1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Commercial supersonic passenger transport represents one of the most prominent unrealized capabilities in modern civil aviation. The Concorde demonstrated sustained Mach 2 passenger flight and achieved significant reductions in long-haul travel time, yet its operational lifespan was limited by regulatory restrictions on sonic booms, high operating costs, and a constrained addressable market [
1,
2,
3]. Since the retirement of Concorde in 2003, commercial aviation has experienced substantial advances in efficiency, safety, and aircraft performance, but cruise speeds for long-haul transport have remained largely unchanged. Recent developments in aerodynamics, propulsion, and materials, alongside renewed industrial and research interest in supersonic aircraft concepts, have therefore revived attention toward the potential return of commercial supersonic flight [
4,
5]. In this context, the central challenge has shifted from demonstrating aircraft-level feasibility to identifying where supersonic operations could realistically be viable within contemporary regulatory, geographic, and economic constraints
Supersonic feasibility is inherently route-dependent. Restrictions on sustained supersonic flight over land impose strong geographic constraints, making over-water routing a primary consideration for candidate routes. At the same time, supersonic aircraft incur higher fuel burn and operating costs, which require sufficient time savings and market demand to justify premium services. As a result, the viability of supersonic transport emerges from the interaction of route geometry, regulatory exposure to sonic booms, achievable reductions in travel time, and the economic strength of origin and destination markets. These factors do not act independently, and their combined influence can lead to threshold behavior in which small changes in routing or time savings alter feasibility for otherwise similar routes.
1.2. Literature Review
Existing research on commercial supersonic transport has approached the feasibility question through market estimation, environmental assessment, airline fleet-level modeling, and routing analysis. Wen et al. developed a bottom-up methodology to estimate future supersonic market demand and evaluate associated fuel burn and emissions under long-term operational scenarios [
6]. Their work provides important insight into the potential scale of supersonic operations and associated environmental impacts, while relying on predefined route assumptions and scenario structures. Jain et al. examined the introduction of supersonic aircraft from the perspective of airline behavior using a profit-seeking fleet simulation framework, focusing on routes touching the United States and evaluating implications for fleet utilization, fuel consumption, and passenger productivity [
7]. Together, these studies highlight the importance of route selection and operational constraints in determining the system-level implications of supersonic transport.
A parallel body of work has focused on the environmental and community constraints that shape supersonic feasibility at scale. Rutherford et al. examined the noise and climate impacts of large-scale supersonic aviation scenarios and emphasized that community noise exposure and sonic boom effects remain binding constraints alongside emissions considerations [
8]. At an institutional level, assessments by the International Civil Aviation Organization have reiterated that most global airspace continues to prohibit routine commercial supersonic flight over land, reinforcing the importance of regulatory exposure as a determinant of feasible operations [
9]. These studies provide context for why geographic exposure to land is not merely a routing preference but a fundamental operational constraint.
Technical research has continued to address the sonic boom challenge through low-boom aircraft concepts and acoustic shaping methods. NASA’s Supersonic Technology Project, including work associated with the X-59, has advanced understanding of low-boom signatures and their validation through flight testing [
10]. Survey and review studies of low-boom design and optimization techniques indicate steady progress in reducing perceived boom levels while leaving open questions regarding how such advances translate into route-level feasibility under real-world regulatory conditions [
11]. Operational assessment studies have further examined how assumed boom limits influence feasible operating envelopes and route constraints, strengthening the link between acoustic compliance assumptions and route viability [
12].
In addition to acoustic and regulatory considerations, routing methodologies have explicitly studied the consequences of sonic-boom-constrained operations. Research on supersonic routing under overland restrictions has examined route deviations, detour penalties, and the trade-off between regulatory compliance and realized time savings [
13]. In this context, tools such as the hiMach package provide practical implementations for constructing great-circle routes, estimating subsonic and supersonic travel times, and quantifying overland versus overwater exposure, thereby supporting large-scale route analysis [
14]. These methods provide physically grounded inputs but do not, on their own, assess overall route feasibility when engineering, regulatory, and economic considerations must be evaluated jointly.
Recent studies have also continued to explore the economic viability of supersonic services and demand sensitivity to operational assumptions. For example, recent AIAA studies have examined candidate operating routes for commercial supersonic aircraft and evaluated economic performance under assumed demand and regulatory scenarios [
15,
16]. Collectively, this literature establishes that supersonic feasibility arises from the combined influence of route geometry, regulatory exposure, achievable time savings, and market characteristics, motivating approaches that can integrate these factors within a unified analytical framework.
1.3. Research Gap and Contribution
Despite substantial progress in aircraft design, market forecasting, environmental assessment, and routing methodologies, there remains a need for scalable frameworks that assess supersonic feasibility directly at the route level by integrating multiple contributing factors within a single representation. Supersonic route feasibility depends on interactions between geographic exposure, achievable time savings, route distance, and economic demand, and these interactions can be non-linear and difficult to capture using fixed thresholds or sequential filtering approaches. Machine learning provides a suitable modeling framework for this class of problem, as it enables feasibility boundaries to be learned from data and allows interactions among multiple features to be represented without restrictive analytical assumptions.
