Submitted:
22 December 2025
Posted:
23 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Methodology
A. Research Questions
- How have the application domains of skyline query on uncertain databases evolved over the years?
- How has the complexity of problems addressed in skyline queries on uncertain databases changed over the years?
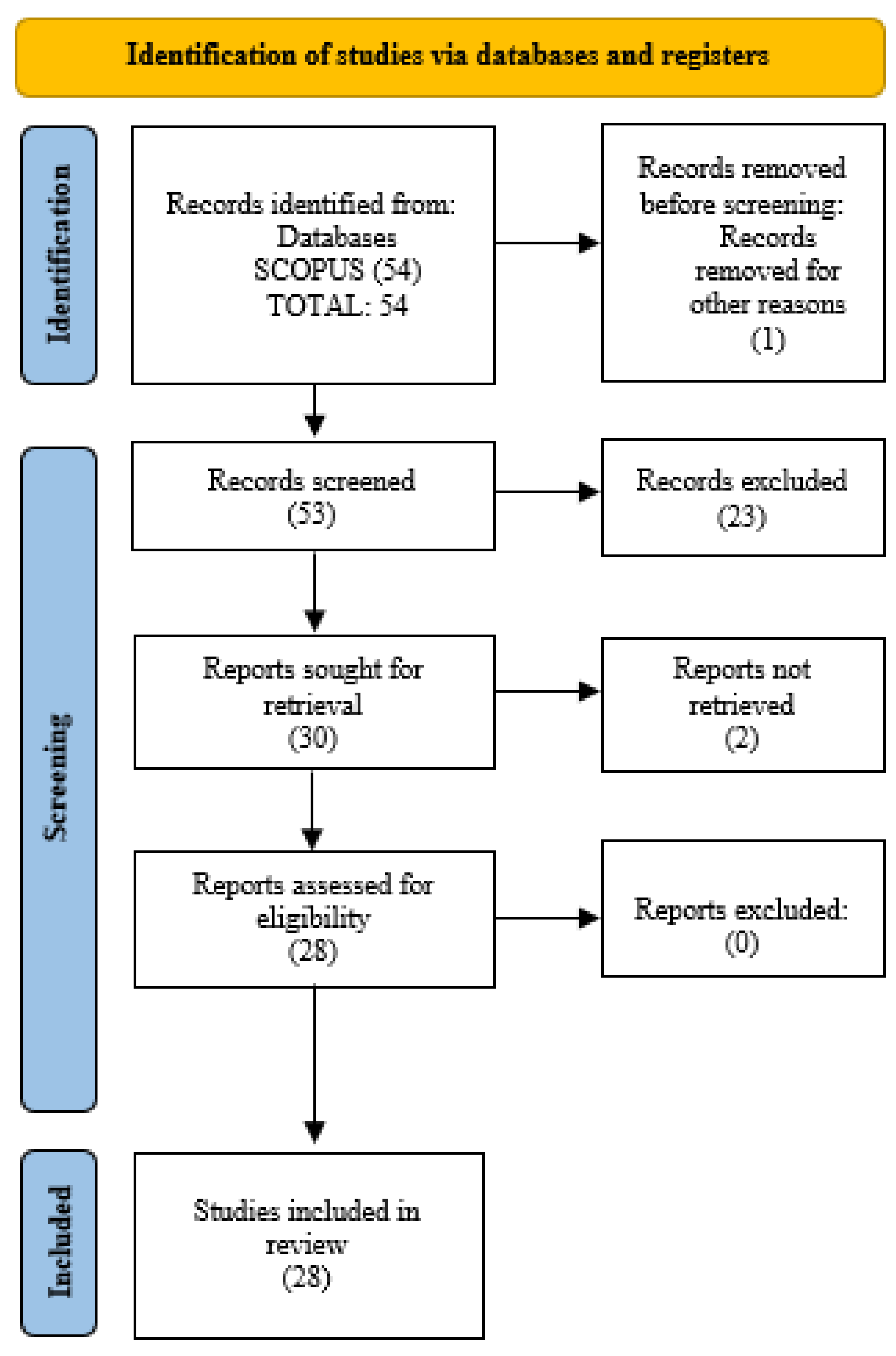
B. Search Strategy
C. Selection Criteria
| No | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Articles retrieved from the SCOPUS database using the specified search strategy. | |
| 2 | Articles related to Skyline queries in the fields of computer science, information technology, and engineering | |
| 3 | Articles specifically focused on computer science. | |
| 4 | Articles categorized as articles only | Articles categorized as other document types |
| 5 | Articles with exact keywords "Skyline Query" or "Uncertain Data" | Articles without the exact keywords specified |
D. Result
III. Results and Discussion
A. Evolution of Application Domains in Skyline Query Research (RQ1)
B. Changes in Problem Complexity in Skyline Query Research (RQ2)
C. Synthesis of Application Domains and Problem Complexity
| Year Range | Papers | Types of Uncertainties | Data Dimensionality & Volume | Main Challenges | Key Application Domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008-2012 | [2,3,6,9,16,20,24] | Probabilistic, existential | High-dimensional data, manageable volumes | Efficient query processing, foundational algorithms | General-purpose databases, foundational algorithmic improvements |
| 2013-2017 | [1,4,7,10,12,17,19,21,26,27] | Real-time, distributed | Dynamic, large volumes | Real-time processing, distributed systems | Intelligent transportation systems, smart cities, big data, distributed computing |
| 2018-2024 | [5,8,11,13,14,15,18,22,23,25,28] | Incomplete, user preferences | Massive volumes, high-dimensional, distributed | Parallel computation, quality of service, user-centric algorithms | Smart cities, IoT environments, personalized services, SaaS platforms, edge computing |
IV. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Nhut, M.; Cao, J.; He, Z. Answering skyline queries on probabilistic data using the dominance of probabilistic skyline tuples. Information Sciences 2016, 340–341, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, M.J.; Qi, Y.; Yuan, H. Asymptotically efficient algorithms for skyline probabilities of uncertain data. ACM Transactions on Database Systems 2011, 36, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lian, X.; Chen, L.; Jin, H. Continuous monitoring of skylines over uncertain data streams. Information Sciences 2012, 184, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Dong, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, K. Continuous probabilistic skyline queries for uncertain moving objects in the road network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, C.M. Distributed indexing schemes for k-Dominant skyline analytics on uncertain edge-iot data. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jin, H. Efficient and progressive algorithms for distributed skyline queries over uncertain data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2012, 24, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, A.K.; Kagita, V.R.; Garg, A.; Padmanabhan, V. Efficient computation for probabilistic skyline over uncertain preferences. Information Sciences 2015, 324, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhwani, N.; Kagita, V.R.; Kumar, V.; Panda, S.K. Efficient computation of top-k skyline objects in data set with uncertain preferences. International Journal of Data Warehousing and Mining 2021, 17, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, M.L.; Mamoulis, N.; Dai, X.; Tao, Y.; Vaitis, M. Efficient evaluation of