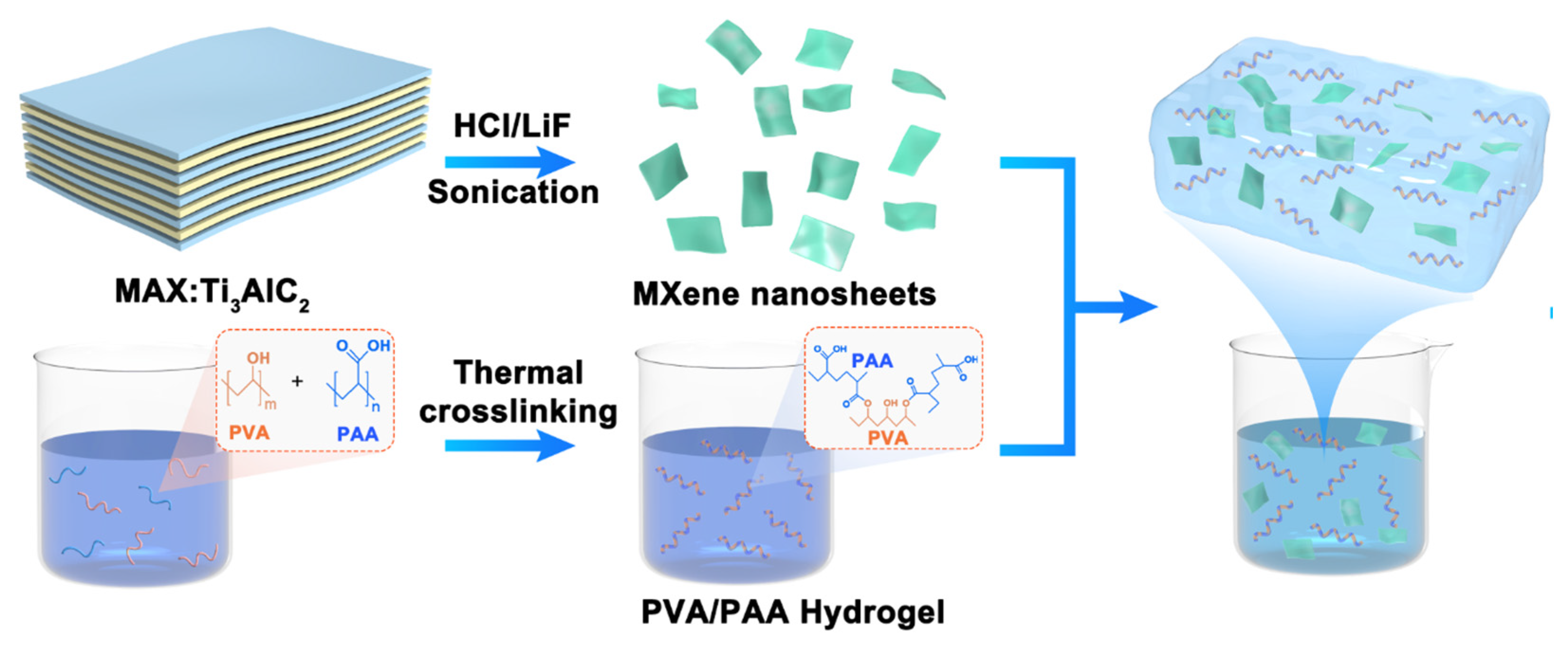
2.4. 3D Printing of MXene-Copolymer Hydrogels
2.5. Mechanical Property Measurement and Analysis
2.6. Electrochemical Response Measurement
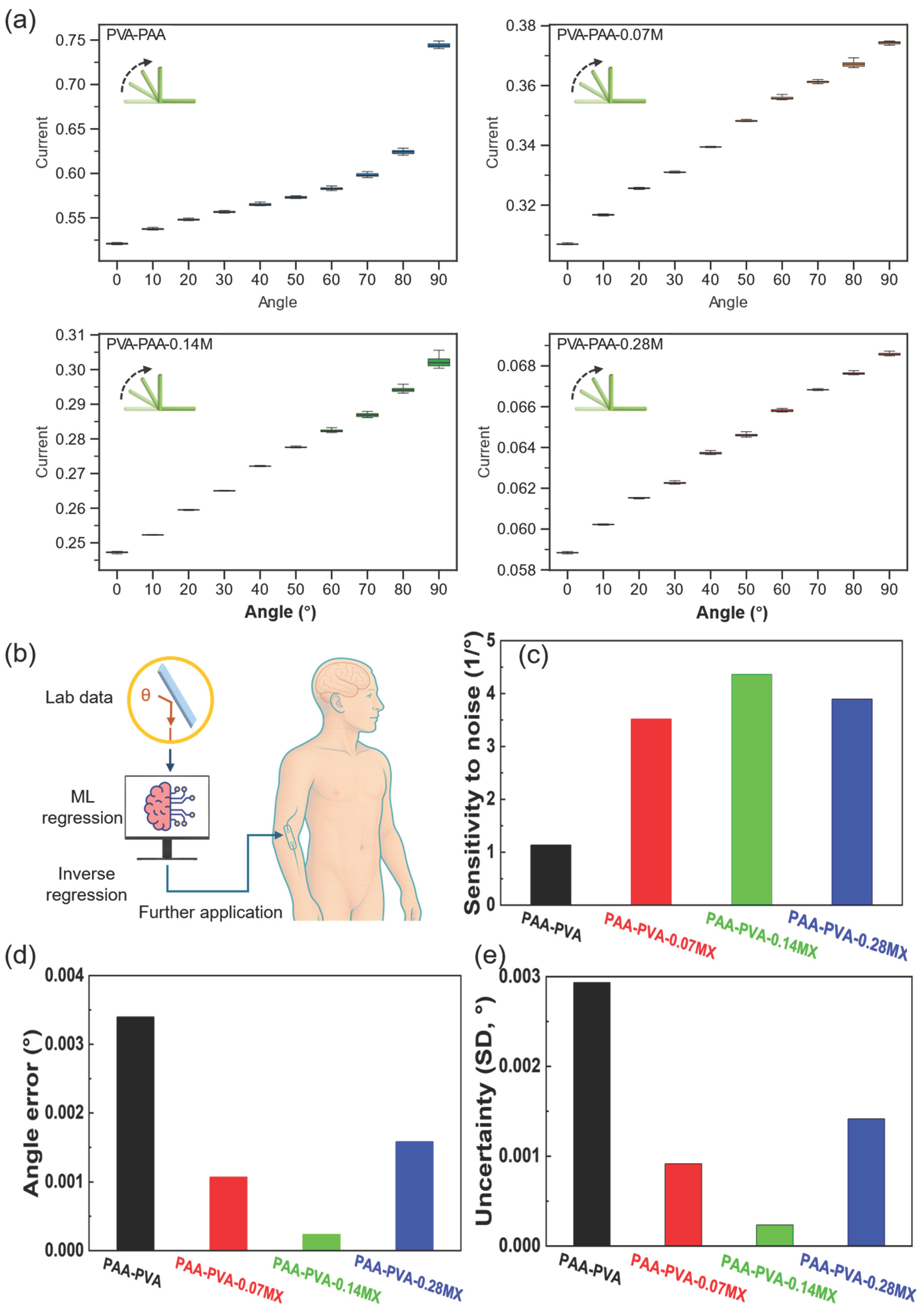
2.7. Machine-Learning-Assisted Current-Angle Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
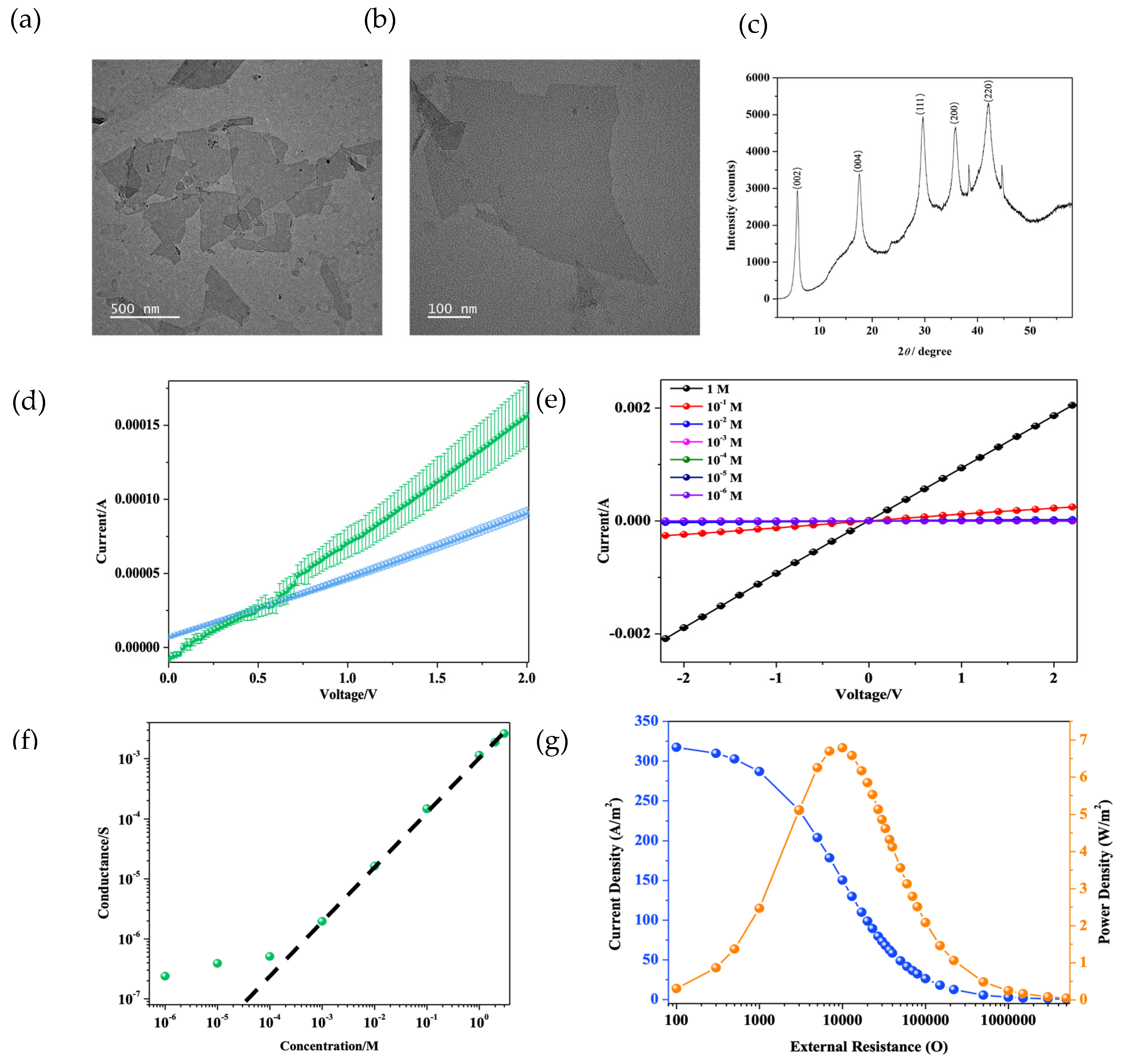
3.1. Structure and Properties of MXene Membranes
3.2. Ion Transport Properties of MXene Membranes
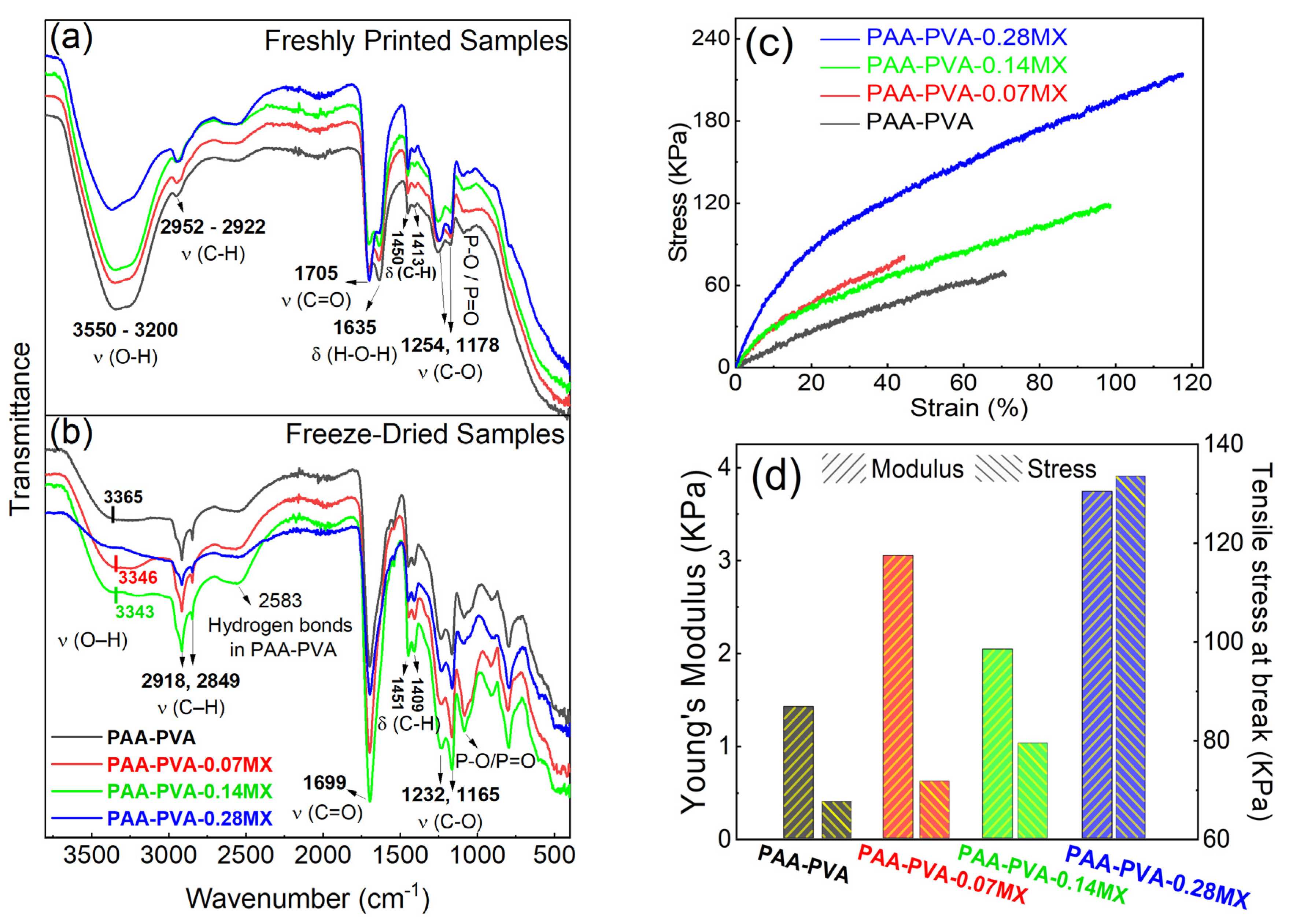
3.3. Molecular Structure and Mechanical Properties of PAA-PVA-MXene Composites
3.4. Electrochemical Properties of 3D Printed MXene-PVA-PAA Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, S. P.; Song, R. Y.; Zeng, H. O.; Wang, L. D. Preanchoring Enabled Directional Modification of Atomically Thin Membrane for High-Performance Osmotic Energy Generation. Nano Lett. 2023, 24(1), 26–34, Article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafa, L.; Breideband, L.; Posada, L. R.; Torras, N.; Martinez, E.; Stelzer, E. H. K.; Pampaloni, F. Light Sheet-Based Laser Patterning Bioprinting Produces Long-Term Viable Full-Thickness Skin Constructs. ADVANCED MATERIALS 2024, 36(8). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gual, R.; Ye, H.; Ueno, T.; Landers, F. C.; Hertle, L.; Deng, S. Y.; Veciana, A.; Xia, Y. M.; Franco, C.; Choi, H.; et al. 3D Printed Template-Assisted Casting of Biocompatible Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Soft Microswimmers with Tunable Stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33(39). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B. J. D.; Zhao, G.; Yan, Z.; Xie, Y. C.; Lin, J. Direct Freeform Laser Fabrication of 3D Conformable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13(8), 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M. A. P.; Huda, N.; Farjana, S. H.; Asadnia, M.; Lang, C. Recent Advances in Nanogenerator-Driven Self-Powered Implantable Biomedical Devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8 (2)(25), Review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A. C. H.; Zhang, J. T.; Hui, K. N.; Hui, K. S.; Huang, H. B. Recent Development and Applications of Advanced Materials via Direct Ink Writing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7(7). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Y.; Sun, Y. Y.; Qin, L. M.; Li, M. R.; Ou, K. T.; Fang, J.; Fu, Q. Direct-ink-writing (DIW) 3D printing functional composite materials based on supra-molecular interaction. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. L.; Deng, Z. M.; Chen, M. J.; Yu, Z. Z.; Russell, T. P.; Zhang, H. B. 3D Printing of Ultralow-Concentration 2D Nanomaterial Inks for Multifunctional Architectures. Nano Lett. 2023, 23(1), 155–162, Article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, K.; Li, T. R.; Sun, Y. C.; Jakubinek, M. B.; Naguib, H. E. 4D Printing of MXene Composites for Deployable Actuating Structures. ACS APPLIED POLYMER MATERIALS 2022, 4(12), 8774–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhulkar, S.; Liu, S. Y.; Vala, P.; Xu, W. H.; Ravichandran, D.; Zhu, Y. X.; Bi, K.; Nian, Q.; Chen, X. F.; Song, K. N. Aligned Ti3C2Tx MXene for 3D Micropatterning via Additive Manufacturing. ACS Nano 2021, 15(7), 12057–12068, Article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P. Z.; Deng, Z. M.; Min, P.; Ye, L. X.; Qi, C. Z.; Zhao, H. Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. B.; Yu, Z. Z. Direct ink writing of multifunctional gratings with gel-like MXene/norepinephrine ink for dynamic electromagnetic interference shielding and patterned Joule heating. Nano Res. 2024, 17(3), 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Y.; Zhao, Y. Y.; Li, L. Z.; Wang, Y. H.; Wang, J. L.; Xiong, J. J.; Du, S. L.; Zhang, P.; Shi, X. R.; Yu, J. H. MXene/Polymer Nanocomposites: Preparation, Properties, and Applications. Polym. Rev.;Review 2021, 61(1), 80–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. H. Y.; Al Marzooqi, F.; El-Demellawi, J. K.; Al Marzooqi, N.; Arafat, H. A.; Alshareef, H. N. Ion-Selective Separation Using MXene-Based Membranes: A Review. ACS Mater. Lett.;Review 2023, 5(2), 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xie, L.