The purpose of this study is to formulate supersonic route feasibility as a supervised learning problem and to develop a data-driven framework for evaluating and comparing global city-pair routes. A dataset of 435 long-haul routes is constructed by combining engineering performance estimates, geographic routing characteristics derived from hiMach-based great-circle path analysis, regulatory exposure proxies based on over-water routing fraction, and economic demand indicators derived from population and gross domestic product data. Supervised learning models are trained to learn a continuous feasibility score between 0 and 1 that reflects the combined influence of these features. A Decision Tree classifier is used to extract interpretable feasibility rules and identify dominant decision thresholds, while an Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) classifier captures non-linear interactions and provides route-level feasibility scores suitable for ranking. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) are applied to analyze feature importance and to verify that learned relationships align with physical, regulatory, and economic intuition.
The resulting framework produces several complementary outputs. Feature-attribution analysis provides insight into which route characteristics most strongly influence feasibility across the dataset. The feasibility scores enable identification and ranking of the most promising routes, including both established transoceanic corridors and less frequently discussed city pairs with favorable geographic and economic conditions. In addition, the trained model and feature-generation pipeline are deployed as an interactive predictive engine that evaluates feasibility for user-specified routes using the same methodology applied during training. Together, these results support systematic route-level assessment and provide a foundation for integrating feasibility analysis into broader studies of future commercial supersonic networks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Creation and Feature Engineering
2.1.1. Route Universe and Data Sources
This study is based on a purpose-built, route-level dataset designed to evaluate the feasibility of future commercial supersonic passenger operations under present-day geographic, regulatory, and economic constraints. Each data record corresponds to a unique origin–destination airport pair, representing a long-haul city-pair market for which supersonic service could plausibly be considered. The final dataset comprises 435 routes, reflecting a diverse global distribution of intercontinental and transoceanic markets.
The dataset integrates information from multiple publicly available sources. Global airport metadata were used to define route endpoints and ensure compatibility with large, long-range aircraft operations. Demographic and economic indicators, including population and gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, were collected at the national or metropolitan level to approximate market demand characteristics. These data sources were combined into a single tabular dataset through a deterministic preprocessing pipeline, ensuring that all features could be recomputed consistently for any route evaluated within the framework.
2.1.2. Route Construction and Performance Estimation Using hiMach
Route geometry and performance-related quantities were derived using the hiMach package, which is designed to support analysis of supersonic routing scenarios where aircraft are permitted to fly supersonically over water while remaining subsonic over land. For each airport pair, a great-circle path was constructed and used as the baseline geometric representation of the route.
Using hiMach, estimates of total great-circle distance, subsonic travel time, and supersonic travel time were computed under consistent cruise assumptions representative of next-generation commercial supersonic transport concepts. The hiMach framework emphasizes routing feasibility and time savings under regulatory constraints rather than full trajectory optimization, making it well suited for large-scale route screening and comparative analysis. All hiMach-derived computations were treated as deterministic preprocessing steps and applied uniformly across all routes to ensure reproducibility and consistency between training data and later inference
2.1.3. Regulatory Exposure Proxy Based on Over-Water Routing
Because sustained overland supersonic flight remains prohibited or severely restricted in most jurisdictions, regulatory exposure to sonic boom constraints constitutes a primary determinant of route feasibility. To capture this constraint in a scalable and route-level manner, a regulatory exposure proxy was constructed based on the fraction of each route flown over water.
For each great-circle route, points were sampled at regular intervals along the path. Each sampled point was classified as land or water using a global land–sea representation. The over-water fraction (water_pct) was then computed as the proportion of sampled points located over water. This variable provides an aggregate representation of a route’s compatibility with sustained supersonic cruise without requiring overland segments and serves as a central regulatory feature in the feasibility assessment.
2.1.4. Market-Demand Feature Construction
Supersonic passenger services have historically targeted time-sensitive travelers and premium markets rather than mass leisure demand. To approximate the ability of a route to support such services using publicly available data, demographic and economic indicators were incorporated into the dataset.
Population and GDP per capita were collected for both origin and destination regions and used to construct market-demand proxies. An economic power indicator was derived to represent the scale of economically capable demand at each endpoint, reflecting both population size and purchasing power. Origin and destination indicators were then combined into a route-level demand score, which serves as a consistent proxy for the potential market strength of each city pair. These features are not intended to predict ticket sales directly but to capture relative differences in market attractiveness across routes.
2.1.5. Feasibility Labelling
Each route was assigned a feasibility label based on domain-informed criteria reflecting present-day constraints on commercial supersonic operations. These criteria account for regulatory exposure, achievable time savings, route distance regime, and market characteristics, and are designed to distinguish routes that could plausibly support supersonic service from those that are unlikely to do so under current conditions.
Two target representations were defined for supervised learning. First, a binary feasibility label (feasible or unfeasible) was used for classification tasks and model evaluation. Second, a continuous feasibility score on the interval [0,1] was derived from model probability outputs and interpreted as a route-level feasibility index suitable for ranking and comparative analysis. The dataset exhibits class imbalance, with feasible routes representing a minority of all observations, reflecting the constrained operational envelope of supersonic transport.
2.2. Machine Learning Models and Predictive Framework
2.2.1. Problem Formulation and Training Protocol
Supersonic route feasibility was formulated as a supervised learning problem in which engineered route-level features are mapped to feasibility outcomes. Input features consist of numerical variables capturing route geometry, performance-driven time savings, regulatory exposure, and market-demand proxies. Model outputs consist of both a binary feasibility classification and a continuous feasibility score derived from probabilistic predictions.