probabilistic advanced spatial queries on existentially uncertain data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2009, 21, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Chen, L. Efficient processing of probabilistic group subspace skyline queries in uncertain databases. Information Systems 2013, 38, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, H.; Ibrahim, H.; Sidi, F.; Yaakob, R.; Alwan, A.A. Efficient skyline computation on uncertain dimensions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 96975–96994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. GDPS: An efficient approach for skyline queries over distributed uncertain data. Big Data Research 2014, 1, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, K. M-Skyline: Taking sunk cost and alternative recommendation in consideration for skyline query on uncertain data. Knowledge-Based Systems 2019, 163, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Li, Q. Optimizing quality for probabilistic skyline computation and probabilistic similarity search. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2018, 30, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagsaz, E. Parallel computation of probabilistic skyline queries using MapReduce. Journal of Supercomputing 2021, 77, 418–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Chen, L. Probabilistic group nearest neighbor queries in uncertain databases. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2008, 20, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, L.; Zeng, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, G. Probabilistic skyline queries on uncertain time series. Neurocomputing 2016, 191, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.T.; Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Ku, W.S.; Qin, X. ProbSky: Efficient computation of probabilistic skyline queries over distributed data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2023, 35, 5173–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, K.; Li, K. Reporting l most influential objects in uncertain databases based on probabilistic reverse top-k queries. Information Sciences 2017, 405, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Chen, L. Reverse skyline search in uncertain databases. ACM Transactions on Database Systems 2010, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, S.; Anis, M.; Hadjali, A.; Yaghlane, B.B. Selecting skyline stars over uncertain databases: Semantics and refining methods in the evidence theory setting. Applied Soft Computing Journal 2017, 57, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagita, V.R.; Pujari, A.K.; Padmanabhan, V.; Kumar, V. Skyline recommendation with uncertain preferences. Pattern Recognition Letters 2019, 125, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, S.; Min, J.K. Spatial skyline queries over incomplete data for smart cities. Journal of Systems Architecture 2018, 90, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheema, M.A.; Zhang, Q. Stochastic skylines. ACM Transactions on Database Systems 2012, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Mei, J.; Gao, Y. Top k probabilistic skyline queries on uncertain data. Neurocomputing 2018, 317, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.H.; Cao, J. Trustworthy answers for top-k queries on uncertain Big Data in decision making. Information Sciences 2015, 318, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, D.N.; Ye, M.; Lee, W.C. U-skyline: A new skyline query for uncertain databases. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2013, 25, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, J. Uncertain big QoS data-driven efficient SaaS decision-making method. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 11196–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).