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Q.; Yan, M.; Zeng, J.; Qiu, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Interfacial Super-Assembly of Ordered Mesoporous Carbon-Silica/AAO Hybrid Membrane with Enhanced Permselectivity for Temperature- and pH-Sensitive Smart Ion Transport. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, 60(50), 26167–26176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xie, L.; Gao, R.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liang, K.; Jiang, L.; Kong, B. Super-Assembled Chiral Mesostructured Heteromembranes for Smart and Sensitive Couple-Accelerated Enantioseparation. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2022, 144(30), 13794–13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, R.; Pan, J.; Liang, K.; Jiang, L.; Kong, B. pH Modulation of Super-Assembled Heteromembranes for Sustainable Chiral Sensing. ACS Nano 2024, 18(19), 12547–12559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. N.; Liang, Q. R.; Yin, H. B.; Zhang, X.; Gao, R. H.; Pan, J. M.; Liang, K.; Jiang, L.; Kong, B. pH Modulation of Super-Assembled Heteromembranes for Sustainable Chiral Sensing. ACS Nano 2024, 18(19), 12547–12559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. A.; Zeng, H.; Xie, L.; Gao, R. H.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Q. R.; Zhang, X.; Liang, K.; Jiang, L.; Kong, B. Super-Assembled Chiral Mesostructured Heteromembranes for Smart and Sensitive Couple-Accelerated Enantioseparation. JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY 2022, 144(30), 13794–13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Qiu, B.; Liu, T.; Liang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Zeng, J.; Yan, M.; et al. Sequential Superassembly of Nanofiber Arrays to Carbonaceous Ordered Mesoporous Nanowires and Their Heterostructure Membranes for Osmotic Energy Conversion. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2021, 143(18), 6922–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.; Jacob, L.; S. M., C; Butt, H.; Barsoum, I.; Al-Rub, A. K. R.; Zaki, W. Mechanical Properties, Energy Absorption, and Shape Memory Behavior of 3D Printed PLA-MXene Nanocomposites and Gyroid Lattices. Advanced Engineering Materials 2024, 26(12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Sheng, X.; Li, X.; Sheng, M.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. A Multifunctional Flexible Composite Film with Excellent Multi-Source Driven Thermal Management, Electromagnetic Interference Shielding, and Fire Safety Performance, Inspired by a “Brick–Mortar” Sandwich Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32(26), 2200570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Jang, H.; Jiong, S.; Chen, X.; Seo, B.; Choi, W. Thermo-Chemo-Mechanically Robust, Multifunctional MXene/PVA/PAA-Hanji Textile with Energy Harvesting, EMI Shielding, Flame-Retardant, and Joule Heating Capabilities. Advanced Materials 2024, 36(47), 2411248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, A.; Eisa, W. H.; Yosef, M.; Hassan, A. Ultra-Thin Films of Poly(acrylic acid)/Silver Nanocomposite Coatings for Antimicrobial Applications. Journal of Spectroscopy 2016, 2016(1), 7489536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ma, K.; Gao, W.; Xin, Y.; Chen, S.; Qiu, W.; Shen, G.; He, X. Enhanced mechanical and electrical properties of starch-based hydrogels incorporating polyacrylic acid and MXene for advanced wearable sensors in sign language recognition. Sensors & Diagnostics 2024, 3(2), 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lu, Y.; Bi, S.; Wang, W.; Lin, F.; Zhu, F.; Yang, P.; Ding, N.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Stretchable and Photothermal MXene/PAA Hydrogel in Strain Sensor for Wearable Human-Machine Interaction Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8(9), 2201767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Bai, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zou, X.; Chen, Y.; Bi, S.