The dataset was divided into training and test subsets using a fixed random seed to ensure reproducibility. Hyperparameters were selected using validation on the training data, and final model evaluation was conducted on a held-out test set. Because feasible routes constitute a minority of the dataset, evaluation emphasizes metrics that remain informative under class imbalance, including threshold-independent measures. All preprocessing steps, feature ordering, and model configurations were preserved to enable exact replication.
2.2.2. Decision Tree Model
A Decision Tree classifier was trained as an interpretable baseline model to extract first-order feasibility logic from the data. Decision Trees operate by recursively partitioning the feature space using axis-aligned splits that maximize class separation according to a purity criterion, such as Gini impurity. Each internal node represents a feature threshold, producing a hierarchical structure of decision rules that can be directly visualized and interpreted.
In this study, the Decision Tree serves a primarily explanatory role. By constraining tree depth and minimum samples per node, the trained tree highlights dominant feasibility thresholds and clarifies how route characteristics interact to determine feasibility outcomes. This model provides a transparent, rule-based view of supersonic feasibility that complements the more expressive ensemble model described below.
2.2.3. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Model
To capture non-linear interactions among route features and achieve stronger predictive performance, an Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) classifier was trained on the same feature set. XGBoost constructs an ensemble of decision trees sequentially, where each new tree is trained to correct residual errors from the existing ensemble by optimizing a regularized objective function. This approach enables the model to represent complex decision boundaries while controlling overfitting through structural and weight regularization.
XGBoost is particularly well suited for structured tabular data in which interactions between variables are important but difficult to specify analytically. In the present application, feasibility emerges from coupled effects between over-water routing fraction, achievable time savings, route distance, and market demand. These interactions are not readily captured by a single decision tree or linear model but can be learned effectively through gradient boosting.
The trained XGBoost model outputs a probability estimate for the feasible class. This probability was interpreted as a continuous feasibility score on the interval [0,1], enabling routes to be ranked by relative feasibility rather than treated as binary outcomes alone. All preprocessing steps, feature ordering, hyperparameters, and trained model artifacts were saved and versioned to support reproducibility.
2.2.4. Model Interpretability Using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)
To interpret the behavior of the XGBoost model, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) were applied. SHAP is a model-agnostic interpretability framework grounded in cooperative game theory that assigns each feature a contribution value representing its marginal effect on the model output. For a given prediction, SHAP decomposes the feasibility score into additive contributions from individual features relative to a baseline expectation.
In this study, SHAP was used to assess both global and local model behavior. Global SHAP summary plots were generated to identify which engineered features most strongly influence feasibility outcomes across the dataset. Route-specific explanations were also examined to understand how individual features contribute to feasibility predictions for particular routes. This analysis provides transparency into the learned model structure and enables verification that predictions are driven by physically, regulatorily, and economically plausible factors.
2.2.5. Predictive Engine Deployment
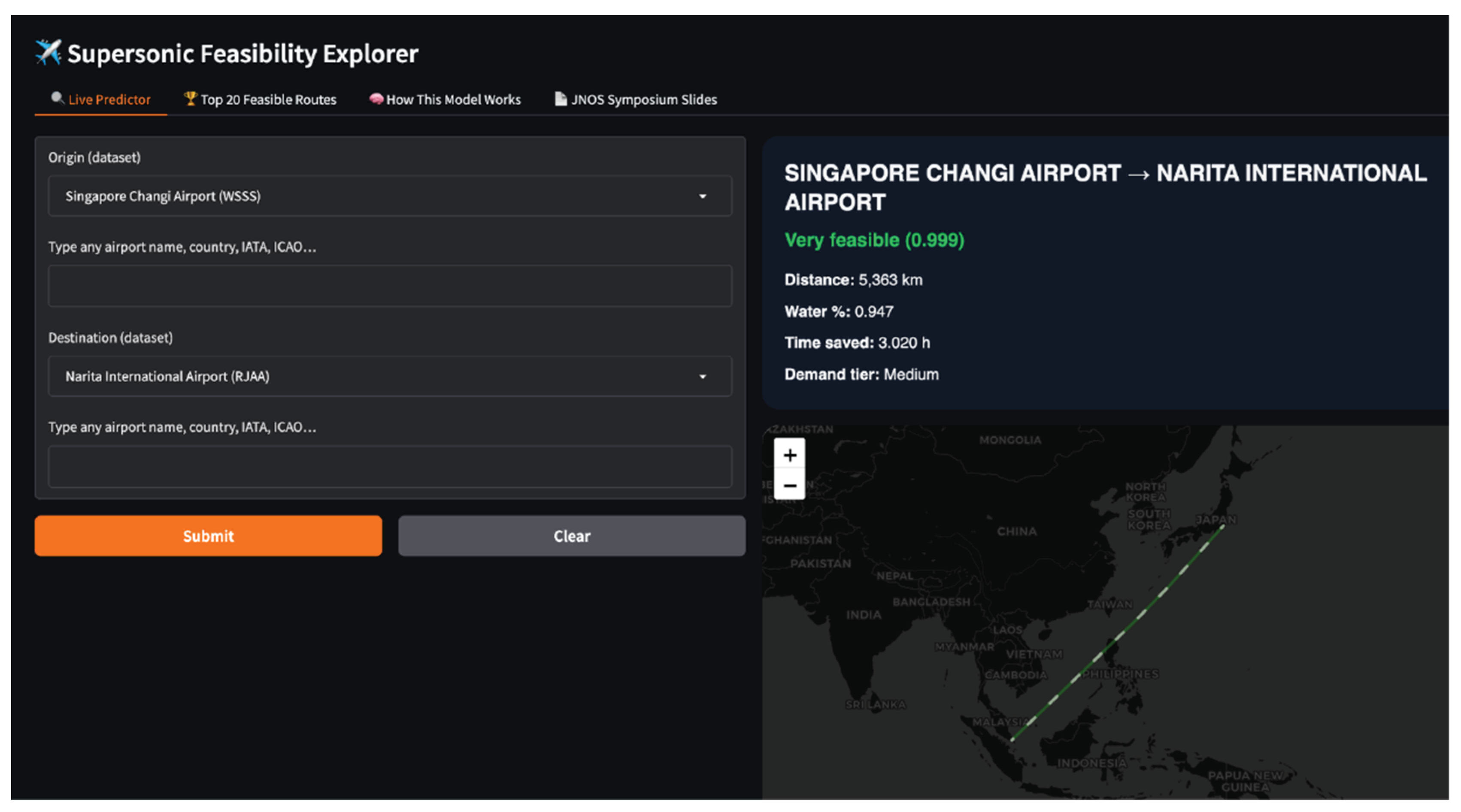
The trained XGBoost model and the complete feature-generation pipeline were deployed as an interactive predictive engine using a Gradio-based web interface. The predictive engine is designed to evaluate both routes present in the training dataset and previously unseen city pairs.
Given an origin and destination airport code, the system reconstructs all route-level features using the same deterministic preprocessing steps applied during dataset creation and model training. The assembled feature vector is then passed directly to the trained XGBoost model to generate a feasibility classification and continuous feasibility score. By embedding the trained model and preprocessing logic directly into the application backend, the predictive engine ensures methodological consistency between training, evaluation, and deployment.
2.3. Code and Data Availability
To enable replication and extension of this work, all datasets, trained model artifacts, and source code are made publicly available through the project repository at
https://huggingface.co/spaces/santushtttttt/supersonic-flight-predictor. The Files section of the repository contains the labeled route-level dataset, machine-learning model code, and required Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) dependencies used in this study. The App section hosts the deployed predictive engine, which implements the trained model and preprocessing pipeline and allows independent evaluation of supersonic route feasibility using the same analytical framework applied in the paper.
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Characteristics and Feasibility Distribution
The final dataset consists of 435 long-haul city-pair routes evaluated for potential commercial supersonic passenger operations. Of these, 61 routes were labeled as feasible and 374 as unfeasible, corresponding to approximately 14% of the dataset. This imbalance reflects the narrow operational envelope imposed by present-day regulatory, geographic, and economic constraints on supersonic flight. The class distribution highlights the importance of probabilistic modeling and ranking-based analysis rather than reliance on binary classification alone.
The evaluated routes span a wide range of distances, geographic regions, and market characteristics, including transoceanic corridors, intercontinental routes with mixed land–sea exposure, and predominantly overland routes. This diversity ensures that the models are exposed to both clearly infeasible routes and marginal cases in which feasibility emerges from interactions among multiple factors.
3.2. Decision Tree Results and Interpretable Feasibility Structure
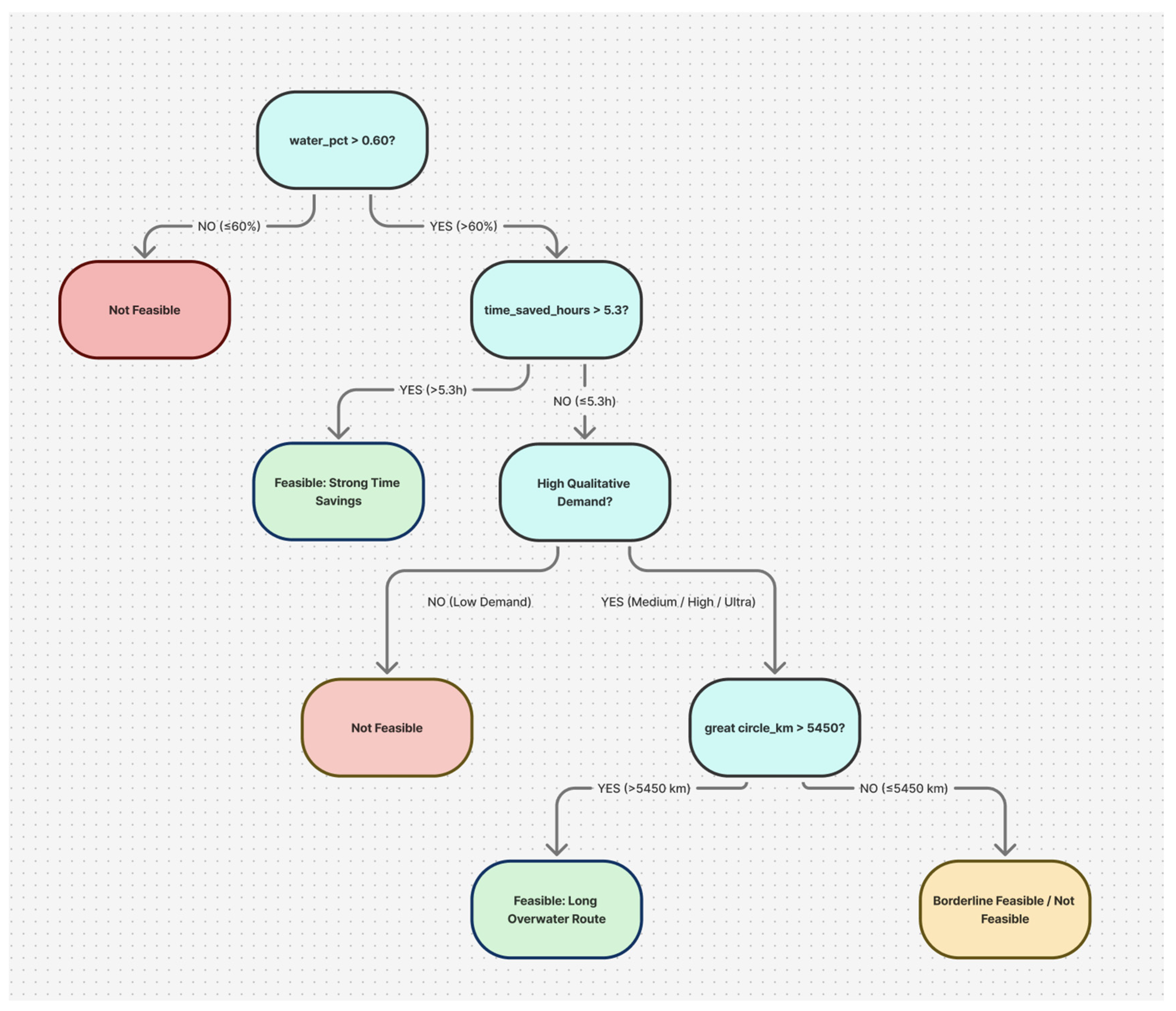
The trained Decision Tree classifier provides an interpretable representation of the dominant feasibility logic learned from the dataset. The resulting tree structure reveals a clear hierarchical decision process in which regulatory exposure, quantified by the over-water routing fraction, appears as the primary determinant of feasibility.
At the root node, the tree splits on the over-water fraction at a threshold of approximately 0.6. Routes below this threshold are almost exclusively classified as unfeasible, reflecting the practical constraint that routes with substantial overland segments are incompatible with sustained supersonic cruise under current sonic-boom regulations. For routes exceeding this threshold, subsequent splits incorporate performance-related variables, most notably achievable time savings. Routes with larger time savings are consistently more likely to be classified as feasible, indicating that regulatory compliance alone is insufficient without a strong performance benefit.