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, Q. Multifunctional MXene/PAA organohydrogel as a flexible strain sensor for wearable human–machine interaction. RSC Applied Polymers 2023, 1(1), 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H. S.; Sadahira, C. M.; Souza, A. N.; Mansur, A. A. P. FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2008, 28(4), 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzębski, W.; Sitarz, M.; Rokita, M.; Bułat, K. Infrared spectroscopy of different phosphates structures. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2011, 79(4), 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Bai, Z. MXene-Based Textile Sensors for Wearable Applications. ACS Sensors 2022, 7(4), 929–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Yong, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Pan, F.; Liang, D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z. Polyaniline-MXene composite electrode with excellent electrochemical properties for all-solid flexible supercapacitors. Journal of Energy Storage 2023, 71, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cao, J.; Wang, F.; Tian, F.; Zheng, W.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; et al. 3D Printing of Stretchable, Adhesive and Conductive Ti3 C2 Tx-Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels. Polymers 2022, 14(10). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cao, J.; Wang, F.; Tian, F.; Zheng, W.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; et al. 3D Printing of Stretchable, Adhesive and Conductive Ti3C2Tx-Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels. Polymers 2022, 14(10). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, R.; Dolatyar, B.; Zandi, N.; Tamjid, E.; Pourjavadi, A.; Simchi, A. Electrically conductive and photocurable MXene-modulated hydrogel conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration: In vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials Advances 2025, 170, 214197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| # |