In intermediate regions of the feature space, where routes satisfy regulatory constraints but offer more modest time savings, the tree relies on market-demand proxies and route distance to refine feasibility decisions. These splits reveal that demand characteristics and distance regime influence feasibility primarily in marginal cases rather than acting as primary drivers. While the Decision Tree does not achieve the highest predictive accuracy, it provides a transparent rule-based structure that aligns closely with physical, regulatory, and economic intuition.
Figure 1.
Simplified visualization of the trained Decision Tree, highlighting the dominant split on over-water fraction and performance and demand-based thresholds.
Figure 1.
Simplified visualization of the trained Decision Tree, highlighting the dominant split on over-water fraction and performance and demand-based thresholds.
3.3. XGBoost Model Performance and Feasibility Scoring
3.3.1. Classification Performance
The Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) classifier demonstrates strong predictive performance on the held-out test set. The model achieves an overall classification accuracy of approximately 97%, indicating that the majority of routes are correctly classified as feasible or unfeasible. More importantly, the model attains a Receiver Operating Characteristic Area Under the Curve (ROC–AUC) of approximately 0.997, demonstrating near-perfect separability between feasible and unfeasible routes across decision thresholds.
Given the pronounced class imbalance in the dataset, ROC–AUC provides a more informative measure of performance than accuracy alone. The high ROC–AUC value indicates that the model consistently assigns higher feasibility scores to truly feasible routes than to unfeasible ones, even in cases where binary classification thresholds may vary. This result suggests that the engineered feature set captures the dominant determinants of supersonic feasibility and that the boosted ensemble effectively models their non-linear interactions.
Table 1.
Performance metrics for XGBoost model, including accuracy and ROC–AUC.
Table 1.
Performance metrics for XGBoost model, including accuracy and ROC–AUC.
| XGBoost Model Performance |
|---|
| |
Precision |
Recall |
F1-Score |
Support |
| False |
0.99 |
0.97 |
0.98 |
75 |
| True |
0.85 |
0.92 |
0.88 |
12 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Accuracy |
|
|
0.97 |
87 |
| Macro Average |
0.92 |
0.95 |
0.93 |
87 |
| Weighted Average |
0.97 |
0.97 |
0.97 |
87 |
3.3.2. Continuous Feasibility Scoring and Route Ranking
Beyond binary classification, the XGBoost model produces probabilistic outputs that are interpreted as continuous feasibility scores on the interval [0,1]. These scores enable routes to be ranked by relative feasibility, providing a more nuanced assessment than categorical labels alone.
The top-ranked routes are dominated by transoceanic and near-transoceanic corridors that combine high over-water routing fractions with substantial time savings and strong economic demand at both endpoints. Well-established candidates such as New York–London appear prominently, providing face validity for the model. At the same time, the ranking highlights several less frequently discussed routes, including Asia–Pacific and trans-North Pacific city pairs, which exhibit favorable combinations of geography, distance regime, and market strength.
The ranked results illustrate that supersonic feasibility is not confined to a small set of legacy routes but instead emerges across a broader global network where regulatory exposure, performance benefits, and demand conditions align.
Table 2.
Top routes ranked by XGBoost feasibility score, including key feature values and predicted scores.
Table 2.
Top routes ranked by XGBoost feasibility score, including key feature values and predicted scores.
| Global Route Ranking* |
|---|
| Origin - Destination IATA Codes |
Dist. (km) |
Over-Water Fraction |
Time Saved (h) |
Demand |
Score |
| SIN - HND |
5304 |
0.954 |
2.99 |
Medium |
0.999 |
| SIN - NRT |
5363 |
0.947 |
3.02 |
Medium |
0.999 |
| JFK - CDG |
5840 |
0.920 |
3.29 |
Ultra |
0.999 |
| JFK - LHR |
5546 |
0.920 |
3.12 |
Ultra |
0.999 |
| JFK - FRA |
6196 |
0.915 |
3.49 |
Ultra |
0.999 |
| HNL - PVG |
7922 |
0.850 |
4.46 |
High |
0.999 |
| JNB - GRU |
7448 |
0.816 |
4.19 |
Medium |
0.999 |
| SFO - NRT |
8245 |
0.987 |
4.64 |
Ultra |
0.999 |
| JFK - AMS |
5854 |
0.920 |
3.30 |
Ultra |
0.998 |
| SYD - PVG |
7874 |
0.632 |
4.43 |
Ultra |
0.998 |
Table 3.
Route key, showing corresponding route full forms of IATA Codes in
Table 2.
Table 3.
Route key, showing corresponding route full forms of IATA Codes in
Table 2.
| Route Key |
|---|
| IATA Codes |
Full Form |
| SIN - HND |
Singapore Changi – Tokyo Haneda |
| SIN - NRT |
Singapore Changi – Tokyo Narita |
| JFK - CDG |
John F. Kennedy Intl – Paris Charles de Gaulle |
| JFK - LHR |
John F. Kennedy Intl – London Heathrow |
| JFK - FRA |
John F. Kennedy Intl – Frankfurt Airport |
| HNL - PVG |
Honolulu Intl – Shanghai Pudong Intl |
| JNB - GRU |
O. R. Tambo Intl – São Paulo–Guarulhos Intl |
| SFO - NRT |
San Francisco Intl – Tokyo Narita |
| JFK - AMS |
John F. Kennedy Intl – Amsterdam Schiphol |
| SYD - PVG |
Sydney Kingsford Smith – Shanghai Pudong Intl |
3.4. Feature Importance and Model Interpretability (SHAP Analysis)
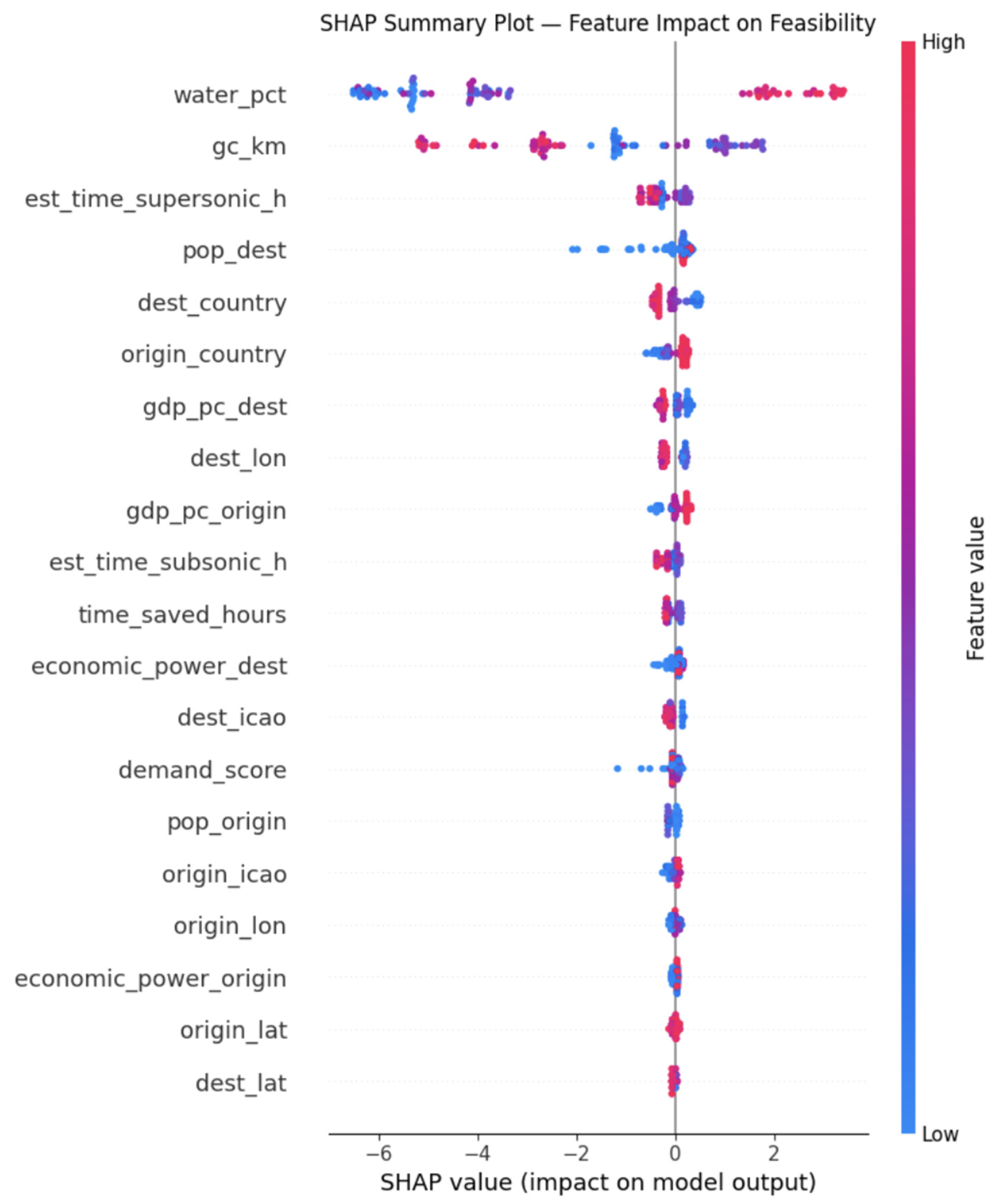
To interpret the behavior of the XGBoost model, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) were applied to quantify feature contributions. The global SHAP summary plot reveals that the over-water routing fraction is the most influential feature across the dataset, consistently exerting the largest impact on feasibility scores. Routes with high over-water fractions receive strong positive contributions, while predominantly overland routes are strongly penalized.