Isotonic regression model
The sensitivity-to-noise index (SNI, units: 1/°) was defined at each bending angle as:
For inverse angle prediction, the mean absolute error (MAE) and its standard deviation (SD) were calculated across grouped cross-validation folds, where each bending angle group was held out once as the test set. For each fold k, the fold-wise MAE was defined as:
The overall MAE and SD were then computed as:
|
| * | The effective distance of the charged surface is described by the Debye length (λD) and can be calculated according to the equation , where , and are the relatively permittivity of the solution, the permittivity of a vacuum, the electron charge, and the Boltzmann constant, respectively. |
| & | The composites were extensively cured to ensure complete polymerization, ruling out assignment of this peak to the C=C bond in AA or PEGDA. |
| MXene Composites | Manufacturing Technique | MXene wt% | Young’s Modulus (KPa) | Tensile strength (KPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA-PAA-MXene (this work) | DLP 3D printing | 0 | 1.4±0.1 | 67±1 | 65.1±6.7 |
| 0.07 | 3.1± 0.1 | 71±7 | 36.2±5.2 | ||
| 0.14 | 2.0±0.1 | 78±26 | 90.5±9.7 | ||
| 0.28 | 3.7± 0.1 | 133±50 | 105.1±15.3 | ||
| GelMa- MXene [34] | Photoinitiating solution casting | 0 | 53.2±9.9 | 14±2 | 26.3±5.6 |
| 0.025 | 45.5±4.7 | 11±4 | 26.4±3.7 | ||
| 0.05 | 35.0±7.2 | 11±1 | 31.4±4.5 | ||
| 0.125 | 26.01±4.3 | 8±2 | 37.3±6.6 | ||
| 0.25 | 35.2±3.5 | 10±2 | 25.3±6.5 | ||
| PAA-Starch-MXene [25] | Solution casting | 0.24 | 211 | 340 | 1237 |
| PAA-MXene [32] | Direct ink writing 3D printing | 1 | 795.8 | 893 | 622 |
| Name | Sensitivity to Noise (1/°) | Mean absolute angle error (°) | Standard deviation (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA-PAA | 1.14 | 0.0034 | 0.003 |
| PVA-PAA-0.07MX | 3.52 | 0.0011 | 0.001 |
| PVA-PAA-0.14MX | 4.36 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 |
| PVA-PAA-0.28MX | 3.90 | 0.0016 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