Achievable time savings (correlated to gc_km) constitute the second most influential factor. Routes offering larger reductions in travel time relative to subsonic flight receive consistently positive SHAP contributions, reinforcing the importance of a strong performance value proposition. Route distance also exhibits a meaningful influence, reflecting the existence of an optimal distance regime for supersonic aircraft in which speed advantages are maximized without incurring excessive operational penalties.
Market-demand proxies, including economic power and population-based indicators, contribute more modest but systematic effects. These features play a particularly important role in marginal cases, where regulatory and performance factors alone do not decisively determine feasibility. Route-specific SHAP explanations further illustrate how feasibility emerges from the combined influence of these factors, confirming that the model’s predictions are driven by physically and operationally plausible relationships rather than spurious correlations.
Figure 2.
SHAP summary plot showing global feature importance and contribution directions.
Figure 2.
SHAP summary plot showing global feature importance and contribution directions.
3.5. Predictive Engine Outputs
The trained XGBoost model and feature-generation pipeline were deployed as an interactive predictive engine to evaluate both routes included in the dataset and previously unseen city pairs. For user-specified origin and destination airports, the system reconstructs all route features and returns a feasibility classification and continuous feasibility score.
Results obtained through the predictive engine are consistent with dataset-level findings. Routes with high over-water fractions and substantial time savings are consistently assigned high feasibility scores, while routes dominated by overland segments are classified as unfeasible. The ability to evaluate unseen routes demonstrates that the model generalizes beyond the training dataset and can function as a practical screening tool for supersonic network planning.
3.6. Summary of Key Results and Contributions
The results of this study demonstrate three primary contributions
First, this work provides a route-level, data-driven feasibility framework that integrates regulatory exposure, performance benefits, and market demand within a single predictive model. Unlike prior studies that rely on predefined route filters or scenario-specific assumptions, the framework learns feasibility boundaries directly from data and produces continuous feasibility scores that support ranking and comparison across a global route set.
Second, the combination of interpretable and high-performance machine-learning models yields both explanatory insight and predictive accuracy. The Decision Tree reveals transparent feasibility rules aligned with regulatory and physical intuition, while the XGBoost model achieves strong predictive performance, with a ROC–AUC of approximately 0.997, indicating near-perfect discrimination between feasible and unfeasible routes. SHAP analysis further confirms that model predictions are driven by meaningful route characteristics rather than opaque correlations.
Third, the deployment of the trained model as an interactive predictive engine demonstrates the practical applicability of the framework. By enabling evaluation of both existing and hypothetical routes under a consistent analytical pipeline, the system bridges the gap between academic feasibility analysis and operational route screening. Together, these results establish supersonic route feasibility as a structured, quantifiable problem and provide a foundation for future studies of supersonic network design under evolving regulatory and technological conditions.
4. Discussion & Conclusion
The results of this study provide a structured perspective on the long-standing question of where commercial supersonic passenger flight could realistically operate under present-day constraints. Across all models and analyses, regulatory exposure, quantified through over-water routing fraction, emerges as the dominant determinant of route feasibility. This finding is consistent with prior work emphasizing sonic boom restrictions as the primary operational barrier to widespread supersonic flight [
6,
7,
8,
9], and it reinforces the view that feasibility is governed at least as much by regulatory geography as by aircraft performance alone.
The Decision Tree analysis offers an interpretable confirmation of this constraint structure. The presence of a clear threshold in over-water routing fraction reflects the binary nature of current regulatory regimes, in which sustained overland supersonic flight remains largely prohibited. Importantly, the Decision Tree also shows that regulatory compliance alone is insufficient to ensure feasibility. Routes that satisfy over-water constraints but offer limited time savings are frequently classified as unfeasible, highlighting the necessity of a strong performance-driven value proposition. This aligns with earlier market studies that emphasize passenger willingness to pay for time savings as a critical factor in supersonic demand [
6,
7].
The XGBoost model extends this understanding by capturing non-linear interactions among regulatory, performance, and economic variables. The model’s high ROC–AUC indicates that these combined features contain sufficient information to discriminate feasible from unfeasible routes with high reliability. The resulting route rankings suggest that supersonic feasibility is not confined to a narrow set of historically discussed corridors, such as New York–London, but instead extends to a broader global network where regulatory exposure, distance regime, and market strength align. This complements fleet-level and scenario-based analyses in the literature by providing a route-centric perspective that does not rely on predefined operating assumptions or airline-specific behavior models.
Feature attribution using SHapley Additive exPlanations further clarifies how feasibility emerges from the interaction of multiple factors. While over-water routing fraction dominates globally, time savings and route distance play decisive roles in distinguishing between marginally feasible and unfeasible routes. Economic demand indicators exert a smaller but consistent influence, particularly in borderline cases. This pattern suggests that market strength functions as an enabling factor rather than a primary driver, amplifying feasibility when regulatory and performance conditions are already favorable. This interpretation aligns with historical experience from Concorde, where high-income markets were necessary but not sufficient to sustain operations.
The deployment of the trained model as an interactive predictive engine demonstrates the practical applicability of the proposed framework. By enabling evaluation of unseen routes under the same analytical pipeline used during training, the system illustrates how feasibility assessment can move beyond static route lists toward a dynamic, data-driven screening process. This capability is particularly relevant in the context of evolving regulatory environments and aircraft technologies, where the set of feasible routes may change over time.
Several limitations of the present study point to clear directions for future research. First, sustainability considerations were incorporated only indirectly through performance and regulatory proxies. Future work could explicitly model fuel burn, emissions intensity, and climate impacts at the route level, enabling joint assessment of economic feasibility and environmental performance. Second, regulatory exposure was represented through a global over-water fraction proxy. While this captures first-order effects, more granular modeling of country-specific regulations, potential low-boom corridors, and evolving certification frameworks would improve fidelity. Third, aircraft performance assumptions were held fixed; incorporating alternative aircraft concepts, fuel types, and propulsion efficiencies would allow exploration of how technological advances shift feasibility boundaries.
Taken together, the results indicate that the feasibility of commercial supersonic passenger flight is governed by the joint interaction of regulatory geography, achievable performance gains, route distance, and market demand, rather than by aircraft capability alone. By formulating feasibility as a route-level, data-driven problem, this study demonstrates that machine-learning models can systematically identify and rank viable supersonic corridors while remaining consistent with physical, regulatory, and economic intuition. The proposed framework, supported by interpretable modeling and a deployable predictive engine, provides a structured and reproducible basis for assessing where supersonic operations could realistically emerge under current constraints, and establishes a foundation for evaluating how future regulatory or technological developments may alter the global feasibility landscape.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr Hannah Rana (Harvard University) and Mr Arun Kumar (Cambridge University) for their guidance and mentorship in my research process.
During the preparation of this study, generative artificial intelligence tools (ChatGPT 5.2, Claude Opus 4.5) were used to assist with code review and user-interface development for the deployed predictive engine. All generated outputs were reviewed and edited by the author, who takes full responsibility for the content, analysis, and conclusions presented in this publication.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SST |
Supersonic Transport |
| XGBoost |
Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| SHAP |
SHapley Additive exPlanations |
| ROC-AUC |
Receiver Operating Characteristic Area Under the Curve |
| GDP |
Gross Domestic Product |
| ICAO |
International Civil Aviation Organization |
| FAA |
Federal Aviation Administration |
| ML |
Machine Learning |
| IATA |
International Airport Transport Association |
| gc_km |
Great-circle distance (kilometres) |
| water_pct |
Fraction of route distance over water |
References
- Orlebar, C.J. The Concorde Story; Osprey Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2004.
- Trubshaw, B. Concorde: The Inside Story; Motorbooks International: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2002.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). 14 CFR Part 91: Supersonic Flight Over Land; Federal Register: Washington, DC, USA, 1973.
- Smith, H.; Bradley, M. Overview of supersonic aircraft research at NASA. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 392–403. [CrossRef]
- Berton, J.; Jones, S.; Seidel, J. Supersonic Technology Project overview. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Dallas, TX, USA, June 2019. [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Weit, C.J.; Mayakonda, M.; Anand, A.; Zaidi, T.; Mavris, D.A. A methodology for supersonic commercial market estimation and environmental impact evaluation (Part II). In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Atlanta, GA, USA, June 2020. [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Ogunsina, K.E.; Chao, H.; Crossley, W.A.; DeLaurentis, D. Predicting routes for, number of operations of, and fleet-level impacts of future commercial supersonic aircraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Atlanta, GA, USA, June 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, D.; Zeinali, M.; Khodayari, A. Noise and Climate Impacts of Unconstrained Commercial Supersonic Aviation; ICCT Working Paper; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). Environmental Protection—Supersonic Aircraft; ICAO: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019.
- Berton, J.; Jones, S.; Seidel, J. Low-boom flight demonstration and validation activities. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Virtual Event, June 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rallabhandi, S.; Mavris, D.N. Survey of low-boom supersonic aircraft design methodologies. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2021, 126, 100731.
- Salamone, J.; Plotkin, K. Operational implications of sonic boom limits on supersonic transport. AIAA J. 2018, 56, 4321–4333.
- Liebhardt, B.; Ehlers, J. Methodology for automated supersonic flight path routing under sonic boom constraints. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 2024.
- Bérard, A.; Gopalan, R. hiMach: Routing and Performance Estimation for Supersonic Aircraft; CRAN R Project, 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=hiMach (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Crossley, W.A.; Mavris, D.N. Economic assessment of commercial supersonic transport operations. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 2024.
- Ogunsina, K.E.; Jain, S.; DeLaurentis, D. Route-level economic feasibility of future supersonic aircraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 2024.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).